Abstract
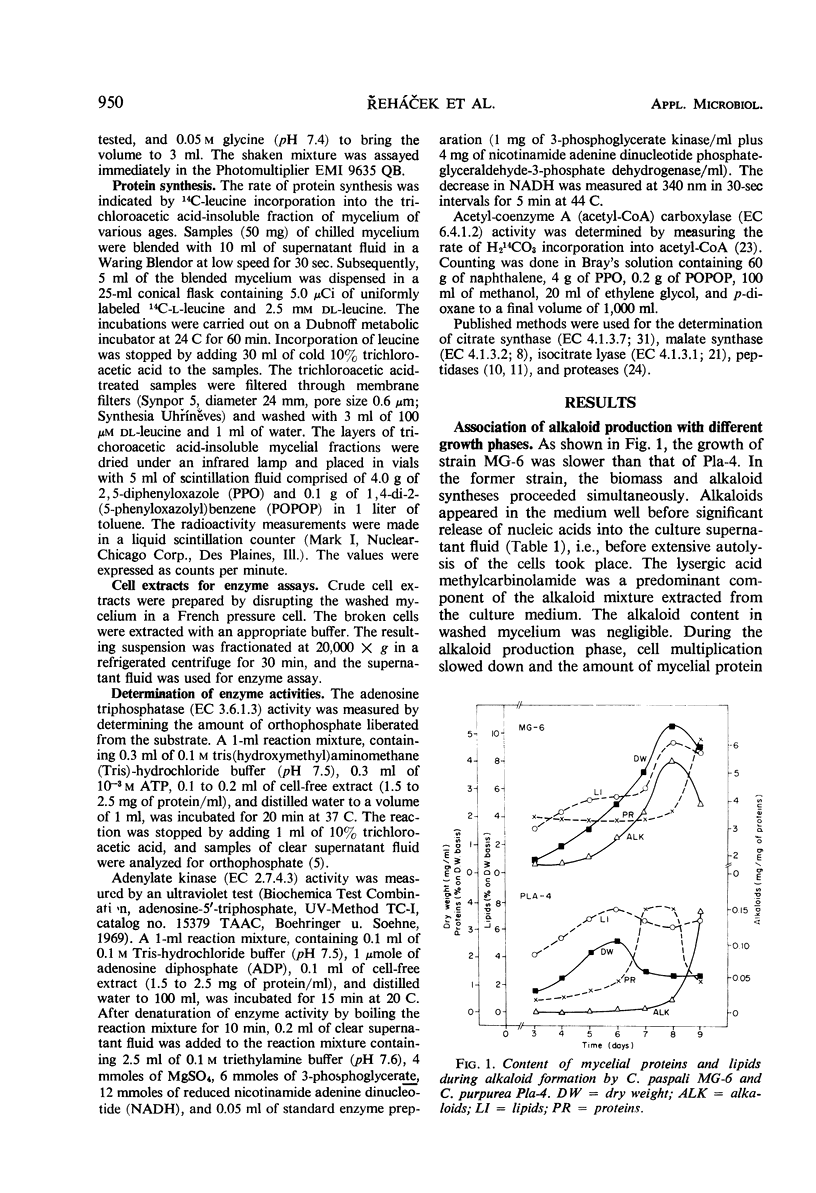
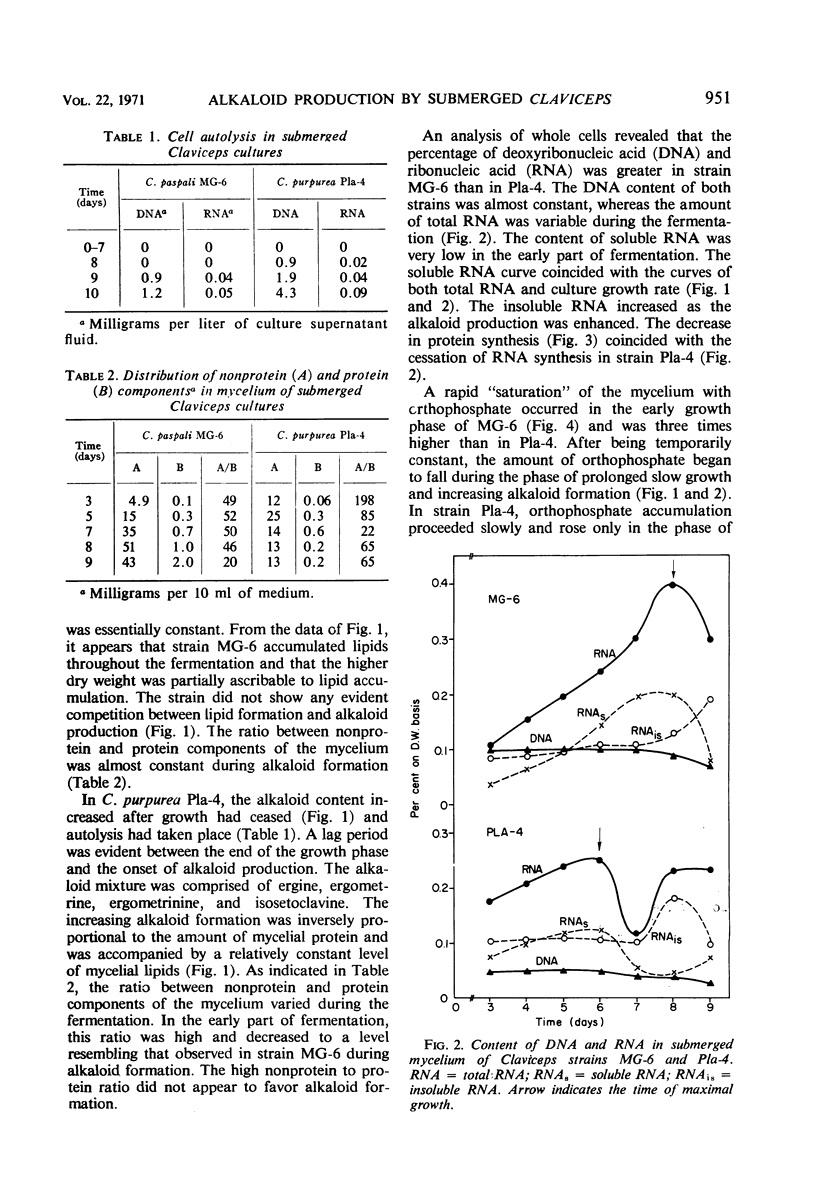
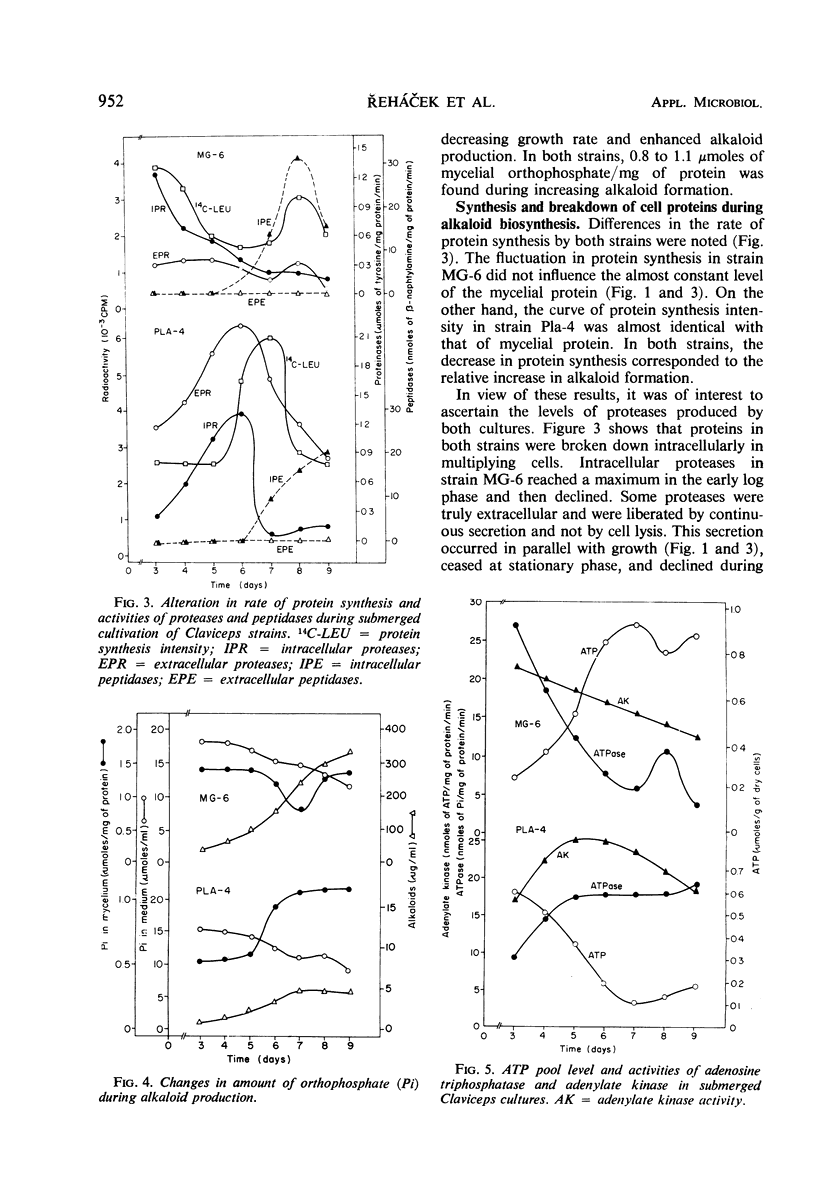
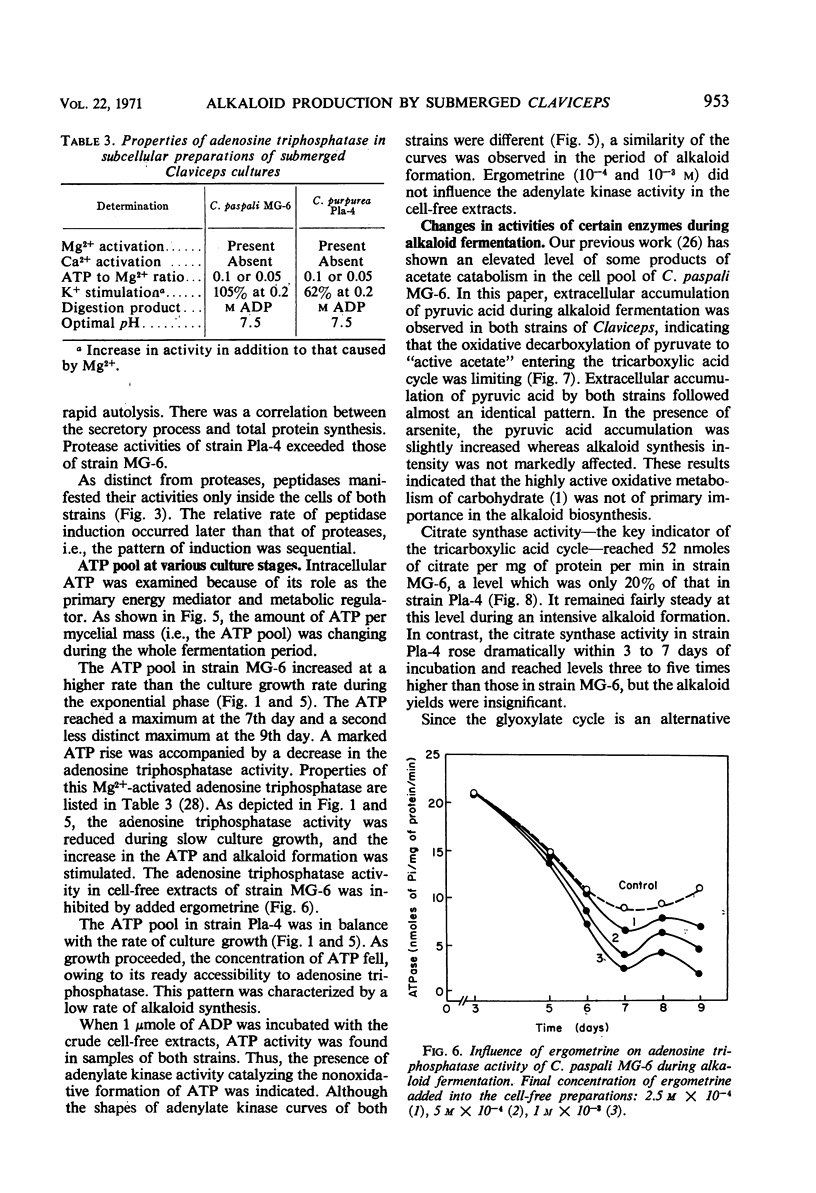
Alkaloid biosynthesis in Claviceps paspali MG-6 was favored by unbalanced growth. A positive correlation between the rate of protein turnover and alkaloid formation was noted. The pattern of the orthophosphate content in the mycelium resembled that in the ripening sclerotia of the parasitic strains. Alkaloids were revealed as potentially effective in energy metabolism. Reduced adenosine triphosphate (ATP) utilization and an increase in the ATP pool were found to be favorable for alkaloid production. Acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase activity and the level of cell lipids were directly related to the intensity of alkaloid biosynthesis. An inverse relationship was observed between the activities of the tricarboxylic acid and glycoxylate cycles and the rate of alkaloid formation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BONTING S. L. Colorimetric determination of pyruvic acid and other alpha-keto acids in submicrogram quantities. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Sep;58(1):100–108. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. C., Seidman I., Teebor G., Lane M. D. Liver acetyl CoA carboxylase and fatty acid synthetase: relative activities in the normal state and in hereditary obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):682–686. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90369-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. V., Ross C. Extraction, separation, and quantitative estimation of soluble nucleotides and sugar phosphates in plant tissues. Anal Biochem. 