Abstract
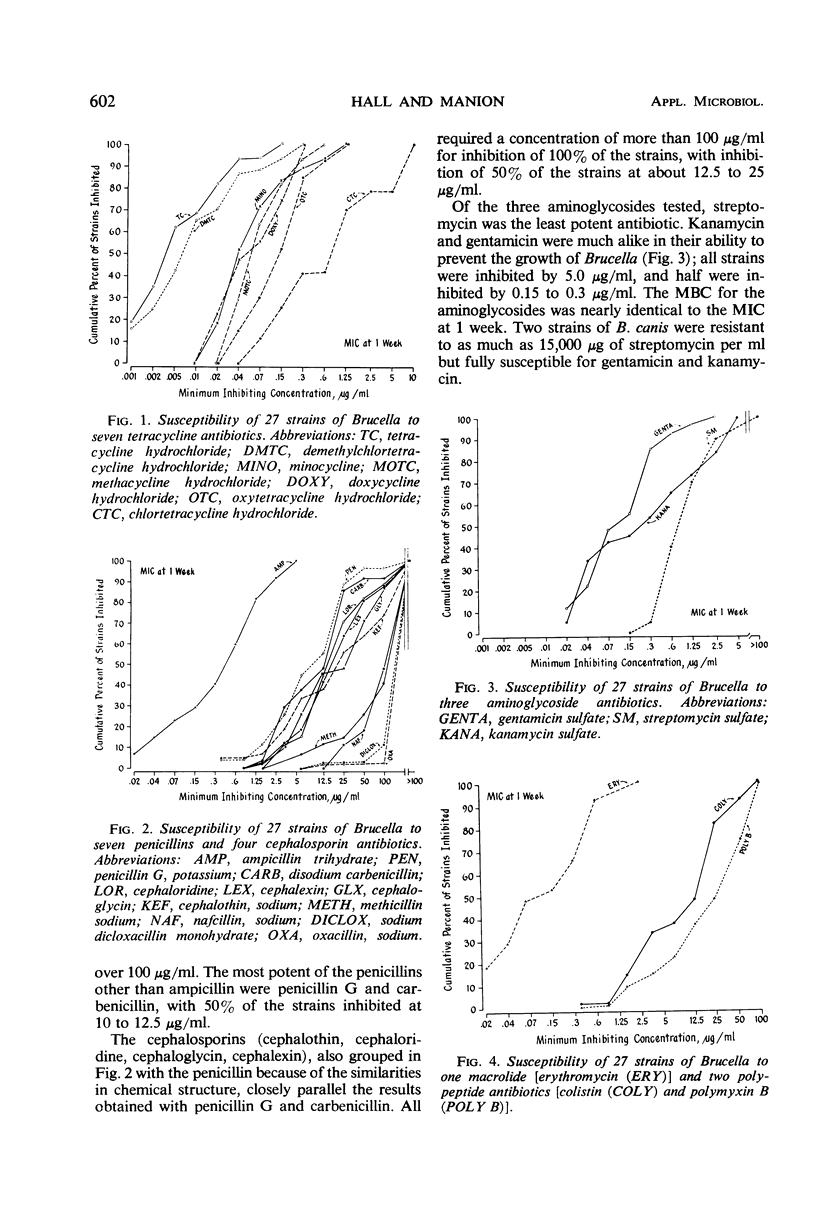
A series of 27 strains of six species of Brucella was tested for susceptibility in vitro to a representative cross section of antibiotics in current use. The activity against each species was plotted, with the cumulative per cent of strains inhibited indicated for each concentration. As a class, the tetracycline antibiotics were the most effective. Erythromycin, gentamicin, streptomycin, and kanamycin, as well as rifampin, were quite active. The penicillin-cephalosporin group, with the exception of ampicillin, was comparatively ineffective, as were the polypeptides and the miscellaneous group of chloramphenicol, lincomycin, cycloserine, and sulfadiazine. Species differences were noticeable, with some strains of B. canis being considerably more resistant to streptomycin and the tetracyclines than B. suis and B. abortus. B. melitensis, B. ovis, and B. neotomae were intermediate in antibiotic susceptibility.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGIUS E., MIFSUD J. The action of "Penbritin" on Brucella micro-organisms. Arch Inst Pasteur Tunis. 1962 Mar;39:97–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzsch W., Abadjieff W. Beitrag zur Differenzierung innerhalb der Spezies Brucella abortus mittels Antibiotika. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1966 Dec;201(4):493–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yow E. M., Spink W. W. EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES ON THE ACTION OF STREPTOMYCIN, AUREOMYCIN, AND CHLOROMYCETIN ON BRUCELLA. J Clin Invest. 1949 Sep;28(5 Pt 1):871–885. doi: 10.1172/JCI102171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



