Abstract
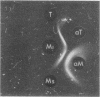
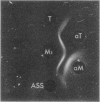
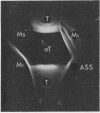
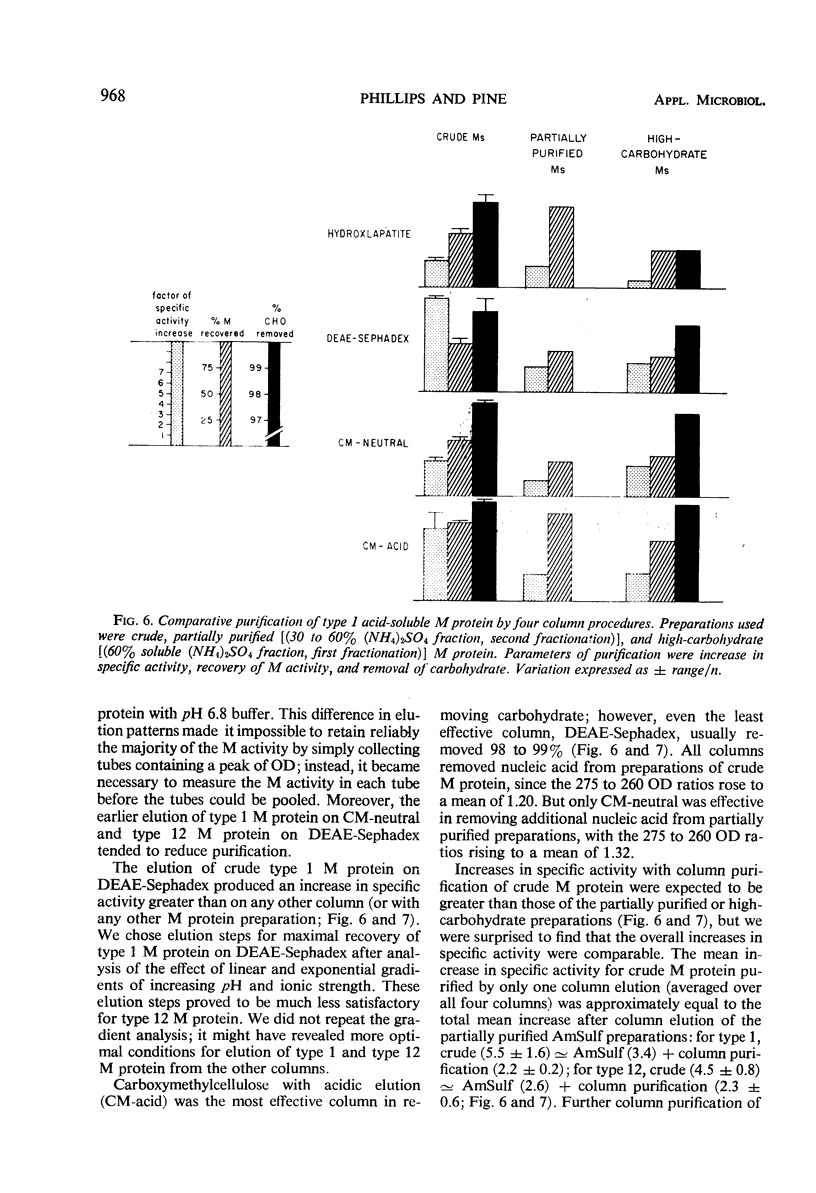
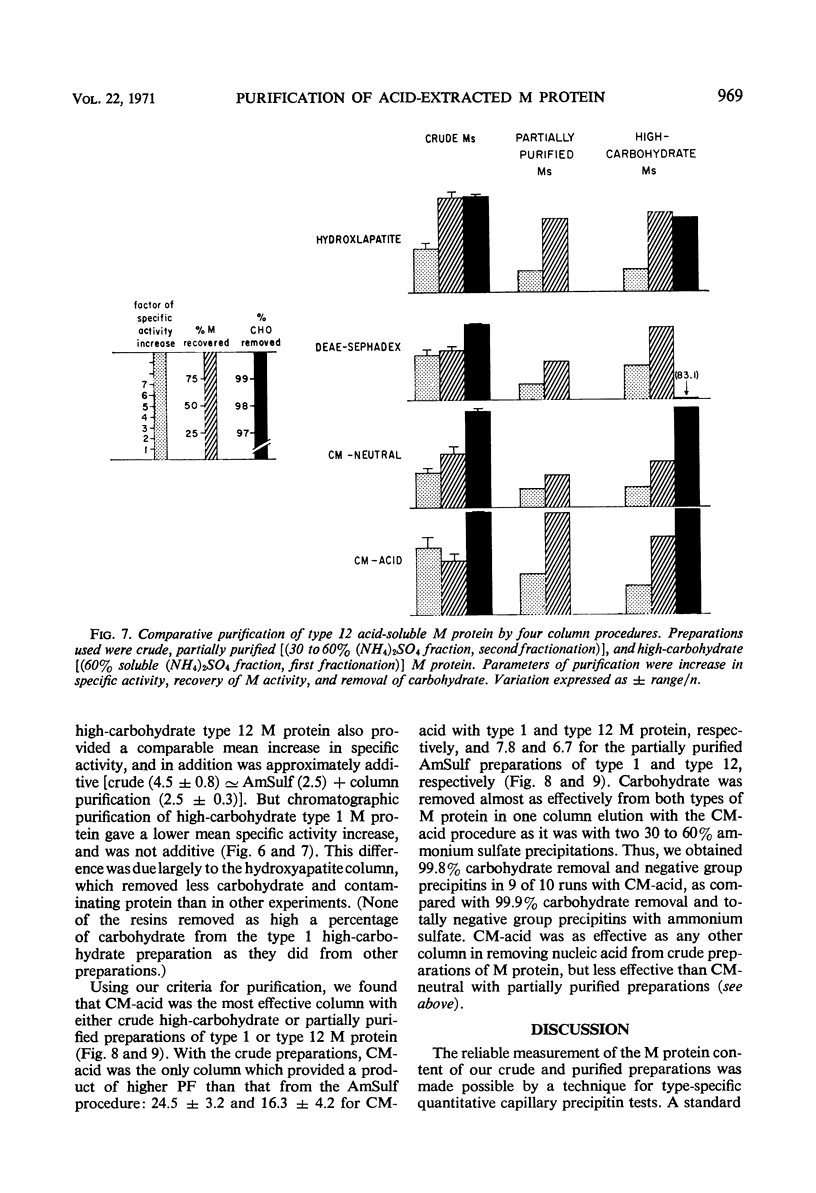
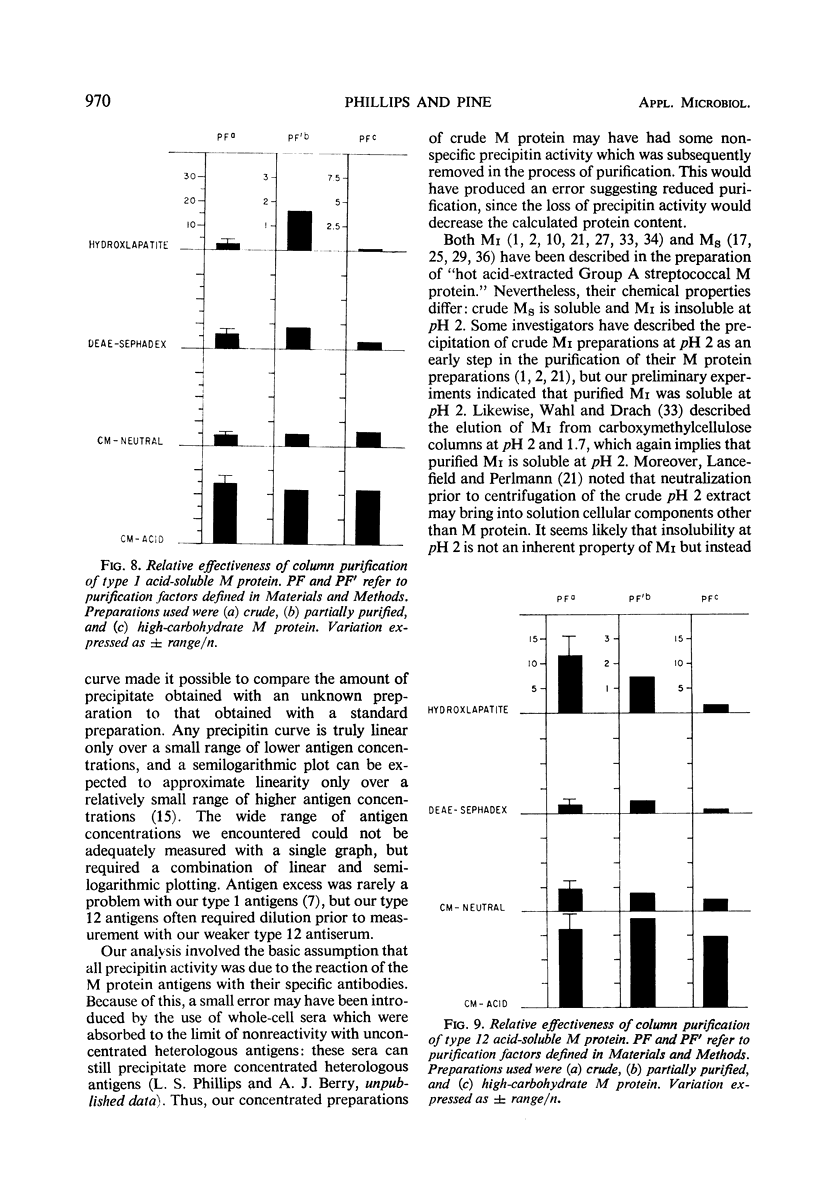
The literature includes descriptions of both acid-soluble and acid-insoluble M protein in the preparation of “hot acid-extracted group A streptococcal M protein.” We present evidence for the contamination of crude type 1 acid-insoluble M protein. The purification of preparations of crude and partially purified acid-soluble type 1 and type 12 M protein is described. Our quantitative criteria for purification were recovery of M precipitin activity, improvement in specific activity, and removal of carbohydrate. Exclusion of nucleic acid is also discussed. Greater purification in a single passage was found with a carboxymethylcellulose column (with acidic elution) than with hydroxyapatite, diethylaminoethyl-Sephadex, or carboxymethyl-cellulose (with neutral elution) columns or with ammonium sulfate fractional precipitation. Carboxymethylcellulose with acidic elution was found to be a satisfactory standard laboratory procedure for the preparation of purified acid-extracted (acid-soluble) group A streptococcal M protein.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARKULIS S. S., JONES M. F. Studies of streptococcal cell walls. I. Isolation, chemical composition, and preparation of M protein. J Bacteriol. 1957 Aug;74(2):207–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.2.207-216.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D. EFFECT OF ANTIBIOTICS AND INHIBITORS ON M PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:527–531. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.527-531.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Alberti H., Stollerman G. H. Delayed hypersensitivity to purified streptococcal m protein in guinea pigs and in man. