Abstract
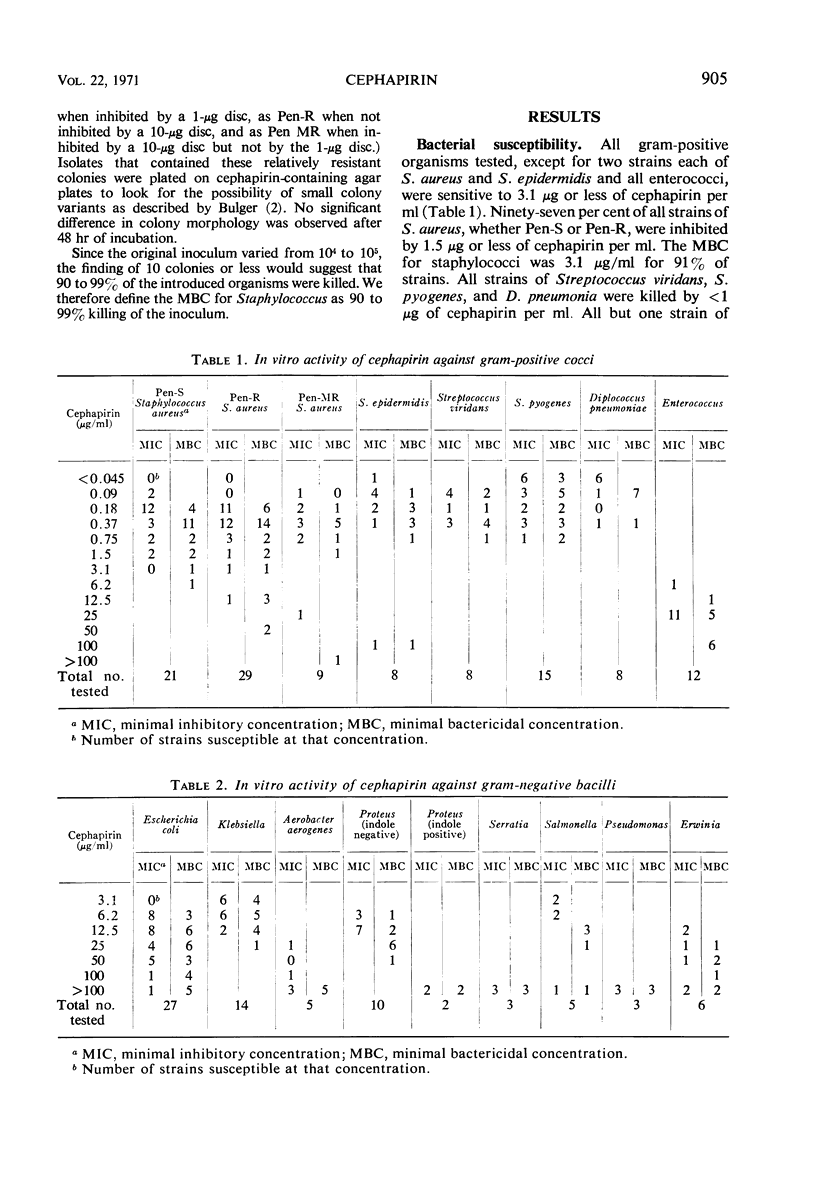
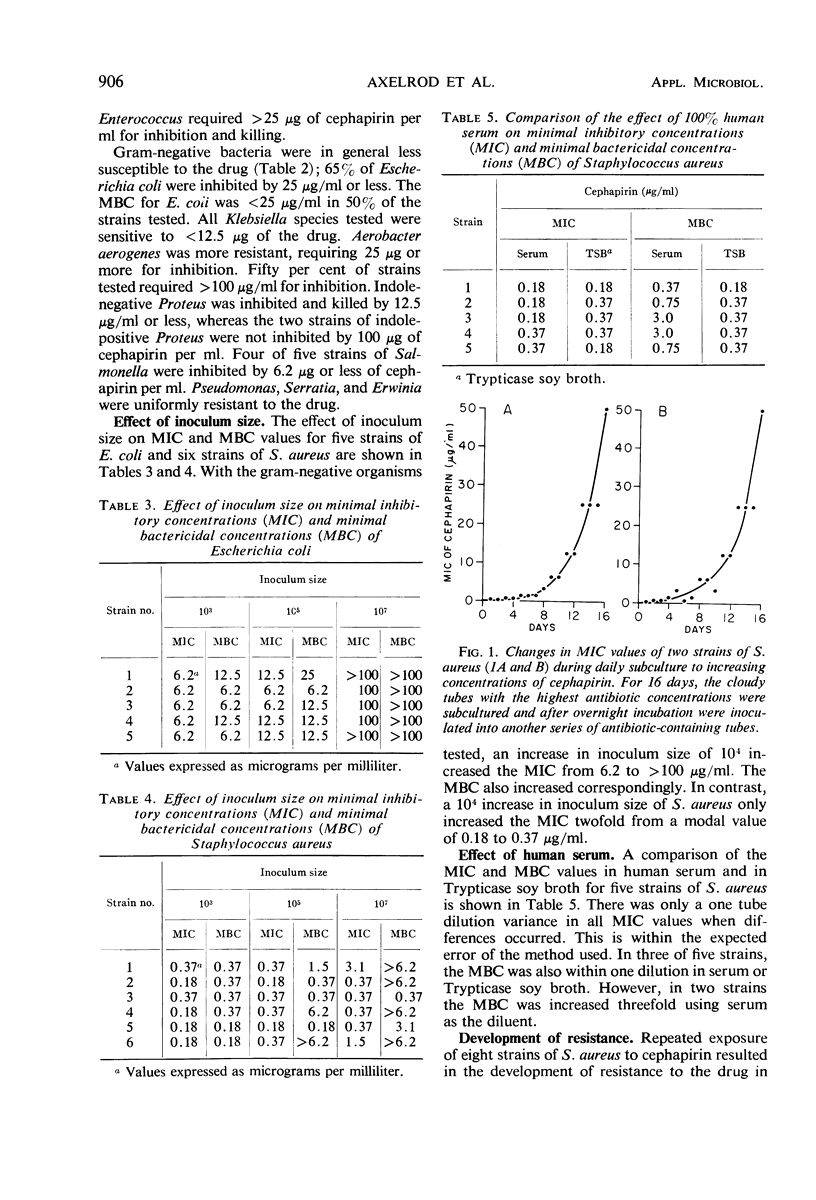
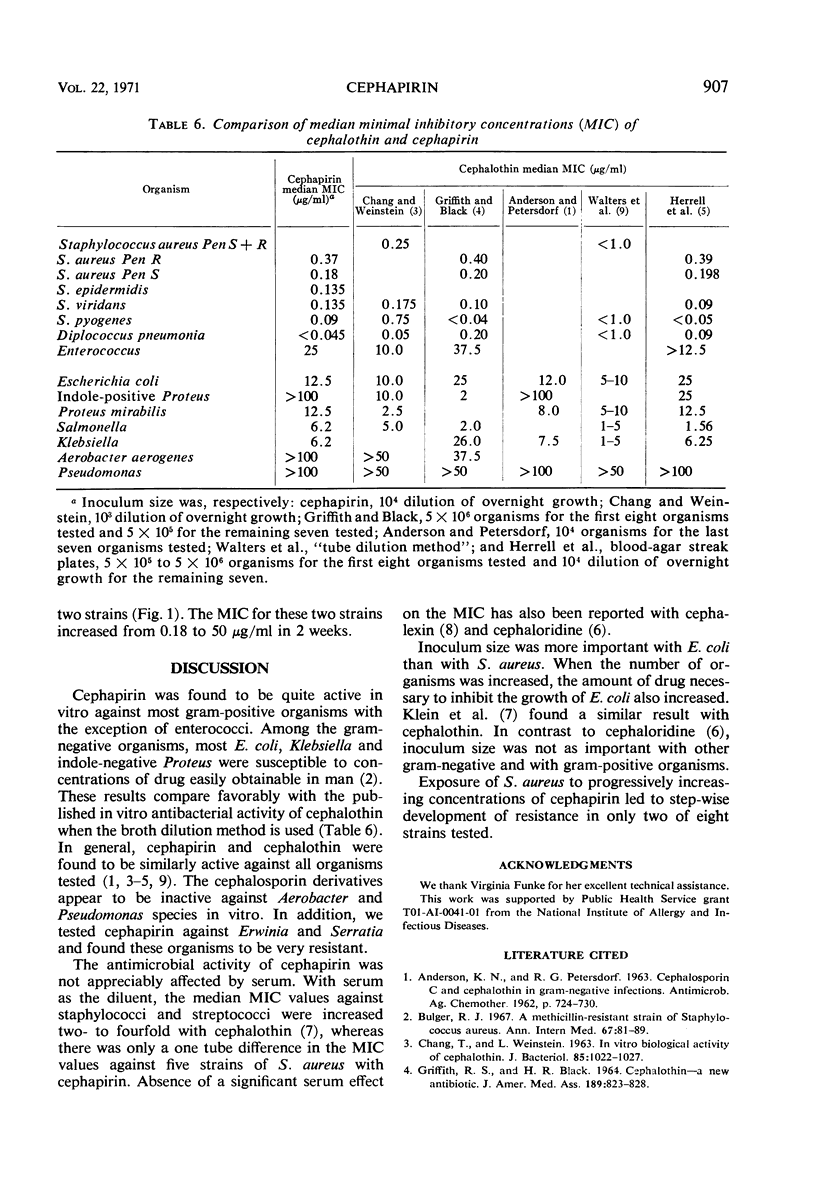
Cephapirin, a new semisynthetic cephalosporin derivative, was found to have an antibacterial spectrum similar to that of cephalothin. Staphylococcus aureus was inhibited by cephapirin concentrations of 0.09 to 12.5 μg/ml. S. epidermidis, S. viridans, S. pyogenes, and Diplococcus pneumonia isolates were inhibited by less than 1 μg/ml. The Enterococcus required a concentration of 25 μg of antibiotic per ml for inhibition. Approximately 65% of Escherichia coli, and all Klebsiella, indole-negative Proteus, and Salmonella strains tested were inhibited by the drug. Serratia, Pseudomonas, indole-positive Proteus, and Erwinia strains were highly resistant. Inoculum size was not an important factor in determining the level of sensitivity of S. aureus to cephapirin. The antibiotic does not appear to be significantly