Abstract
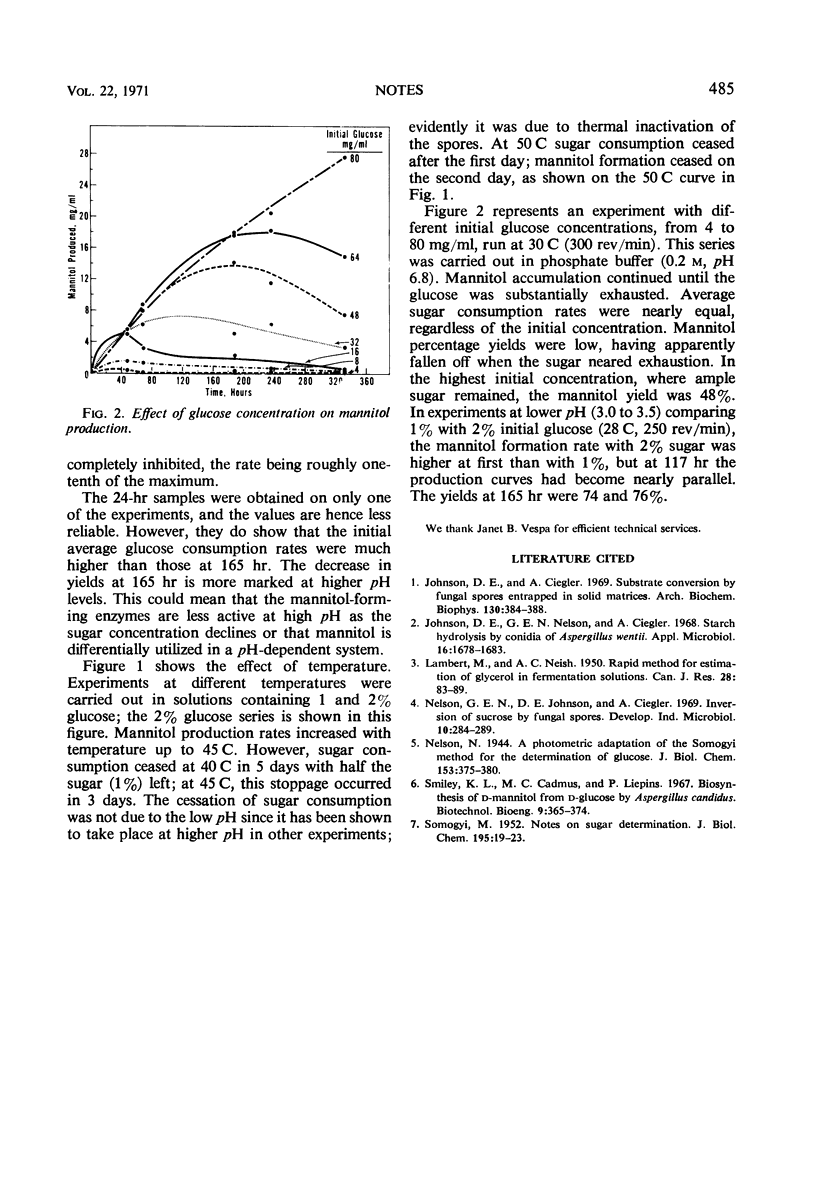
Conidia of Aspergillus candidus converted glucose and other sugars to mannitol. Low pH (ca. 3.0) apparently favored the percentage yield but decreased the fermentation rate.
Full text
PDF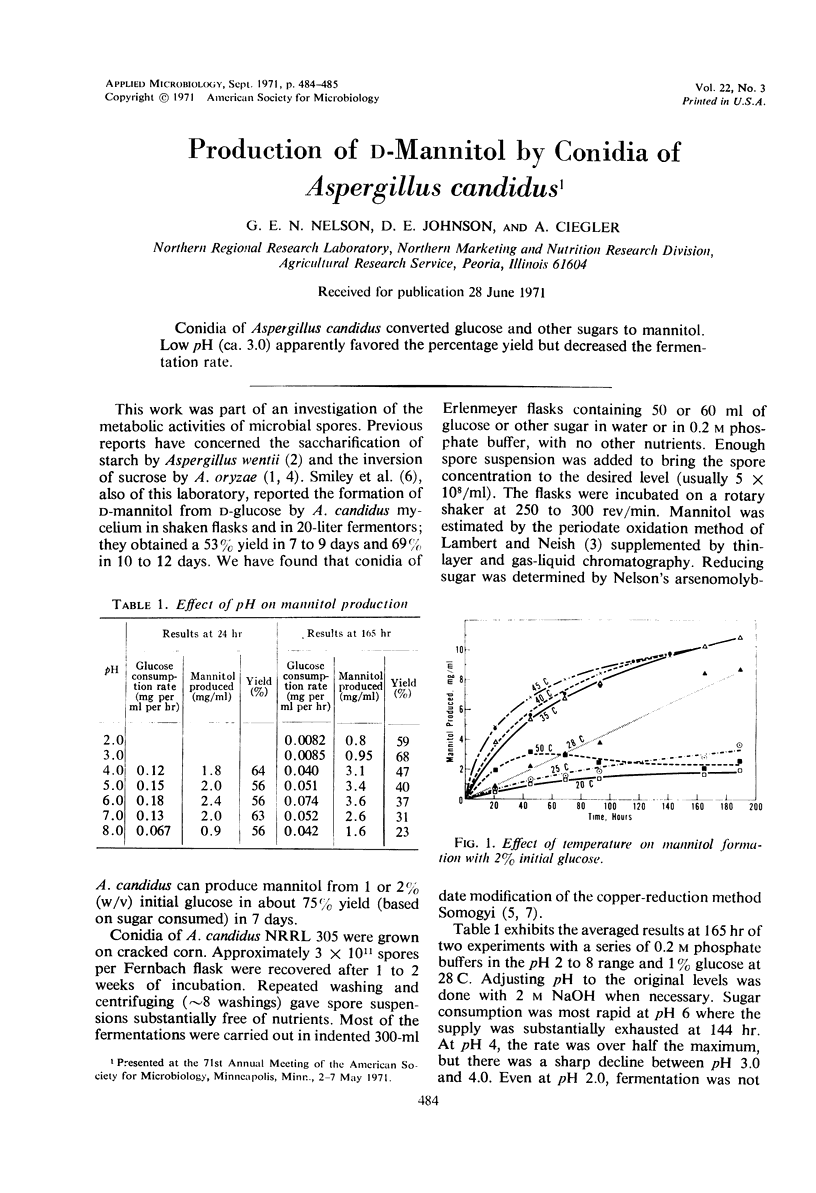
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Johnson D. E., Ciegler A. Substrate conversion by fungal spores entrapped in solid matrices. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):384–388. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Nelson G. E., Ciegler A. Starch Hydrolysis by Conidia of Aspergillus wentii. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Nov;16(11):1678–1683. doi: 10.1128/am.16.11.1678-1683.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOGYI M. Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