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):42–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. G. Enhancing effect of type specific antistreptococcal antibodies on emergence of streptococci rich in M-protein. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jan;124(1):331–335. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besdine R. W., Pine L. Preparation and description of high-molecular-weight soluble surface antigens from a group A Streptococcus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):1953–1960. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.1953-1960.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAYEUX P., WAHL R. M'ETHODE NOUVELLE D'EXTRACTION ET DE PURIFICATION DE LA PROT'EINE M DE STREPTOCOCCUS PYOGENES DU GROUPE A APPLIQU'EE AU TYPE 24. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1963 Dec;105:1063–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. O., Pine L. Quantitative aspects of the M protein capillary precipitin test. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jan;16(1):122–127. doi: 10.1128/am.16.1.122-127.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M., WEBB E. C. Enzyme fractionation by salting-out: a theoretical note. Adv Protein Chem. 1961;16:197–219. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N. ANTIGENICITY OF THE M PROTEINS OF GROUP A HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:826–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K. New observations on the structure and antigenicity of the M proteins of the group A streptococcus. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K. The multiple molecular structure of the M proteins of group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1118–1125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMBLY J. S. The precipitating antigen of Streptococcus pyogenes type 4. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Feb;18(1):285–293. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-1-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. H., Vosti K. L. Purification of two fragments of M protein from a strain of group A, type 12 streptococcus. J Immunol. 