Abstract
Caenorhabditis elegans has become a powerful experimental organism with which to study meiotic processes that promote the accurate segregation of chromosomes during the generation of haploid gametes. Haploid reproductive cells are produced through one round of chromosome replication followed by two successive cell divisions. Characteristic meiotic chromosome structure and dynamics are largely conserved in C. elegans. Chromosomes adopt a meiosis-specific structure by loading cohesin proteins, assembling axial elements, and acquiring chromatin marks. Homologous chromosomes pair and form physical connections though synapsis and recombination. Synaptonemal complex and crossover formation allow for the homologs to stably associate prior to remodeling that facilitates their segregation. This chapter will cover conserved meiotic processes as well as highlight aspects of meiosis that are unique to C. elegans.
Keywords: Meiosis, Pairing, Recombination, Synapsis, Cohesion, Germline, C. elegans
6.1 Introduction
Meiosis is a specialized cell division process by which sexually reproducing diploid organisms, including humans, produce haploid gametes (i.e., eggs and sperm) to be used for fertilization. This halving in the number of chromosomes is accomplished by following one round of DNA replication with two consecutive rounds of chromosome segregation (meiosis I and meiosis II). Whereas homologous chromosomes segregate away from each other at meiosis I, sister chromatids segregate to opposite poles of the spindle at meiosis II. The accurate segregation of chromosomes at every cell division is required to prevent aneuploidy, which consists of the formation of cells carrying an incorrect number of chromosomes. This is of tremendous importance given that meiotic chromosome missegregation has a significant impact on human health, as indicated by it being the leading cause of congenital birth defects and miscarriages (Hassold and Hunt 2001). Therefore, there are several mechanisms set in place to ensure proper chromosome segregation, as exemplified by meiosis I, where homologous chromosomes must pair, align, and form physical connections prior to the first division. Several key processes promote the normal progression of these steps during meiosis I. These include the formation of connections between sister chromatids afforded by the establishment of sister chromatid cohesion, the establishment of stable interactions between homologs achieved through the formation of a proteinaceous structure known as the synaptonemal complex (SC), and the repair of programmed meiotic DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) into crossovers (CO).
Caenorhabditis elegans has several unique features that make it an advantageous model organism to study both meiosis and chromosome dynamics. It has a relatively short generation time and is a tractable genetic system that can be used in both forward and reverse genetic approaches. RNA-mediated interference (RNAi), cosuppression and the generation of transgenic lines with targeted deletions can all be used to examine loss-of-function phenotypes (Frokjaer-Jensen et al. 2010; Dernburg et al. 2000; Timmons and Fire 1998). Chromosome nondisjunction is easily assessed by missegregation of the X chromosome, which determines sex in C. elegans. While males have a single sex chromosome (X0), hermaphrodites have two copies (XX). Self-fertilizing hermaphroditic worms lay mostly hermaphroditic progeny and produce males at a very low frequency (<0.2%) (Hodgkin et al. 1979). Mutations affecting meiotic prophase I events result in increased chromosome non-disjunction. Rather than arresting as a result of these defects, aneuploid gametes in C. elegans become fertilized but result in inviable offspring as indicated by increased embryonic lethality (Emb). The Emb phenotype is typically accompanied by a high incidence of males (Him) phenotype.
Distinct morphological changes during its life cycle, as well as its transparency, aid in the developmental staging of worms. Transparency of the entire body of the worm, including the gonad, also facilitates the analysis via whole-mount preparations for immunofluorescence, live or fixed imaging of fluorescent fusions in vivo, and in situ hybridization (Motohashi et al. 2006; Lee and Schedl 2006; Duerr 2006; Phillips et al. 2009a). This allows for 3D analysis of chromosome dynamics as well as the localization of proteins and specific chromosomal regions in the context of intact meiotic nuclei.
In this chapter, we will focus on the meiosis in hermaphrodite worms as they are producing oocytes. Since the germline contains over half of the total number of nuclei comprising an adult hermaphrodite worm, it provides ample biomass for the study of meiosis (MacQueen et al. 2005; Hirsh et al. 1976). The C. elegans gonad is a bi-lobed structure in which nuclei are ordered in a spatial–temporal gradient such that sequential stages of meiosis are easily visualized (Fig. 6.1) (Crittenden et al. 1994). The most distal end, or proliferative zone, contains germ cell nuclei that are undergoing mitotic divisions and meiotic S-phase (Crittenden et al. 2006; Jaramillo-Lambert et al. 2007; Fox et al. 2011). As nuclei move proximally, they enter the early stages of meiosis (leptotene and zygotene) that correspond to the transition zone, in which chromosomes acquire a polarized organization (Dernburg et al. 1998; Crittenden et al. 1994; Hirsh et al. 1976). In the transition zone, chromosomes pair, initiate recombination, and begin to synapse (Fig. 6.2; Dernburg et al. 1998; MacQueen et al. 2002; Alpi et al. 2003; Colaiacovo et al. 2003). Synapsis is completed by entrance into pachytene, when chromosomes redistribute throughout the nuclear periphery. Crossover recombination is then completed during pachytene within the context of fully synapsed chromosomes. By late pachytene, the synaptonemal complex (SC) starts to disassemble, a process that continues during diplotene. Finally, at diakinesis, six pairs of homologous chromosomes (bivalents) are observed held together by chiasmata, the cytological manifestation resulting from the earlier crossover event between homologous chromosomes underpinned by flanking sister chromatid cohesion (Villeneuve 1994).
Fig. 6.1.
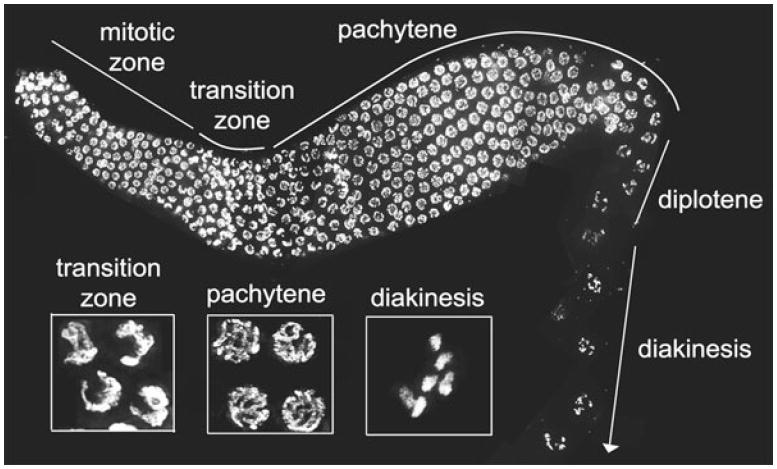
The C. elegans gonad. A dissected and DAPI-stained gonad of a hermaphrodite adult worm. Progression from the distal to the proximal end is depicted from left to right. The image is a projection of three-dimensional data stacks of intact nuclei, which were taken approximately halfway through the gonad, to facilitate visualization of nuclear morphology
Fig. 6.2.
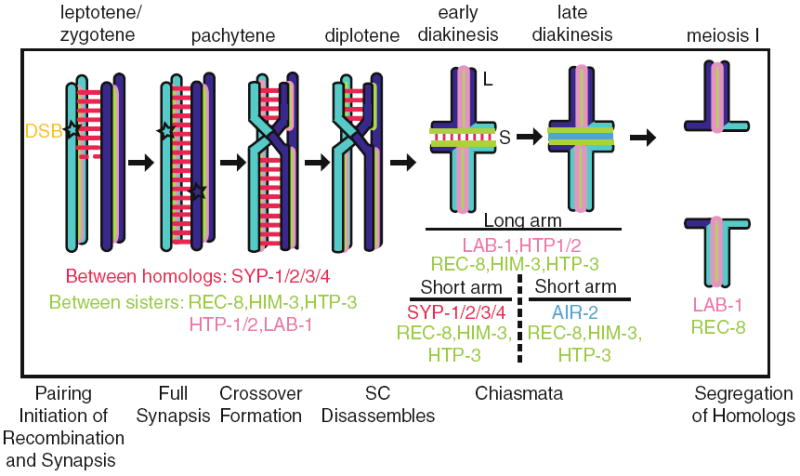
Events during meiotic progression that contribute to the proper segregation of homologs during the first meiotic division
The distinct meiotic stages, basic mechanisms, and genes involved in meiotic chromosome dynamics are largely conserved across taxa (Tables 6.1 and 6.2). Thus, meiotic studies in C. elegans, a model system amenable to a wide range of genetic, molecular, cytological, and biochemical approaches, can provide significant insight into the meiotic processes occurring in other organisms.
Table 6.1.
Conservation of meiotic processes across species
| Species | Homologous pairing | Chromosome movement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||
| Primary mediator | Primary mediator | SUN and KASH | Polarized chromosomes | |
| A. thaliana | DSB repair | Unknown, but maize uses microtubules (mt) and actin | SUN-1/2 | None, but bouquet in rye, maize, and wheat |
| S. cerevisiae | DSB repair | Actin cables | Mps3 and Csm4 | Bouquet; telomere-mediated |
| S. pombe | Horsetail movement | mt/dynein | Sad1 and Kms1 | Horsetail; telomere-mediated |
| C. elegans | Pairing centers interact via ZIM proteins (autosomes) and HIM-8 (X) | mt/dynein | SUN-1 and ZYG-12 | Crescent-shaped organization; PC mediated |
| D. melanogaster | Females: heterochromatin | mt | – | None |
| Males: X–Y pairing uses rDNA repeats, SNM and MNM | ||||
| M. musculus | DSB repair | mt | SUN-1/2 | Bouquet; telomere-mediated |
| Species | Synapsis | Recombination | |||
|
| |||||
| Axial/lateral elements | Central region | DSB-dependent? | Meiotic DSBs/nucleus | CO interference? | |
|
| |||||
| A. thaliana | ASY1 | ZYP1 | Yes | 153 ± 33 Rad51 foci (Mercier et al. 2005) | Yes |
| S. cerevisiae | Red1, Hop1, and Mek1 | Zip1 | Yes | 140–170 DSBs (Buhler et al. 2007) | Yes |
| S. pombe | Rec10, Hop1, and Mek1 | None | N/A | Mean: 22.2 Rad51 foci; maximum: 50 Rad51 foci (Lorenz et al. 2006) | No |
| C. elegans | HIM-3 and HTP-1/2/3 | SYP-1/2/3/4 | No | 23–39 RAD-51 foci (during mid/late pachytene; Nottke et al. 2011; Gao, Saito, and Colaiácovo, personal communication) | Yes |
| D. melanogaster | CONA | C(3)G and C(2)M | No | Males: none | Females: Yes |
| Females: 24.3 γ-HIS2AV foci (Jang et al. 2003) | |||||
| M. musculus | SYCP2/3 and HORMAD1/2 | SYCP 1, SYCE1/2/3, and TEX12 | Yes | 230–420 Rad51 foci (reviewed in Baudat and de Massy 2007) | Yes |
Table 6.2.
Conservation of meiotic recombination across species
| Species | Strand-exchange proteins
|
Pro-CO factors | Meiotic CO intermediate resolution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dmc1, Mnd1/Hop2 | Rad51 | |||
| A. thaliana | Yes | Rad51C | MSH4/5, ZIP3, ZYP1, ZIP4, and RCK (MER3) | MUS81 (9–12% of COs (Berchowitz et al. 2007)) |
| S. cerevisiae | Yes | Rad51 | Msh4/5, Zip3, Zip1, Zip2, Spo22 (Zip4), Spo16, and Mer3 | Mus81-Mms4 [20% of COs (Argueso et al. 2004; de los Santos et al. 2003)] |
| S. pombe | Yes | Rhp51 | – | Mus81-Eme1 [95–99% of COs (Smith et al. 2003)] |
| C. elegans | No | RAD-51 | MSH-4/5, ZHP-3, SYP-1, SYP-2, SYP-3, SYP-4, and COSA-1 | HIM-18 [30% on autosome; 50% on X (Saito et al. 2009)], XPF-1 [21% autosome; and 24% X (Saito et al. 2009)], and MUS-81 (Youds et al. 2010) |
| D. melanogaster | No | SpnA and SpnB | C(3)G, C(2)M, REC (MCM8), and MEI-218 | MEI9-MUS312 [86–92% of COs (Yildiz et al. 2002)] with ERCC1 and HDM; MUS81 [9% of COs (Trowbridge et al. 2007)] |
| M. musculus | Yes | Rad51 | MSH4/5, RNF212, SYCP 1, SYCE1/2/3, TEX12, and TEX11 (ZIP4H) | MUS81 (only required for subset of MLH1-independent COs (Holloway et al. 2008)) |
| Species | Anti-CO factors
|
Meiotic DSBs/nucleus (references in Table 6.1) | Intersister (IS):interhomolog (IH) ratio | IH NCO:CO ratio | |
| Sgs1/BLM/RecQ helicases | Disruptors of strand invasion | ||||
|
| |||||
| A. thaliana | RECQ4A; recq4A-4 mutants have normal fertility (Mannuss et al. 2010) | SRS2 and AT1G79950? * (Knoll and Puchta 2011) | 153 ± 33 | – | – |
| S. cerevisiae | Sgs1; deletion increases IS COs and multi-chromatid joint molecules (Oh et al. 2007) | Srs2 and Hed1 | 140–170 | Total events: 1:5 (Goldfarb and Lichten 2010); JM: 1:2.4 (Schwacha and Kleckner 1994)–1:4.7 (Oh et al. 2007) | 1:1 (Allers and Lichten 2001); 2:3 (Mancera et al. 2008); 1:3 (McMahill et al. 2007) |
| S. pombe | Rqh1; deletion reduces IH CO (Cromie et al. 2008) | Fml1? *(prevents mitotic COs) | 22.2 | 3:1 (Cromie et al. 2006) | 1:4 (Cromie et al. 2005) |
| C. elegans | HIM-6; him-6 mutants have reduced IH COs (Wicky et al. 2004) | RTEL-1 | 23–39 | – | – |
| D. melanogaster | Blm/Mus309; mus309N2 have reduced IH COs (Wicky et al. 2004) | – | 24.3 | 40% of events on ring chromosomes are IS COs (Webber et al. 2004) | 4:1 (Hilliker and Chovnick 1981) |
| M. musculus | BLM; Blm-/- spermatocytes have increased chiasmata (Holloway et al. 2010) | RTEL1 | 230–420 | – | – |
| Species | Number of chromosomes (2N) | CO/meiosis | NCO/meiosis | % COs subject to interference | Gene conversion tract length |
|
| |||||
| A. thaliana | 10 | 9.2 (Mercier et al. 2005) | – | 75–84% (Mercier et al. 2005; Higgins et al. 2004) | – |
| S. cerevisiae | 32 | 90.5 (Mancera et al. 2008) | 66.1 (Mancera et al. 2008) | 40% (Argueso et al. 2004) | CO: 2 kb (Mancera et al. 2008) |
| NCO: 1.8 kb (Mancera et al. 2008) | |||||
| S. pombe | 6 | 45 (Munz 1994) | – | None | – |
| C. elegans | 12 | 6 (genetic map) | – | All (Zalevsky et al. 1999; Kelly et al. 2000) | |
| D. melanogaster | 8 | 5.6 (genetic map) | – | All (Copenhaver et al. 2002; Baker and Carpenter 1972) | CO: 343 ± 143 bp |
| NCO: 1,208 ± 790 bp (Curtis et al. 1989) | |||||
| M. musculus | 40 | Males: 22.6–23.9 | – | 92% (Holloway et al. 2008) | CO: 500 bp |
| Females: 24.1 (Baudat and de Massy 2007) | NCO: 187 bp (Cole et al. 2010) | ||||
suggested but not fully demonstrated
6.2 Sister Chromatid Cohesion
Universally, sister chromatid cohesion joins sister chromatids (Oliveira and Nasmyth 2010). By tethering sister chromatids together at distinct chromosomal loci, the cohesin complex mediates the formation of the loop-axis structure of chromatin (Blat et al. 2002). In the absence of cohesion, sister chromatids segregate prematurely during meiosis I. Specifically, the attachment of chromosomes through cohesion permits cosegregation of sister chromatids at the first meiotic division, whereas it facilitates bi-orientation of sister chromatids on the spindle at the second meiotic division.
The cohesin complex contains four evolutionarily conserved subunits: two structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) subunits, SMC-1/HIM-1 and SMC-3, the non-SMC component SCC-3, and a kleisin subunit (Hagstrom and Meyer 2003). As in plants and mammals, several meiotic α-kleisins exist in C. elegans to ensure cohesion between sister chromatids: REC-8, COH-3, and COH-4 (Severson et al. 2009; Pasierbek et al. 2001; Lee and Hirano 2011; Jiang et al. 2007; Bai et al. 1999; Parisi et al. 1999; Lee et al. 2003). The coiled-coil domains of the SMC proteins connect the ATPase-containing “head” domain to the hinge region (Melby et al. 1998). By folding at the hinge region, SMC proteins form intramolecular coiled-coils (Haering et al. 2002). The two SMC proteins, SMC-1 and SMC-3, can then interact at their hinge regions with the N- and C-terminal regions of the kleisin subunits (Haering et al. 2002). Current models suggest that the complex forms a ring structure that acts to embrace the sister chromatids (Haering et al. 2002).
