Abstract
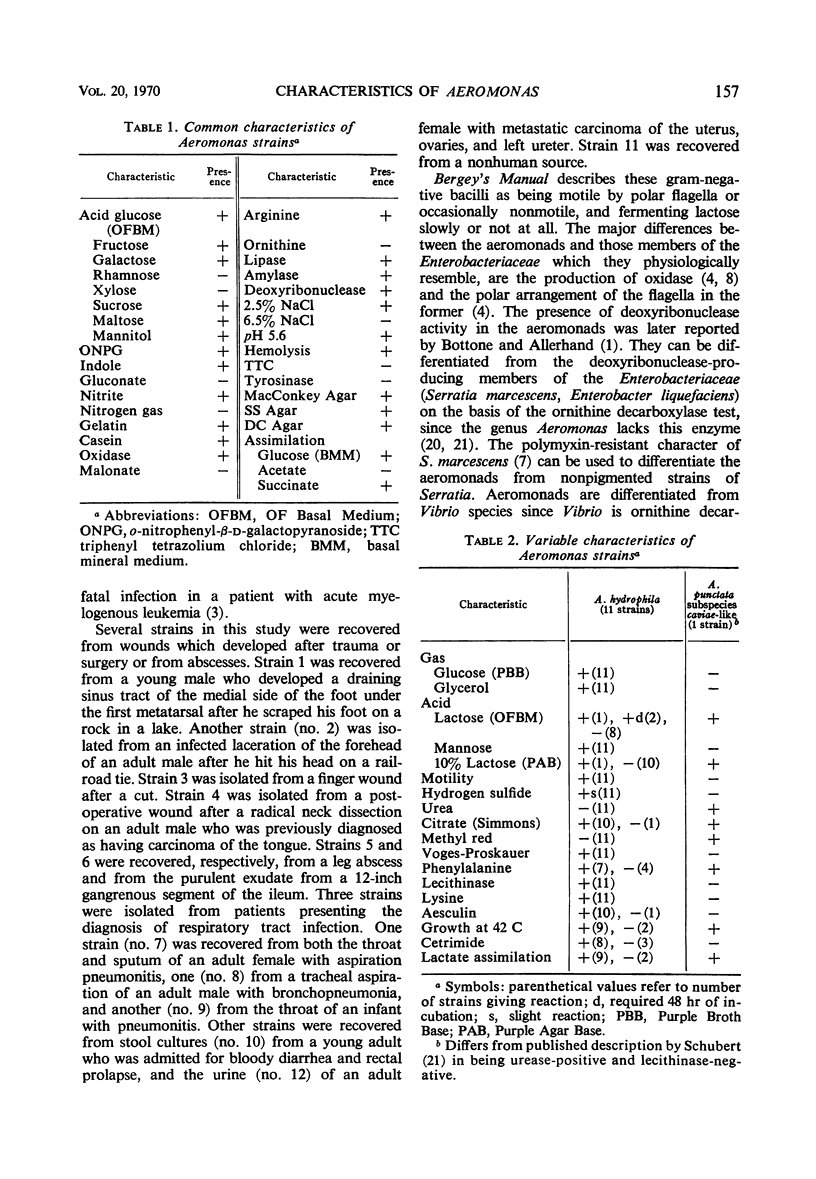
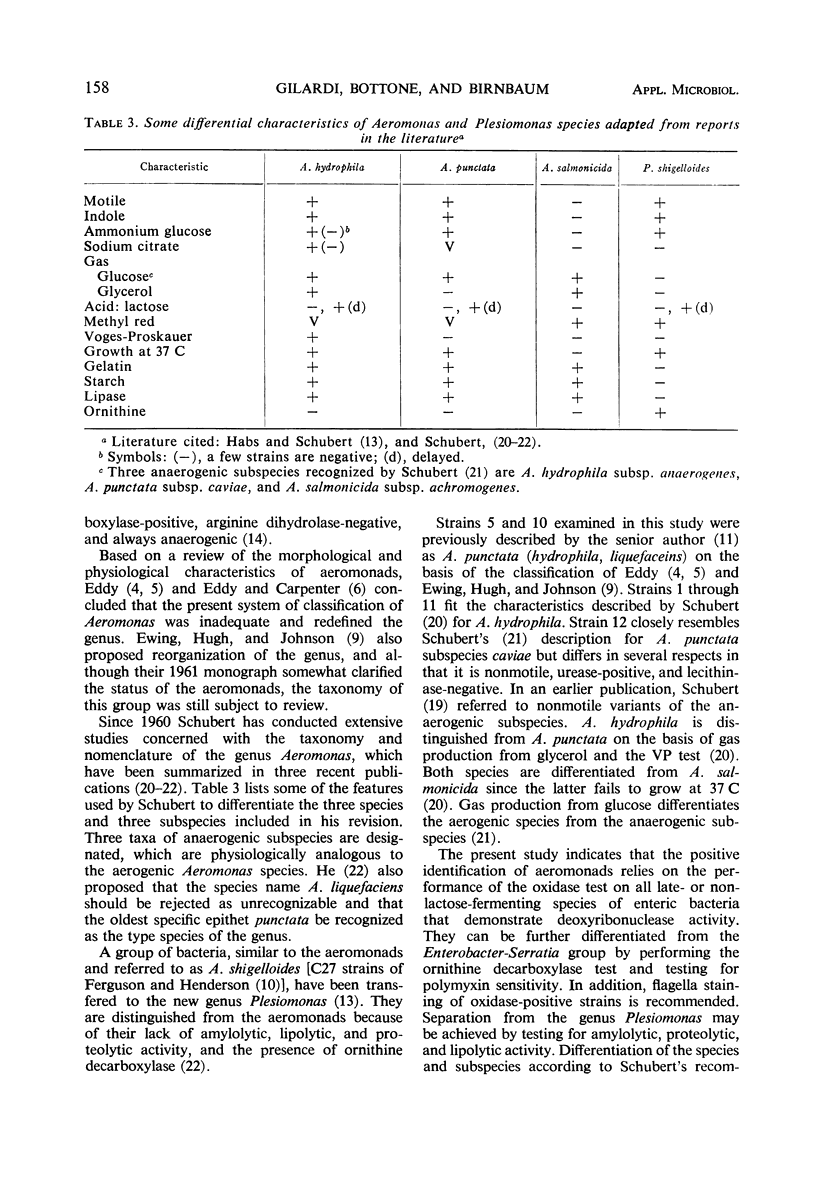
Morphological and physiological characterization of 12 Aeromonas strains isolated from clinical specimens demonstrated several important diagnostic features. These included polar arrangement of the flagella; production of oxidase, deoxyribonuclease, amylase, gelatinase, and lipase; lack of ornithine decarboxylase; and sensitivity to polymyxin. Awareness of these features should result in more frequent differentiation of aeromonads from the physiologically similar members of the genus Plesiomonas and the late- or non-lactose-fermenting species of Enterobacteriaceae.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottone E., Allerhand J. Aeromonas and serratia. Comparative study of extracellular deoxyribonuclease production and other biochemical characteristics. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Mar;53(3):378–382. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.3.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulger R. J., Sherris J. C. The clinical significance of Aeromonas hydrophila. Report of two cases. Arch Intern Med. 1966 Dec;118(6):562–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean H. M., Post R. M. Fatal infection with Aeromonas hydrophila in a patient with acute myelogenous leukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Jun;66(6):1177–1179. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-66-6-1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson E. B., Sanford J. P. The Klebsiella-Enterobacter (Aerobacter)-Serratia group. A clinical and bacteriological evaluation. Medicine (Baltimore) 1967 Jul;46(4):323–340. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196707000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson W. W., Henderson N. D. Description of Strain C27: A Motile Organism with the Major Antigen of Shigella sonnei Phase I. J Bacteriol. 