Volume 442 (2012), pp. 681–692
The published version of Figure 3(B) incorrectly featured an additional panel; the corrected figure is shown here.
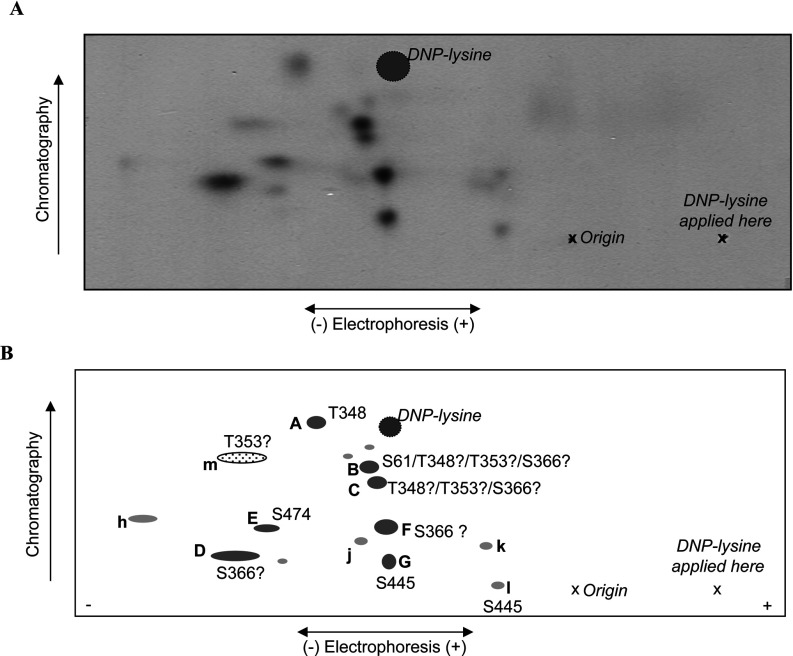
Figure 3. 2D peptide maps from autophosphorylated wild-type eEF2K.
Wild-type eEF2K was allowed to undergo autophosphorylation in the presence of Ca2+/CaM and then subjected to tryptic digestion. Phosphopeptides were resolved by electrophoresis and chromatography (polarity and directions are indicated). Also shown are the position of the origin, where the peptide samples were applied, “X”, and the final migration position of the DNP–lysine marker (cross-hatched circle). (A) Representative map of wild-type eEF2K; (B) schematic summary of peptides; lettering in capitals for major peptides (shown in dark grey) and in lower case for minor ones (light grey). The peptide shown by the dotted oval (‘m’) was only observed on maps from the eEF2K[T348A] mutant.