Sister chromatid cohesion is established during replication (Sherwood et al. 2010). The HEAT/armadillo repeat-containing protein TIM-1, a paralog of the Drosophila circadian clock protein TIMELESS, mediates association of the non-SMC components of cohesin onto chromatin (Chan et al. 2003). HEAT-repeat-containing protein Scc2 and TPR-protein Scc4 are components of the highly conserved cohesin loading complex found in yeast, Xenopus, and humans (Gillespie and Hirano 2004; Watrin et al. 2006; Ciosk et al. 2000; Rollins et al. 2004; Tonkin et al. 2004; Seitan et al. 2006). In C. elegans, the ortholog for Scc4 is MAU-2, which likely plays a similar role to its yeast and human counterparts, whereas SCC-2 has been shown to mediate the meiotic loading of cohesin subunits on chromatin (Seitan et al. 2006; Lightfoot et al. 2011).
Maintenance of sister chromatid cohesion requires cohesin subunits and the HEAT-repeat-containing protein PDS-5/EVL-14 (Wang et al. 2003; Nasmyth and Haering 2005). Absence of either PDS-5 or the cohesin subunit SCC-3 results in premature separation of sister chromatids during meiotic prophase in C. elegans (Wang et al. 2003). Previously, it was thought that cohesin may act as a scaffold for the loading of additional axis-associated components, which promote chromosome synapsis (Page and Hawley 2004). Recent work, however, suggests that axial components contribute to sister chromatid cohesion, as exemplified by the observation that cohesin components are interdependent with axial/lateral component HTP-3 for stable association on chromosomes (Severson et al. 2009; Kim et al. 2010; Goodyer et al. 2008).
Stepwise removal of sister chromatid cohesion allows for proper segregation of chromosomes at each of the meiotic divisions. Specifically, whereas homologs must segregate away from each other in the first meiotic division, sister chromatids only separate in the second meiotic division. In most eukaryotes, this is accomplished through the incorporation of the meiosis-specific kleisin Rec8 in cohesin complexes. During the meiosis I division, REC-8 cleavage elicits bivalent resolution by releasing the connection holding homologs together (Rogers et al. 2002). However, REC-8 is protected from cleavage at defined regions between sister chromatids to prevent their premature separation at meiosis I (Rogers et al. 2002; Pasierbek et al. 2001). At the second division, the residual REC-8 is cleaved to permit segregation of sister chromatids (Rogers et al. 2002; Pasierbek et al. 2001).
The persistence of sister chromatid cohesion in the absence of REC-8 is due to the presence of the other two meiotic kleisins, COH-3 and COH-4 (Severson et al. 2009). Sister chromatid cohesion is only significantly reduced in the absence of all three kleisins (Severson et al. 2009). However, these paralogs apparently only share partial overlap for other functions during meiosis. This is suggested in part by the observation that coh-3 coh-4 double mutants are more severely defective for the assembly of the SC than rec-8 single mutants (Severson et al. 2009). Moreover, REC-8 alone is sufficient to maintain sister chromatid cohesion during the second meiotic division (Severson et al. 2009).
Finally, aside from mediating cohesion between sister chromatids, work in C. elegans and other organisms suggests that cohesin may play additional roles. Absence of Rec8 in budding yeast results in a shortened length of meiotic S-phase (Cha et al. 2000). Since REC-8 localizes to mitotic nuclei in the C. elegans gonad (Goodyer et al. 2008; Pasierbek et al. 2001), it has been proposed that REC-8 may also have a function in both the mitotically cycling nuclei and the progression of meiotic S-phase in the germline (Jaramillo-Lambert et al. 2007). Premeiotic nuclei in the germlines of rec-8 mutants exhibit increased levels of DSBs (Hayashi et al. 2007). Failure to load cohesin subunits also results in an accumulation of meiotic DSBs, which indicates impaired meiotic DSB repair (Pasierbek et al. 2003; Smolikov et al. 2007a; Baudrimont et al. 2011; Lightfoot et al. 2011). This is in line with work in yeast that suggests that cohesin may have a significant role in mediating DNA metabolism. Specifically, absence of cohesin results in altered distribution of meiotic DSBs because cohesin mediates the localization of axial components that recruit factors involved in DSB formation (Kugou et al. 2009; Ellermeier and Smith 2005; Panizza et al. 2011). Moreover, loading of the cohesin complex surrounding DSB sites facilitates the use of the sister chromatid as a template for repair in mitotic cells in budding yeast (Heidinger-Pauli et al. 2008). During meiosis, axial elements promote homolog bias in budding yeast by stimulating the local loss of cohesion in order to release one end of the DSB to undergo repair using the homolog as a template (Kim et al. 2010). However, as recombination progresses, cohesion functions to maintain homolog bias by promoting formation of interhomolog recombination intermediates by inhibiting activity of the other end of the DSB (Kim et al. 2010). rec8 deletion mutants in yeast and ord Drosophila mutants, which fail to localize cohesin on chromosomes, undergo increased recombination between sister chromatids (Webber et al. 2004; Kim et al. 2010). Similarly, DSBs in rec-8 mutants are likely repaired by intersister recombination given that the univalents observed in diakinesis oocytes in this background have a mostly intact appearance, lacking elevated levels of either chromosome fragments or aggregates (Pasierbek et al. 2001; Colaiacovo et al. 2003; Smolikov et al. 2007a). In C. elegans, loading of meiotic cohesin appears to be required for the DNA damage checkpoint to sense and eliminate nuclei with persistent unrepaired DSBs. Specifically, scc-2 mutants fail to recruit a component of the DNA damage checkpoint to unrepaired meiotic DSBs and activate the apoptotic checkpoint (Lightfoot et al. 2011). Therefore, the regulated establishment, maintenance, and removal of sister chromatid cohesion plays several key roles during meiosis throughout species. Moreover, cohesin also plays important roles in the regulation of DSB distribution and repair.
6.3 Meiotic Pairing of Homologous Chromosomes
In the transition zone of the C. elegans germline, chromosomes polarize towards one side of the nuclei, which imparts a crescent-shaped appearance to the DAPI-stained chromatin. This reorganization of the chromosomes is coincident with the pairing of chromosomes as determined by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) (Dernburg et al. 1998). The formation of the crescent-shaped morphology is thought to serve the same purpose as the clustering of chromosomes that is observed in most other organisms during meiotic prophase. In other organisms, both ends of the chromosome localize preferentially near the spindle pole body or the centrosome to form the arrangement known as the “bouquet” (Zickler and Kleckner 1998). Traditionally, the bouquet is thought to assist in the homology search by reducing the volume of searchable space from a three-dimensional to a two-dimensional space in the nucleus, and simplifying the homology search by sorting chromosomes by their lengths (Schlecht et al. 2004; Roeder 1997; Loidl 1990). Since in C. elegans only one end of each chromosome attaches to the nuclear envelope, there is not a formation of a classic “bouquet” arrangement, but the reorganization of the chromosomes detected at transition zone is thought to accomplish the same goal by assisting in the pairing of chromosomes (Goldstein 1982).
Defects in crossing over due to either chromosome deletions or the presence of translocations suggested that C. elegans chromosomes require cis-acting regions to pair their homologs (Rose et al. 1984; McKim et al. 1988; Villeneuve 1994; Rosenbluth and Baillie 1981; Herman et al. 1982). These regions were first defined as homology recognition regions (HRR) and were later given the name “pairing centers” (PCs) (Villeneuve 1994; McKim et al. 1988). PCs were roughly mapped by genetic analysis to the ends of the chromosomes in C. elegans (reviewed in Zetka and Rose 1995). PCs contain highly repeated DNA sequence motifs that recruit the C2H2 zinc-finger proteins, ZIM-1, ZIM-2, ZIM-3, and HIM-8 (Phillips et al. 2005, 2009b; Phillips and Dernburg 2006; Sanford and Perry 2001). While HIM-8 binds specifically to the X chromosome, the ZIM proteins mediate the interactions between the autosomes (Phillips and Dernburg 2006; Phillips et al. 2005). Interestingly, there are only three ZIM proteins to mediate pairing between the five autosomes (Phillips and Dernburg 2006). ZIM-1 and ZIM-3 each mediate pairing of two autosomes (Phillips and Dernburg 2006). This suggests that the stable pairing between chromosomes must require a yet unknown additional mechanism to prevent interactions between the nonhomologous chromosomes that share the same ZIM proteins.
It is important to note that pairing centers are not unique to C. elegans. Both Drosophila males and budding yeast have cis-acting regions that promote chromosome pairing as well. Repetitive sequences in the rDNA are required for sex chromosome pairing in Drosophila males (McKee 1996). The interaction between the rDNA repeats is mediated by the cohesin Scc3 homolog SNM and the BTB domain-containing protein MNM, which also facilitate the pairing of autosomes in Drosophila males (Thomas and McKee 2007; Thomas et al. 2005). While the pairing centers in C. elegans and Drosophila males promote homologous pairing of chromosomes, centromere coupling, the pairing of centromeric regions during meiosis in budding yeast, occurs between nonhomologous chromosomes (Tsubouchi and Roeder 2005). Centromere pairing of nonhomologous chromosomes precedes homologous pairing and can occur in the absence of recombination (Tsubouchi and Roeder 2005; Obeso and Dawson 2010). This centromere pairing requires both the cohesin component Rec8 and Zip1, a structural component of the central region of the SC in yeast (Tsubouchi and Roeder 2005; Bardhan et al. 2010). Therefore, studies on the mechanism by which pairing centers allow for homolog recognition in C. elegans can be informative for the understanding of how cis-acting regions promote chromosome associations in other organisms.
X chromosome pairing is particularly robust compared to the autosomes in C. elegans. When dynein is depleted, X chromosome pairing is not affected, but the autosomes fail to pair (Sato et al. 2009). The X chromosome pairing is also more resistant to defects in axis morphogenesis and SC formation. Specifically, pairing of the X chromosome is less affected than the pairing of the autosomes in htp-1 mutants, him-3 hypomorphs, and cra-1 mutants (Nabeshima et al. 2004; Martinez-Perez and Villeneuve 2005; Couteau et al. 2004; Smolikov et al. 2008). This efficient pairing of the X chromosome in the him-3 hypomorphs and cra-1 mutants translates into less severe synapsis and recombination defects of X chromosomes compared to the autosomes that fail to pair (Smolikov et al. 2008; Couteau et al. 2004). The mechanism by which the X chromosomes pair more efficiently is unknown, but the answer may lie in the chromatin state of the X chromosome. In C. elegans, the X chromosome adopts a heterochromatic state and is silenced during meiotic prophase (Kelly et al. 2002). Since transcriptionally silenced regions are often compartmentalized within the nucleus (Cremer et al. 2006), the silenced X chromosomes may preferentially be associated by recruitment to that subnuclear position. On the other hand, it is possible that the heterochromatin of the X may promote pairing more directly as it does in Drosophila females (Hawley et al. 1992; Karpen et al. 1996; Dernburg et al. 1996).
Gross changes in chromosome morphology suggest that chromosome movement is highly dynamic during meiotic prophase. In C. elegans, meiotic chromosome movement facilitates the timely pairing of chromosomes and is dependent on microtubules (Sato et al. 2009). Depletion of dynein, the microtubule motor, results in pairing delays and failure to synapse chromosomes in this system (Sato et al. 2009). This is analogous to the dynein-mediated horsetail chromosome movement observed in fission yeast that promotes chromosome pairing (Ding et al. 2004; Hiraoka et al. 2000; Miki et al. 2002). However, chromosome movement and pairing is largely independent of dynein in budding yeast and instead requires actin (Koszul et al. 2008; Lui et al. 2006; Trelles-Sticken et al. 2005). Universally, the SUN and KASH proteins that bridge the nuclear membrane in worms, flies, yeast, and humans allow for the transduction of force from the cytoplasm to the nucleus (Starr and Fridolfsson 2010). In C. elegans, the KASH protein ZYG-12 is a transmembrane protein that interacts with dynein and spans the outer nuclear membrane (Malone et al. 2003). Meanwhile, ZYG-12 interacts with SUN-1 in the perinuclear space (Minn et al. 2009). Importantly, nocodazole treatment, which depolymerizes microtubles, results in nonhomologous synapsis in C. elegans (Sato et al. 2009). It has therefore been proposed that meiotic chromosome movement not only facilitates pairing but also disrupts nonhomologous interactions (Koszul and Kleckner 2009).
Modification of the phosphorylation state of SUN-1 is required for proper chromosome morphogenesis during meiotic prophase. Specifically, phosphorylation of SUN-1 by the Polo-like kinase PLK-2 allows for its aggregation and polarization of the aggregates on one half of the nuclear periphery (Penkner et al. 2009; Harper et al. 2011). Moreover, CHK-2, the ortholog of the checkpoint protein kinases Cds1 in S. pombe and Chk2 in mammals, also mediates the phosphorylation of SUN-1, and chk-2 mutants fail to cluster their chromosomes and pair (MacQueen and Villeneuve 2001; Penkner et al. 2009). More recently it has been shown that CHK-2 is required for the association of the PBD-domain of PLK-2 with HIM-8 (Harper et al. 2011). Furthermore, the ZIM proteins, but not HIM-8, require CHK-2 to associate with the nuclear membrane, and the ZIM/HIM-8 proteins associate with the nuclear envelope in distinct clusters rather than forming a single cluster (Phillips and Dernburg 2006). Therefore, the crescent-shaped organization acquired by the chromosomes in the transition zone likely results from the ZIM/HIM-8 proteins associating with the polarized SUN-1 aggregates. Interestingly, although the ZIM/HIM-8 proteins colocalize with the SUN/KASH aggregates and PLK-2 (Sato et al. 2009; Harper et al. 2011; Labella et al. 2011), only HIM-8 was found to interact with PLK-2 by yeast two-hybrid (Harper et al. 2011). PC-associated proteins may recruit PLK-2 to the nuclear envelope to phosphorylate SUN-1, which results in its aggregation and polarization (Penkner et al. 2009; Harper et al. 2011; Labella et al. 2011). Finally, SUN-1 dephosphorylation is required to redisperse chromosomes in the nucleus during pachytene (Penkner et al. 2009).
The interaction of PCs on homologous chromosomes facilitates their alignment and may act to stabilize homologous interactions, thereby allowing synapsis to proceed. Although PC interactions are sufficient to stabilize the local pairing of homologs in the absence of synapsis (MacQueen et al. 2005), stable pairing between the homologs along the full length of chromosomes requires synapsis (MacQueen et al. 2002). Pairing of homologs at the non-PC regions of autosomes is mediated by the chromodomain protein MRG-1, which prevents nonhomologous synapsis along regions away from the PCs (Dombecki et al. 2011). In the absence of either PCs or the zinc-finger proteins ZIMs/HIM-8, synapsis of the corresponding chromosome pair does not occur (Phillips and Dernburg 2006; MacQueen et al. 2005; Phillips et al. 2005). However, failure of a single PC to interact does not affect synapsis of the other chromosomes, but it does result in delays in both DSB repair and release from the polarized configuration for the other chromosomes (Phillips and Dernburg 2006; Phillips et al. 2005). Mutants that have defects in synapsis often exhibit an extended transition zone with nuclei that persist in the clustered configuration throughout what corresponds to the pachytene stage in wild-type germlines (MacQueen et al. 2002; Colaiacovo et al. 2003; Smolikov et al. 2007a). PLK-2 is required for prolonging the transition zone in mutants with defects in pairing and/or synapsis (Harper et al. 2011). Therefore, a checkpoint may perhaps exist to help coordinate pairing with synapsis and PLK-2 appears to be involved with this checkpoint (Martinez-Perez and Villeneuve 2005; Harper et al. 2011; Labella et al. 2011).
6.4 Chromosome Synapsis
Synapsis is the zipping-up of paired homologs along their lengths by the proteinaceous scaffold referred to as the synaptonemal complex or SC. The SC is a tripartite structure comprised of a pair of lateral elements and a central region. Lateral elements are formed via the assembly of proteins along the homologous axes, which in turn are connected via central region components, consisting of transverse filament proteins that bridge the homologous axes. This results in a “ladder-like” organization along the length of paired and aligned homologous chromosomes (Fig. 6.3a; Moses 1968). Within the context of a fully formed SC, homologs are held together with their axes ~100 nm apart throughout most species (Westergaard and von Wettstein 1972). This is also the case in C. elegans where axes are separated by an average distance of 118 nm (90–125 nm range; Smolikov et al. 2008). Synapsis begins in the transition zone, where short segments of the central region are observed to associate with chromosomes (MacQueen et al. 2002). Synapsis is completed by pachytene, when thick parallel DAPI-stained tracks are visible in meiotic nuclei, flanking the signal of central region proteins, which localize throughout the full length of the chromosomes (Fig. 6.3c).
