Abstract
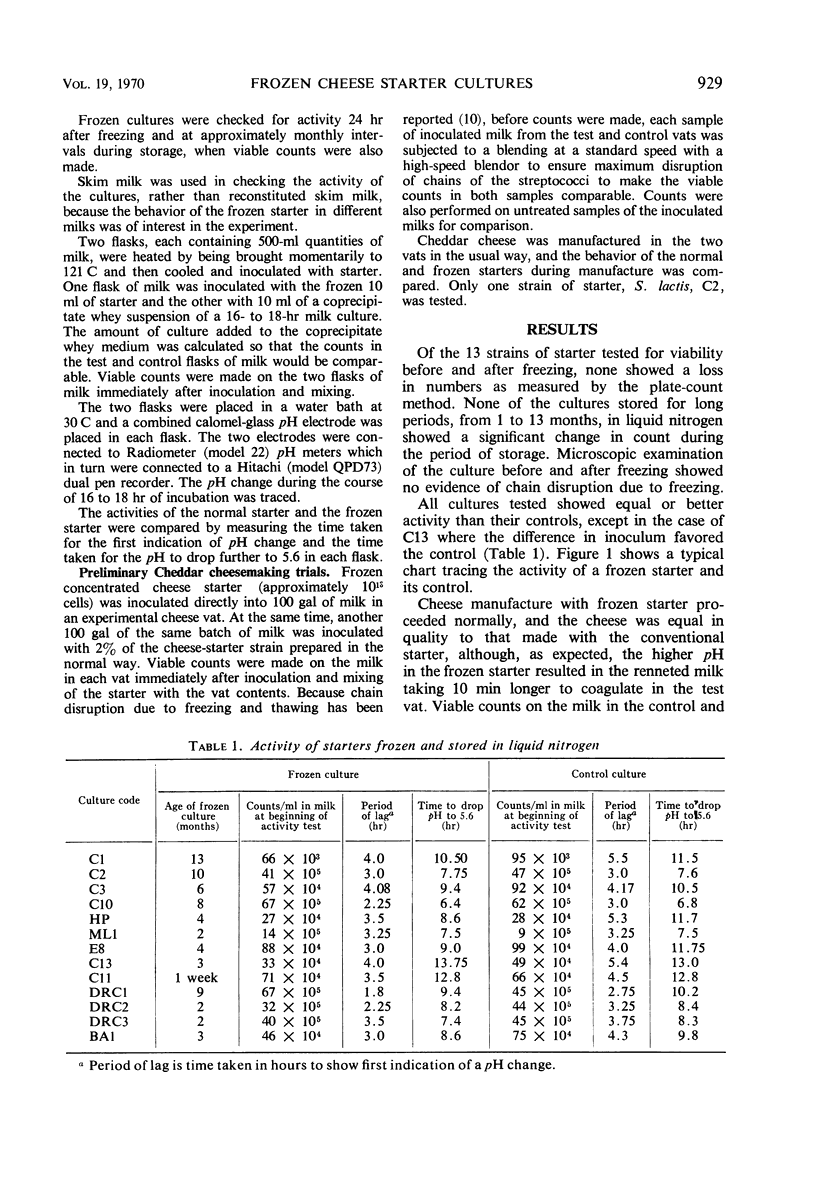
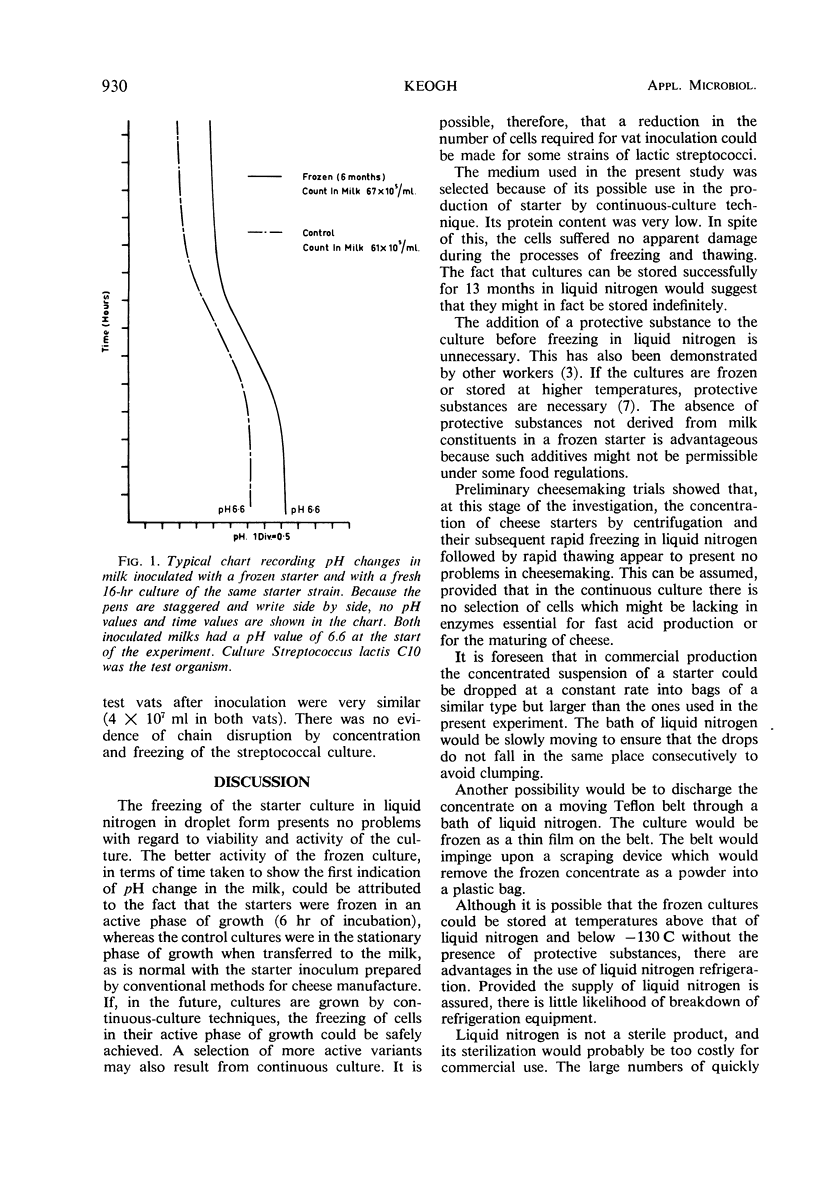
A study has been conducted on the effect of freezing and storage in liquid nitrogen on 13 strains of lactic streptococci. Cultures were frozen in droplet form and collected in mesh bags. After rapid thawing, the activity of the frozen cultures was compared with a culture of the same organism of the age usually used in cheese-making. The activities of the test and control cultures were traced simultaneously by continuous recording of the pH changes in inoculated milks. Viable counts were performed before and after freezing in liquid nitrogen and after storage in liquid nitrogen. There was no decrease in viable count or loss in activity of the cultures due to freezing and storage. Frozen cultures of some strains showed a shorter lag period after inoculation of milk than control cultures. Frozen concentrated cheese-starter cultures behaved normally in the manufacture of Cheddar cheese.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann D. P., Reinbold G. W. Freezing of lactic cultures. J Dairy Sci. 1966 Mar;49(3):259–264. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(66)87846-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman R. A., Speck M. L. Ultra-low temperature storage of lactic streptococci. J Dairy Sci. 1965 Nov;48(11):1531–1532. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(65)88514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson C. A., Landerkin G. B., Morse P. M. Effects of additives on the survival of lactic streptococci in frozen storage. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Jul;14(4):665–669. doi: 10.1128/am.14.4.665-669.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSS C. W., SPECK M. L. Injury and death of Streptococcus lactis due to freezing and frozen storage. Appl Microbiol. 1963 Jul;11:326–329. doi: 10.1128/am.11.4.326-329.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


