Abstract
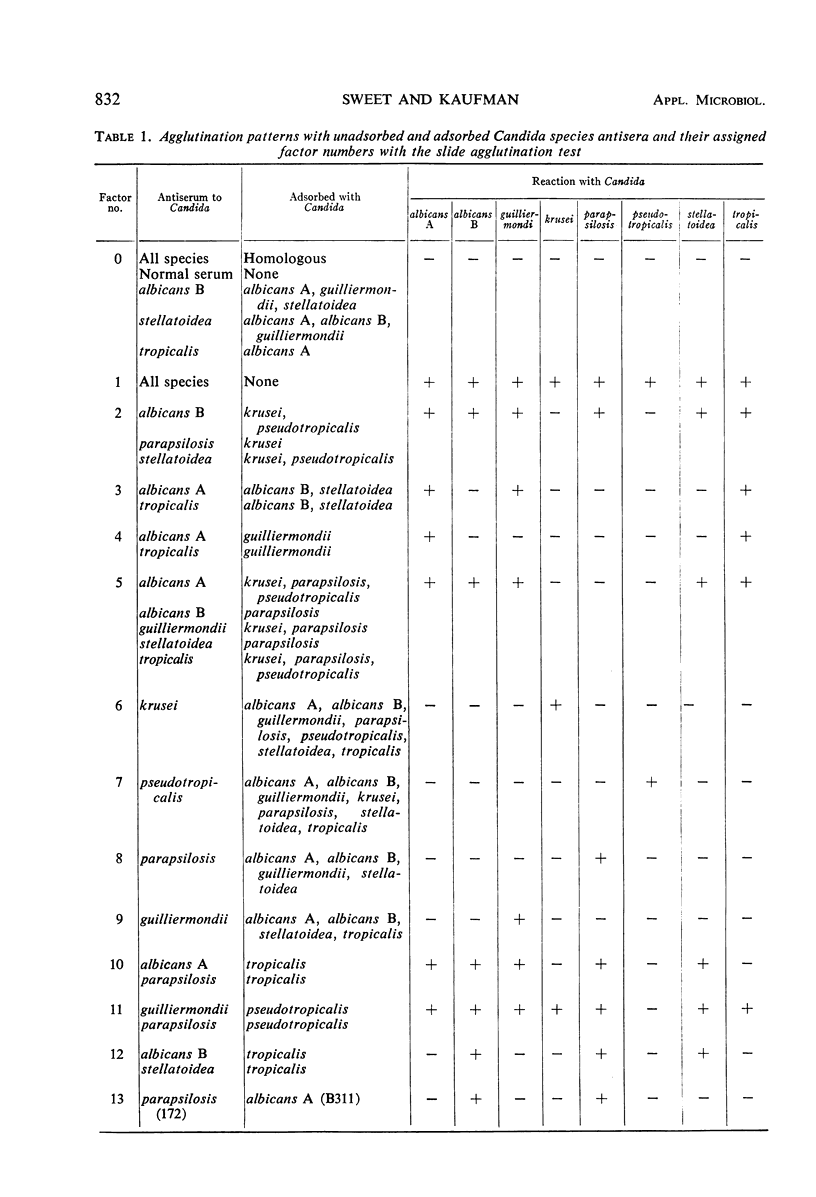
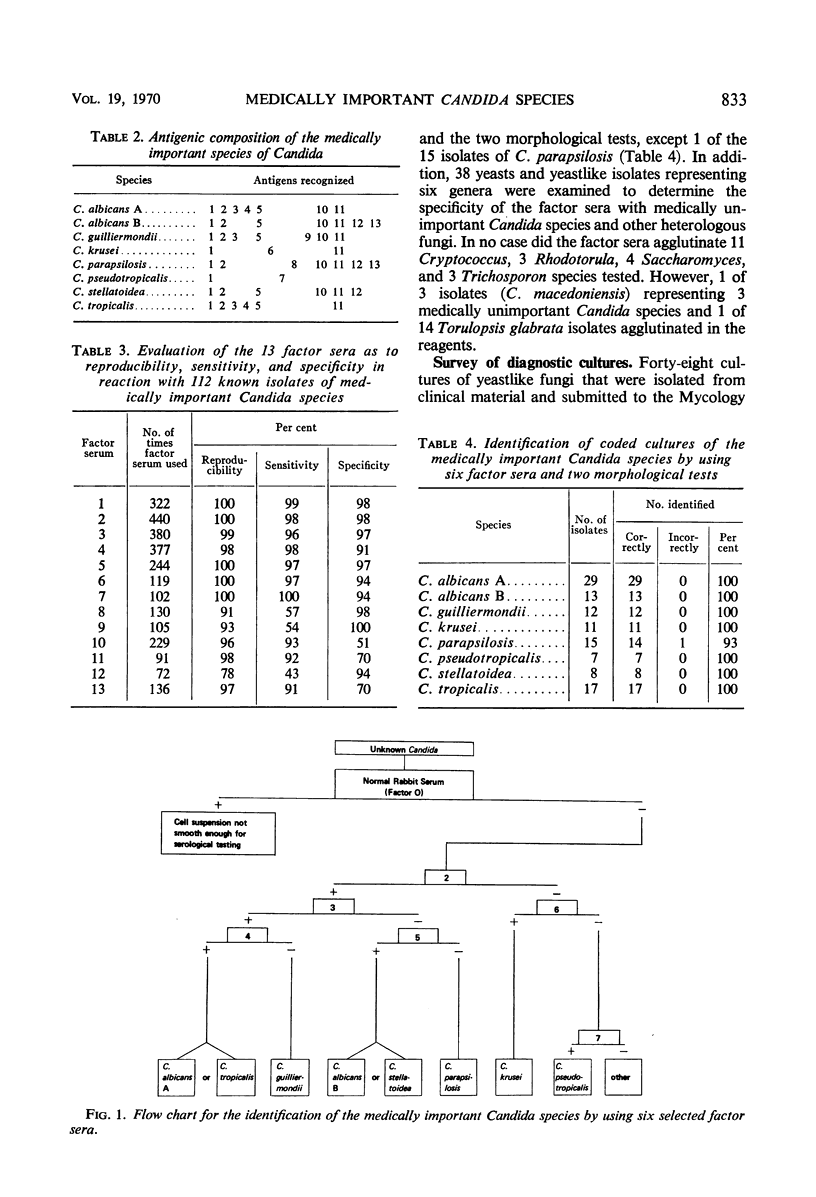
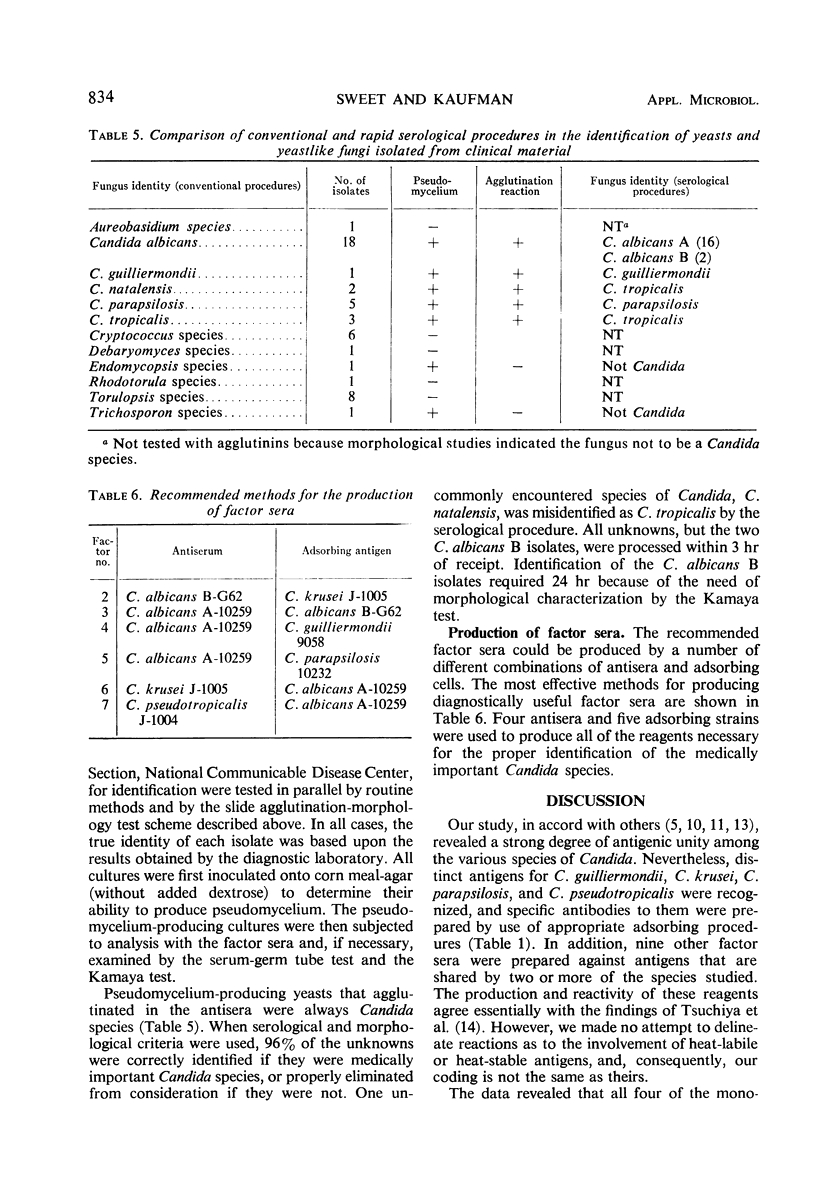
Agglutinins have been prepared against the medically important Candida species. Crude antisera to the various species demonstrated intense cross-reactions with heterologous yeastlike fungi as well as with many true yeasts. However, carefully monitored adsorptions of selected antisera allowed the production of six factor sera that proved useful in a slide agglutination test. These six sera permitted the rapid and specific identification of C. guilliermondii, C. krusei, C. parapsilosis, and C. pseudotropicalis. They also allowed the delineation of two groups: (i) C. albicans (type A)-C. tropicalis and (ii) C. albicans (type B)-C. stellatoidea. C. albicans type A could be readily distinguished from C. tropicalis by its ability to form germ tubes in serum. C. stellatoidea could be distinguished from C. albicans type B by its predominantly