Abstract
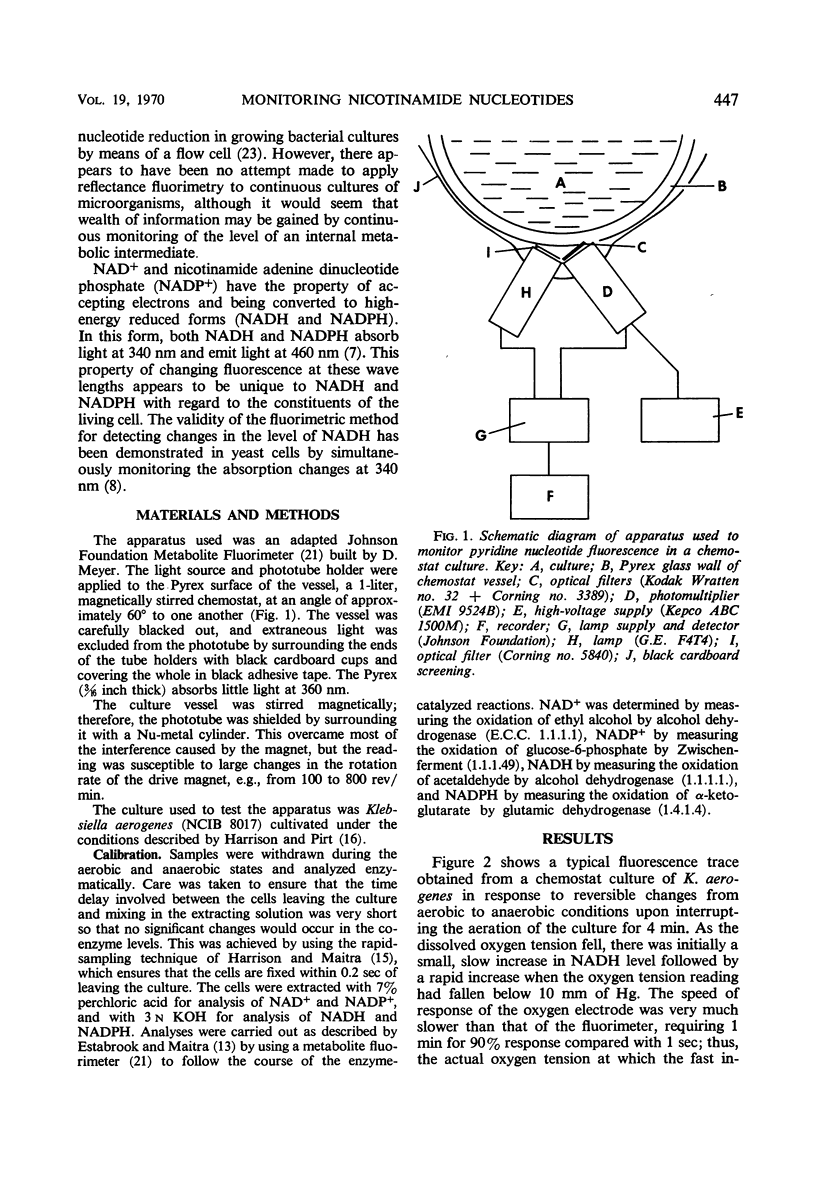
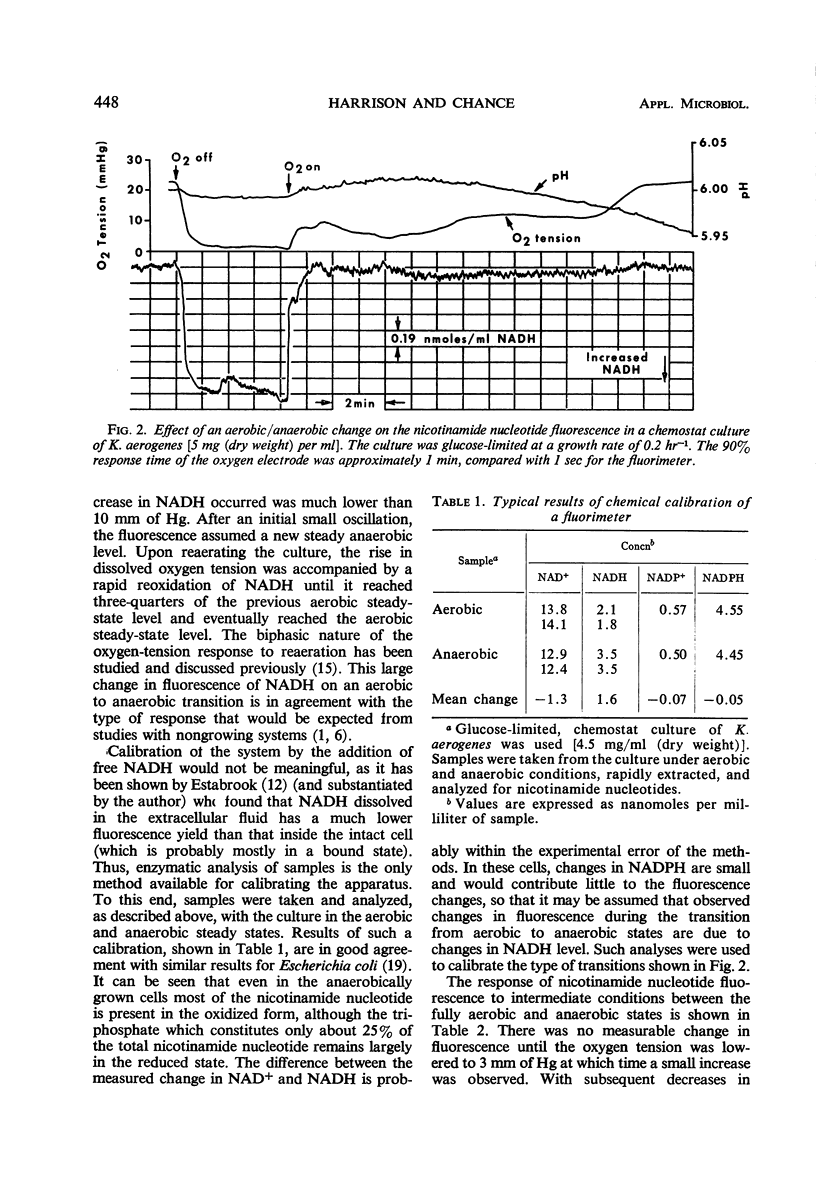
A metabolite fluorimeter was modified to monitor nicotinamide nucleotides in cells growing in a chemostat culture. By illuminating and collecting fluorescence over a relatively large area of the side of the culture vessel, the noise level was kept low even in highly turbulent cultures. Calibration of the system was by enzymatic assay of samples. Changes in nicotinamide nucleotide of concentration less than 0.1 nmoles/ml could be detected [i.e., less than 10% aerobic/anaerobic response for a cell concentration of 5 mg (dry wt) per ml].
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BETZ A., CHANCE B. INFLUENCE OF INHIBITORS AND TEMPERATURE ON THE OSCILLATION OF REDUCED PYRIDINE NUCLEOTIDES IN YEAST CELLS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Mar;109:579–584. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90403-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B., BALTSCHEFFSKY H. Respiratory enzymes in oxidative phosphorylation. VII. Binding of intramitochondrial reduced pyridine nucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1958 Sep;233(3):736–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B., ESTABROOK R. W., GHOSH A. DAMPED SINUSOIDAL OSCILLATIONS OF CYTOPLASMIC REDUCED PYRIDINE NUCLEOTIDE IN YEAST CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1244–1251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B. FEEDBACK CONTROL OF METABOLISM IN ASCITES TUMOR CELLS. Acta Unio Int Contra Cancrum. 1964;20:1028–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B. Spectra and reaction kinetics of respiratory pigments of homogenized and intact cells. Nature. 1952 Feb 9;169(4293):215–221. doi: 10.1038/169215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B. Spectrophotometry of intracellular respiratory pigments. Science. 1954 Nov 12;120(3124):767–775. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3124.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B., WILLIAMS G. R. The respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1956;17:65–134. doi: 10.1002/9780470122624.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUYSENS L. N., AMESZ J. Fluorescence spectrophotometry of reduced phosphopyridine nucleotide in intact cells in the near-ultraviolet and visible region. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Apr;24(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90141-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESTABROOK R. W. Fluorometric measurement of reduced pyridine nucleotide in cellular and subcellular particles. Anal Biochem. 1962 Sep;4:231–245. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESTABROOK R. W., MAITRA P. K. A fluorimetric method for the quantitative microanalysis of adenine and pyridine nucleotides. Anal Biochem. 1962 May;3:369–382. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. E., Maitra P. K. Control of respiration and metabolism in growing Klebsiella aerogenes. The role of adenine nucleotides. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(5):647–656. doi: 10.1042/bj1120647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. E., Pirt S. J. The influence of dissolved oxygen concentration on the respiration and glucose metabolism of Klebsiella aerogenes during growth. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Feb;46(2):193–211. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-2-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempfling W. P., Höfer M., Harris E. J., Pressman B. C. Correlation between changes in metabolite concentrations and rate of ion transport following glucose addition to Escherichia coli B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jul 25;141(2):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London J., Knight M. Concentrations of nicotinamide nucleotide coenzymes in micro-organisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Aug;44(2):241–254. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-2-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURVIS J. L. Forms of pyridine nucleotides in rat-liver mitochondria. Nature. 1958 Sep 13;182(4637):711–712. doi: 10.1038/182711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön G., Drews G. Der Redoxzustand des NAD(P) und der Cytochrome b und c2 in Abhängigkeit vom pO2 bei einigen Athiorhodaceae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;61(4):317–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



