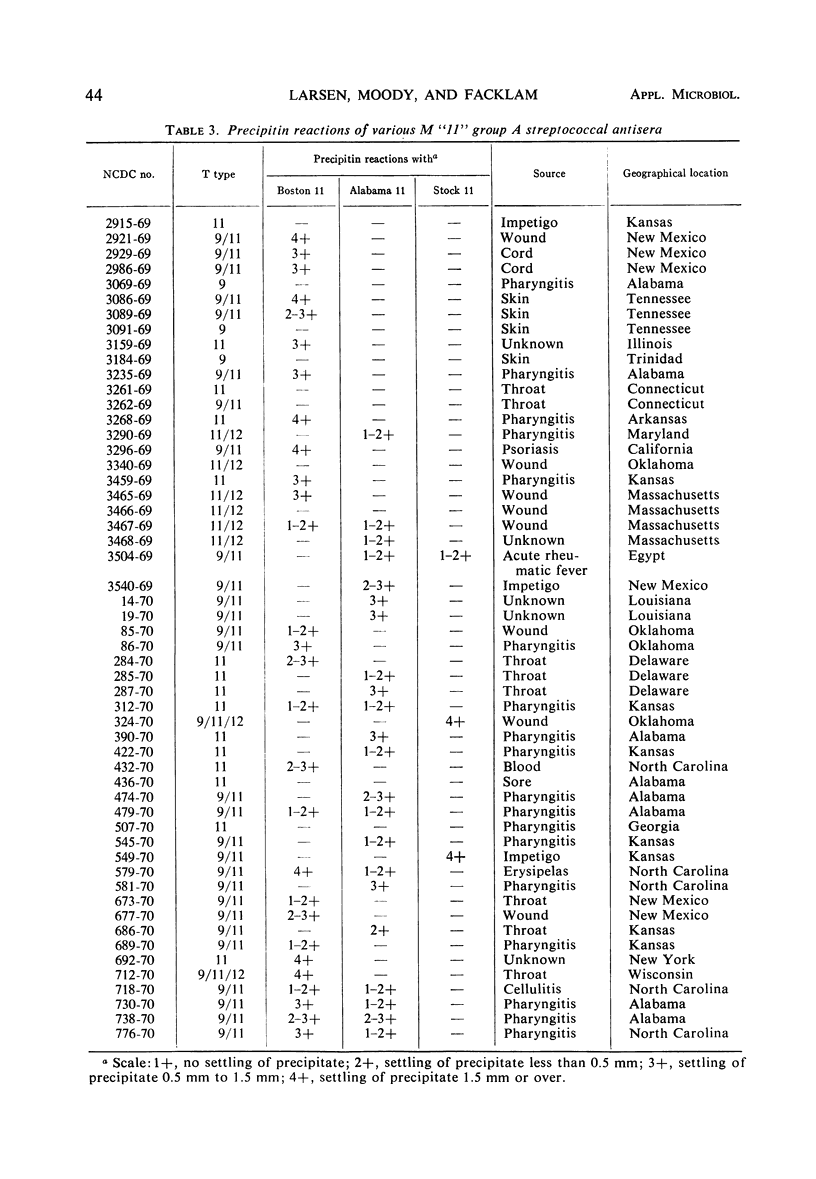
Abstract
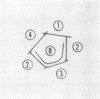
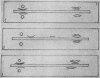
A strain of group A Streptococcus which was virulent but M-nontypable was isolated from patients in a hospital nursery during an epidemic. This strain, Boston 11, reacted in T-agglutination tests with antisera for types 9 and 11, an unusual combination. A comparison of this strain with Lancefield's M-11 strain (NCDC SS-721) and Alabama 11 (Provisional 61) revealed three serologically related but distinct strains. Antiserum produced with the Boston 11 strain exhibited similar reactivity with all three “11” strains as well as with M-9 (SS-501) as demonstrated in precipitin tests. Immunodiffusion studies indicated that the Boston 11 antigen was partially identical with the M-11 and M-9 strains and shared at least one antigen with the Alabama 11 strain. The Boston 11 antiserum could be made specific for precipitin tests, but bactericidal activity for the Alabama 11, M-11, and Boston 11 strains was essentially negative.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker C. G. Enhancing effect of type specific antistreptococcal antibodies on emergence of streptococci rich in M-protein. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jan;124(1):331–335. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONROY E., UPDYKE E. L. Clarification of serum for storage in liquid or lyophile state. J Bacteriol. 1956 Aug;72(2):277–278. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.2.277-278.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K. Antigenicity of the M proteins of group A hemolytic streptococci. IV. Cross-reactivity between serotypes. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMBLY J. S. The precipitating antigen of Streptococcus pyogenes type 4. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Feb;18(1):285–293. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-1-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrell W. K., Ashworth H. Absorption of group A streptococcus anti-M typing sera with broken cells. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Mar;15(2):422–425. doi: 10.1128/am.15.2.422-425.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Differentiation of group A streptococci with a common R antigen into three serological types, with special reference to the bactericidal test. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):525–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOODY M. D., PADULA J., LIZANA D., HALL C. T. EPIDEMIOLOGIC CHARACTERIZATION OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI BY T-AGGLUTINATION AND M-PRECIPITATION TESTS IN THE PUBLIC HEALTH LABORATORY. Health Lab Sci. 1965 Jul;2:149–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padula J. F., Facklam R. R., Moody M. D. Effect of incubation temperature on T-agglutination typing of Streptococcus pyogenes. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):878–880. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.878-880.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Top F. H., Jr, Wannamaker L. W., Maxted W. R., Anthony B. F. M antigens among group A streptococci isolated from skin lesions. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):667–685. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILEY G. G., WILSON A. T. The occurrence of two M antigens in certain group A streptococci related to type 14. J Exp Med. 1961 Feb 1;113:451–465. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley G. G., Bruno P. N. Cross-reactions among Group A streptococci. I. Precipitin and bactericidal cross-reactions among types 33, 41, 43, 52, and Ross. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):959–968. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]