Abstract
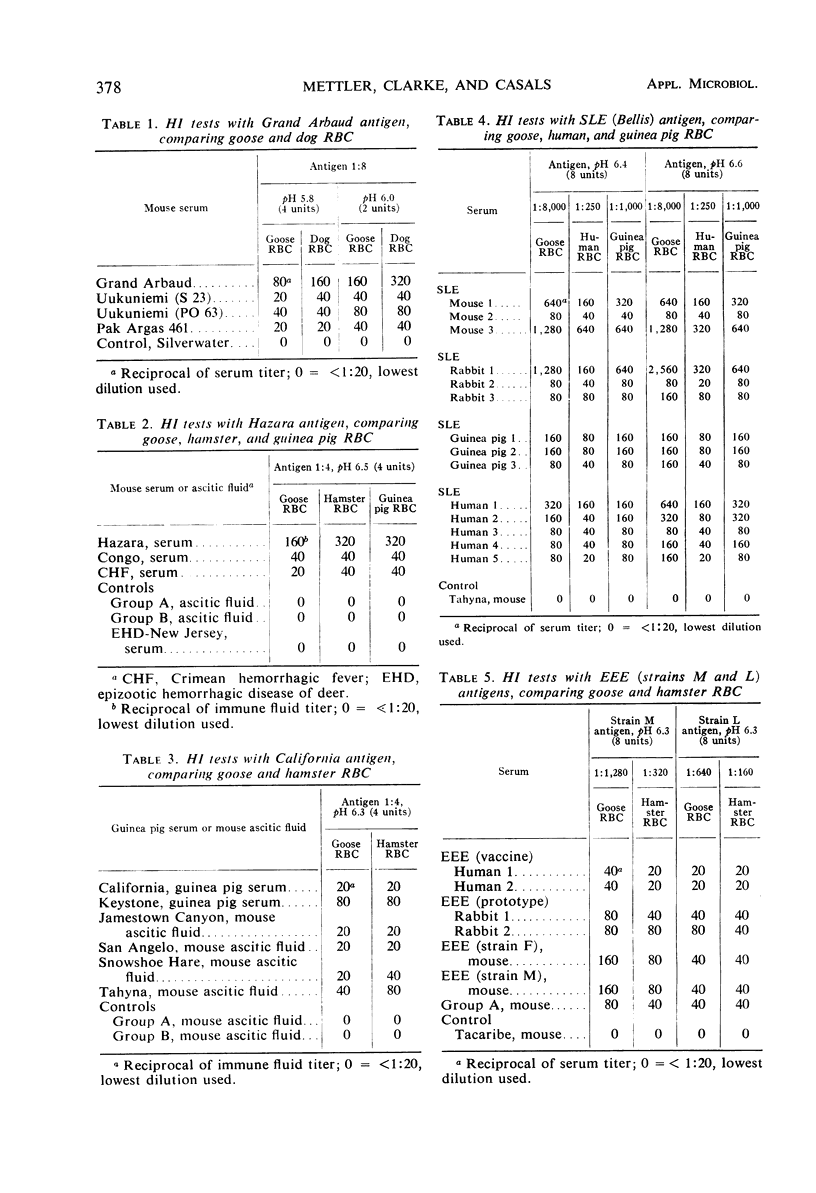
Antigens for Grand Arbaud, Hazara, and California arboviruses were able to agglutinate goose and either dog, hamster and guinea pig, or hamster red blood cells (RBC) to the same titer at the same pH; in hemagglutination-inhibition (HI) tests, titers for homologous and related sera were the same with these different types of RBC or occasionally one dilution higher with the mammalian cells. Antigens for St. Louis encephalitis and Eastern equine encephalitis viruses required use of lower antigen dilutions with human, guinea pig, and hamster RBC than with goose RBC. The results of comparative HI testing with these latter antigens and types of RBC indicate that HI titer is not directly related to the antigen dilution used with different types of RBC.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANERJEE K. COMPARATIVE AGGLUTINABILITY OF ERYTHROCYTES OF DIFFERENT SPECIES OF ANIMALS WITH ARBOVIRUSES. Indian J Med Res. 1965 Mar;53:199–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTERFIELD J. S. Use of goose cells in haemagglutination tests with arthropod-borne viruses. Nature. 1957 Nov 30;180(4596):1201–1202. doi: 10.1038/1801201b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli A. C., Fischer D. S., Downs W. G. Use of sarcoma 180/TG to prepare hyperimmune ascitic fluid in the mouse. J Immunol. 1966 Apr;96(4):676–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