1947 Aug;54(2):179–181. doi: 10.1128/jb.54.2.179-181.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi G. L., Bottone E., Birnbaum M. Unusual fermentative, gram-negative bacilli isolated from clinical specimens. I. Characterization of Erwinia strains of the "lathyri-herbicola group". Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jul;20(1):151–155. doi: 10.1128/am.20.1.151-155.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi G. L. Morphological and biochemical characteristics of Aeromonas punctata (hydrophila, liquefaciens) isolated from human sources. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Mar;15(2):417–421. doi: 10.1128/am.15.2.417-421.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. F., Quesada J., Saied A. Bacteremia and osteomyelitis due to Aeromon as hydrophila. A complication during the treatment of acute leukemia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968 Nov;50(5):587–591. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/50.5.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumann G., Gärtner L., Schade R. Aeromonas hydrophila als Eitererreger. Med Welt. 1969 Aug 2;31:1711–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert H. W. Zur Taxonomie der anaerogenen Aeromonaden. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1964 Jul;193(3):343–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilkin K. B., Annear D. I., Rowett L. R., Laurence B. H. Infection due to Aeromonas hydrophila. Med J Aust. 1968 Mar 2;1(9):351–353. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1968.tb28545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Graevenitz A., Mensch A. H. The genus aeromonas in human bacteriology report of 30 cases and review of the literature. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 1;278(5):245–249. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802012780504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