1966 Dec;17(3):526–539. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Beevers H. Mitochondria and glyoxysomes from castor bean endosperm. Enzyme constitutents and catalytic capacity. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3507–3513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell R. B., Fincham J. R. Acetate-nonutilizing mutants of Neurospora rassa. II. Biochemical deficiencies and the roles of certain enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1063–1068. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1063-1068.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANGULY J. Studies on the mechanism of fatty acid synthesis. VII. Biosynthesis of fatty acids from malonyl CoA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 May 6;40:110–118. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91320-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBARG J. A., RUTENBURG A. M. The colorimetric determination of leucine aminopeptidase in urine and serum of normal subjects and patients with cancer and other diseases. Cancer. 1958 Mar-Apr;11(2):283–291. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195803/04)11:2<283::aid-cncr2820110209>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin T. B., Prescott J. M. Some physical characteristics of a proteinase from Aeromonas proteolytica. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 25;245(6):1348–1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janglová Z., Suchý J., Vanek Z. Regulation of biosynthesis of secondary metabolites. VII. Intracellular adenosine-5'-triphosphate concentration in Streptomyces aureofaciens. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1969;14(3):208–210. doi: 10.1007/BF02872780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T., Williams P. H. Effect of nutritional factors on extracellular protease production by Pseudomonas lachrymans. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Jul;13(7):863–871. doi: 10.1139/m67-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobr M. J., Vanderhaeghe F., Combépine G. Particulate enzymes of the glyoxylate cycle in Neurospora crassa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Nov 6;37(4):640–645. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90858-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELSTAM J. Turnover of protein in starved bacteria and its relationship to the induced synthesis of enzyme. Nature. 1957 Jun 8;179(4571):1179–1181. doi: 10.1038/1791179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN D. B., VAGELOS P. R. The mechanism of tricarboxylic acid cycle regulation of fatty acid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1787–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Hogg J. F., De Duve C. Distribution of tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes and glyoxylate cycle enzymes between mitochondria and peroxisomes in Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5385–5395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehácek Z., Basappa S. C. Effect of Tween 80 on alkaloid-producing cultures of Claviceps paspali. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1971;16(2):110–113. doi: 10.1007/BF02887480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehácek Z., Kozová J., Ricicová A., Kaslík J., Sajdl P., Svarc S., Basappa S. C. Role of endogenous tryptophan during submerged fermentation of ergot alkaloids. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1971;16(1):35–40. doi: 10.1007/BF02887333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehácek Z., Malik K. A. Cell-pool tryptophan phases in ergot alkaloid fermentation. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1971;16(5):359–363. doi: 10.1007/BF02875754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SRERE P. A., KOSICKI G. W. The purification of citrate-condensing enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1961 Oct;236:2557–2559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABER W. A. SEQUENTIAL FORMATION AND ACCUMULATION OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY SHUNT METABOLIC PRODUCTS IN CLAVICEPS PURPUREA. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:321–326. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.321-326.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turková J., Gancev M. K., Boublík M. Isolation and characterization of alkaline proteinase of Aspergillus flavus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 18;178(1):100–111. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N. S. Protein degradation during diauxic growth of Escerichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Sep 22;20(6):692–696. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



