Abstract
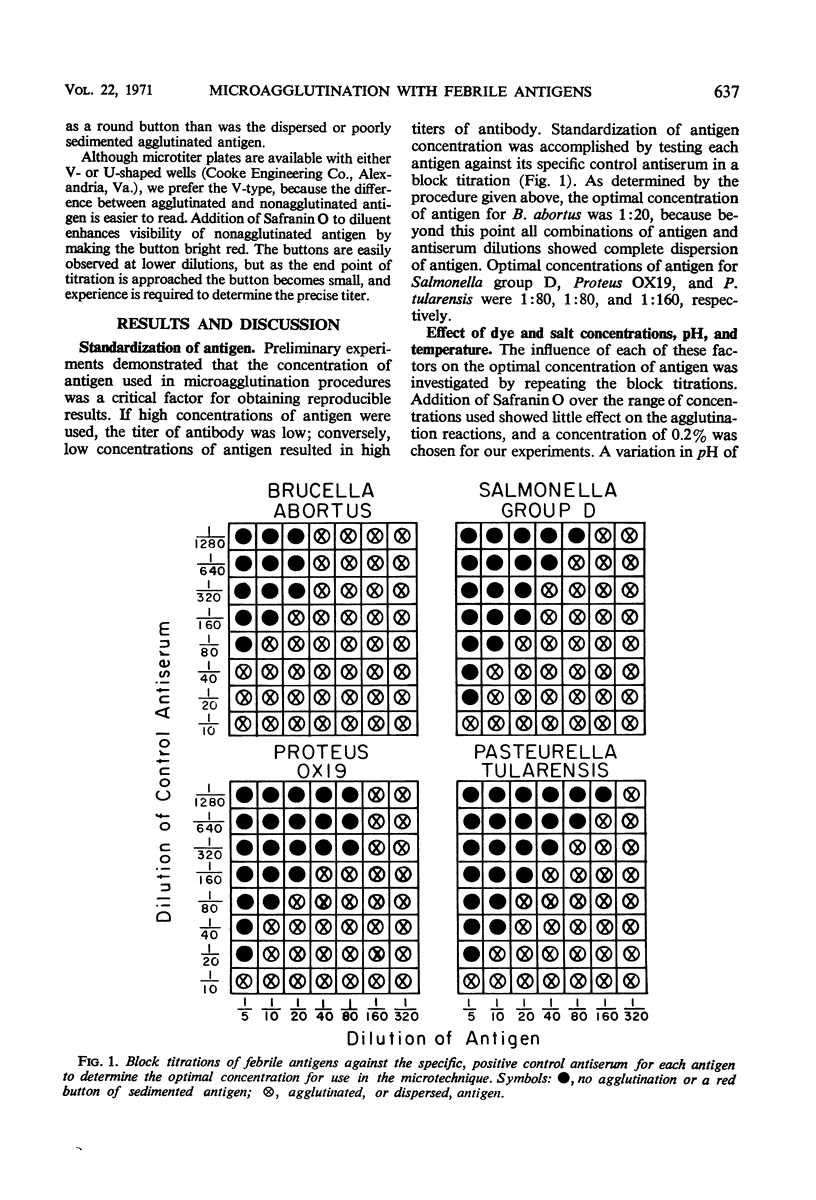
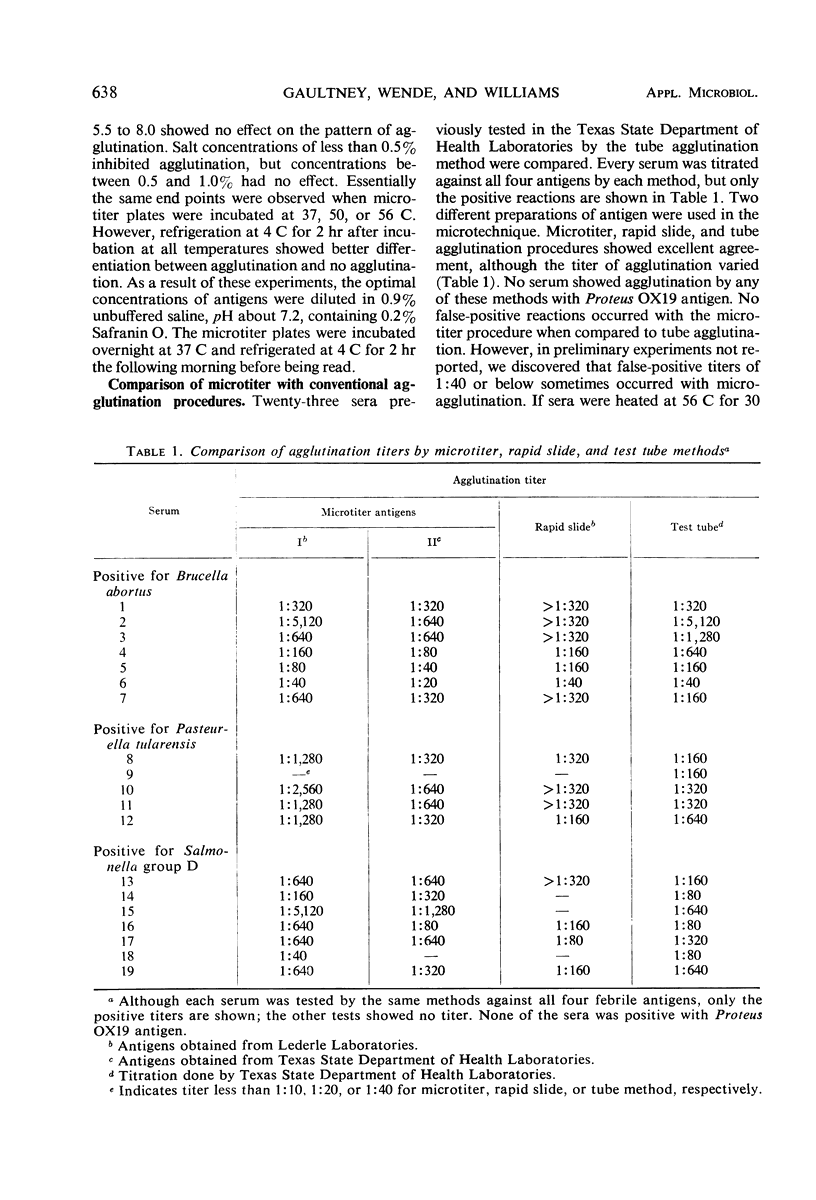
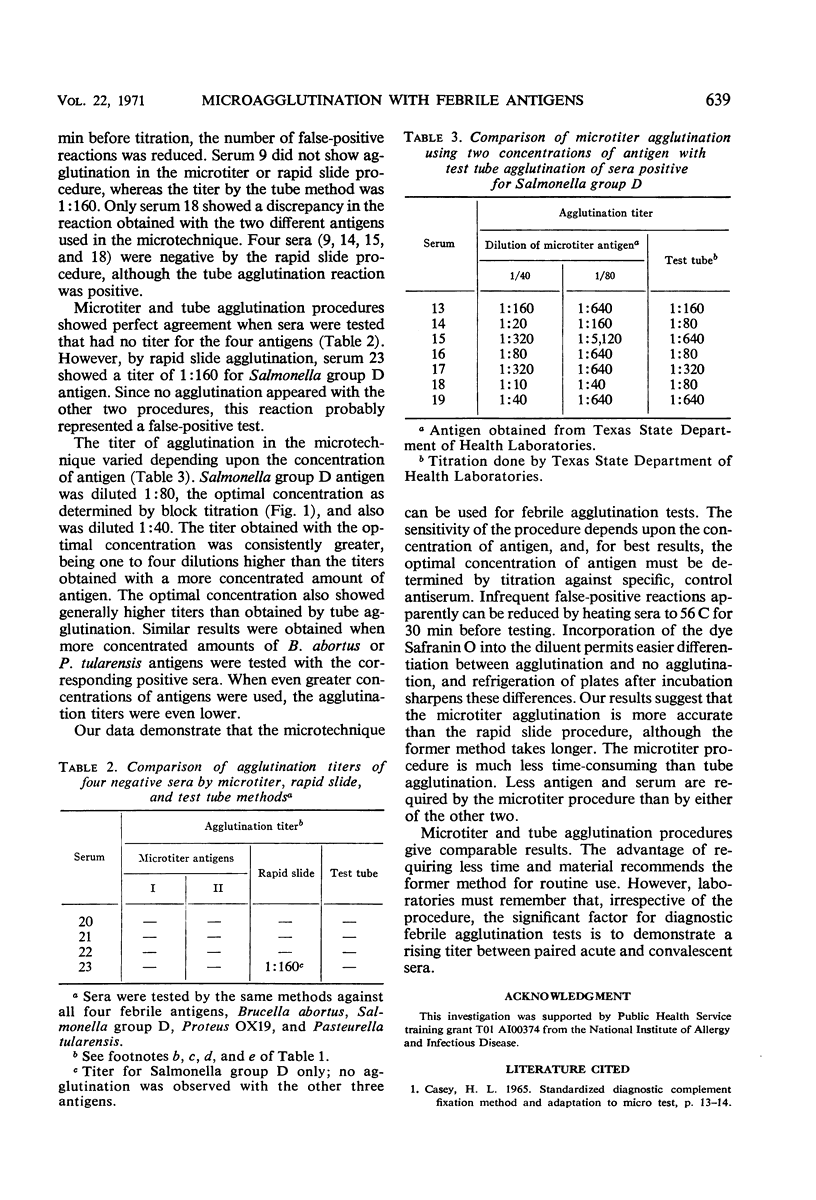
Febrile agglutination tests were done by using as antigens Brucella abortus, Salmonella group D, Proteus OX19, and Pasteurella tularensis. Comparison of results from 23 sera showed that the microtechnique, rapid slide, and test tube methods gave similar titers, although those from the microtechnique were generally higher. The sensitivity of the microtechnique depended upon the concentration of antigen, and, to obtain reproducible results, the optimal concentration of antigens had to be determined by preliminary titrations against specific, positive control antisera. Readability of reactions in the microtechnique was enhanced by adding the dye Safranin O to diluent for antigen and by use of V-type, rather than U-type, microtiter plates. Tests were also done to determine the effects of dye and salt concentrations, pH, and temperature of incubation upon the titer of agglutinations by the microtechnique. Our results indicated that the microtechnique