Fig. 6.3.
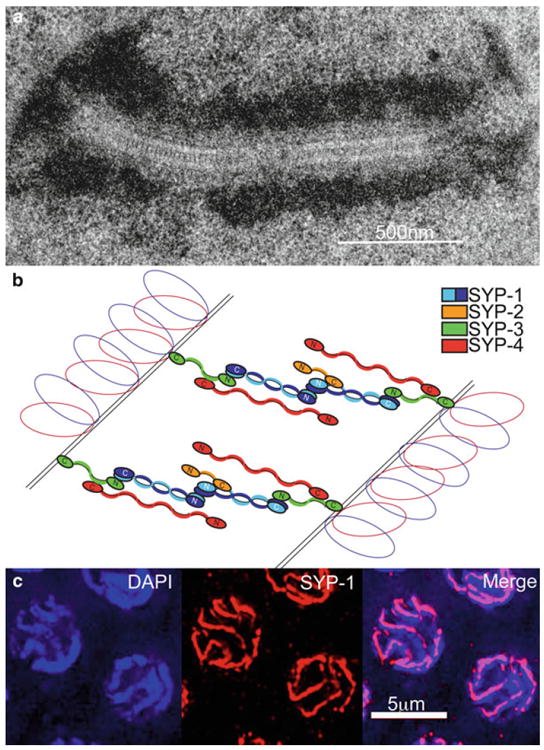
The synaptonemal complex. (a) TEM (transmission electron microscopy) image of the structure of the SC between chromosomes in a pachytene nucleus in the C. elegans germline. The continuous zipper-like track, comprised of the transverse filaments, is flanked by electron-dense patches of chromatin. (b) Schematic of the arrangement of the four central region proteins in the SC of C. elegans. (c) Immunolocalization of SC proteins in pachytene nuclei. Central region protein SYP-1 (red) forms tracks at the interface between DAPI-stained chromosomes (blue). The images are projections halfway through three-dimensional data stacks of whole nuclei
Axial element proteins assemble along the lengths of sister chromatids prior to pairing. As axes become closely juxtaposed and homologs start to synapse, the axial elements are referred to as lateral elements. C. elegans has multiple HORMA (Hop1, Rev7, and Mad2) domain-containing proteins: HIM-3, HTP-1/2, and HTP-3 (Goodyer et al. 2008; Aravind and Koonin 1998; Martinez-Perez and Villeneuve 2005; Zetka et al. 1999). These are non-cohesin proteins that associate along the longitudinal axes of chromosomes (Martinez-Perez and Villeneuve 2005; Zetka et al. 1999; Couteau et al. 2004; Goodyer et al. 2008; Martinez-Perez et al. 2008). Localization of HTP-3 is interdependent with cohesin components (Goodyer et al. 2008; Severson et al. 2009), and HTP-3 mediates the association of HTP-1/2 and HIM-3 on chromosomes (Severson et al. 2009; Goodyer et al. 2008). While association of HTP-1/2 with chromosomes does not require either the meiosis-specific cohesin REC-8 or HIM-3, bulk loading of HIM-3 requires cohesin, and HTP-1 mediates additional association of HIM-3 with chromosomes (Martinez-Perez et al. 2008; Pasierbek et al. 2003; Couteau and Zetka 2005).
The lateral/axial elements play essential roles in meiotic events and serve to coordinate pairing, synapsis, and recombination. HIM-3, HTP-1/2, and HTP-3 have specialized functions in mediating pairing and proper loading of the central region components of the SC (Martinez-Perez and Villeneuve 2005; Zetka et al. 1999; Couteau et al. 2004; Goodyer et al. 2008). him-3 null mutants completely fail to cluster and pair their chromosomes (Zetka et al. 1999; Couteau et al. 2004). The failure to cluster chromosomes in him-3 mutants may reflect the reduced association between the SUN-1 and the ZIM proteins in those mutants (Baudrimont et al. 2010). In contrast, htp-1 mutants have a less severe defect in pairing than him-3 mutants and exhibit a few polarized nuclei (Martinez-Perez and Villeneuve 2005; Couteau et al. 2004). In budding yeast, the lack of axial element formation impairs chromosome movement and delays pairing (Trelles-Sticken et al. 2005). Similarly, chromosome axis morphogenesis in C. elegans could be coupled to regulation of chromosome movement. Absence of HTP-1/2 can result in nonhomologous synapsis of the autosomes (Martinez-Perez and Villeneuve 2005; Couteau et al. 2004; Couteau and Zetka 2005). By inhibiting the polymerization of the SC when pairing has failed, HTP-1/2 coordinates pairing with SC formation. HTP-3 does not only play a role in pairing and synapsis but is also required for meiotic DSB formation (Goodyer et al. 2008). While him-3 mutants have normal levels of break formation, but delayed DSB turnover (Couteau et al. 2004), htp-3 mutants do not form breaks, but can repair breaks induced by irradiation. Therefore, the expansion of the HORMA domain protein class in C. elegans has allowed for each of the proteins to attain specialized functions during meiosis.
The central region of the SC consists of an ordered array of transverse filaments repeating along the length of the homologs. In budding yeast, where Zip1 is the only central region protein identified to date, it forms homodimers through its coiled-coil domains (Zickler and Kleckner 1999; Dong and Roeder 2000). The homodimers then interact in an antiparallel manner to span the distance between the lateral elements of the homologs (Liu et al. 1996; Schmekel et al. 1996). However, the organization of the central region of the SC is apparently more complex in higher eukaryotes. In fact, the assembly of the SC in C. elegans may be more analogous to that in mammals than in yeast. As opposed to the single central region component present in budding yeast, both mice and C. elegans have several central region proteins (Costa et al. 2005; Schramm et al. 2011; Bolcun-Filas et al. 2007; Smolikov et al. 2007b, 2009; Colaiacovo et al. 2003; MacQueen et al. 2002; Hamer et al. 2006; de Vries et al. 2005; Sym et al. 1993). In C. elegans, the central region proteins SYP-1/2/3/4 localize between the axes of synapsed homologs (Smolikov et al. 2007b, 2009; Colaiacovo et al. 2003; MacQueen et al. 2002). Moreover, the central region components are interdependent upon each other for their assembly on chromosome axes (Smolikov et al. 2007b, 2009; Colaiacovo et al. 2003). The predicted length of each of the central region proteins is not sufficient to span the entire width of the SC (Smolikov et al. 2009). By assembling into a multi-protein complex, the SYP proteins maintain the characteristic organization and conserved dimensions of the SC (Schild-Prufert et al. 2011). Through a series of immunogold labeling and protein interaction studies, the structure of the SC was determined to consist of a homodimer of SYP-1 that can interact with the C-terminus of SYP-2 and the N-terminus of SYP-3, which in turn interacts with SYP-4 and has its C-terminus located at the chromosome axes (Fig. 6.3b; Schild-Prufert et al. 2011).
Synapsis tends to initiate at the PC end of the chromosome and polymerize down the rest of the chromosome (MacQueen et al. 2005). Moreover, SC polymerization is highly processive once it is nucleated, and can accommodate regions of nonhomology located away from the pairing center (MacQueen et al. 2005). The processivity of SC polymerization is mediated, at least in part, by the tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain-containing protein CRA-1 (Smolikov et al. 2008). cra-1 mutants form uneven, discontinuous stretches of SC (Smolikov et al. 2008). Unlike yeast, plants and mammals, but similar to flies, synapsis in C. elegans can occur even in the absence of recombination initiation (Dernburg et al. 1998; McKim et al. 1998; Giroux et al. 1989; Baudat et al. 2000; Grelon et al. 2001). Importantly, the polymerization of SC components along chromosome axes in the absence of recombination is dependent on CRA-1 (Smolikov et al. 2008). Taken together, this suggests that the dependence of SC formation on DSB formation is largely conserved across taxa. However, the evolution of CRA-1 has allowed meiosis in C. elegans to bypass the requirement of DSB initiation for synapsis, but not accurate chromosome segregation.
The formation of a fully mature SC between homologs mediates the progression of meiotic events. Although mutants of central region components can pair their chromosomes, chromosomes fail to stabilize pairing interactions along their lengths (Colaiacovo et al. 2003; MacQueen et al. 2002; Smolikov et al. 2007b, 2009). Moreover, the clustered configuration characteristic of transition zone is prolonged in mutants that lack central region components of the SC (Smolikov et al. 2009; MacQueen et al. 2002). Thus, similar to budding yeast and mice, SC formation appears to be required for maximal levels of pairing between homologs in C. elegans (Nag et al. 1995; Peoples-Holst and Burgess 2005; Peoples et al. 2002; Daniel et al. 2011). The SC also promotes recombination between homologous chromosomes. Mutants defective in SC formation accumulate recombination intermediates, which are visualized as persistent foci of the strand invasion protein RAD-51 in late pachytene (MacQueen et al. 2002; Colaiacovo et al. 2003; Smolikov et al. 2007a, 2009). Synapsis is universally important for the formation of crossovers between homologs, as exemplified by the observation that defects in synapsis result in reduced crossing over in plants, yeast, flies, mammals, and C. elegans (de Vries et al. 2005; Page and Hawley 2001; Colaiacovo et al. 2003). Late recombination nodules, which are the dark silver staining bodies visible by electron microscopy (EM) on pachytene chromosomes and represent sites of future crossover formation, tend to be associated with the SC in fungi, flies, plants, and humans (Rasmussen and Holm 1984; Maguire 1966; Carpenter 1975; Zickler 1977). Therefore, the SC plays a key and conserved role in promoting the progression of interhomolog recombination.
Differentiation of the bivalent occurs as chromosomes remodel at the pachytene–diplotene transition around the off-center placed single crossover undergone by every pair of homologs (Nabeshima et al. 2005). Chromosomes therefore acquire a cruciform structure comprised of a pair of long and short arms (Fig. 6.2). Later, this configuration results in the long arms facing the poles and short arms being aligned along the metaphase plate. The SC begins to disassemble during late pachytene and is completely absent from the long arms of the bivalent by diakinesis (MacQueen et al. 2002; Nabeshima et al. 2005). The asymmetric disassembly of the SC requires components involved in crossover formation: ZHP-3, MSH-4, and MSH-5 (Nabeshima et al. 2005; Bhalla et al. 2008). ZHP-3 is a SUMO E3 ligase homologous to yeast Zip3, a protein that plays key roles in crossover formation and promoting the assembly of the central region of the SC (Jantsch et al. 2004; Agarwal and Roeder 2000; Borner et al. 2004). In C. elegans, ZHP-3 is not required for SC formation but plays a role in promoting crossover formation (Jantsch et al. 2004; Bhalla et al. 2008). ZHP-3 initially localizes along the length of the chromosome axes during pachytene and then relocalizes during late pachytene to the boundary between the short and long arms of the bivalent to mark the site of crossover formation (Bhalla et al. 2008; Jantsch et al. 2004). Both transgenic worms expressing zhp-3∷gfp at the restrictive temperature and mutants lacking SUMO polypeptide expression (smo-1) fail to remove the SC from the long arms of the bivalent (Bhalla et al. 2008). Finally, proper bivalent maturation also requires proper maintenance of sister chromatid cohesion at the long arms of the bivalent during diakinesis via restriction of the C. elegans Aurora B kinase homolog AIR-2 (de Carvalho et al. 2008). This is mediated by LAB-1, a proposed functional analog of the mammalian Shugoshin protein implicated in the regulated two-step removal of sister chromatid cohesion (Kitajima et al. 2004; Marston et al. 2004; Rabitsch et al. 2004; Lee et al. 2008; Llano et al. 2008; de Carvalho et al. 2008). When AIR-2 is no longer limited to the short arms in the absence of LAB-1, bivalents have aberrant localization of SC components and SC disassembly is delayed until the last oocyte in diakinesis (de Carvalho et al. 2008). Therefore, there are several different elements regulating the timely disassembly of the SC.
Defects in SC formation are detected by the synaptic checkpoint that operates during pachytene to cull nuclei by apoptosis (Bhalla and Dernburg 2005). Moreover, the synapsis checkpoint, which can detect a single pair of asynaptic chromosomes, requires PLK-2 and the AAA–adenosine triphosphatase PCH-2 (Harper et al. 2011; Bhalla and Dernburg 2005). However, in addition to monitoring chromosome asynapsis, the PCH-2 homologs in yeast and Drosophila have been implicated in axis morphogenesis and mediating the outcome of recombination by enforcing homolog bias and crossover interference (COI; Joyce and McKim 2009; Joshi et al. 2009; Wu and Burgess 2006). Taken together, several mechanisms are set in place across species to regulate SC assembly and disassembly, as well as the “quality” of the SC formed throughout meiotic prophase.
6.5 Meiotic Recombination
Crossovers provide sufficient tension to align chromosomes on the spindle (Östergren 1951; Nicklas 1974). Therefore, failure to from crossovers results in chromosomes that segregate randomly during the first meiotic division and subsequent aneuploidy. Chiasmata are the physical manifestation of crossovers between homologs, and crossovers are the product of homologous recombination. Recombination events between homologs allow for exchange of genetic information, and by shuffling the genetic information distributed to gametes that will be used in reproduction, this exchange promotes genetic diversity.
Each C. elegans chromosome undergoes multiple DSBs, but only one crossover (CO) forms between each chromosome pair (Mets and Meyer 2009; Barnes et al. 1995; Nottke et al. 2011; Gao, Saito and Colaiacovo, personal communication). Meiotic DSBs that do not become crossovers are repaired as noncrossovers (NCO). There are at least three layers of regulation determining the frequency and distribution of COs: crossover assurance, crossover interference, and crossover homeostasis.
Crossover assurance ensures that each chromosome receives at least one crossover, which is the obligate crossover (Jones 1984). Crossover interference ensures that crossovers are distributed nonrandomly and places them further apart from each other than would be expected by chance (Muller 1916). Therefore, the formation of a CO in a given location is proposed to “interfere” with or inhibit the formation of additional COs nearby. Since C. elegans chromosomes only undergo one CO per chromosome, it is an organism that exemplifies strong crossover interference. In other organisms, there are two types of COs that occur in wild-type meiosis: COs either subject or not to interference. In budding yeast, COs subject to interference are mediated by the ZMM proteins [Zip1/2/3, Spo16 (Zip4), Mer3, Msh4, and Msh5], while interference-independent COs are dependent on Mms4 and Mus81 (Borner et al. 2004; Chen et al. 2008; de los Santos et al. 2003). In C. elegans, all COs are normally dependent on HIM-14/MSH-4 and MSH-5, which are the homologs of the yeast ZMM proteins Msh4 and Msh5, respectively (Kelly et al. 2000; Zalevsky et al. 1999). MUS-81-dependent CO formation occurs only in aberrant situations, in which DSBs are in excess or cannot be repaired as NCOs. A subset of crossovers is MUS-81-dependent after X-ray induction and in the absence of the helicase RTEL-1, which is the homolog of Srs2 in budding yeast (Youds et al. 2010).
Crossover interference may require continuous stretches of SC along the chromosomes in C. elegans. A three-chromosome fusion consisting of homologous autosomes flanking an unpaired X chromosome that disrupts SC formation between the autosomal segments results in each autosomal segment forming crossovers (Hillers and Villeneuve 2003). Moreover, crossover interference is reduced and double COs occur more frequently in him-3 hypomorphs that form short SC stretches (Nabeshima et al. 2004). However, continuous SC polymerization along chromosomes does not seem to be required for crossover interference in yeast and mice (Shinohara et al. 2008; de Boer et al. 2006). The decision to make COs as opposed to NCOs is thought to occur very early in budding yeast (Bishop and Zickler 2004; Allers and Lichten 2001; Borner et al. 2004). While not much is known about NCO regulation in C. elegans, there is evidence suggesting that an early control/decision regarding COs is exerted at the level of DSB formation. Specifically, CO analysis in condensin I mutants, which exhibit increased DSB formation, revealed both elevated levels and an altered distribution of COs (Mets and Meyer 2009; Tsai et al. 2008). It has been hypothesized that the extended chromatin axes in condensin I mutants result in a higher density of smaller chromatin loops (Mets and Meyer 2009). Moreover, DSBs have been proposed to occur preferentially at chromatin loops and then be recruited to non-sister homologous axes for repair (Blat et al. 2002; Maleki et al. 2007). Since HTP-3 interacts with the nuclease MRE-11, which facilitates resection of DSBs (Goodyer et al. 2008), recruitment of resected DSBs to the axis may occur via this direct interaction. Therefore, by having a higher density of chromatin loops, the potential for DSB formation may be increased in condensin I mutants. More recent work in C. elegans suggests that the CO decision is also made during later stages of meiosis. In one study, it was shown that DSBs created after completion of SC assembly (using heat-shock inducible transposon excision) are both subject to and confer interference, competing with endogenous DSBs to become the sole CO (Rosu et al. 2011). In a second study, the introduction of exogenous DSBs by irradiation resulted in the separation of chromosome axes during late pachytene (Couteau and Zetka 2011). Given that axis separation was observed in the CO-deficient mutant msh-5, this study inferred that axis separation allowed for DSBs to be repaired as NCO events (Couteau and Zetka 2011). Interestingly, the separation of axes is correlated with a reduction in histone 2A lysine 5 acetylation (H2AK5Ac), which in turn is dependent on HTP-3 (Couteau and Zetka 2011). Taken together, these data suggest that CO control may be exerted by various factors affecting axis morphogenesis at different points during meiotic progression, namely early leptotene/zygotene, when the first meiotic DSBs occur and synapsis is initiating, and late pachytene, when chromosomes are fully synapsed.
