Abstract
Characterization studies were performed on two psychrophilic phages which were isolated from ground beef samples. Phage inactivation by exposure to heat, low pH, osmotic shock conditions, and freezing showed that these two isolates were different. One-step growth experiments indicated that one isolate had a burst size five times as large (500) and a latent period two times as long (4 hr) as the other when tested at 7 C. Nucleic acid type was 2-deoxyribonucleic acid for both. Electron micrographs showed one to belong to Bradley's phage group A and the other to phage group C.
Full text
PDF


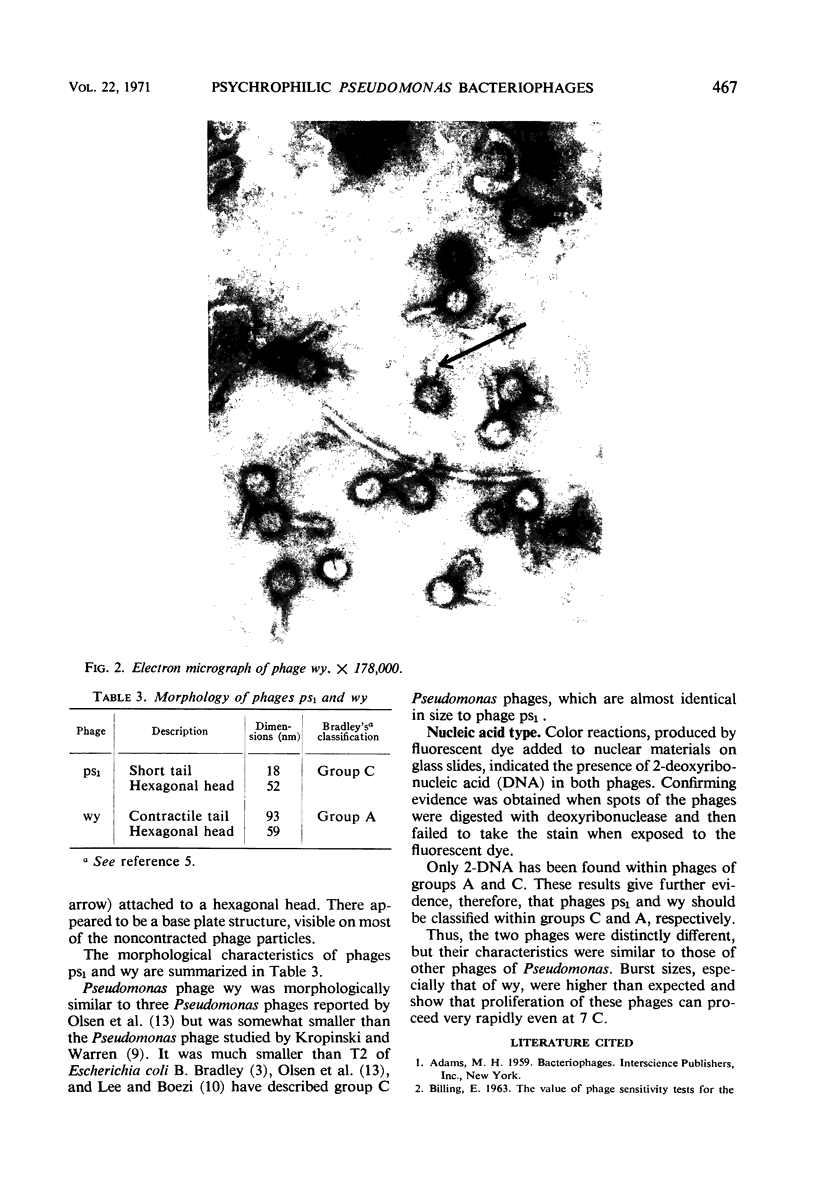

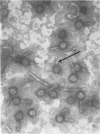
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADLEY D. E. The structure of some Staphylococcus and Pseudomonas phages. J Ultrastruct Res. 1963 Jun;8:552–565. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(63)80055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. The fluorescent staining of bacteriophage nucleic acids. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Sep;44(3):383–391. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-3-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das N. K., Marshall R. T. Adsorption of staphylococcal bacteriophage by milk proteins. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):1095–1098. doi: 10.1128/am.15.5.1095-1098.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delisle A. L., Levin R. E. Bacteriophages of psychrophilic pseudomonads. I. Host range of phage pools active against fish spoilage and fish-pathogenic pseudomonads. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(3):307–317. doi: 10.1007/BF02219151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Warren R. A. Isolation and properties of a Pseudomonas acidovorans bacteriophage. J Gen Virol. 1970 Jan;6(1):85–93. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-6-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. F., Boezi J. A. Characterization of bacteriophage gh-1 for Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1821–1827. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1821-1827.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan R. J., O'Mara W. O., Grogen J. B. Physical stability and biological and physicochemical properties of twelve Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophages. Virology. 1969 Apr;37(4):642–648. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90282-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H. Isolation and growth of psychrophilic bacteriophage. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jan;15(1):198–198. doi: 10.1128/am.15.1.198-.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Metcalf E. S., Todd J. K. Characteristics of bacteriophages attacking psychrophilic and mesophilic pseudomonads. J Virol. 1968 Apr;2(4):357–364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.4.357-364.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIZVI S., MORA P. T. BACTERIOPHAGE PLAQUE-COUNT ASSAY AND CONFLUENT LYSIS ON PLATES WITHOUT BOTTOM AGAR LAYER. Nature. 1963 Dec 28;200:1324–1325. doi: 10.1038/2001324a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER R. A marine bacteriophage. Nature. 1955 Apr 16;175(4459):690–691. doi: 10.1038/175690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman P. A., Marshall R. T. Interaction between streptococcal bacteriophage and milk. J Dairy Sci. 1969 Sep;52(9):1368–1371. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(69)86756-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman P. A., Marshall R. T. Isolation of psychrophilic bacteriophage-host systems from refrigerated food products. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Aug;22(2):220–223. doi: 10.1128/am.22.2.220-223.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]