could be used for agglutination tests involving febrile antigens. The procedure is less time-consuming than the tube method and requires less antigen and serum than the latter method or the rapid slide method.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cox P. S. A comparison of the rapid slide and standard tube agglutination tests for brucellosis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1968;62(4):517–521. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(68)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elek P., Vizy L. Annex I. New agglutination methods for the diagnosis of brucellosis using stained antigens. An Microbiol (Rio J) 1966 1967;14:127–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiset P., Ormsbee R. A., Silberman R., Peacock M., Spielman S. H. A microagglutination technique for detection and measurement of rickettsial antibodies. Acta Virol. 1969 Jan;13(1):60–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL W. H., MANION R. E. Comparison of the Coombs test with other methods for Brucella agglutinins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1953 Jan;32(1):96–106. doi: 10.1172/JCI102716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkman J. B., Jr, Fischer J., Pagano J. S. A microtiter plate technique for the agglutination typing of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1970 Feb;121(2):217–221. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPINK W. W., ANDERSON D. Correlation of a rapid slide-agglutination test (Castaneda) with a tube-agglutination test in screening suspected cases of human brucellosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1952 Oct;40(4):593–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKATSY G. The use of spiral loops in serological and virological micro-methods. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;3(1-2):191–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedros N. A., Hill P. R. Microagglutination technique for Neisseria meningitidis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):900–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.900-901.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