filamentous growth on a nutritionally deficient medium. The medically important Candida species could be identified within 24 hr by the combined use of serological and morphological procedures.
Full text
PDF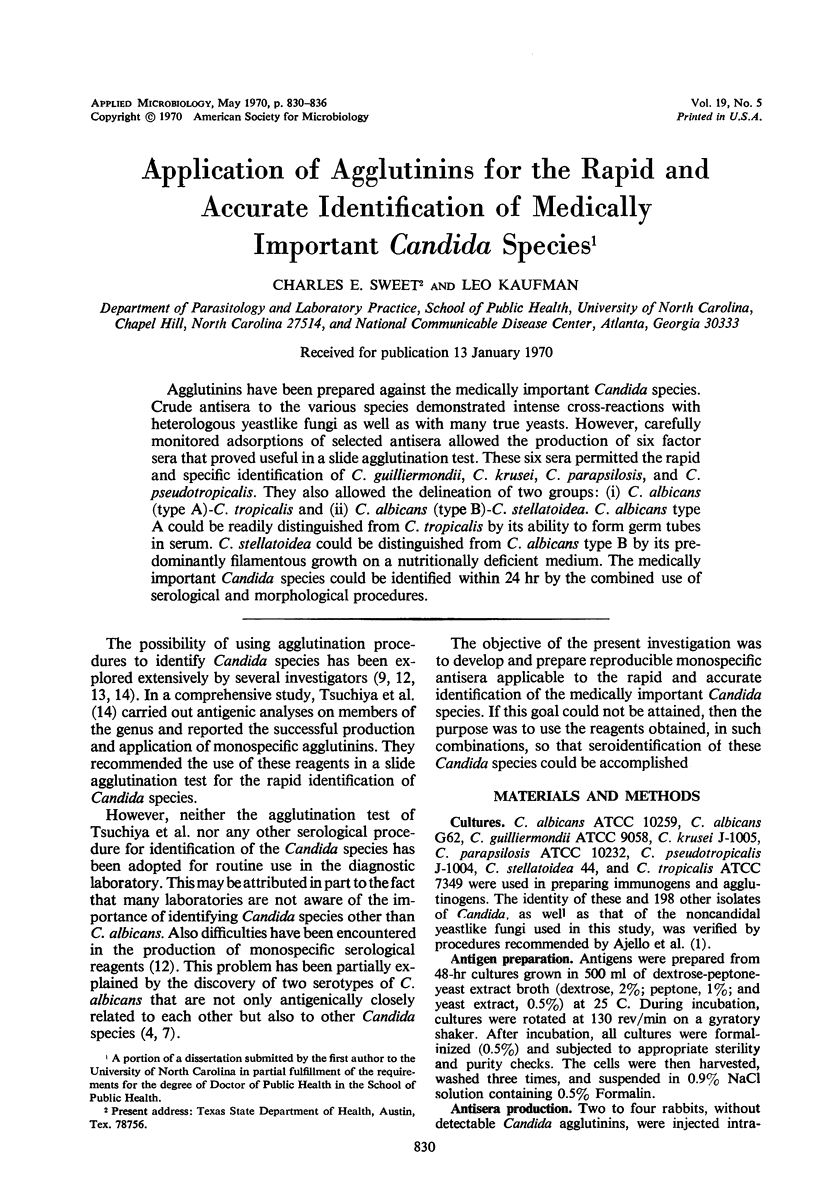



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bump C. M., Kunz L. J. Routine identification of yeasts with the aid of molybdate-agar medium. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Oct;16(10):1503–1506. doi: 10.1128/am.16.10.1503-1506.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASENCLEVER H. F., MITCHELL W. O. Antigenic relationships of Torulopsis glabrata and seven species of the genus Candida. J Bacteriol. 1960 May;79:677–681. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.5.677-681.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASENCLEVER H. F., MITCHELL W. O. Antigenic studies of Candida. I. Observation of two antigenic groups in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:570–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.570-573.