bound to serum protein. In vitro development of resistance to the drug was demonstrated with two isolates of S. aureus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bulger R. J. A methicillin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Clinical and laboratory experience. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Jul;67(1):81–89. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-1-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG T. W., WEINSTEIN L. IN VITRO BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF CEPHALOTHIN. J Bacteriol. 1963 May;85:1022–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.5.1022-1027.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIFFITH R. S., BLACK H. R. CEPHALOTHIN--A NEW ANTIBIOTIC. PRELIMINARY CLINICAL AND LABORATORY STUDIES. JAMA. 1964 Sep 14;189:823–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRELL W. E., BALOWS A., BECKER J. SOME EXPERIMENTAL AND CLINICAL STUDIES ON CEPHALOTHIN. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1963 Nov-Dec;4:709–719. doi: 10.1002/cpt196346709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN J. O., EICKHOFF T. C., TILLES J. G., FINLAND M. CEPHALOTHIN: ACTIVITY IN VITRO, ABSORPTION AND EXCRETION IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND CLINICAL OBSERVATIONS IN 40 PATIENTS. Am J Med Sci. 1964 Dec;248:640–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kislak J. W., Steinhauer B. W., Finland M. Cephaloridine activity in vitro and absorption and urinary excretion in normal young men. Am J Med Sci. 1966 Apr;251(4):433–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers B. R., Kaplan K., Weinstein L. Cephalexin: microbiological effects and pharmacologic parameters in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1969 Nov-Dec;10(6):810–816. doi: 10.1002/cpt1969106810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


