Abstract
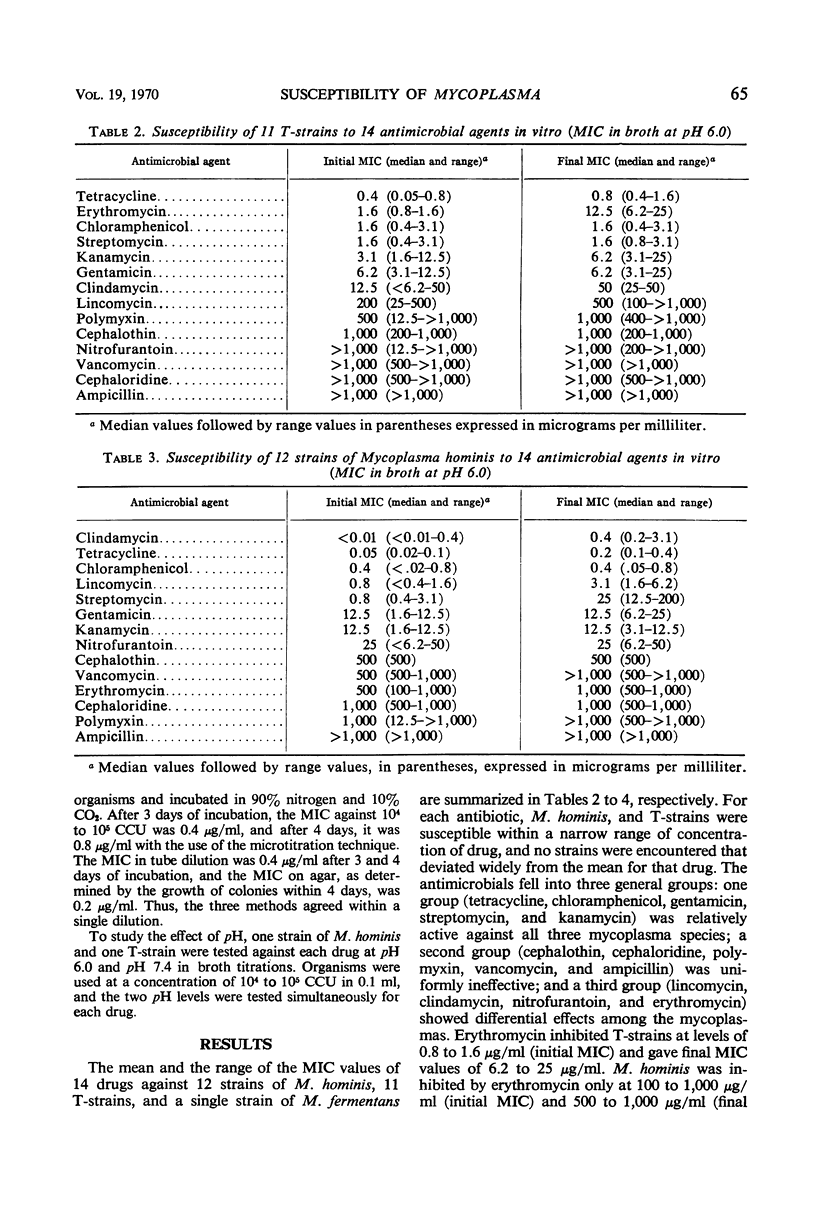
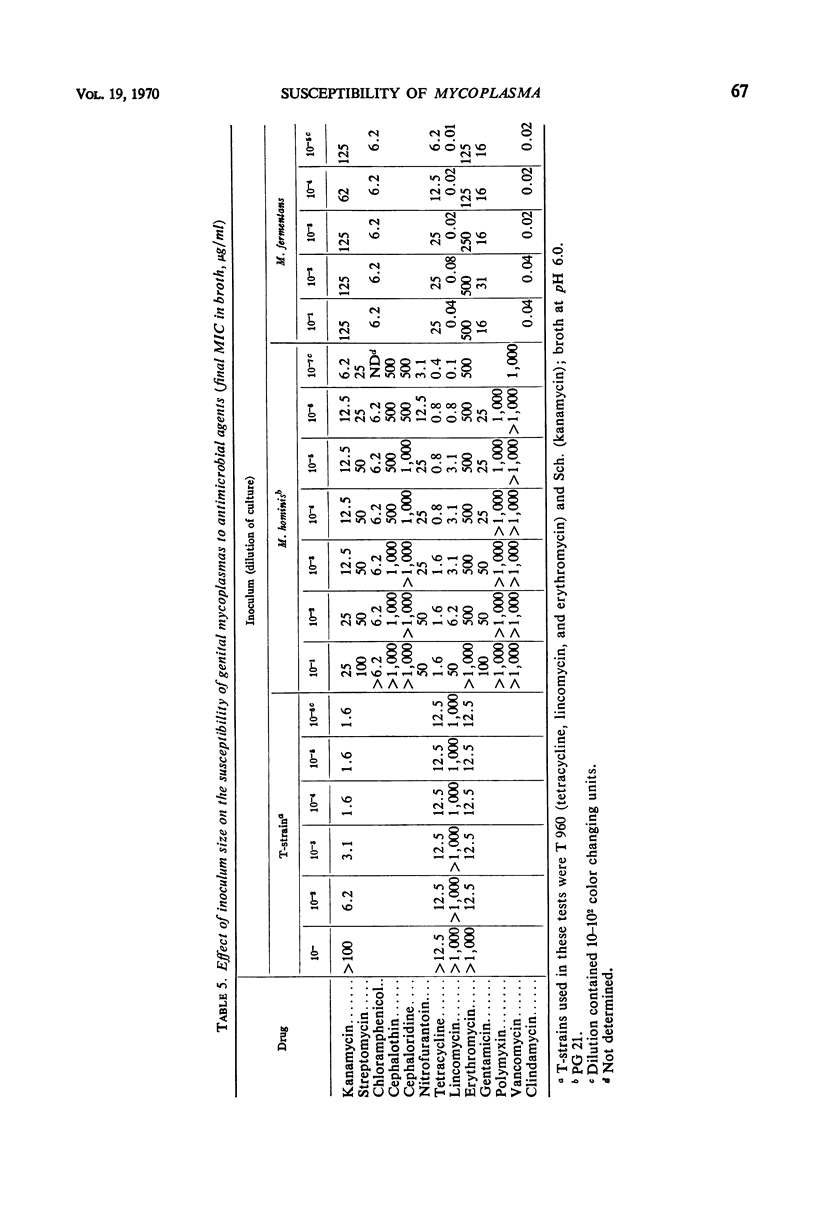
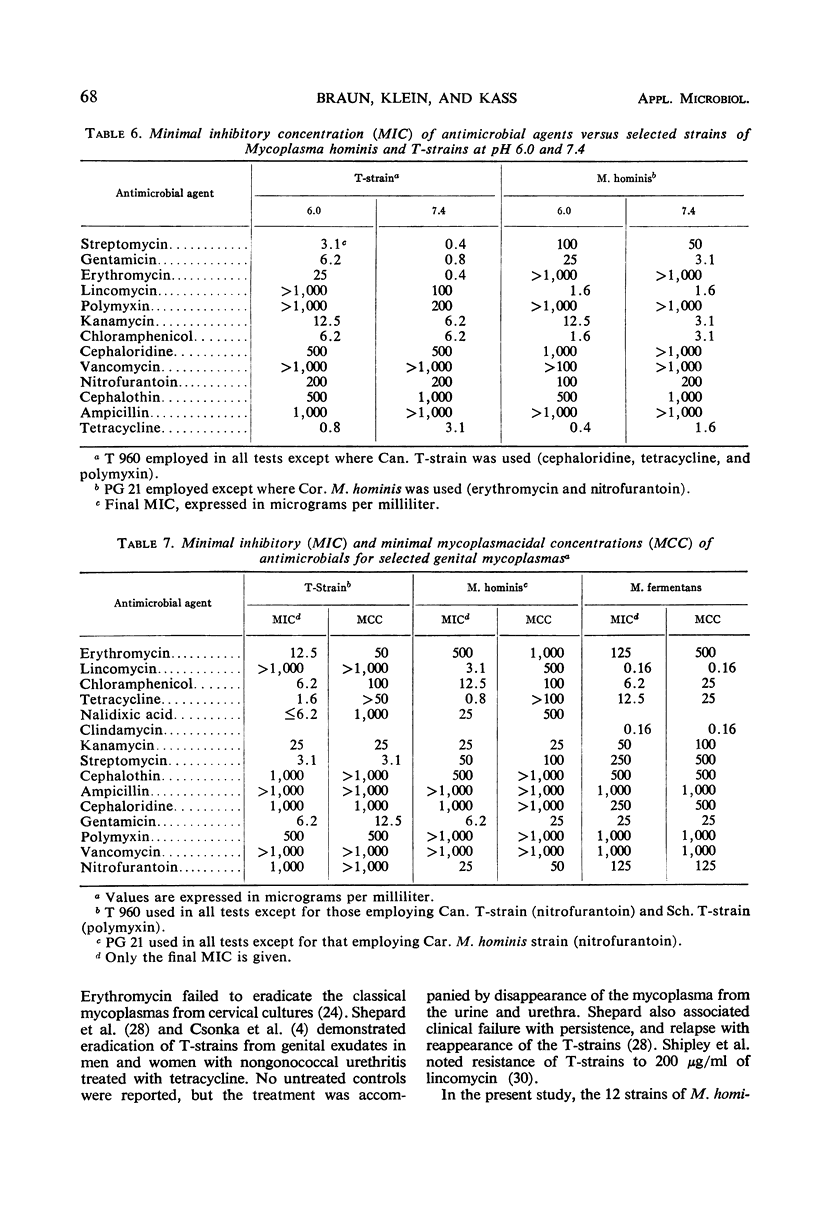
The susceptibility of 11 T-strains, 12 strains of Mycoplasma hominis, and a single strain of M. fermentans to 15 antimicrobial agents was determined by study of inhibition of metabolic activity in a broth dilution system. All three species were inhibited by tetracycline, chloramphenicol, streptomycin, gentamicin, and kanamycin, and were relatively resistant to cephalothin, cephaloridine, polymyxin, vancomycin, and ampicillin. Three antimicrobial agents had significant differential effects on these species. Erythromycin was more active against T-strains than against M. hominis or M. fermentans. Lincomycin, clindamycin, and nitrofurantoin had greater activity against M. hominis and M. fermentans than against T-strains. The activity of the drugs tested was generally uniform over a wide range of inocula. The effect of pH and the difference between minimal inhibiting and minimal mycoplasmacidal concentrations of the drugs tested were consistent with expectations based on the effects of these drugs on bacteria.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanock R. M. Mycoplasma infections of man. N Engl J Med. 1965 Dec 2;273(23):1257–concl. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196512022732307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka G. W., Williams R. E., Corse J. T strain mycoplasma in nongonococcal urethritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):794–798. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka G. W., Williams R. E., Corse J. T-strain mycoplasma in non-gonococcal urethritis. Lancet. 1966 Jun 11;1(7450):1292–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD D. K., DUVERNET M. Genital strains of human pleuropneumonia-like organisms. Br J Vener Dis. 1963 Mar;39:18–20. doi: 10.1136/sti.39.