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASENCLEVER H. F., MITCHELL W. O. IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON POLYSACCHARIDES OF YEASTS. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:763–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN W., KAUFMAN L. The aplication of fluorescent antibody techniques to medical mycology--a review. Sabouraudia. 1961 Oct;1:137–144. doi: 10.1080/00362176285190301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamaya T. Simple rapid identification of Candida albicans with emphasis on the differentiation between Candida albicans and Candida stellatoidea. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1968 Jul 12;35(2):105–112. doi: 10.1007/BF02049573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie D. W. Serum tube identification of Candida albicans. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Nov;15(6):563–565. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.6.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUMMERS D. F., GROLLMAN A. P., HASENCLEVER H. F. POLYSACCHARIDE ANTIGENS OF CANDIDA CELL WALL. J Immunol. 1964 Mar;92:491–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner C. E., Fletcher D. W. A REVIEW OF THE GENUS CANDIDA. Bacteriol Rev. 1960 Dec;24(4):397–416. doi: 10.1128/br.24.4.397-416.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUCHIYA T., FUKAZAWA Y., KAWAKITA S. A method for the rapid identification of the genus Candida. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1959 Mar 31;10(3):191–206. doi: 10.1007/BF02053014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUCHIYA T., FUKAZAWA Y., MIYASAKI F., KAWAKITA S. Studies on the classification of the genus Candida; thermostable and thermolabile antigens of the seven species of the genus Candida. Jpn J Exp Med. 1955 Jun;25(3):75–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



