Abstract
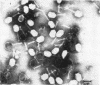
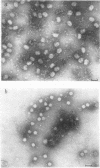
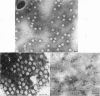
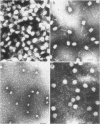
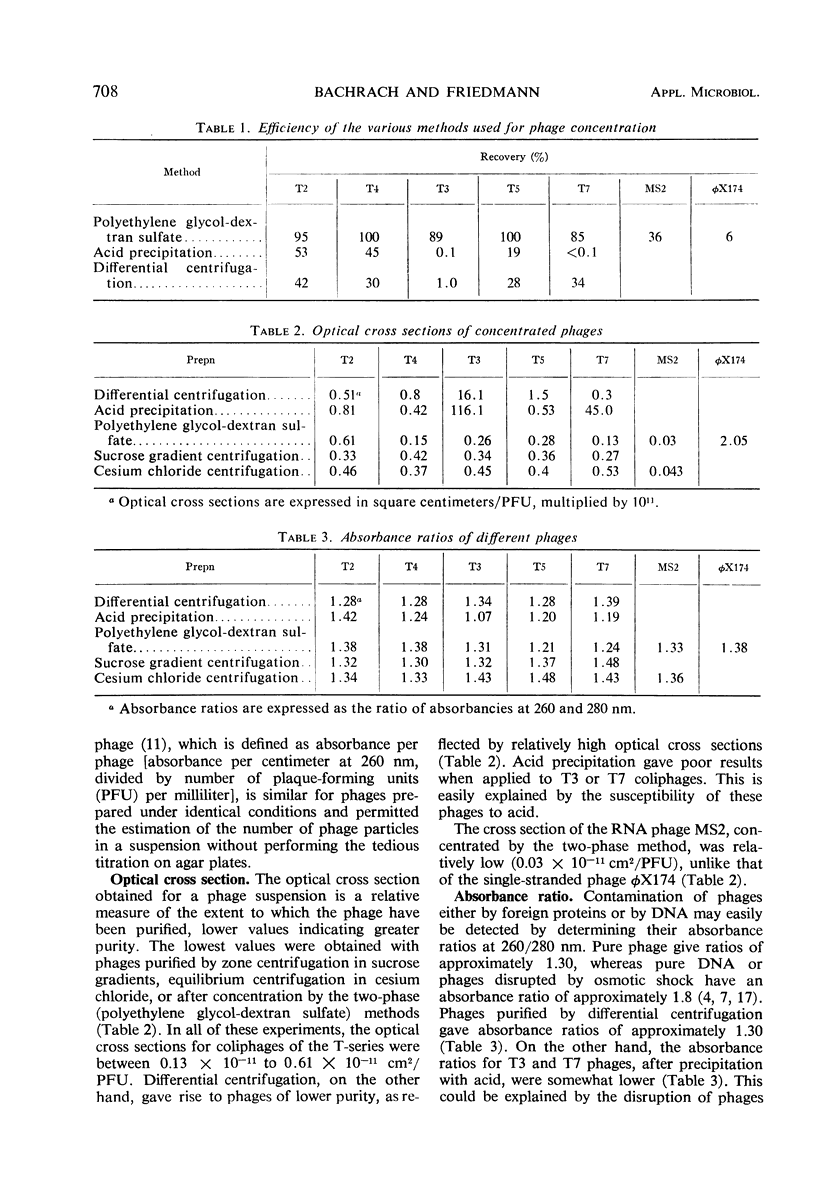
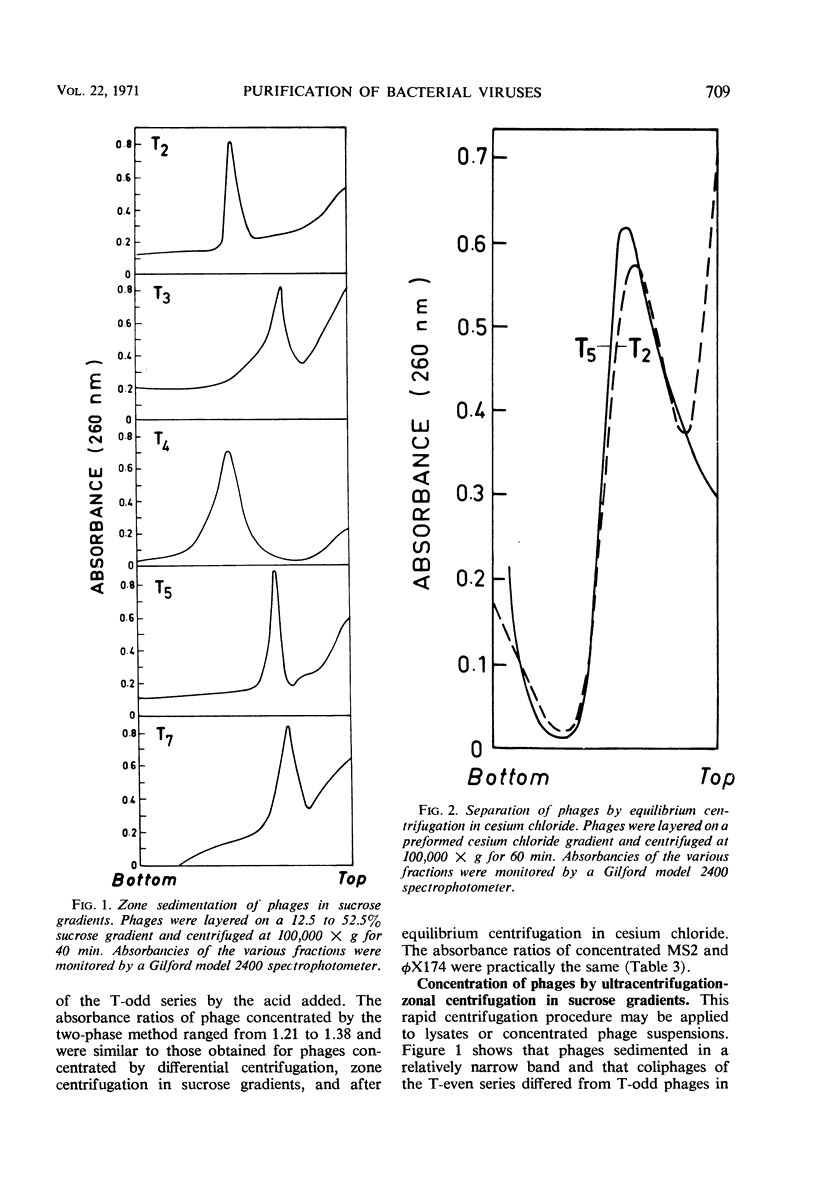
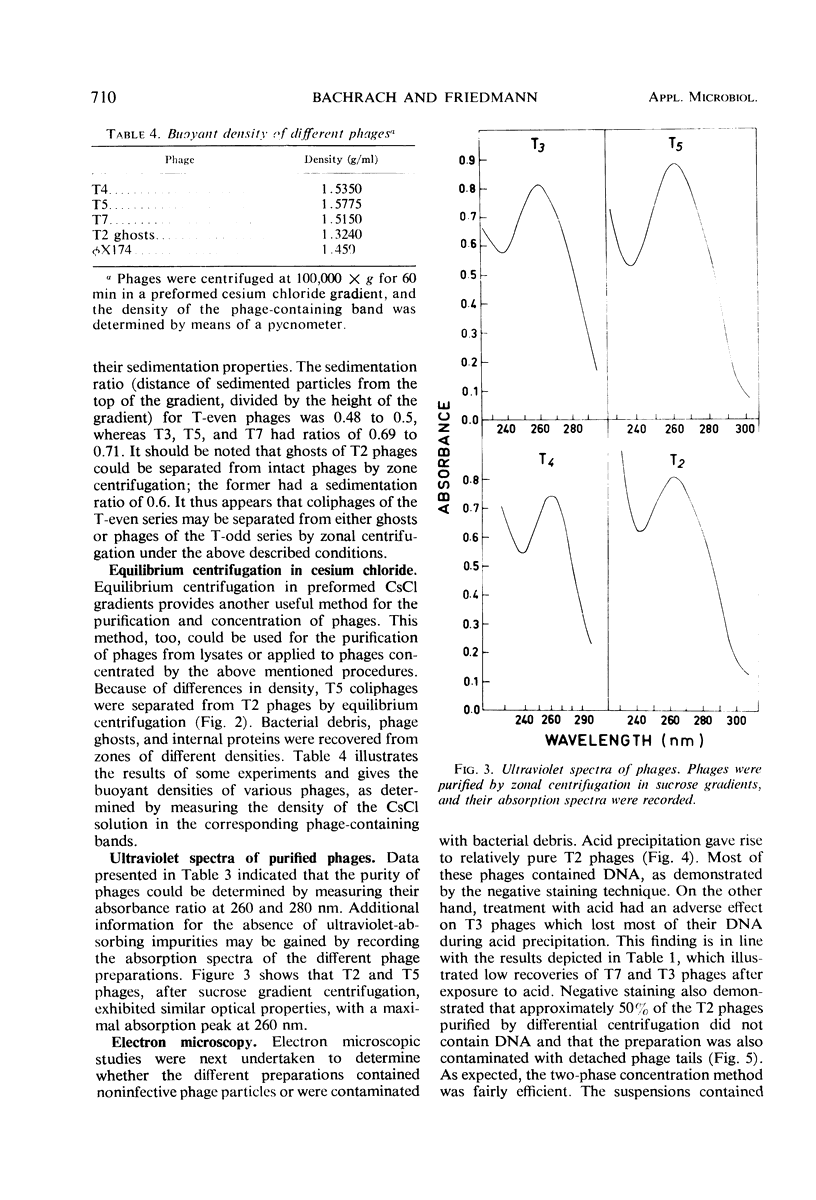
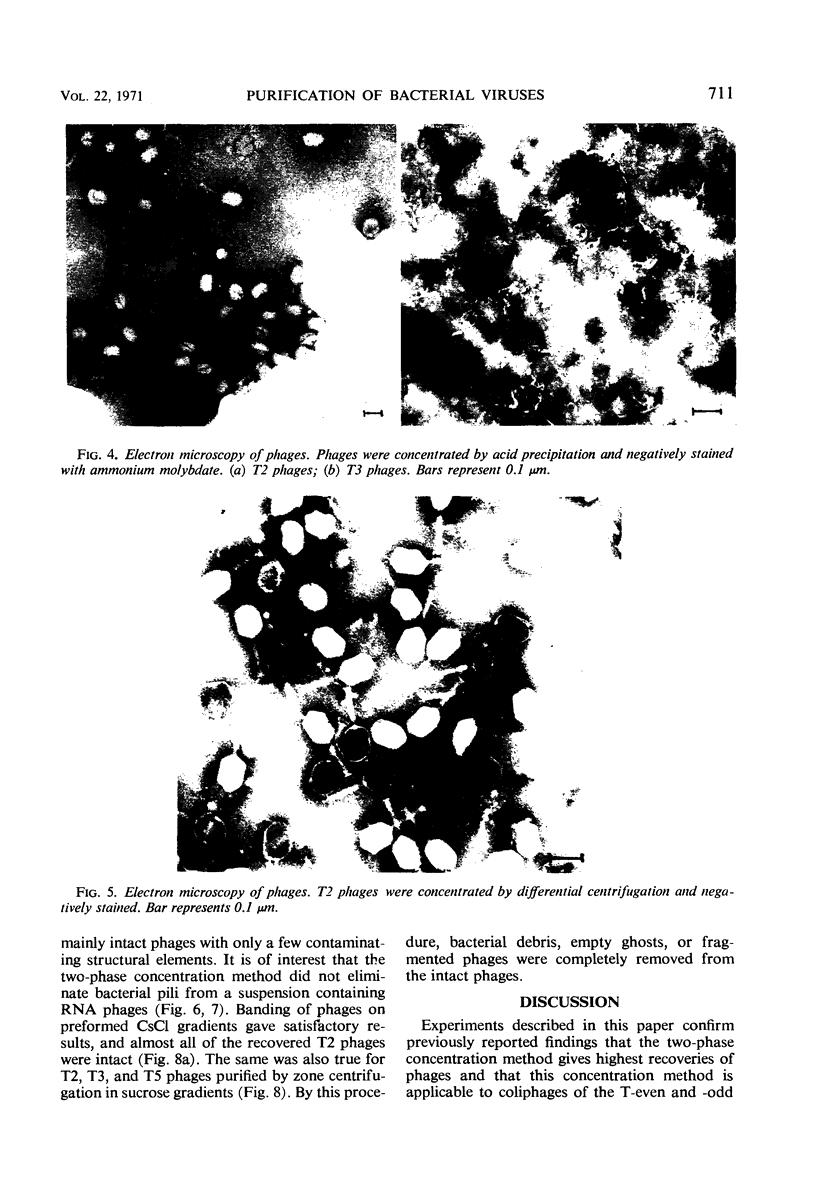
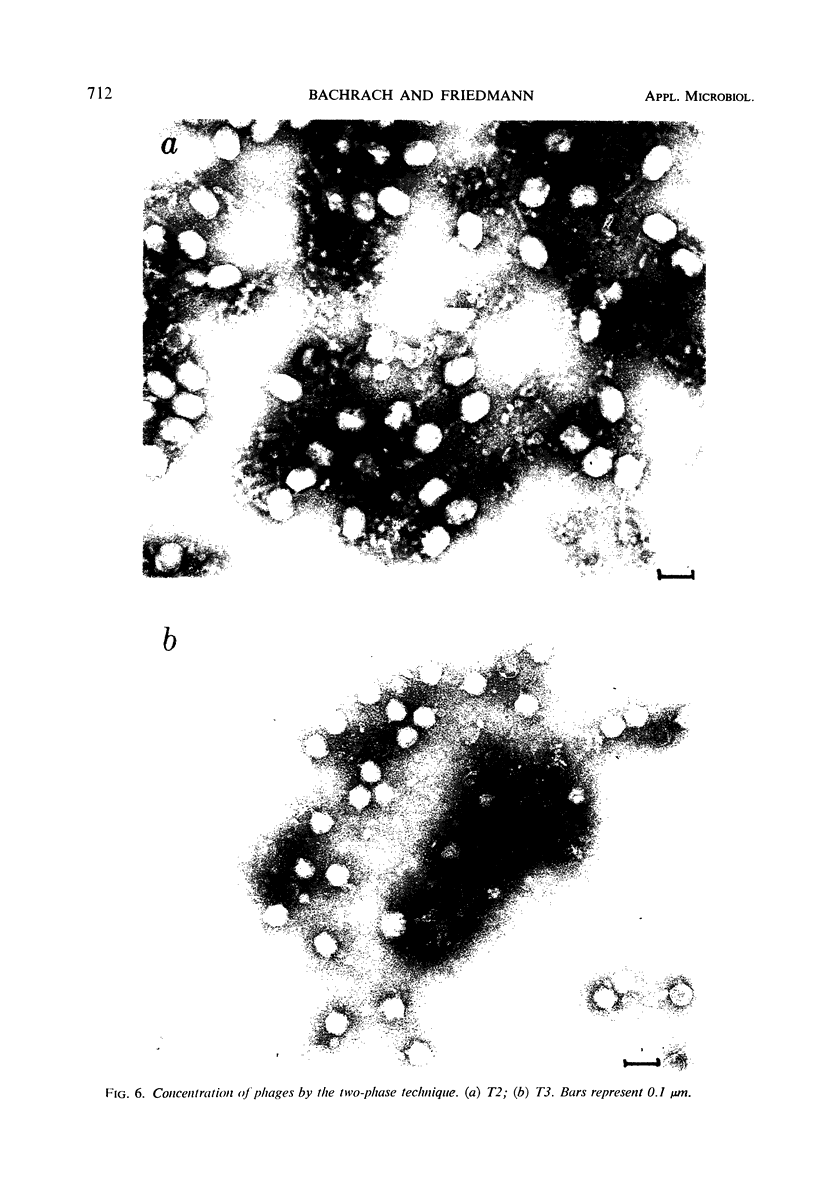
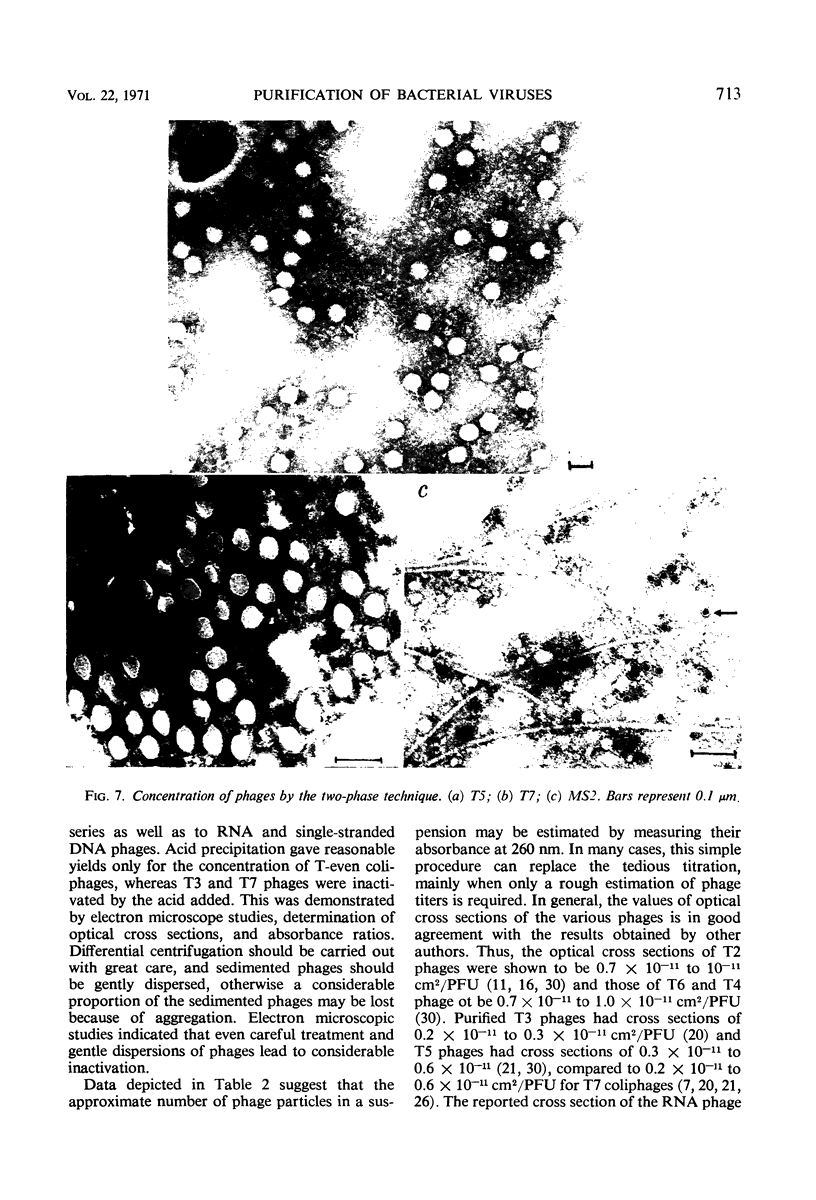
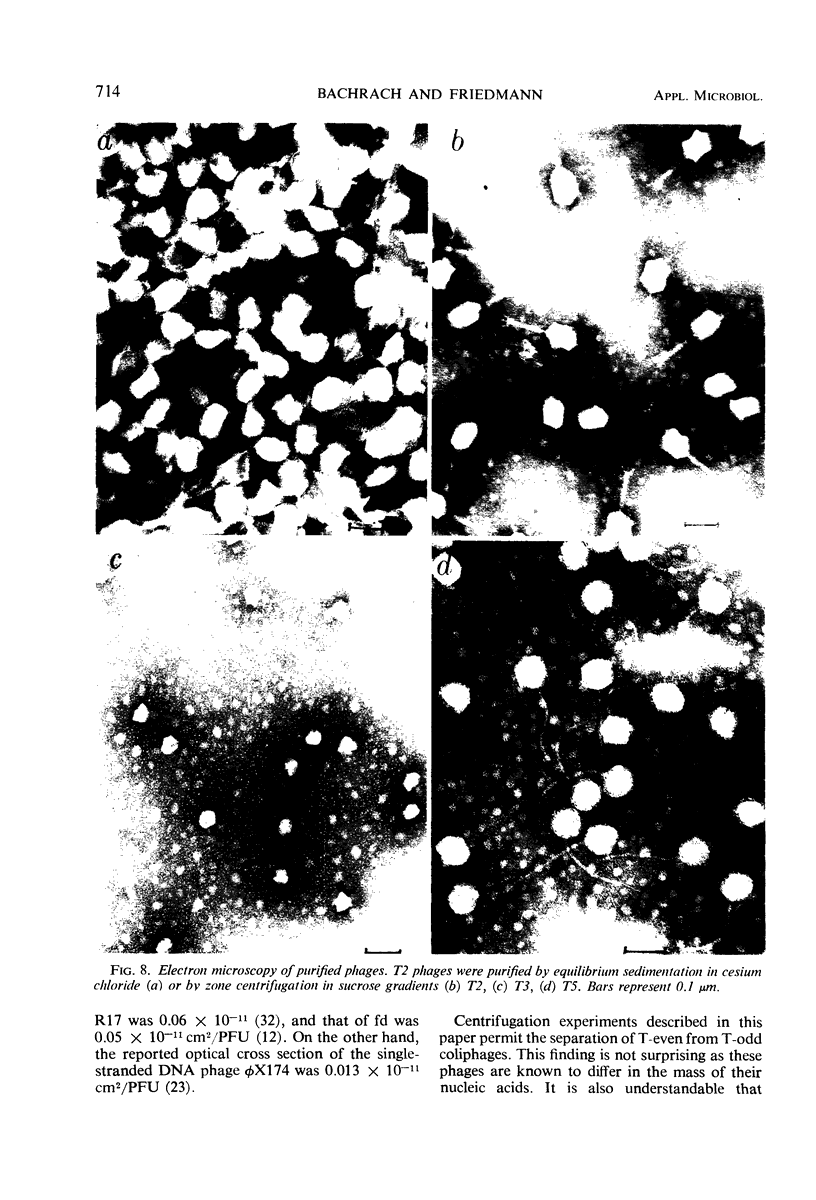
The efficiencies of the various methods used for phage concentration have been compared. The two-phase concentration method (with polyethylene glycol and dextran sulfate) gave maximal recoveries of infectivity for coliphages of the T-even and T-odd series and for ribonucleic acid phages and single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid phages. Precipitation of phages by acid gave high yields when applied