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD D. K., RASMUSSEN G., MINKEN J. T-strain pleuropneumonia-like organisms as one cause of non-gonococcal urethritis. Br J Vener Dis. 1962 Mar;38:22–25. doi: 10.1136/sti.38.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford D. K. CULTURE OF HUMAN GENITAL "T-STRAIN" PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS. J Bacteriol. 1962 Nov;84(5):1028–1034. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.5.1028-1034.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford D. K., DuVernet M. E. Antypesigenic types of "large colony" human genital mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):899–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.899-899.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford D. K. Relationships between mycoplasma and the etiology of nongonococcal urethritis and Reiter's syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):501–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L., CHANOCK R. M. MYCOPLASMA SPECIES OF MAN. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Jun;29:185–221. doi: 10.1128/br.29.2.185-221.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham H. R., MacFarlane W. V., Hale J. H., Selkon J. B., Codd A. A. Controlled study of the prevalence of T strain mycoplasmata in males with non-gonococcal urethritis. Br J Vener Dis. 1966 Dec;42(4):269–271. doi: 10.1136/sti.42.4.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jao R. L. Susceptibility of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to 21 antibiotics in vitro. Am J Med Sci. 1967 Jun;253(6):639–650. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196706000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M. Mycoplasma hominis in abortion. Br Med J. 1967 Feb 11;1(5536):338–340. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5536.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M. Mycoplasma hominis in pregnancy. J Clin Pathol. 1967 Jul;20(4):633–635. doi: 10.1136/jcp.20.4.