1968 Sep;101(3):381–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Occurrence of R antigen specific for Group A type 3 streptococci. J Exp Med. 1958 Sep 1;108(3):329–341. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.3.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C., PERLMANN G. E. Preparation and properties of type-specific M antigen isolated from a group A, type 1 hemolytic streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1952 Jul;96(1):71–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOODY M. D., PADULA J., LIZANA D., HALL C. T. EPIDEMIOLOGIC CHARACTERIZATION OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI BY T-AGGLUTINATION AND M-PRECIPITATION TESTS IN THE PUBLIC HEALTH LABORATORY. Health Lab Sci. 1965 Jul;2:149–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCARTY M. The occurrence of polyglycerophosphate as an antigenic component of various gram-positive bacterial species. J Exp Med. 1959 Apr 1;109(4):361–378. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.4.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden P., Anthony B. F., Farr R. S. A comparison of seven procedures to detect the primary binding of antigen by antibody. J Immunol. 1969 Apr;102(4):832–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAKULA R. Extraction of the T antigen of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Oct;5(4):640–647. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-4-640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLADE H. D., VETTER J. K. Studies on Streptococcus pyogenes. I. Observations on the microscopical and biological aspects of the disintegration and solubilization of a type 6 strain by sonic oscillation. J Bacteriol. 1956 Feb;71(2):236–243. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.2.236-243.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOLLERMAN G. H., EKSTEDT R. Long chain formation by strains of group A streptococci in the presence of homologous antiserum: a type-specific reaction. J Exp Med. 1957 Sep 1;106(3):345–356. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.3.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent W. F., Borman E. K., Pranitis P. Chromatographic procedure for the preparation of M protein testing antigens. Health Lab Sci. 1966 Oct;3(4):225–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADSWORTH C. A slide microtechnique for the analysis of immune precipitates in gel. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1957;10(6):355–360. doi: 10.1159/000228394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. E. Laboratory diagnosis of streptococcal infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1958;19(1):153–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON A. T., WILEY G. G. THE CELLULAR ANTIGENS OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI; IMMUNOELECTROPHORETIC STUDIES OF THE C, M, T, PGP, E4, F, AND E ANTIGENS OF SEROTYPE 17 STREPTOCOCCI. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:527–556. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl R., Drach G. Recherches immunologiques sur les antigènes protéiques basiques spécifiques et non spécifiques de type de Streptococcus pyogenes (groupe A). II. Réactions de précipitation et de diffusion en gélose. Propriétés immunogènes. Allergie cutanée. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Jun;108(6):736–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson J. P., Maxted W. R., Grant D. L., Pinney A. M. The relationship between M-antigen and opacity factor in group A streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Jan;65(1):69–80. doi: 10.1099/00221287-65-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman R. A., Mathews J., Wilson E. Microtiter indirect hemagglutination procedure for identification of streptococcal M-protein antibodies. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Nov;16(11):1640–1645. doi: 10.1128/am.16.11.1640-1645.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]