Abstract
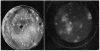
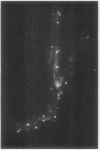
A method is presented to identify esterase-synthesizing microbial colonies within mixed culture plates by utilizing induced esterase hydrolysis of nonfluorescent butyryl ester of 7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin to the highly fluorescent 7-hydroxy-4 methyl umbelliferone. Microscopy procedures for making esterase loci of fungal mycelia visible with this reaction are described.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHEN R. F., BOWMAN R. L. FLUORESCENCE POLARIZATION: MEASUREMENT WITH ULTRAVIOLET-POLARIZING FILTERS IN A SPECTROPHOTOFLUOROMETER. Science. 1965 Feb 12;147(3659):729–732. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3659.729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. M., Lynd J. Q. Soil microfloral interactions with aflatoxin synthesis and degradation. Mycologia. 1970 Sep-Oct;62(5):978–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. J., Kircher H. W. Fluorometric assay for the hydrolytic activity of lipase using fatty acyl esters of 4-methylumbelliferone. Anal Biochem. 1967 Nov;21(2):279–285. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90190-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynd J. Q., Lynd F. T. Hepatic cholesterol-lipid anomalies induced by aflatoxin. Pathol Vet. 1970;7(6):509–516. doi: 10.1177/030098587000700606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]