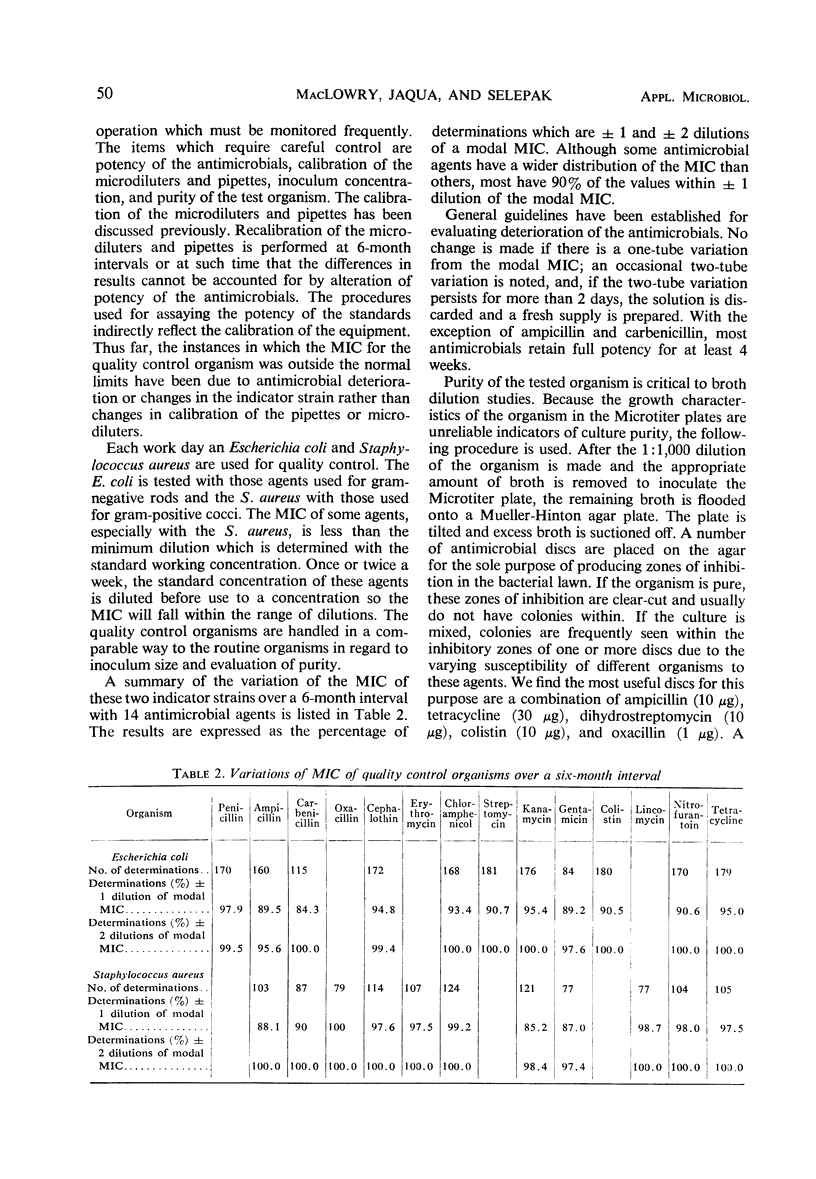
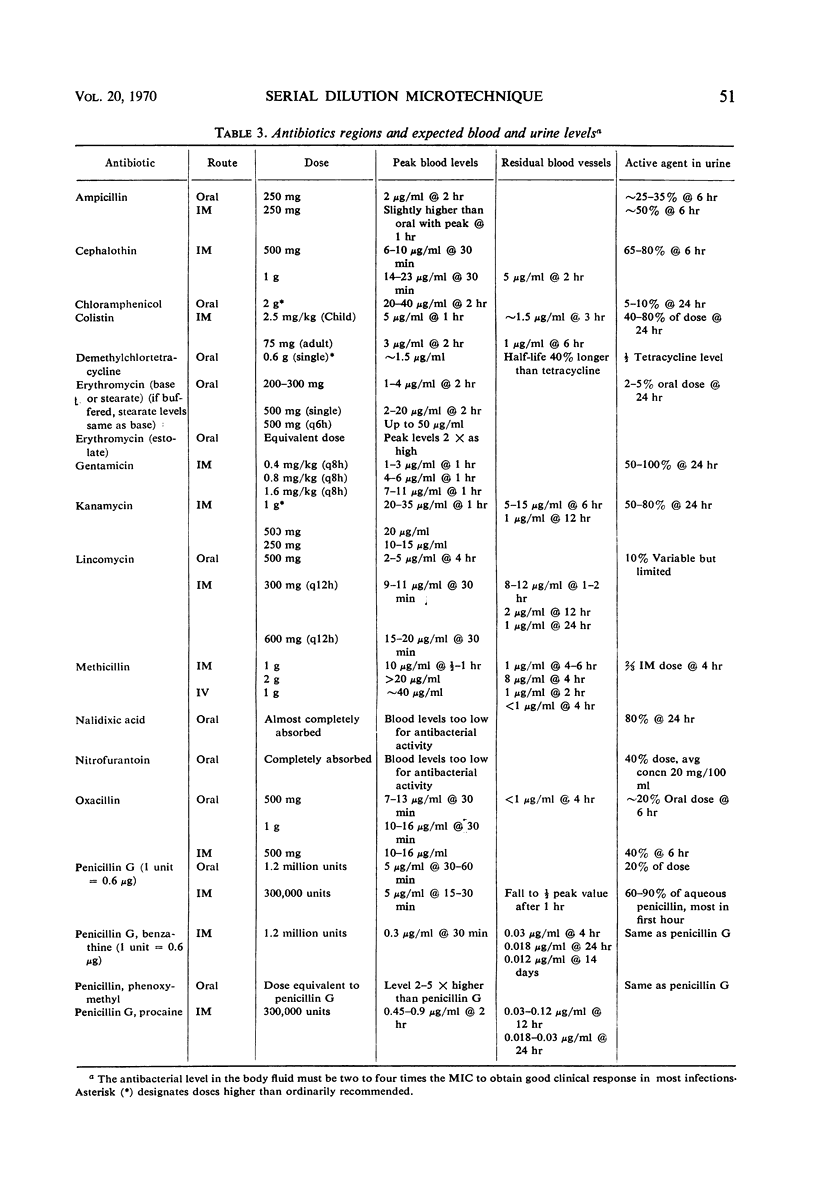
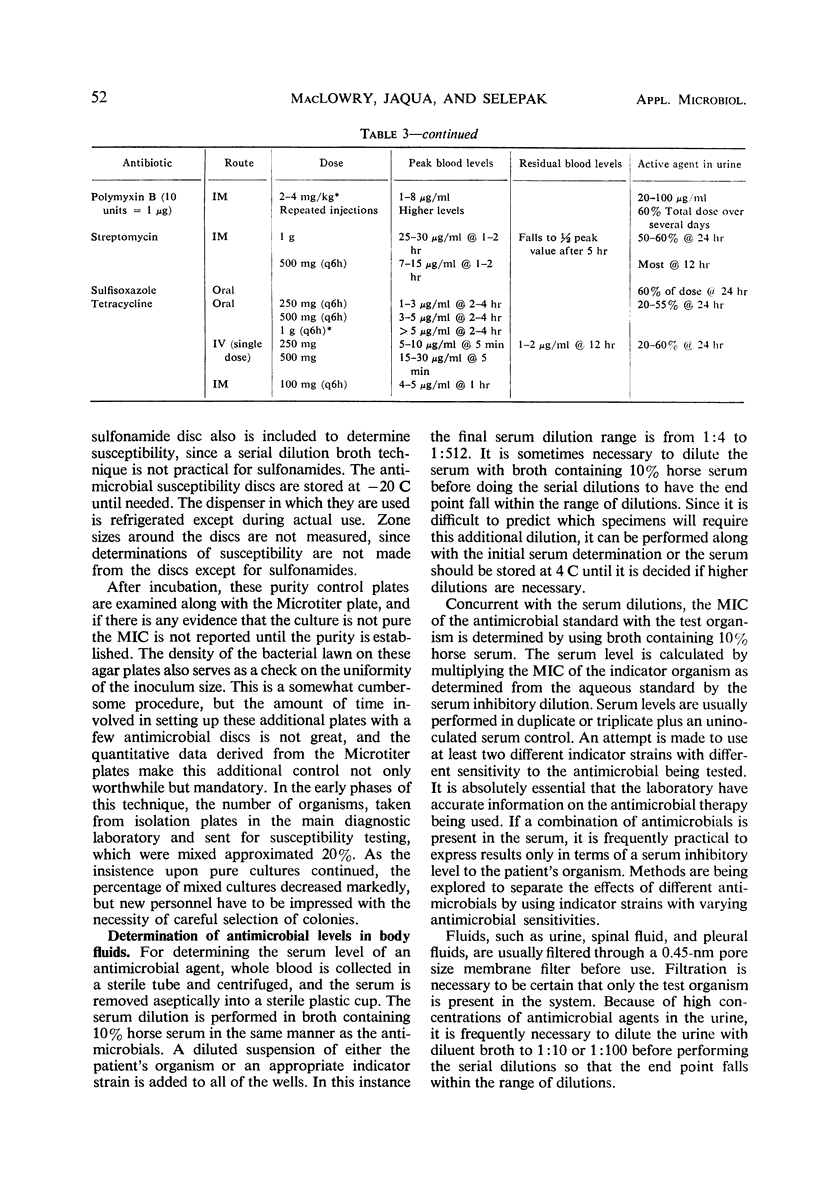
Abstract
The detailed methodology and implementation of a semiautomatic microtechnique for performing serial dilution antimicrobial susceptibility studies are described. Quantitative susceptibility studies to a battery of antimicrobials are performed routinely on all significant clinical isolates. Results are reported as the minimal inhibitory concentration in micrograms per milliliter of broth. Guidelines relating standard doses of antimicrobials with expected blood and urine levels are presented to facilitate the use of the quantitative data. This microtechnique is used to measure serum and other body fluid levels of antimicrobial agents to document the level attained with a specific course of therapy. This technique is highly reproducible and has a high correlation with, and is at least 10 times faster than, standard glass tube techniques.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chitwood L. A. Tube dilution antimicrobial susceptibility testing: efficacy of a microtechnique applicable to diagnostic laboratories. Appl Microbiol. 1969 May;17(5):707–709. doi: 10.1128/am.17.5.707-709.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwick H. J., Weiss P., Fekety F. R., Jr Application of microtitration techniques to bacteriostatic and bactericidal antibiotic susceptibility testing. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Sep;72(3):511–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLowry J. D., Marsh H. H. Semiautomatic microtechnique for serial dilution-antibiotic sensitivity testing in the clinical laboratory. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Oct;72(4):685–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marymont J. H., Jr, Wentz R. M. Serial dilution antibiotic sensitivity testing with the microtitrator system. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 May;45(5):548–551. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/45.5.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