to T2 and T4 phages but not with T3 and T7 coliphages. Differential centrifugation was efficient when sedimented phages were gently dispersed before repeating the centrifugation cycle. The efficiencies of the various methods have also been confirmed by electron microscope studies, which also show that the two-phase concentration method gave rise to intact phages. Zone centrifugations in sucrose gradients (12.5 to 52.5%) indicated that coliphages of the T-even series sediment faster than T-odd coliphages; they may thus be separated from each other and from empty ghosts by centrifugation at 100,000 × g for 40 min. Equilibrium centrifugation in preformed cesium chloride gradients was also useful for phage concentration and purification. This study also deals with some optical properties of purified phages; optical cross sections and absorbance ratios (at 260 and 280 nm) of the various preparations are given.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachrach U., Levin R., Friedmann A. Studies on phage internal proteins: isolation of protein-DNA complexes from T2 phages and from phage-infected bacteria. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):882–892. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G. Chromatography of nucleic acids on hydroxyapatite. Nature. 1965 May 22;206(4986):779–783. doi: 10.1038/206779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody E. N., Diggelmann H., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription of the bacteriophage T4 template. Obligate synthesis of T4 prereplicative RNA in vitro. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 17;9(6):1289–1299. doi: 10.1021/bi00808a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON P. F., FREIFELDER D. The physical properties of T7 bacteriophage. J Mol Biol. 1962 Dec;5:635–642. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRIOTT R. M., BARLOW J. L. Preparation, purification, and properties of E. coli virus T2. J Gen Physiol. 1952 May;36(1):17–28. doi: 10.1085/jgp.36.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERSHEY A. D. An upper limit to the protein content of the germinal substance of bacteriophage T2. Virology. 1955 May;1(1):108–127. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN-BERLING H., MARVIN D. A., DUERWALD H. EIN FAEDIGER DNS-PHAGE (FD) UND EIN SPHAERISCHER RNS-PHAGE (FR), WIRTSSPEZIFISCH FUER MAENNLICHE STAEMME VON E. COLI. 1. PRAEPARATION UND CHEMISCHE EIGENSCHAFTEN VON FD UND FR. Z Naturforsch B. 1963 Nov;18:876–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Sinsheimer R. L. The process of infection with bacteriophage phiX174. XXVII. Synthesis of a viral-specific chloramphenicol-resistant protein in phiX174-infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 14;39(3):655–668. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIYAZAWA Y., THOMAS C. A., Jr NUCLEOTIDE COMPOSITION OF SHORT SEGMENTS OF DNA MOLECULES. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:223–237. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacHattie L. A., Ritchie D. A., Thomas C. A., Jr, Richardson C. C. Terminal repetition in permuted T2 bacteriophage DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1967 Feb 14;23(3):355–363. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra D. N., Sinha R. K., Das Gupta N. N. Molecular weight of DNA from coliphage T7 by electron microscopy. Virology. 1969 Oct;39(2):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILIPSON L., ALBERTSSON P. A., FRICK G. The purification and concentration of viruses by aqueous polymerphase systems. Virology. 1960 Jul;11:553–571. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. A., Thomas C. A., Jr, MacHattie L. A., Wensink P. C. Terminal repetition in non-permuted T3 and T7 bacteriophage DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1967 Feb 14;23(3):365–376. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein I. Heat-stable mutants of T5 phage. I. The physical properties of the phage and their DNA molecules. Virology. 1968 Nov;36(3):356–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEDAT J., SINSHEIMER R. L. STRUCTURE OF THE DNA OF BACTERIOPHAGE PHI-X174. V. PURINE SEQUENCES. J Mol Biol. 1964 Aug;9:489–497. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80221-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone K. R., Cummings D. J. Isolation and characterization of two basic internal proteins from the T-even bacteriophages. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):445–454. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.445-454.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. The genetics and physiology of bacteriophage T7. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):562–574. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS C. A., Jr, BERNS K. I. The physical characterization of DNA molecules released from T2 and T4 bacteriophage. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:277–288. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zárybnický V., Horácek P. Influence of ionic strength on the stability of phage T2r to osmotic shock. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1968;13(5):391–400. doi: 10.1007/BF02869189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]