Abstract
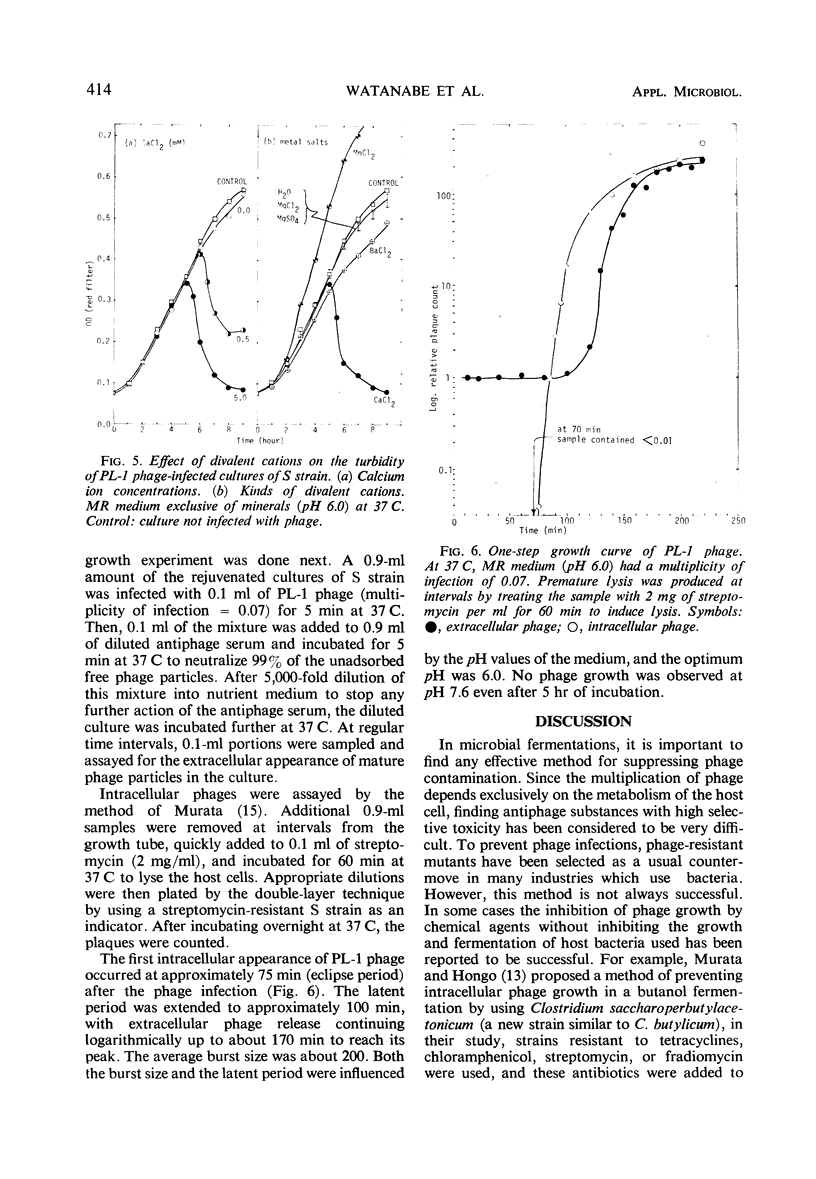
A virulent bacteriophage which causes a decrease in acid production during fermentation of a lactic acid beverage named Yakult with Lactobacillus casei was isolated from the abnormal fermentation tank and named PL-1. L. casei S strain was the exclusive host cell among 18 lactic acid bacteria tested. The plaque was round with an average diameter of about 0.5 mm. It exhibited serological cross-reaction with previously isolated J1 phage. Under an electron microscope, the phage had a spermatozoon shape, with an icosahedral head (63 nm) and a long tail (12.5 by 275 nm) with about 55 striae. The free phage particles were stable at pH 5 to 8. The phage was quite sensitive to ultraviolet irradiation or to heating (60 C, 5 min), and the host was more sensitive than the phage to these treatments. Many kinds of antimicrobial chemicals were also phagocidal. Calcium ion (5 mm) was specifically essential for the phage growth cycle. A one-step growth experiment under optimum conditions (37 C and pH 6.0) showed that the eclipse period was about 75 min, that the latent period was 100 min after the phage infection, and that the average burst size was about 200. The possibility of arresting phage development in lactic acid fermentation is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BABEL F. J. The importance of bacterial viruses in industrial processes, especially in the dairy industry. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1962;4:51–75. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COETZEE J. N., DE KLERK H. C. Lysogeny in the genus Lactobacillus. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:505–505. doi: 10.1038/194505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COETZEE J. N., DE KLERK H. C., SACKS T. G. Host-range of Lactobacillus bacteriophages. Nature. 1960;187:348–349. doi: 10.1038/187348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS E. B., NELSON F. E., PARMELEE C. E. The relation of calcium and other constituents of a defined medium to proliferation of lactic Streptococcus bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1950 Nov;60(5):533–542. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.5.533-542.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., STEINER D. L. The role of calcium in the penetration of bacteriophage T5 into its host. J Bacteriol. 1954 Jun;67(6):635–639. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.6.635-639.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYERS C. E., WALTER E. L., GREEN L. B. Isolation of a bacteriophage specific for a Lactobacillus casei from human oral material. J Dent Res. 1958 Feb;37(1):175–178. doi: 10.1177/00220345580370011201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onose H., Sasaki I., Kim T. E. [Isolation of Lactobacillus phage and its biological character]. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 1966 Jul;21(6):307–311. doi: 10.3412/jsb.21.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLMAN D., LANGLYKKE A. F., ROTHBERG H. D., Jr Observations on the chemical inhibition of Streptomyces griseus bacteriophage multiplication. J Bacteriol. 1951 Feb;61(2):135–143. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.2.135-143.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUNTREE P. M. The role of divalent cations in the multiplication of staphylococcal bacteriophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Apr;12(2):275–287. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-2-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssef M., Müller-Beuthow W., Haenel H. Isolierung von Bakteriophagen für anaerobe Laktobazillen aus dem Stuhl des Menschen. Naturwissenschaften. 1966 Nov;53(22):589–590. doi: 10.1007/BF00600548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]