Crossover homeostasis maintains CO levels. As a result of crossover homeostasis, the number of COs does not scale to the number of DSBs formed. Specifically, the number of COs is maintained despite a reduction in the number of DSBs formed and probably at the expense of non-crossovers (NCOs). Crossover homeostasis has been most clearly demonstrated in budding yeast by using hypomorhic alleles of the conserved Spo11 endonuclease, which reduce the number of DSBs to varying degrees. Despite a reduction in the number of recombination initiation events, the spo11 hypomorphs still exhibit normal CO levels (Martini et al. 2006). The existence of crossover homeostasis in C. elegans remains to be determined.
Meiotic recombination initiates with the formation of programmed DSBs, which begin in the transition zone (Mets and Meyer 2009). SPO-11 is a topoisomerase II-like protein that forms the DSBs (Dernburg et al. 1998; Keeney 2001) (Fig. 6.4). The DSBs are then resected primarily by MRE-11, RAD-50, and COM-1 to reveal long, 3′ single-stranded DNA tails (Chin and Villeneuve 2001; Hayashi et al. 2007; Penkner et al. 2007; Sun et al. 1991). The single-stranded tails are coated with the RecA homolog RAD-51, whose nucleation on ssDNA and stabilization of the nucleoprotein filament is promoted by BRC-2, the BRCA2 homolog (Petalcorin et al. 2007). Human and yeast homologs of RAD-54, a SWI2/SNF2 chromatin remodeling protein, promote strand invasion of homologous duplex DNA by the nucleoprotein filament (Alexeev et al. 2003; Mets and Meyer 2009; Mazin et al. 2000; Mazina and Mazin 2004). In the absence of RAD-54, DSBs are not repaired and accumulate (Mets and Meyer 2009). Interestingly, strand exchange, which is visualized by the presence of Rad51/Dmc1 foci, typically peaks during leptotene and zygotene in yeast, plants, and mice (Tarsounas et al. 1999; Terasawa et al. 1995; Bishop 1994). In contrast, RAD-51 foci peak during pachytene in C. elegans (Alpi et al. 2003; Colaiacovo et al. 2003). DSBs in budding yeast mostly disappear at the transition between zygotene and pachytene as they are converted into either NCO or CO intermediates (Allers and Lichten 2001; Hunter and Kleckner 2001). However, whereas in budding yeast DSB initiation is essential for homolog pairing and synapsis, these processes are primarily mediated by PCs in C. elegans (Weiner and Kleckner 1994; Giroux et al. 1989; Peoples et al. 2002; Phillips et al. 2005; MacQueen et al. 2005). Therefore, the earlier kinetics of recombination may not be necessary to promote the progression of those meiotic events in C. elegans.
Fig. 6.4.
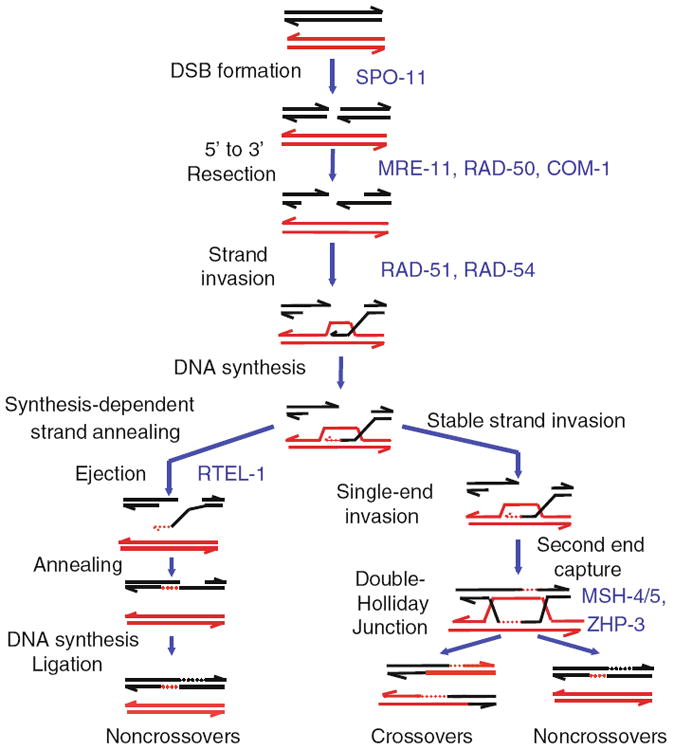
The meiotic recombination pathway in C. elegans. Here one homolog is depicted in black and the other is shown in red. Meiotic recombination is initiated by formation of DSBs. The topoisomerase-like enzyme SPO-11 catalyzes the cleavage of the double-stranded DNA of one sister chromatid. Both 5′ ends of the DSB are rapidly resected by MRE-11, RAD-50, and COM-1 to reveal 3′ single-stranded tails, on which RAD-51 forms a filament. RAD-54 promotes invasion by one end of the DSB into the DNA duplex of the homolog to form the nascent D-loop structure. As DNA synthesis occurs, the D-loop expands. The D-loop structure is processed by two major pathways to yield COs and NCOs. COs, which hold bivalents together, arise from the formation of stable single-end invasions, followed by second end capture and then the formation of double Holliday junctions, which are cleaved by a currently unknown resolvase. NCOs arise from either processing of double Holliday junctions or the synthesis-dependent strand-annealing pathway, through which the invading end of the DSB is ejected so that it can anneal with its sister chromatid. Following annealing, DNA synthesis and ligation occur to complete the formation of NCOs
After strand exchange by formation of the D-loop structure, the DSB can be processed into COs or NCOs. NCO formation is promoted by the ortholog of Srs2, RTEL-1, which assists in the ejection of the single-stranded DNA undergoing strand invasion and DNA synthesis (Youds et al. 2010; Barber et al. 2008). DSBs that are destined to become COs are processed into single-end invasions (SEI) and then double Holliday junctions (dHJ) (Allers and Lichten 2001; Hunter and Kleckner 2001). ZHP-3, the homolog of the crossover promoting protein Zip3 in budding yeast, localizes to the sites of obligate crossover formation in late pachytene/diplotene (Youds et al. 2010; Bhalla et al. 2008; Jantsch et al. 2004; Borner et al. 2004). Following DNA synthesis, the second end of the DSB anneals to form a dHJ (Sun et al. 1991; Szostak et al. 1983). Yeast Rad52 has been shown to promote second end capture through its N-terminal region, which promotes single strand annealing (Lao et al. 2008; Sugiyama et al. 1998; Krejci et al. 2002). This property is also conserved in the Rad52 ortholog BRC-2, which may therefore serve the same function and assist in second end capture during CO formation in C. elegans (Petalcorin et al. 2006). Finally, MSH-4/HIM-14 and MSH-5, which are proposed to form a heterodimer at dHJs in humans, are required for CO formation and assist in the timely processing of NCO products (Winand et al. 1998; Zalevsky et al. 1999; Colaiacovo et al. 2003; Kelly et al. 2000; Snowden et al. 2004).
HJ resolution to yield COs requires cleavage of the structure across the junction followed by ligation. Symmetric cleavage of the HJ allows for ligation immediately following cleavage, but asymmetric cleavage of the HJ requires further processing prior to religation. The main meiotic HJ resolvase in C. elegans and most other eukaryotes has yet to be identified (Schwartz and Heyer 2011). Fission yeast utilizes Mus81 as its primary HJ resolvase (Boddy et al. 2001). Although mus-81 single mutants in C. elegans have increased embryonic lethality, recombination intermediates do not persist into late meiotic prophase (Saito et al. 2009). However, MUS-81 is required to process COs stemming from the repair of exposure to gamma-irradiation and those that arise in a rtel-1 mutant background (Youds et al. 2010). A mutation in mus-81 is synthetic lethal with a mutation in him-6, which encodes for the homolog of the yeast Sgs1 helicase in C. elegans (Saito et al. 2009). In budding yeast, Sgs1 prevents multichromatid joint molecules, which involves invasion of the sister chromatid (Oh et al. 2008). Thus, it is likely that MUS-81 is required to process the toxic intermediates that form in him-6 mutants. The majority of CO products in Drosophila is dependent on the MEI-9(XPF-1)/MUS312(HIM-18)/ERCC1 complex (Yildiz et al. 2002; Boyd et al. 1976; Radford et al. 2007). HIM-18/SLX-4 interacts with XPF-1 and SLX-1, but an interaction with ERCC-1 could not be detected by yeast two-hybrid (Saito et al. 2009). HIM-18 appears to be responsible for resolution of only a subset of Holliday junctions during normal meiosis in C. elegans because chromatin bridges are visible in some of the bivalents of pro-metaphase I in him-18 oocytes and COs are reduced to ~51–70% of wild-type levels (Saito et al. 2009). Human GEN1 and yeast Yen1 have HJ resolvase activity in vitro most similar to bacterial RuvC, which cleaves HJ symmetrically (Bennett et al. 1993; Ip et al. 2008). Ectopically expressed human GEN1 in fission yeast can rescue mus81 mutants (Lorenz et al. 2010). However, gen-1 mutants in C. elegans have normal brood size and do not exhibit a Him phenotype (Bailly et al. 2010). Since gen-1 mutants do not show chromosome segregation defects, GEN-1 does not appear to be involved in the processing of HJs during meiosis in C. elegans. Alternatively, there could be redundant mechanisms that preclude the analysis of the role of GEN-1 during meiosis in C. elegans. Therefore, its role in meiotic recombination remains to be further examined in C. elegans as well as in other systems.
Typically, the repair of meiotic DSBs is biased towards HR such that repair will favor CO production, which in turn are required for accurate chromosome segregation. Therefore, alternative forms of DSB repair are suppressed during meiosis to prevent either the use of the sister chromatid as a template for repair or nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ). However, when progression of HR is impaired, alternative forms of DSB repair are engaged. During normal meiosis, NHEJ does not play significant role in the repair of meiotic DSBs (Martin et al. 2005; Clejan et al. 2006). However, either in the absence of synapsis or in the presence of defective sister chromatid cohesion, NHEJ is used to repair DSB breaks (Smolikov et al. 2009; Colaiacovo et al. 2003; Couteau et al. 2004). Specifically, while syp-3 C-terminal truncation mutants fail to synapse, DSBs eventually turn over to yield a few viable progeny in those mutants (Smolikov et al. 2007a). However, DSB turnover is further impaired in the syp-3 C-terminal truncation mutant when REC-8 is depleted by RNAi and in the absence of LIG-4, a component of the NHEJ machinery (Smolikov et al. 2007a). There is also no evidence of chromosome fragmentation in rad-51 and brc-1 mutants when HTP-3 is depleted by RNAi suggesting that DSB repair is completed in these mutants when barriers against alternative modes of DSB repair imposed by axis-associated components are no longer in place (Goodyer et al. 2008). BRC-1 is not required for repair of DSBs by HR but functions to repair DSBs in syp-2 mutants (Adamo et al. 2008). Additionally, breaks form at normal levels and get repaired in him-3 mutants despite the failure to pair and synapse chromosomes (Couteau et al. 2004). The DSBs in him-3 mutants may be repaired using the intersister recombination or NHEJ pathways (Couteau et al. 2004). Thus, both the axes and the central region actively inhibit both NHEJ and intersister recombination. Notably, orthologs for proteins involved in homolog bias such as the meiosis-specific strand invasion proteins Dmc1, Hop2, and Mnd1 have not been identified in C. elegans (MacQueen et al. 2002; Villeneuve and Hillers 2001). This suggests that C. elegans may rely more extensively on just the axes to enforce homolog bias.
Homolog bias may be enforced by axes mediating processing of DSBs at the level of resection prior to late pachytene. RAD-50-dependent loading of RAD-51 in early meiotic prophase is correlated with the ability to form crossovers between homologs (Hayashi et al. 2007). However, the loading of RAD-51 no longer requires RAD-50 in early meiotic prophase when htp-1 and him-3 are depleted (Hayashi et al. 2007). Since HTP-3 interacts with MRE-11 (Goodyer et al. 2008), axial elements may promote homolog bias perhaps through direct interaction with components of the DSB repair machinery. Given that homolog bias appears to be restricted to mid-pachytene (Hayashi et al. 2007), the axis may impose a “kinetic constraint” as opposed to a permanent barrier to nonhomologous forms of repair (Goldfarb and Lichten 2010).
Repair of a subset of DSBs has been proposed to help align homologous chromosomes to prevent nonhomologous interactions (Smithies and Powers 1986; Getz et al. 2008). However, C. elegans may rely less on DSBs to align chromosomes because they have evolved PCs. The requirement of CO formation to promote homolog alignment is also not present in Drosophila, which relies on cis-acting regions to pair their chromosomes, and fission yeast, which uses the horsetail movement to promote homolog pairing (discussed above). Importantly, in C. elegans COs are nonrandomly distributed on chromosomes and are five times more likely to form at the terminal third of chromosomes (Hillers and Villeneuve 2003). Finally, these hotspots for recombination tend to occur in gene-poor regions of the chromosomes (Barnes et al. 1995). Similarly, in budding yeast, DSB hotspots mostly occur at promoters, but at interstitial regions of chromosomes (Petes 2001; Pan et al. 2011). In contrast, almost half of mouse recombination hotspots occur within genes (Smagulova et al. 2011).
The nonrandom distribution of crossovers reflects the nonrandom distribution of DSBs and DSB formation is influenced by the state of meiotic chromatin. An open chromatin state, modulated in part by post-translationally derived histone modifications, can make the DNA more competent for DSB formation by increasing the accessibility of the recombination machinery (Petes 2001). In support of this model, hotspots for recombination are typically devoid of nucleosomes (Pan et al. 2011; Fan and Petes 1996). However, histone H3 methylation on lysine 9 (H3K9me), which is a modification associated with closed chromatin, is also required for DSB formation in C. elegans (Reddy and Villeneuve 2004; Lachner and Jenuwein 2002). him-17 mutants, which fail to accumulate the H3K9me chromatin mark, phenocopy spo-11 mutants and lack meiotic DSBs (Reddy and Villeneuve 2004). Thus, compaction of chromatin also plays a role in DSB formation, perhaps by facilitating proper loop-axis conformation. Furthermore, H3K9me patterns in a somatic background also correlate with recombination rates along chromosomes (Liu et al. 2011). One may extrapolate from data on somatic cells and suspect that a similar pattern of H3K9me exists on meiotic chromatin. Specifically, H3K9 methylation is enriched on chromosome arms compared to the central region of chromosomes, where crossover formation tends to be excluded (Liu et al. 2011). Regulation of histone acetylation is apparently also important as suggested by the analysis of XND-1, an AT hook motif-containing protein, which is enriched on autosomes and required for formation of DSBs on the X chromosome (Wagner et al. 2010; Harris et al. 2010). The germlines of xnd-1 mutants have accumulated histone H2A lysine 5 acetylation (H2AK5Ac) and crossover distribution is altered in this background (Wagner et al. 2010). In xnd-1 mutants, COs occur more frequently in the middle of chromosomes, which are gene-rich, rather than at the arms of the chromosomes (Wagner et al. 2010). The histone acetyltransferase Tip60 mediates accumulation of H2AK5Ac to allow for exchange of phosphorylated H2Av for unmodified H2Av following induction of DSBs in somatic cells in Drosophila and removal of γ-H2AX after DNA damage in human cell culture (Kusch et al. 2004; Ikura et al. 2007). MYS-1, the homolog of Tip60, maybe required for accumulation of H2AK5Ac in C. elegans (Wagner et al. 2010); however, more recent data suggests that this may not be the case, as H2K5Ac levels are not affected by RNAi depletion of MYS-1 (Couteau and Zetka 2011). Moreover, CRA-1 localizes to autosomes and is also required for accumulation of H2AK5Ac (J. Gao and M.P. Colaiácovo, personal communication). Therefore, while XND-1 acts to remove H2AK5Ac, CRA-1 and MYS-1 may both act to promote H2AK5Ac (J. Gao and M. Colaiacovo, personal communication). However, further studies will be required to uncover how the interplay between these factors promotes the dynamic regulation of histone modifications in the germline ultimately impacting meiotic DSB formation and repair.