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUFSON M. A., LUDWIG W. M., PURCELL R. H., CATE T. R., TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., CHANOCK R. M. EXUDATIVE PHARYNGITIS FOLLOWING EXPERIMENTAL MYCOPLASMA HOMINIS: TYPE 1 INFECTION. JAMA. 1965 Jun 28;192:1146–1152. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080260034010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWNHAM A. G., CHU H. P. AN IN VITRO COMPARISON OF THE EFFECT OF SOME ANTIBACTERIAL, ANTIFUNGAL AND ANTIPROTOZOAL AGENTS ON VARIOUS STRAINS OF MYCOPLASMA (PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS: P.P.L.O.). J Hyg (Lond) 1965 Mar;63:1–23. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400044922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICOL C. S., EDWARD D. G. Role of organisms of the pleuropneumonia group in human genital infections. Br J Vener Dis. 1953 Sep;29(3):141–150. doi: 10.1136/sti.29.3.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURCELL E. M., WRIGHT S. S., MOU T. W., FINLAND M. Blood levels and urinary excretion in normal subjects after ingestion of tetracycline analogues. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Jan;85(1):61–65. doi: 10.3181/00379727-85-20785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pease P., Rogers K. B., Cole B. C. A cytopathogenic strain of Mycoplasma hominis type 1 isolated from the lung of a stillborn infant. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(2):460–462. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Taylor-Robinson D., Wong D., Chanock R. M. Color test for the measurement of antibody to T-strain mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):6–12. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.6-12.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN A., SOMERSON N. L., SMITH P. F., MORTON H. E. The effects of the administration of erythromycin upon Neisseria gonorrhoeae and pleuropneumonia-like organisms in the uterine cervix. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1954 Sep;38(5):472–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD M. C., ALEXANDER C. E., Jr, LUNCEFORD C. D., CAMPBELL P. E. POSSIBLE ROLE OF T-STRAIN MYCOPLASMA IN NONGONOCOCCAL URETHRITIS. A SIXTH VENEREAL DISEASE? JAMA. 1964 May 25;188:729–735. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03060340027007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD M. C. The recovery of pleuropneumonia-like organisms from Negro men with and without nongonococcal urethritis. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1954 Mar;38(2):113–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard M. C. Cultivation and properties of T-strains of mycoplasma associated with nongonococcal urethritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):505–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard M. C., Lunceford C. D., Baker R. L. T-strain Mycoplasma. Selective inhibition by erythromycin in vitro. Br J Vener Dis. 1966 Mar;42(1):21–24. doi: 10.1136/sti.42.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley A., Bowman S. J., O'Connor J. J. T-strain mycoplasmas in non-specific urethritis. Med J Aust. 1968 May 11;1(19):794–796. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1968.tb28909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D. Mycoplasmas of various hosts and their antibiotic sensitivities. Postgrad Med J. 1967 Mar;43(Suppl):100–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Purcell R. H. Mycoplasmas of the human urogenital tract and oropharynx and their possible role in disease: a review with some recent observations. Proc R Soc Med. 1966 Nov;59(11 Pt 1):1112–1116. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Brown M. S., Sheagren J. N., Young V. M., Wolff S. M. Septicemia due to Mycoplasma hominis type 1. N Engl J Med. 1965 Sep 16;273(12):648–650. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196509162731207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Smith L. G. Postpartum septicemia with Mycoplasma hominis. JAMA. 1968 May 27;204(9):827–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