6.6 Late Prophase: Setting the Stage for the Metaphase I—Anaphase I Transition
Chromosomes become highly condensed and remodeled as they approach late pro-phase to form the characteristic “cruciform bivalent.” This remodeling revolves around the site of crossover formation (Nabeshima et al. 2005). Since crossovers form at the terminal third of chromosomes, crossovers asymmetrically divide chromosomes into a long and short arm. During remodeling, different components of the SC adopt distinct localizations along the arms of the bivalent. HTP-1 and HTP-2 are retained along the long arms of the bivalent (Martinez-Perez et al. 2008), while SYP-1 only localizes to the short arm of the bivalent (Fig. 6.2; Martinez-Perez et al. 2008). However, HIM-3 and HTP-3 localize to both arms of the bivalent with REC-8 (Goodyer et al. 2008; Zetka et al. 1999).
Cleavage of REC-8 along the short arms has been proposed to allow the homologs to segregate to opposite poles and is dependent on its phosphorylation state (Rogers et al. 2002; Schumacher et al. 1998). In yeast, Casein kinase or Dbf4-dependent Cdc7 kinase (DDK)-dependent phosphorylation is responsible for Rec8 cleavage (Ishiguro et al. 2010; Katis et al. 2010). In monocentric organisms, Rec8 is protected at centromeric/pericentromeric regions resulting in a defined region of preservation of cohesion. Shugoshin-mediated dephosphorylation by phosphatase PP2A allows for evasion of Rec8 cleavage in monocentric organisms (Riedel et al. 2006; Kitajima et al. 2006).
As an organism with holocentric chromosomes, C. elegans has developed an alternative strategy to designate sites of cohesion retention. The chromosomal passenger complex (CPC), which includes AIR-2 (Aurora B kinase), CSC-1 (Borealin), BIR-1 (Survivin), and ICP-1 (Incenp), localizes to the short arms of the bivalents (Kaitna et al. 2002; Romano et al. 2003; Speliotes et al. 2000). AIR-2 localization is restricted to the short arms by LAB-1 and HTP-1/2 (de Carvalho et al. 2008; Martinez-Perez et al. 2008). Moreover, phosphorylation of REC-8 by AIR-2 licenses cleavage of REC-8 (Rogers et al. 2002). Histone H3 along the short arms is an additional phosphorylation target of AIR-2 (Kaitna et al. 2002; Hsu et al. 2000). Interestingly, the C. elegans Shugoshin homolog SGO-1 is dispensable for the retention of REC-8 along the long arms and does not appear to localize to the long arms (de Carvalho et al. 2008). Instead, sgo-1 mutants have chromosome segregation defects that become evident during meiosis II divisions; sgo-1 mutants exhibit lagging chromosomes and polar body extrusion (de Carvalho et al. 2008). Therefore, LAB-1 is proposed to antagonize AIR-2-mediated phosphorylation of REC-8 along the long arms of the bivalent by recruiting the C. elegans PP1 phosphatases GSP-1 (GLC-7α) and GSP-2 (GLC-7β) (de Carvalho et al. 2008; Rogers et al. 2002), which dephoshorylate REC-8, thereby preventing its cleavage by separase at the long arm (Rogers et al. 2002).
The holocentric nature of C. elegans chromosomes requires a unique assembly of the segregation-promoting machinery during meiosis compared to monocentric organisms. This is due in part to the fact that the first meiotic division presents an additional challenge because homologs must segregate to opposite poles. Therefore, kinetochore assembly during the first meiotic division is different from that during mitotic divisions. During mitotic divisions, the kinetochore assembles along the full length of the sister chromatids with microtubules attaching along the length of the chromosomes (Albertson and Thomson 1982). During meiosis I, the holocentric kinetochore forms cup-like structures that surround the long arms of bivalents (Dumont et al. 2010; Monen et al. 2005). Microtubules form bundles that run parallel to the long axis of the bivalents (Wignall and Villeneuve 2009; Howe et al. 2001). Since only a few microtubules attach to the ends of the bivalents, orientation of the bivalents on the spindle is largely driven by interaction of the kinetochores along the length of the long arms with the lateral microtubule bundles (Wignall and Villeneuve 2009; Dumont et al. 2010). This allows one pair of sisters to face one spindle pole and the other pair of sisters belonging to the homolog to face the opposite pole. The short arms of the bivalents align in the center of the meiotic spindle during congression. Although kinetochores promote proper orientation of chromosomes on the spindle axis, they are dispensable for chromosome segregation during anaphase I (Dumont et al. 2010). Instead, microtubules form bundles between the short arms during anaphase that may push outwards to segregate the homologs (Dumont et al. 2010). At the short arms, AIR-2 recruits the spindle checkpoint kinase BUB-1, motor proteins KLP-19 and CEMP-F, and the microtubule-stabilizing protein CLS-1(CLASP) (Dumont et al. 2010). Thus, AIR-2 plays multiple roles to promote the segregation of the homologs: AIR-2 marks REC-8 for cleavage and recruits machinery to actively separate the homologs (Kaitna et al. 2002).
6.7 Summary and Future Perspectives
Multiple processes contribute to ensuring the accurate segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I in C. elegans. (1) Chromosomes undergo structural changes via the loading of cohesin protein complexes, assembly of axial elements, and dynamic changes in chromatin marks. (2) Pairing centers facilitate homolog recognition. (3) The SC forms to stabilize pairing interactions and promote crossover formation between homologs. (4) A subset of programmed DSBs are repaired to form COs. (5) The bivalent is differentiated by regulated retention and loss of various proteins along chromosome arms to allow for proper chromosome alignment at the metaphase plate, followed by homolog separation at anaphase I. Although we have gained some understanding of how these meiotic processes function to properly segregate chromosomes in C. elegans, a more thorough molecular understanding of the mechanisms promoting accurate segregation remains to be achieved, and we still do not fully understand how these processes are regulated to act coordinately.
C. elegans shares a high degree of gene conservation with higher eukaryotes. While 20–77% of genes in C. elegans have a mouse ortholog, approximately 60–80% of all genes in C. elegans have a human ortholog and most physiological and stress signaling pathways are also conserved (Lai et al. 2000; Leung et al. 2008; Kaletta and Hengartner 2006). This is a powerful model system that allows for studies of complex biological processes in the context of a multicellular organism. Investigations using C. elegans have already fostered a better understanding of meiotic processes that are universal to other organisms (Colaiacovo 2006; Garcia-Muse and Boulton 2007). C. elegans is a relevant model organism for the study of reproductive biology that can be utilized to study the impact of environmental factors on meiotic progression. For example, exposure to Bisphenol A, a plasticizer highly prevalent in our environment and which is linked to meiotic chromosome segregation defects in mammals, was demonstrated to alter expression of DSB repair factors resulting in impaired DSB repair in C. elegans (Allard and Colaiacovo 2010; Hunt et al. 2003).
Many of the remaining significant questions centered on meiotic processes can be addressed in this model system to further advance our knowledge of what happens in higher eukaryotes. Additional studies can reveal how axis-associated components coordinate both synapsis and recombination to determine the outcome of recombination events. It is still unclear how pairing and synapsis are monitored to avoid nonhomologous interactions. Although there have been extensive studies on both the mechanisms and the proteins involved in recombination, this remains a complex process whose regulation is still poorly understood. Therefore, more studies will be required to tease out both the direct and indirect roles of cohesin, axial elements, and the SC in mediating recombination. Moreover, further studies addressing the dynamic regulation of chromatin marks throughout the germline will enhance our understanding of how sites of recombination are determined and how it can affect downstream repair events. Furthermore, it remains to be determined how bivalent asymmetry is assessed to allow for its differentiation. Importantly, much of our understanding of the meiotic processes in C. elegans can shed light on how these processes occur in other organisms including mammals, therefore significantly contributing to our understanding of the mechanisms promoting human reproductive health.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Anne Villeneuve and members of the Colaiácovo lab for early access to unpublished results. We also thank Tim Schedl, Sara Beese-Sims, Takamune Saito, and Patrick Allard for critical reading of this manuscript. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant R01GM072551 (to M.P.C.).
References
- Adamo A, Montemauri P, Silva N, Ward JD, Boulton SJ, La Volpe A. BRC-1 acts in the inter-sister pathway of meiotic double-strand break repair. EMBO Rep. 2008;9(3):287–292. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7401167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal S, Roeder GS. Zip3 provides a link between recombination enzymes and synaptonemal complex proteins. Cell. 2000;102(2):245–255. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albertson DG, Thomson JN. The kinetochores of Caenorhabditis elegans. Chromosoma. 1982;86(3):409–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00292267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexeev A, Mazin A, Kowalczykowski SC. Rad54 protein possesses chromatin-remodeling activity stimulated by the Rad51-ssDNA nucleoprotein filament. Nat Struct Biol. 2003;10(3):182–186. doi: 10.1038/nsb901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allard P, Colaiacovo MP. Bisphenol A impairs the double-strand break repair machinery in the germline and causes chromosome abnormalities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(47):20405–20410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010386107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allers T, Lichten M. Differential timing and control of noncrossover and crossover recombination during meiosis. Cell. 2001;106(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00416-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpi A, Pasierbek P, Gartner A, Loidl J. Genetic and cytological characterization of the recombination protein RAD-51 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Chromosoma. 2003;112(1):6–16. doi: 10.1007/s00412-003-0237-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aravind L, Koonin EV. The HORMA domain: a common structural denominator in mitotic checkpoints, chromosome synapsis and DNA repair. Trends Biochem Sci. 1998;23(8):284–286. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(98)01257-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argueso JL, Wanat J, Gemici Z, Alani E. Competing crossover pathways act during meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 2004;168(4):1805–1816. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.032912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai X, Peirson BN, Dong F, Xue C, Makaroff CA. Isolation and characterization of SYN1, a RAD21-like gene essential for meiosis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1999;11(3):417–430. doi: 10.1105/tpc.11.3.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly AP, Freeman A, Hall J, Declais AC, Alpi A, Lilley DM, Ahmed S, Gartner A. The Caenorhabditis elegans homolog of Gen1/Yen1 resolvases links DNA damage signaling to DNA double-strand break repair. PLoS Genet. 2010;6(7):e1001025. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker BS, Carpenter AT. Genetic analysis of sex chromosomal meiotic mutants in Drosophilia melanogaster. Genetics. 1972;71(2):255–286. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber LJ, Youds JL, Ward JD, McIlwraith MJ, O’Neil NJ, Petalcorin MI, Martin JS, Collis SJ, Cantor SB, Auclair M, Tissenbaum H, West SC, Rose AM, Boulton SJ. RTEL1 maintains genomic stability by suppressing homologous recombination. Cell. 2008;135(2):261–271. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardhan A, Chuong H, Dawson DS. Meiotic cohesin promotes pairing of non-homologous centromeres in early meiotic prophase. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21(11):1799–1809. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E09-05-0392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes TM, Kohara Y, Coulson A, Hekimi S. Meiotic recombination, noncoding DNA and genomic organization in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1995;141(1):159–179. doi: 10.1093/genetics/141.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudat F, de Massy B. Regulating double-stranded DNA break repair towards crossover or non-crossover during mammalian meiosis. Chromosome Res. 2007;15(5):565–577. doi: 10.1007/s10577-007-1140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudat F, Manova K, Yuen JP, Jasin M, Keeney S. Chromosome synapsis defects and sexually dimorphic meiotic progression in mice lacking Spo11. Mol Cell. 2000;6(5):989–998. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudrimont A, Penkner A, Woglar A, Machacek T, Wegrostek C, Gloggnitzer J, Fridkin A, Klein F, Gruenbaum Y, Pasierbek P, Jantsch V. Leptotene/zygotene chromosome movement via the SUN/KASH protein bridge in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 2010;6(11):e1001219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudrimont A, Penkner A, Woglar A, Mamnun YM, Huliek M, Struck C, Schnabel R, Loidl J, Jantsch V. A new thermosensitive smc-3 allele reveals involvement of cohesin in homologous recombination in C. elegans. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24799. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett RJ, Dunderdale HJ, West SC. Resolution of Holliday junctions by RuvC resolvase: cleavage specificity and DNA distortion. Cell. 1993;74(6):1021–1031. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90724-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berchowitz LE, Francis KE, Bey AL, Copenhaver GP. The role of AtMUS81 in interference-insensitive crossovers in A. thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2007;3(8):e132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla N, Dernburg AF. A conserved checkpoint monitors meiotic chromosome synapsis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2005;310(5754):1683–1686. doi: 10.1126/science.1117468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla N, Wynne DJ, Jantsch V, Dernburg AF. ZHP-3 acts at crossovers to couple meiotic recombination with synaptonemal complex disassembly and bivalent formation in C. elegans. PLoS Genet. 2008;4(10):e1000235. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop DK. RecA homologs Dmc1 and Rad51 interact to form multiple nuclear complexes prior to meiotic chromosome synapsis. Cell. 1994;79(6):1081–1092. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop DK, Zickler D. Early decision: meiotic crossover interference prior to stable strand exchange and synapsis. Cell. 2004;117(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00297-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blat Y, Protacio RU, Hunter N, Kleckner N. Physical and functional interactions among basic chromosome organizational features govern early steps of meiotic chiasma formation. Cell. 2002;111(6):791–802. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)01167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy MN, Gaillard PH, McDonald WH, Shanahan P, Yates JR, 3rd, Russell P. Mus81-Eme1 are essential components of a Holliday junction resolvase. Cell. 2001;107(4):537–548. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00536-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolcun-Filas E, Costa Y, Speed R, Taggart M, Benavente R, De Rooij DG, Cooke HJ. SYCE2 is required for synaptonemal complex assembly, double strand break repair, and homologous recombination. J Cell Biol. 2007;176(6):741–747. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200610027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borner GV, Kleckner N, Hunter N. Crossover/noncrossover differentiation, synaptonemal complex formation, and regulatory surveillance at the leptotene/zygotene transition of meiosis. Cell. 2004;117(1):29–45. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd JB, Golino MD, Setlow RB. The mei-9 alpha mutant of Drosophila melanogaster increases mutagen sensitivity and decreases excision repair. Genetics. 1976;84(3):527–544. doi: 10.1093/genetics/84.3.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhler C, Borde V, Lichten M. Mapping meiotic single-strand DNA reveals a new landscape of DNA double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS Biol. 2007;5(12):e324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter AT. Electron microscopy of meiosis in Drosophila melanogaster females: II. The recombination nodule—a recombination-associated structure at pachytene? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1975;72(8):3186–3189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cha RS, Weiner BM, Keeney S, Dekker J, Kleckner N. Progression of meiotic DNA replication is modulated by interchromosomal interaction proteins, negatively by Spo11p and positively by Rec8p. Genes Dev. 2000;14(4):493–503. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan RC, Chan A, Jeon M, Wu TF, Pasqualone D, Rougvie AE, Meyer BJ. Chromosome cohesion is regulated by a clock gene paralogue TIM-1. Nature. 2003;423(6943):1002–1009. doi: 10.1038/nature01697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen SY, Tsubouchi T, Rockmill B, Sandler JS, Richards DR, Vader G, Hochwagen A, Roeder GS, Fung JC. Global analysis of the meiotic crossover landscape. Dev Cell. 2008;15(3):401–415. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin GM, Villeneuve AM. C. elegans mre-11 is required for meiotic recombination and DNA repair but is dispensable for the meiotic G(2) DNA damage checkpoint. Genes Dev. 2001;15(5):522–534. doi: 10.1101/gad.864101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciosk R, Shirayama M, Shevchenko A, Tanaka T, Toth A, Nasmyth K. Cohesin’s binding to chromosomes depends on a separate complex consisting of Scc2 and Scc4 proteins. Mol Cell. 2000;5(2):243–254. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80420-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clejan I, Boerckel J, Ahmed S. Developmental modulation of nonhomologous end joining in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 2006;173(3):1301–1317. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.058628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colaiacovo MP. The many facets of SC function during C. elegans meiosis. Chromosoma. 2006;115(3):195–211. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colaiacovo MP, MacQueen AJ, Martinez-Perez E, McDonald K, Adamo A, La Volpe A, Villeneuve AM. Synaptonemal complex assembly in C. elegans is dispensable for loading strand-exchange proteins but critical for proper completion of recombination. Dev Cell. 2003;5(3):463–474. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(03)00232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole F, Keeney S, Jasin M. Comprehensive, fine-scale dissection of homologous recombination outcomes at a hot spot in mouse meiosis. Mol Cell. 2010;39(5):700–710. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.08.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copenhaver GP, Housworth EA, Stahl FW. Crossover interference in Arabidopsis. Genetics. 2002;160(4):1631–1639. doi: 10.1093/genetics/160.4.1631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa Y, Speed R, Ollinger R, Alsheimer M, Semple CA, Gautier P, Maratou K, Novak I, Hoog C, Benavente R, Cooke HJ. Two novel proteins recruited by synaptonemal complex protein 1 (SYCP1) are at the centre of meiosis. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 12):2755–2762. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couteau F, Zetka M. HTP-1 coordinates synaptonemal complex assembly with homolog alignment during meiosis in C. elegans. Genes Dev. 2005;19(22):2744–2756. doi: 10.1101/gad.1348205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couteau F, Zetka M. DNA damage during meiosis induces chromatin remodeling and synaptonemal complex disassembly. Dev Cell. 2011;20(3):353–363. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couteau F, Nabeshima K, Villeneuve A, Zetka M. A component of C. elegans meiotic chromosome axes at the interface of homolog alignment, synapsis, nuclear reorganization, and recombination. Curr Biol. 2004;14(7):585–59. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.03.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer T, Cremer M, Dietzel S, Muller S, Solovei I, Fakan S. Chromosome territories–a functional nuclear landscape. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18(3):307–316. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2006.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden SL, Troemel ER, Evans TC, Kimble J. GLP-1 is localized to the mitotic region of the C. elegans germ line. Development. 1994;120(10):2901–2911. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.10.2901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden SL, Leonhard KA, Byrd DT, Kimble J. Cellular analyses of the mitotic region in the Caenorhabditis elegans adult germ line. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17(7):3051–3061. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E06-03-0170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromie GA, Rubio CA, Hyppa RW, Smith GR. A natural meiotic DNA break site in Schizosaccharomyces pombe is a hotspot of gene conversion, highly associated with crossing over. Genetics. 2005;169(2):595–605. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.037176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromie GA, Hyppa RW, Taylor AF, Zakharyevich K, Hunter N, Smith GR. Single Holliday junctions are intermediates of meiotic recombination. Cell. 2006;127(6):1167–1178. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromie GA, Hyppa RW, Smith GR. The fission yeast BLM homolog Rqh1 promotes meiotic recombination. Genetics. 2008;179(3):1157–1167. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.088955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D, Clark SH, Chovnick A, Bender W. Molecular analysis of recombination events in Drosophila. Genetics. 1989;122(3):653–661. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel K, Lange J, Hached K, Fu J, Anastassiadis K, Roig I, Cooke HJ, Stewart AF, Wassmann K, Jasin M, Keeney S, Toth A. Meiotic homologue alignment and its quality surveillance are controlled by mouse HORMAD1. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(5):599–610. doi: 10.1038/ncb2213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer E, Stam P, Dietrich AJ, Pastink A, Heyting C. Two levels of interference in mouse meiotic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(25):9607–9612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600418103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Carvalho CE, Zaaijer S, Smolikov S, Gu Y, Schumacher JM, Colaiacovo MP. LAB-1 antagonizes the Aurora B kinase in C. elegans. Genes Dev. 2008;22(20):2869–2885. doi: 10.1101/gad.1691208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de los Santos T, Hunter N, Lee C, Larkin B, Loidl J, Hollingsworth NM. The Mus81/Mms4 endonuclease acts independently of double-Holliday junction resolution to promote a distinct subset of crossovers during meiosis in budding yeast. Genetics. 2003;164(1):81–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/164.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries FA, de Boer E, van den Bosch M, Baarends WM, Ooms M, Yuan L, Liu JG, van Zeeland AA, Heyting C, Pastink A. Mouse Sycp1 functions in synaptonemal complex assembly, meiotic recombination, and XY body formation. Genes Dev. 2005;19(11):1376–1389. doi: 10.1101/gad.329705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dernburg AF, Sedat JW, Hawley RS. Direct evidence of a role for heterochromatin in meiotic chromosome segregation. Cell. 1996;86(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80084-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dernburg AF, McDonald K, Moulder G, Barstead R, Dresser M, Villeneuve AM. Meiotic recombination in C. elegans initiates by a conserved mechanism and is dispensable for homologous chromosome synapsis. Cell. 1998;94(3):387–398. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81481-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dernburg AF, Zalevsky J, Colaiacovo MP, Villeneuve AM. Transgene-mediated cosuppression in the C. elegans germ line. Genes Dev. 2000;14(13):1578–1583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding DQ, Yamamoto A, Haraguchi T, Hiraoka Y. Dynamics of homologous chromosome pairing during meiotic prophase in fission yeast. Dev Cell. 2004;6(3):329–341. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(04)00059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombecki CR, Chiang AC, Kang HJ, Bilgir C, Stefanski NA, Neva BJ, Klerkx EP, Nabeshima K. The chromodomain protein MRG-1 facilitates the SC-independent homologous pairing during meiosis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Cell. 2011;21(6):1092–1103. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.09.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong H, Roeder GS. Organization of the yeast Zip1 protein within the central region of the synaptonemal complex. J Cell Biol. 2000;148(3):417–426. doi: 10.1083/jcb.148.3.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerr JS. Immunohistochemistry. WormBook. 2006:1–61. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.105.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J, Oegema K, Desai A. A kinetochore-independent mechanism drives anaphase chromosome separation during acentrosomal meiosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12(9):894–901. doi: 10.1038/ncb2093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellermeier C, Smith GR. Cohesins are required for meiotic DNA breakage and recombination in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(31):10952–10957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504805102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan QQ, Petes TD. Relationship between nuclease-hypersensitive sites and meiotic recombination hot spot activity at the HIS4 locus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16(5):2037–2043. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.5.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox PM, Vought VE, Hanazawa M, Lee MH, Maine EM, Schedl T. Cyclin E and CDK-2 regulate proliferative cell fate and cell cycle progression in the C. elegans germline. Development. 2011;138(11):2223–2234. doi: 10.1242/dev.059535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frokjaer-Jensen C, Davis MW, Hollopeter G, Taylor J, Harris TW, Nix P, Lofgren R, Prestgard-Duke M, Bastiani M, Moerman DG, Jorgensen EM. Targeted gene deletions in C. elegans using transposon excision. Nat Methods. 2010;7(6):451–453. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Muse T, Boulton SJ. Meiotic recombination in Caenorhabditis elegans. Chromosome Res. 2007;15(5):607–621. doi: 10.1007/s10577-007-1146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Getz TJ, Banse SA, Young LS, Banse AV, Swanson J, Wang GM, Browne BL, Foss HM, Stahl FW. Reduced mismatch repair of heteroduplexes reveals “non”-interfering crossing over in wild-type Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 2008;178(3):1251–1269. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.067603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie PJ, Hirano T. Scc2 couples replication licensing to sister chromatid cohesion in Xenopus egg extracts. Curr Biol. 2004;14(17):1598–1603. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.07.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giroux CN, Dresser ME, Tiano HF. Genetic-control of chromosome synapsis in yeast meiosis. Genome. 1989;31(1):88–94. doi: 10.1139/g89-017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb T, Lichten M. Frequent and efficient use of the sister chromatid for DNA double-strand break repair during budding yeast meiosis. PLoS Biol. 2010;8(10):e1000520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein P. The synaptonemal complexes of Caenorhabditis elegans: pachytene karyotype analysis of male and hermaphrodite wild-type and him mutants. Chromosoma. 1982;86(4):577–593. doi: 10.1007/BF00330128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodyer W, Kaitna S, Couteau F, Ward JD, Boulton SJ, Zetka M. HTP-3 links DSB formation with homolog pairing and crossing over during C. elegans meiosis. Dev Cell. 2008;14(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grelon M, Vezon D, Gendrot G, Pelletier G. AtSPO11-1 is necessary for efficient meiotic recombination in plants. EMBO J. 2001;20(3):589–600. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haering CH, Lowe J, Hochwagen A, Nasmyth K. Molecular architecture of SMC proteins and the yeast cohesin complex. Mol Cell. 2002;9(4):773–788. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00515-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagstrom KA, Meyer BJ. Condensin and cohesin: more than chromosome compactor and glue. Nat Rev Genet. 2003;4(7):520–534. doi: 10.1038/nrg1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer G, Gell K, Kouznetsova A, Novak I, Benavente R, Hoog C. Characterization of a novel meiosis-specific protein within the central element of the synaptonemal complex. J Cell Sci. 2006;119(Pt 19):4025–4032. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper NC, Rillo R, Jover-Gil S, Assaf ZJ, Bhalla N, Dernburg AF. Pairing centers recruit a Polo-like kinase to orchestrate meiotic chromosome dynamics in C. elegans. Dev Cell. 2011;21(5):934–947. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris TW, Antoshechkin I, Bieri T, Blasiar D, Chan J, Chen WJ, De La Cruz N, Davis P, Duesbury M, Fang R, Fernandes J, Han M, Kishore R, Lee R, Muller HM, Nakamura C, Ozersky P, Petcherski A, Rangarajan A, Rogers A, Schindelman G, Schwarz EM, Tuli MA, Van Auken K, Wang D, Wang X, Williams G, Yook K, Durbin R, Stein LD, Spieth J, Sternberg PW. WormBase: a comprehensive resource for nematode research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(Database issue):D463–D467. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassold T, Hunt P. To err (meiotically) is human: the genesis of human aneuploidy. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2(4):280–291. doi: 10.1038/35066065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley RS, Irick H, Zitron AE, Haddox DA, Lohe A, New C, Whitley MD, Arbel T, Jang J, McKim K, et al. There are two mechanisms of achiasmate segregation in Drosophila females, one of which requires heterochromatic homology. Dev Genet. 1992;13(6):440–467. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020130608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M, Chin GM, Villeneuve AM. C. elegans germ cells switch between distinct modes of double-strand break repair during meiotic prophase progression. PLoS Genet. 2007;3(11):e191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidinger-Pauli JM, Unal E, Guacci V, Koshland D. The kleisin subunit of cohesin dictates damage-induced cohesion. Mol Cell. 2008;31(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman RK, Kari CK, Hartman PS. Dominant X-chromosome nondisjunction mutants of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1982;102(3):379–400. doi: 10.1093/genetics/102.3.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins JD, Armstrong SJ, Franklin FC, Jones GH. The Arabidopsis MutS homolog AtMSH4 functions at an early step in recombination: evidence for two classes of recombination in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 2004;18(20):2557–2570. doi: 10.1101/gad.317504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillers KJ, Villeneuve AM. Chromosome-wide control of meiotic crossing over in C. elegans. Curr Biol. 2003;13(18):1641–1647. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2003.08.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliker AJ, Chovnick A. Further observations on intragenic recombination in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res. 1981;38(3):281–296. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300020619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka Y, Ding DQ, Yamamoto A, Tsutsumi C, Chikashige Y. Characterization of fission yeast meiotic mutants based on live observation of meiotic prophase nuclear movement. Chromosoma. 2000;109(1–2):103–109. doi: 10.1007/s004120050417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh D, Oppenheim D, Klass M. Development of the reproductive system of Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1976;49(1):200–219. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J, Horvitz HR, Brenner S. Nondisjunction mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1979;91(1):67–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway JK, Booth J, Edelmann W, McGowan CH, Cohen PE. MUS81 generates a subset of MLH1-MLH3-independent crossovers in mammalian meiosis. PLoS Genet. 2008;4(9):e1000186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway JK, Morelli MA, Borst PL, Cohen PE. Mammalian BLM helicase is critical for integrating multiple pathways of meiotic recombination. J Cell Biol. 2010;188(6):779–789. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200909048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe M, McDonald KL, Albertson DG, Meyer BJ. HIM-10 is required for kinetochore structure and function on Caenorhabditis elegans holocentric chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 2001;153(6):1227–1238. doi: 10.1083/jcb.153.6.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu JY, Sun ZW, Li X, Reuben M, Tatchell K, Bishop DK, Grushcow JM, Brame CJ, Caldwell JA, Hunt DF, Lin R, Smith MM, Allis CD. Mitotic phosphorylation of histone H3 is governed by Ipl1/aurora kinase and Glc7/PP1 phosphatase in budding yeast and nematodes. Cell. 2000;102(3):279–291. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt PA, Koehler KE, Susiarjo M, Hodges CA, Ilagan A, Voigt RC, Thomas S, Thomas BF, Hassold TJ. Bisphenol a exposure causes meiotic aneuploidy in the female mouse. Curr Biol. 2003;13(7):546–553. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00189-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter N, Kleckner N. The single-end invasion: an asymmetric intermediate at the double-strand break to double-Holliday junction transition of meiotic recombination. Cell. 2001;106(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00430-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikura T, Tashiro S, Kakino A, Shima H, Jacob N, Amunugama R, Yoder K, Izumi S, Kuraoka I, Tanaka K, Kimura H, Ikura M, Nishikubo S, Ito T, Muto A, Miyagawa K, Takeda S, Fishel R, Igarashi K, Kamiya K. DNA damage-dependent acetylation and ubiquitination of H2AX enhances chromatin dynamics. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27(20):7028–7040. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00579-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip SC, Rass U, Blanco MG, Flynn HR, Skehel JM, West SC. Identification of Holliday junction resolvases from humans and yeast. Nature. 2008;456(7220):357–361. doi: 10.1038/nature07470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro T, Tanaka K, Sakuno T, Watanabe Y. Shugoshin-PP2A counteracts casein-kinase-1-dependent cleavage of Rec8 by separase. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12(5):500–506. doi: 10.1038/ncb2052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang JK, Sherizen DE, Bhagat R, Manheim EA, McKim KS. Relationship of DNA double-strand breaks to synapsis in Drosophila. J Cell Sci. 2003;116(Pt 15):3069–3077. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantsch V, Pasierbek P, Mueller MM, Schweizer D, Jantsch M, Loidl J. Targeted gene knockout reveals a role in meiotic recombination for ZHP-3, a Zip3-related protein in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(18):7998–8006. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.18.7998-8006.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo-Lambert A, Ellefson M, Villeneuve AM, Engebrecht J. Differential timing of S phases, X chromosome replication, and meiotic prophase in the C. elegans germ line. Dev Biol. 2007;308(1):206–221. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang L, Xia M, Strittmatter LI, Makaroff CA. The Arabidopsis cohesin protein SYN3 localizes to the nucleolus and is essential for gametogenesis. Plant J. 2007;50(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones GH. The control of chiasma distribution. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1984;38:293–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi N, Barot A, Jamison C, Borner GV. Pch2 links chromosome axis remodeling at future crossover sites and crossover distribution during yeast meiosis. PLoS Genet. 2009;5(7):e1000557. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce EF, McKim KS. Drosophila PCH2 is required for a pachytene checkpoint that monitors double-strand-break-independent events leading to meiotic crossover formation. Genetics. 2009;181(1):39–51. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.093112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaitna S, Pasierbek P, Jantsch M, Loidl J, Glotzer M. The aurora B kinase AIR-2 regulates kinetochores during mitosis and is required for separation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis. Curr Biol. 2002;12(10):798–812. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00820-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaletta T, Hengartner MO. Finding function in novel targets: C. elegans as a model organism. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5(5):387–398. doi: 10.1038/nrd2031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen GH, Le MH, Le H. Centric heterochromatin and the efficiency of achiasmate disjunction in Drosophila female meiosis. Science. 1996;273(5271):118–122. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5271.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katis VL, Lipp JJ, Imre R, Bogdanova A, Okaz E, Habermann B, Mechtler K, Nasmyth K, Zachariae W. Rec8 phosphorylation by casein kinase 1 and Cdc7-Dbf4 kinase regulates cohesin cleavage by separase during meiosis. Dev Cell. 2010;18(3):397–409. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.01.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeney S. The mechanism and control of meiotic recombination initiation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2001;52:1–53. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(01)52008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly KO, Dernburg AF, Stanfield GM, Villeneuve AM. Caenorhabditis elegans msh-5 is required for both normal and radiation-induced meiotic crossing over but not for completion of meiosis. Genetics. 2000;156(2):617–630. doi: 10.1093/genetics/156.2.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly WG, Schaner CE, Dernburg AF, Lee MH, Kim SK, Villeneuve AM, Reinke V. X-chromosome silencing in the germline of C. elegans. Development. 2002;129(2):479–492. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim KP, Weiner BM, Zhang L, Jordan A, Dekker J, Kleckner N. Sister cohesion and structural axis components mediate homolog bias of meiotic recombination. Cell. 2010;143(6):924–937. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.11.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima TS, Kawashima SA, Watanabe Y. The conserved kinetochore protein shugoshin protects centromeric cohesion during meiosis. Nature. 2004;427(6974):510–517. doi: 10.1038/nature02312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima TS, Sakuno T, Ishiguro K, Iemura S, Natsume T, Kawashima SA, Watanabe Y. Shugoshin collaborates with protein phosphatase 2A to protect cohesin. Nature. 2006;441(7089):46–52. doi: 10.1038/nature04663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll A, Puchta H. The role of DNA helicases and their interaction partners in genome stability and meiotic recombination in plants. J Exp Bot. 2011;62(5):1565–1579. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koszul R, Kleckner N. Dynamic chromosome movements during meiosis: a way to eliminate unwanted connections? Trends Cell Biol. 2009;19(12):716–724. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.09.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koszul R, Kim KP, Prentiss M, Kleckner N, Kameoka S. Meiotic chromosomes move by linkage to dynamic actin cables with transduction of force through the nuclear envelope. Cell. 2008;133(7):1188–1201. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krejci L, Song B, Bussen W, Rothstein R, Mortensen UH, Sung P. Interaction with Rad51 is indispensable for recombination mediator function of Rad52. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(42):40132–40141. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206511200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugou K, Fukuda T, Yamada S, Ito M, Sasanuma H, Mori S, Katou Y, Itoh T, Matsumoto K, Shibata T, Shirahige K, Ohta K. Rec8 guides canonical Spo11 distribution along yeast meiotic chromosomes. Mol Biol Cell. 2009;20(13):3064–3076. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E08-12-1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusch T, Florens L, Macdonald WH, Swanson SK, Glaser RL, Yates JR, 3rd, Abmayr SM, Washburn MP, Workman JL. Acetylation by Tip60 is required for selective histone variant exchange at DNA lesions. Science. 2004;306(5704):2084–2087. doi: 10.1126/science.1103455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labella S, Woglar A, Jantsch V, Zetka M. Polo kinases establish links between meiotic chromosomes and cytoskeletal forces essential for homolog pairing. Dev Cell. 2011;21(5):948–958. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachner M, Jenuwein T. The many faces of histone lysine methylation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002;14(3):286–298. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(02)00335-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai CH, Chou CY, Ch’ang LY, Liu CS, Lin W. Identification of novel human genes evolutionarily conserved in Caenorhabditis elegans by comparative proteomics. Genome Res. 2000;10(5):703–713. doi: 10.1101/gr.10.5.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lao JP, Oh SD, Shinohara M, Shinohara A, Hunter N. Rad52 promotes postinvasion steps of meiotic double-strand-break repair. Mol Cell. 2008;29(4):517–524. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.12.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J, Hirano T. RAD21L, a novel cohesin subunit implicated in linking homologous chromosomes in mammalian meiosis. J Cell Biol. 2011;192(2):263–276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201008005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee MH, Schedl T. RNA in situ hybridization of dissected gonads. WormBook. 2006:1–7. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.107.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J, Iwai T, Yokota T, Yamashita M. Temporally and spatially selective loss of Rec8 protein from meiotic chromosomes during mammalian meiosis. J Cell Sci. 2003;116(Pt 13):2781–2790. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J, Kitajima TS, Tanno Y, Yoshida K, Morita T, Miyano T, Miyake M, Watanabe Y. Unified mode of centromeric protection by shugoshin in mammalian oocytes and somatic cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(1):42–52. doi: 10.1038/ncb1667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung MC, Williams PL, Benedetto A, Au C, Helmcke KJ, Aschner M, Meyer JN. Caenorhabditis elegans: an emerging model in biomedical and environmental toxicology. Toxicol Sci. 2008;106(1):5–28. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfn121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot J, Testori S, Barroso C, Martinez-Perez E. Loading of meiotic cohesin by SCC-2 is required for processing of DSBs and for the DNA damage checkpoint. Curr Biol. 2011;32(17):1421–1430. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu JG, Yuan L, Brundell E, Bjorkroth B, Daneholt B, Hoog C. Localization of the N-terminus of SCP1 to the central element of the synaptonemal complex and evidence for direct interactions between the N-termini of SCP1 molecules organized head-to-head. Exp Cell Res. 1996;226(1):11–19. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.0197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T, Rechtsteiner A, Egelhofer TA, Vielle A, Latorre I, Cheung MS, Ercan S, Ikegami K, Jensen M, Kolasinska-Zwierz P, Rosenbaum H, Shin H, Taing S, Takasaki T, Iniguez AL, Desai A, Dernburg AF, Kimura H, Lieb JD, Ahringer J, Strome S, Liu XS. Broad chromosomal domains of histone modification patterns in C. elegans. Genome Res. 2011;21(2):227–236. doi: 10.1101/gr.115519.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llano E, Gomez R, Gutierrez-Caballero C, Herran Y, Sanchez-Martin M, Vazquez-Quinones L, Hernandez T, de Alava E, Cuadrado A, Barbero JL, Suja JA, Pendas AM. Shugoshin-2 is essential for the completion of meiosis but not for mitotic cell division in mice. Genes Dev. 2008;22(17):2400–2413. doi: 10.1101/gad.475308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loidl J. The initiation of meiotic chromosome pairing: the cytological view. Genome. 1990;33(6):759–778. doi: 10.1139/g90-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz A, Estreicher A, Kohli J, Loidl J. Meiotic recombination proteins localize to linear elements in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Chromosoma. 2006;115(4):330–340. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz A, West SC, Whitby MC. The human Holliday junction resolvase GEN1 rescues the meiotic phenotype of a Schizosaccharomyces pombe mus81 mutant. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(6):1866–1873. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lui DY, Peoples-Holst TL, Mell JC, Wu HY, Dean EW, Burgess SM. Analysis of close stable homolog juxtaposition during meiosis in mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 2006;173(3):1207–1222. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.050658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacQueen AJ, Villeneuve AM. Nuclear reorganization and homologous chromosome pairing during meiotic prophase require C. elegans chk-2. Genes Dev. 2001;15(13):1674–1687. doi: 10.1101/gad.902601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacQueen AJ, Colaiacovo MP, McDonald K, Villeneuve AM. Synapsis-dependent and -independent mechanisms stabilize homolog pairing during meiotic prophase in C. elegans. Genes Dev. 2002;16(18):2428–2442. doi: 10.1101/gad.1011602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacQueen AJ, Phillips CM, Bhalla N, Weiser P, Villeneuve AM, Dernburg AF. Chromosome sites play dual roles to establish homologous synapsis during meiosis in C. elegans. Cell. 2005;123(6):1037–1050. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire MP. The relationship of crossing over to chromosome synapsis in a short paracentric inversion. Genetics. 1966;53(6):1071–1077. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.6.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maleki S, Neale MJ, Arora C, Henderson KA, Keeney S. Interactions between Mei4, Rec114, and other proteins required for meiotic DNA double-strand break formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chromosoma. 2007;116(5):471–486. doi: 10.1007/s00412-007-0111-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone CJ, Misner L, Le Bot N, Tsai MC, Campbell JM, Ahringer J, White JG. The C. elegans hook protein, ZYG-12, mediates the essential attachment between the centrosome and nucleus. Cell. 2003;115(7):825–836. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00985-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancera E, Bourgon R, Brozzi A, Huber W, Steinmetz LM. High-resolution mapping of meiotic crossovers and non-crossovers in yeast. Nature. 2008;454(7203):479–485. doi: 10.1038/nature07135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannuss A, Dukowic-Schulze S, Suer S, Hartung F, Pacher M, Puchta H. RAD5A, RECQ4A, and MUS81 have specific functions in homologous recombination and define different pathways of DNA repair in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell. 2010;22(10):3318–3330. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.078568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston AL, Tham WH, Shah H, Amon A. A genome-wide screen identifies genes required for centromeric cohesion. Science. 2004;303(5662):1367–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.1094220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin JS, Winkelmann N, Petalcorin MI, McIlwraith MJ, Boulton SJ. RAD-51-dependent and -independent roles of a Caenorhabditis elegans BRCA2-related protein during DNA double-strand break repair. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(8):3127–3139. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.8.3127-3139.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Perez E, Villeneuve AM. HTP-1-dependent constraints coordinate homolog pairing and synapsis and promote chiasma formation during C. elegans meiosis. Genes Dev. 2005;19(22):2727–2743. doi: 10.1101/gad.1338505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Perez E, Schvarzstein M, Barroso C, Lightfoot J, Dernburg AF, Villeneuve AM. Crossovers trigger a remodeling of meiotic chromosome axis composition that is linked to two-step loss of sister chromatid cohesion. Genes Dev. 2008;22(20):2886–2901. doi: 10.1101/gad.1694108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini E, Diaz RL, Hunter N, Keeney S. Crossover homeostasis in yeast meiosis. Cell. 2006;126(2):285–295. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.05.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazin AV, Bornarth CJ, Solinger JA, Heyer WD, Kowalczykowski SC. Rad54 protein is targeted to pairing loci by the Rad51 nucleoprotein filament. Mol Cell. 2000;6(3):583–592. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazina OM, Mazin AV. Human Rad54 protein stimulates DNA strand exchange activity of hRad51 protein in the presence of Ca2+ J Biol Chem. 2004;279(50):52042–52051. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410244200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee BD. The license to pair: identification of meiotic pairing sites in Drosophila. Chromosoma. 1996;105(3):135–141. doi: 10.1007/BF02509494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKim KS, Howell AM, Rose AM. The effects of translocations on recombination frequency in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1988;120(4):987–1001. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.4.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKim KS, Green-Marroquin BL, Sekelsky JJ, Chin G, Steinberg C, Khodosh R, Hawley RS. Meiotic synapsis in the absence of recombination. Science. 1998;279(5352):876–878. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5352.876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahill MS, Sham CW, Bishop DK. Synthesis-dependent strand annealing in meiosis. PLoS Biol. 2007;5(11):e299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melby TE, Ciampaglio CN, Briscoe G, Erickson HP. The symmetrical structure of structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) and MukB proteins: long, antiparallel coiled coils, folded at a flexible hinge. J Cell Biol. 1998;142(6):1595–1604. doi: 10.1083/jcb.142.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier R, Jolivet S, Vezon D, Huppe E, Chelysheva L, Giovanni M, Nogue F, Doutriaux MP, Horlow C, Grelon M, Mezard C. Two meiotic crossover classes cohabit in Arabidopsis: one is dependent on MER3, whereas the other one is not. Curr Biol. 2005;15(8):692–701. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.02.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mets DG, Meyer BJ. Condensins regulate meiotic DNA break distribution, thus crossover frequency, by controlling chromosome structure. Cell. 2009;139(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki F, Okazaki K, Shimanuki M, Yamamoto A, Hiraoka Y, Niwa O. The 14-kDa dynein light chain-family protein Dlc1 is required for regular oscillatory nuclear movement and efficient recombination during meiotic prophase in fission yeast. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(3):930–946. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-11-0543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minn IL, Rolls MM, Hanna-Rose W, Malone CJ. SUN-1 and ZYG-12, mediators of centrosome-nucleus attachment, are a functional SUN/KASH pair in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Biol Cell. 2009;20(21):4586–4595. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E08-10-1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monen J, Maddox PS, Hyndman F, Oegema K, Desai A. Differential role of CENP-A in the segregation of holocentric C. elegans chromosomes during meiosis and mitosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7(12):1248–1255. doi: 10.1038/ncb1331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses MJ. Synaptinemal complex. Annu Rev Genet. 1968;2:363–412. [Google Scholar]
- Motohashi T, Tabara H, Kohara Y. Protocols for large scale in situ hybridization on C. elegans larvae. WormBook. 2006:1–8. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.103.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller HJ. The mechanism of crossing over. Am Nat. 1916;50:193–221. [Google Scholar]
- Munz P. An analysis of interference in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genetics. 1994;137(3):701–707. doi: 10.1093/genetics/137.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima K, Villeneuve AM, Hillers KJ. Chromosome-wide regulation of meiotic crossover formation in Caenorhabditis elegans requires properly assembled chromosome axes. Genetics. 2004;168(3):1275–1292. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.030700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima K, Villeneuve AM, Colaiacovo MP. Crossing over is coupled to late meiotic prophase bivalent differentiation through asymmetric disassembly of the SC. J Cell Biol. 2005;168(5):683–689. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200410144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag DK, Scherthan H, Rockmill B, Bhargava J, Roeder GS. Heteroduplex DNA formation and homolog pairing in yeast meiotic mutants. Genetics. 1995;141(1):75–86. doi: 10.1093/genetics/141.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K, Haering CH. The structure and function of SMC and kleisin complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:595–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.74.082803.133219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas RB. Chromosome segregation mechanisms. Genetics. 1974;78(1):205–213. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nottke AC, Beese-Sims SE, Pantelena LF, Reinke V, Shi Y, Colaiacovo MP. SPR-5 is a histone H3K4 demethylase with a role in meiotic double-strand break repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(31):12805–12810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102298108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obeso D, Dawson DS. Temporal characterization of homology-independent centromere coupling in meiotic prophase. PLoS One. 2010;5(4):e10336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh SD, Lao JP, Hwang PY, Taylor AF, Smith GR, Hunter N. BLM ortholog, Sgs1, prevents aberrant crossing-over by suppressing formation of multichromatid joint molecules. Cell. 2007;130(2):259–272. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh SD, Lao JP, Taylor AF, Smith GR, Hunter N. RecQ helicase, Sgs1, and XPF family endonuclease, Mus81-Mms4, resolve aberrant joint molecules during meiotic recombination. Mol Cell. 2008;31(3):324–336. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira RA, Nasmyth K. Getting through anaphase: splitting the sisters and beyond. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010;38(6):1639–1644. doi: 10.1042/BST0381639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Östergren G. The mechanism of co-orientation in bivalents, and multivalents. Berlingska boktr; Lund: 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Page SL, Hawley RS. c(3)G encodes a Drosophila synaptonemal complex protein. Genes Dev. 2001;15(23):3130–3143. doi: 10.1101/gad.935001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page SL, Hawley RS. The genetics and molecular biology of the synaptonemal complex. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:525–558. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.19.111301.155141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan J, Sasaki M, Kniewel R, Murakami H, Blitzblau HG, Tischfield SE, Zhu X, Neale MJ, Jasin M, Socci ND, Hochwagen A, Keeney S. A hierarchical combination of factors shapes the genome-wide topography of yeast meiotic recombination initiation. Cell. 2011;144(5):719–731. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panizza S, Mendoza MA, Berlinger M, Huang L, Nicolas A, Shirahige K, Klein F. Spo11-accessory proteins link double-strand break sites to the chromosome axis in early meiotic recombination. Cell. 2011;146(3):372–383. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi S, McKay MJ, Molnar M, Thompson MA, van der Spek PJ, van Drunen-Schoenmaker E, Kanaar R, Lehmann E, Hoeijmakers JH, Kohli J. Rec8p, a meiotic recombination and sister chromatid cohesion phosphoprotein of the Rad21p family conserved from fission yeast to humans. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19(5):3515–3528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.5.3515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasierbek P, Jantsch M, Melcher M, Schleiffer A, Schweizer D, Loidl J. A Caenorhabditis elegans cohesion protein with functions in meiotic chromosome pairing and disjunction. Genes Dev. 2001;15(11):1349–1360. doi: 10.1101/gad.192701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasierbek P, Fodermayr M, Jantsch V, Jantsch M, Schweizer D, Loidl J. The Caenorhabditis elegans SCC-3 homologue is required for meiotic synapsis and for proper chromosome disjunction in mitosis and meiosis. Exp Cell Res. 2003;289(2):245–255. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(03)00266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penkner A, Portik-Dobos Z, Tang L, Schnabel R, Novatchkova M, Jantsch V, Loidl J. A conserved function for a Caenorhabditis elegans Com1/Sae2/CtIP protein homolog in meiotic recombination. EMBO J. 2007;26(24):5071–5082. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penkner AM, Fridkin A, Gloggnitzer J, Baudrimont A, Machacek T, Woglar A, Csaszar E, Pasierbek P, Ammerer G, Gruenbaum Y, Jantsch V. Meiotic chromosome homology search involves modifications of the nuclear envelope protein Matefin/SUN-1. Cell. 2009;139(5):920–933. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.10.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peoples TL, Dean E, Gonzalez O, Lambourne L, Burgess SM. Close, stable homolog juxtaposition during meiosis in budding yeast is dependent on meiotic recombination, occurs independently of synapsis, and is distinct from DSB-independent pairing contacts. Genes Dev. 2002;16(13):1682–1695. doi: 10.1101/gad.983802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peoples-Holst TL, Burgess SM. Multiple branches of the meiotic recombination pathway contribute independently to homolog pairing and stable juxtaposition during meiosis in budding yeast. Genes Dev. 2005;19(7):863–874. doi: 10.1101/gad.1293605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petalcorin MI, Sandall J, Wigley DB, Boulton SJ. CeBRC-2 stimulates D-loop formation by RAD-51 and promotes DNA single-strand annealing. J Mol Biol. 2006;361(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.06.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petalcorin MI, Galkin VE, Yu X, Egelman EH, Boulton SJ. Stabilization of RAD-51-DNA filaments via an interaction domain in Caenorhabditis elegans BRCA2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(20):8299–8304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702805104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petes TD. Meiotic recombination hot spots and cold spots. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2(5):360–369. doi: 10.1038/35072078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips CM, Dernburg AF. A family of zinc-finger proteins is required for chromosome-specific pairing and synapsis during meiosis in C. elegans. Dev Cell. 2006;11(6):817–829. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.09.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips CM, Wong C, Bhalla N, Carlton PM, Weiser P, Meneely PM, Dernburg AF. HIM-8 binds to the X chromosome pairing center and mediates chromosome-specific meiotic synapsis. Cell. 2005;123(6):1051–1063. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips CM, McDonald KL, Dernburg AF. Cytological analysis of meiosis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Methods Mol Biol. 2009a;558:171–195. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-103-5_11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips CM, Meng X, Zhang L, Chretien JH, Urnov FD, Dernburg AF. Identification of chromosome sequence motifs that mediate meiotic pairing and synapsis in C. elegans. Nat Cell Biol. 2009b;11(8):934–942. doi: 10.1038/ncb1904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabitsch KP, Gregan J, Schleiffer A, Javerzat JP, Eisenhaber F, Nasmyth K. Two fission yeast homologs of Drosophila Mei-S332 are required for chromosome segregation during meiosis I and II. Curr Biol. 2004;14(4):287–301. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radford SJ, McMahan S, Blanton HL, Sekelsky J. Heteroduplex DNA in meiotic recombination in Drosophila mei-9 mutants. Genetics. 2007;176(1):63–72. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.070557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen SW, Holm PB. The synaptonemal complex, recombination nodules and chiasmata in human spermatocytes. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1984;38:271–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy KC, Villeneuve AM. C. elegans HIM-17 links chromatin modification and competence for initiation of meiotic recombination. Cell. 2004;118(4):439–452. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.07.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel CG, Katis VL, Katou Y, Mori S, Itoh T, Helmhart W, Galova M, Petronczki M, Gregan J, Cetin B, Mudrak I, Ogris E, Mechtler K, Pelletier L, Buchholz F, Shirahige K, Nasmyth K. Protein phosphatase 2A protects centromeric sister chromatid cohesion during meiosis I. Nature. 2006;441(7089):53–61. doi: 10.1038/nature04664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder GS. Meiotic chromosomes: it takes two to tango. Genes Dev. 1997;11(20):2600–2621. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.20.2600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers E, Bishop JD, Waddle JA, Schumacher JM, Lin R. The aurora kinase AIR-2 functions in the release of chromosome cohesion in Caenorhabditis elegans meiosis. J Cell Biol. 2002;157(2):219–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200110045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins RA, Korom M, Aulner N, Martens A, Dorsett D. Drosophila Nipped-B protein supports sister chromatid cohesion and opposes the stromalin/Scc3 cohesion factor to facilitate long-range activation of the cut gene. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(8):3100–3111. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.8.3100-3111.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A, Guse A, Krascenicova I, Schnabel H, Schnabel R, Glotzer M. CSC-1: a subunit of the Aurora B kinase complex that binds to the Survivin-like protein BIR-1 and the Incenplike protein ICP-1. J Cell Biol. 2003;161(2):229–236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200207117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose AM, Baillie DL, Curran J. Meiotic pairing behavior of two free duplications of linkage group I in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1–2):52–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00332723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluth RE, Baillie DL. The genetic analysis of a reciprocal translocation, eT1(III; V), in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1981;99(3–4):415–428. doi: 10.1093/genetics/99.3-4.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosu S, Libuda DE, Villeneuve AM. Robust crossover assurance and regulated intehomolog access maintain meiotic crossover number. Science. 2011;334(6060):1286–1289. doi: 10.1126/science.1212424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito TT, Youds JL, Boulton SJ, Colaiacovo MP. Caenorhabditis elegans HIM-18/SLX-4 interacts with SLX-1 and XPF-1 and maintains genomic integrity in the germline by processing recombination intermediates. PLoS Genet. 2009;5(11):e1000735. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford C, Perry MD. Asymmetrically distributed oligonucleotide repeats in the Caenorhabditis elegans genome sequence that map to regions important for meiotic chromosome segregation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29(14):2920–2926. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.14.2920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A, Isaac B, Phillips CM, Rillo R, Carlton PM, Wynne DJ, Kasad RA, Dernburg AF. Cytoskeletal forces span the nuclear envelope to coordinate meiotic chromosome pairing and synapsis. Cell. 2009;139(5):907–919. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.10.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild-Prufert K, Saito TT, Smolikov S, Gu Y, Hincapie M, Hill DE, Vidal M, McDonald K, Colaiacovo MP. Organization of the synaptonemal complex during meiosis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 2011;189:411–421. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.132431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlecht HB, Lichten M, Goldman ASH. Compartmentalization of the yeast meiotic nucleus revealed by analysis of ectopic recombination. Genetics. 2004;168(3):1189–1203. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.029157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmekel K, Meuwissen RL, Dietrich AJ, Vink AC, van Marle J, van Veen H, Heyting C. Organization of SCP1 protein molecules within synaptonemal complexes of the rat. Exp Cell Res. 1996;226(1):20–30. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.0198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm S, Fraune J, Naumann R, Hernandez-Hernandez A, Hoog C, Cooke HJ, Alsheimer M, Benavente R. A novel mouse synaptonemal complex protein is essential for loading of central element proteins, recombination, and fertility. PLoS Genet. 2011;7(5):e1002088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher JM, Golden A, Donovan PJ. AIR-2: An Aurora/Ipl1-related protein kinase associated with chromosomes and midbody microtubules is required for polar body extrusion and cytokinesis in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. J Cell Biol. 1998;143(6):1635–1646. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.6.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwacha A, Kleckner N. Identification of joint molecules that form frequently between homologs but rarely between sister chromatids during yeast meiosis. Cell. 1994;76(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz EK, Heyer WD. Processing of joint molecule intermediates by structure-selective endonucleases during homologous recombination in eukaryotes. Chromosoma. 2011;120(2):109–127. doi: 10.1007/s00412-010-0304-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitan VC, Banks P, Laval S, Majid NA, Dorsett D, Rana A, Smith J, Bateman A, Krpic S, Hostert A, Rollins RA, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Benard CY, Hekimi S, Newbury SF, Strachan T. Metazoan Scc4 homologs link sister chromatid cohesion to cell and axon migration guidance. PLoS Biol. 2006;4(8):e242. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson AF, Ling L, van Zuylen V, Meyer BJ. The axial element protein HTP-3 promotes cohesin loading and meiotic axis assembly in C. elegans to implement the meiotic program of chromosome segregation. Genes Dev. 2009;23(15):1763–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.1808809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood R, Takahashi TS, Jallepalli PV. Sister acts: coordinating DNA replication and cohesion establishment. Genes Dev. 2010;24(24):2723–2731. doi: 10.1101/gad.1976710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara M, Oh SD, Hunter N, Shinohara A. Crossover assurance and crossover interference are distinctly regulated by the ZMM proteins during yeast meiosis. Nat Genet. 2008;40(3):299–309. doi: 10.1038/ng.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smagulova F, Gregoretti IV, Brick K, Khil P, Camerini-Otero RD, Petukhova GV. Genome-wide analysis reveals novel molecular features of mouse recombination hotspots. Nature. 2011;472(7343):375–378. doi: 10.1038/nature09869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith GR, Boddy MN, Shanahan P, Russell P. Fission yeast Mus81.Eme1 Holliday junction resolvase is required for meiotic crossing over but not for gene conversion. Genetics. 2003;165(4):2289–2293. doi: 10.1093/genetics/165.4.2289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O, Powers PA. Gene conversions and their relation to homologous chromosome pairing. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986;312(1154):291–302. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1986.0008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolikov S, Eizinger A, Hurlburt A, Rogers E, Villeneuve AM, Colaiacovo MP. Synapsis-defective mutants reveal a correlation between chromosome conformation and the mode of double-strand break repair during Caenorhabditis elegans meiosis. Genetics. 2007a;176(4):2027–2033. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.076968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolikov S, Eizinger A, Schild-Prufert K, Hurlburt A, McDonald K, Engebrecht J, Villeneuve AM, Colaiacovo MP. SYP-3 restricts synaptonemal complex assembly to bridge paired chromosome axes during meiosis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 2007b;176(4):2015–2025. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.072413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolikov S, Schild-Prufert K, Colaiacovo MP. CRA-1 uncovers a double-strand break-dependent pathway promoting the assembly of central region proteins on chromosome axes during C. elegans meiosis. PLoS Genet. 2008;4(6):e1000088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolikov S, Schild-Prufert K, Colaiacovo MP. A yeast two-hybrid screen for SYP-3 interactors identifies SYP-4, a component required for synaptonemal complex assembly and chiasma formation in Caenorhabditis elegans meiosis. PLoS Genet. 2009;5(10):e1000669. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snowden T, Acharya S, Butz C, Berardini M, Fishel R. hMSH4-hMSH5 recognizes Holliday Junctions and forms a meiosis-specific sliding clamp that embraces homologous chromosomes. Mol Cell. 2004;15(3):437–451. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.06.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speliotes EK, Uren A, Vaux D, Horvitz HR. The survivin-like C. elegans BIR-1 protein acts with the Aurora-like kinase AIR-2 to affect chromosomes and the spindle midzone. Mol Cell. 2000;6(2):211–223. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr DA, Fridolfsson HN. Interactions between nuclei and the cytoskeleton are mediated by SUN-KASH nuclear-envelope bridges. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010;26:421–444. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100109-104037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T, New JH, Kowalczykowski SC. DNA annealing by RAD52 protein is stimulated by specific interaction with the complex of replication protein A and single-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95(11):6049–6054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H, Treco D, Szostak JW. Extensive 3′-overhanging, single-stranded DNA associated with the meiosis-specific double-strand breaks at the ARG4 recombination initiation site. Cell. 1991;64(6):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sym M, Engebrecht JA, Roeder GS. ZIP1 is a synaptonemal complex protein required for meiotic chromosome synapsis. Cell. 1993;72(3):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak JW, Orr-Weaver TL, Rothstein RJ, Stahl FW. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarsounas M, Morita T, Pearlman RE, Moens PB. RAD51 and DMC1 form mixed complexes associated with mouse meiotic chromosome cores and synaptonemal complexes. J Cell Biol. 1999;147(2):207–220. doi: 10.1083/jcb.147.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasawa M, Shinohara A, Hotta Y, Ogawa H, Ogawa T. Localization of RecA-like recombination proteins on chromosomes of the lily at various meiotic stages. Genes Dev. 1995;9(8):925–934. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.8.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas SE, McKee BD. Meiotic pairing and disjunction of mini-X chromosomes in Drosophila is mediated by 240-bp rDNA repeats and the homolog conjunction proteins SNM and MNM. Genetics. 2007;177(2):785–799. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.073866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas SE, Soltani-Bejnood M, Roth P, Dorn R, Logsdon JM, Jr, McKee BD. Identification of two proteins required for conjunction and regular segregation of achiasmate homologs in Drosophila male meiosis. Cell. 2005;123(4):555–568. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmons L, Fire A. Specific interference by ingested dsRNA. Nature. 1998;395(6705):854. doi: 10.1038/27579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonkin ET, Wang TJ, Lisgo S, Bamshad MJ, Strachan T. NIPBL, encoding a homolog of fungal Scc2-type sister chromatid cohesion proteins and fly Nipped-B, is mutated in Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Nat Genet. 2004;36(6):636–641. doi: 10.1038/ng1363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trelles-Sticken E, Adelfalk C, Loidl J, Scherthan H. Meiotic telomere clustering requires actin for its formation and cohesin for its resolution. J Cell Biol. 2005;170(2):213–223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200501042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge K, McKim K, Brill SJ, Sekelsky J. Synthetic lethality of Drosophila in the absence of the MUS81 endonuclease and the DmBlm helicase is associated with elevated apoptosis. Genetics. 2007;176(4):1993–2001. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.070060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai CJ, Mets DG, Albrecht MR, Nix P, Chan A, Meyer BJ. Meiotic crossover number and distribution are regulated by a dosage compensation protein that resembles a condensin subunit. Genes Dev. 2008;22(2):194–211. doi: 10.1101/gad.1618508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubouchi T, Roeder GS. A synaptonemal complex protein promotes homology-independent centromere coupling. Science. 2005;308(5723):870–873. doi: 10.1126/science.1108283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeneuve AM. A cis-acting locus that promotes crossing over between X chromosomes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1994;136(3):887–902. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeneuve AM, Hillers KJ. Whence meiosis? Cell. 2001;106(6):647–650. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00500-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner CR, Kuervers L, Baillie DL, Yanowitz JL. xnd-1 regulates the global recombination landscape in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2010;467(7317):839–843. doi: 10.1038/nature09429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F, Yoder J, Antoshechkin I, Han M. Caenorhabditis elegans EVL-14/PDS-5 and SCC-3 are essential for sister chromatid cohesion in meiosis and mitosis. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(21):7698–7707. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.21.7698-7707.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watrin E, Schleiffer A, Tanaka K, Eisenhaber F, Nasmyth K, Peters JM. Human Scc4 is required for cohesin binding to chromatin, sister-chromatid cohesion, and mitotic progression. Curr Biol. 2006;16(9):863–874. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.03.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber HA, Howard L, Bickel SE. The cohesion protein ORD is required for homologue bias during meiotic recombination. J Cell Biol. 2004;164(6):819–829. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200310077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner BM, Kleckner N. Chromosome pairing via multiple interstitial interactions before and during meiosis in yeast. Cell. 1994;77(7):977–991. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90438-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard M, von Wettstein D. The synaptinemal complex. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6:71–110. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicky C, Alpi A, Passannante M, Rose A, Gartner A, Muller F. Multiple genetic pathways involving the Caenorhabditis elegans Bloom’s syndrome genes him-6, rad-51, and top-3 are needed to maintain genome stability in the germ line. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(11):5016–5027. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.11.5016-5027.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wignall SM, Villeneuve AM. Lateral microtubule bundles promote chromosome alignment during acentrosomal oocyte meiosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(7):839–844. doi: 10.1038/ncb1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winand NJ, Panzer JA, Kolodner RD. Cloning and characterization of the human and Caenorhabditis elegans homologs of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae MSH5 gene. Genomics. 1998;53(1):69–80. doi: 10.1006/geno.1998.5447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu HY, Burgess SM. Two distinct surveillance mechanisms monitor meiotic chromosome metabolism in budding yeast. Curr Biol. 2006;16(24):2473–2479. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.10.069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz O, Majumder S, Kramer B, Sekelsky JJ. Drosophila MUS312 interacts with the nucleotide excision repair endonuclease MEI-9 to generate meiotic crossovers. Mol Cell. 2002;10(6):1503–1509. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00782-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youds JL, Mets DG, McIlwraith MJ, Martin JS, Ward JD, NJ ON, Rose AM, West SC, Meyer BJ, Boulton SJ. RTEL-1 enforces meiotic crossover interference and homeostasis. Science. 2010;327(5970):1254–1258. doi: 10.1126/science.1183112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalevsky J, MacQueen AJ, Duffy JB, Kemphues KJ, Villeneuve AM. Crossing over during Caenorhabditis elegans meiosis requires a conserved MutS-based pathway that is partially dispensable in budding yeast. Genetics. 1999;153(3):1271–1283. doi: 10.1093/genetics/153.3.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetka M, Rose A. The genetics of meiosis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Trends Genet. 1995;11(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)88983-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetka MC, Kawasaki I, Strome S, Muller F. Synapsis and chiasma formation in Caenorhabditis elegans require HIM-3, a meiotic chromosome core component that functions in chromosome segregation. Genes Dev. 1999;13(17):2258–2270. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.17.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zickler D. Development of the synaptonemal complex and the “recombination nodules” during meiotic prophase in the seven bivalents of the fungus Sordaria macrospora Auersw. Chromosoma. 1977;61(4):289–316. doi: 10.1007/BF00288615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zickler D, Kleckner N. The leptotene-zygotene transition of meiosis. Annu Rev Genet. 1998;32:619–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.32.1.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zickler D, Kleckner N. Meiotic chromosomes: integrating structure and function. Annu Rev Genet. 1999;33:603–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.33.1.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


