Abstract
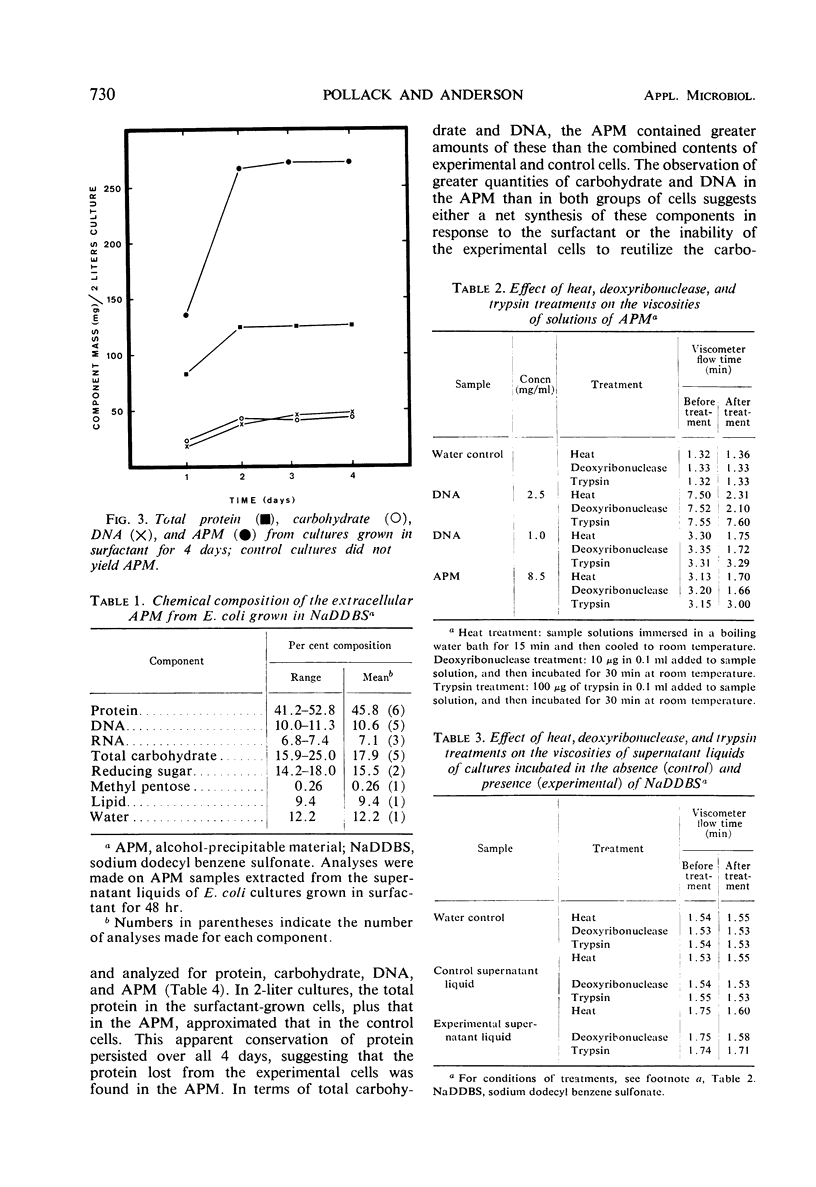
When strains of Escherichia coli are grown in broth cultures containing the anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (NaDDBS), they exhibit unique growth responses. After 20 to 24 hr of incubation, they become slimy and viscous, and an addition of ethanol to the supernatant liquid yields a distinctive white, fibrous precipitate. The production of this material was shown to be dependent on the presence of NaDDBS in the medium. This precipitate from E. coli ATCC 11303 was found to contain 41 to 53% protein, 10 to 11% deoxyribonucleic acid, 6.8 to 7.4% ribonucleic acid, 15 to 25% carbohydrate, and 9% lipid. It is distinctive from naturally occurring E. coli slimes in several respects. Our data suggest that its formation is the primary result of the leakage of intracellular components into the medium. However, the rate of cell proliferation indicates a partial but not complete or lethal lysis. A limited utilization of NaDDBS as a carbon source was also shown.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akashi S., Goto H., Sasaki M., Tsuyama A., Sai Y., Kuno T. Chemical, immunochemical and electronmicroscopical studies on the polysaccharide produced by a certain mucous strain of E. coli. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1965;47(6):1011–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEISER S. M., DAVIS B. D. Mucoid mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1957 Sep;74(3):303–307. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.3.303-307.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL J. N., EVANS J. B., PERRY J. J., NIVEN C. F., Jr An extracellular material elaborated by Micrococcus sodonensis. J Bacteriol. 1961 Dec;82:828–837. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.6.828-837.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARSON K. J., EAGON R. G. CELLULAR DISINTEGRATION WITH CONCOMITANT RELEASE OF SLIME AND PRODUCTION OF EXTRACELLULAR MANNAN BY PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA: TWO SEPARATE PHENOMENA. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Jun;10:467–472. doi: 10.1139/m64-056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATLIN B. W., CUNNINGHAM L. S. Studies of extracellular and intracellular bacterial deoxyribonucleic acids. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Dec;19(3):522–539. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-3-522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATLIN B. W. Extracellular deoxyribonucleic acid of bacteria and a deoxyribonuclease inhibitor. Science. 1956 Sep 7;124(3219):441–442. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3219.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGUID J. P. The demonstration of bacterial capsules and slime. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1951 Oct;63(4):673–685. doi: 10.1002/path.1700630413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demain A. L., Birnbaum J. Alteration of permeability for the release of metabolites from the microbial cell. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1968;46:1–25. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46121-7_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEFFRIES C. D., HOLTMAN D. F., GUSE D. G. Rapid method for determining the activity of microorganisms on nucleic acids. J Bacteriol. 1957 Apr;73(4):590–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.4.590-591.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang S., Markovitz A. Induction of capsular polysaccharide synthesis by rho-fluorophenylalanine in Escherichia coli wild type and strains with altered phenylalanyl soluble ribonucleic acid synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):584–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.584-591.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRIS R. F., DE SIPIN M., ZILLIKEN F. W., HARVEY T. S., GYORGY P. Occurrence of mucoid variants of Lactobacillus bifidus; demonstration of extracellular and intracellular polysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1954 Feb;67(2):159–166. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.2.159-166.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Raufuss E. M. The induction of the enzymes of fatty acid degradation in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Oct 11;29(1):28–33. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90535-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAPELLI R. V., GOEBEL W. F. THE CAPSULAR POLYSACCHARIDE OF A MUCOID VARIANT OF E. COLI K 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:265–271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARMAN S. H. EXTENSIVE BIODEGRADATION OF SYNTHETIC DETERGENTS. Nature. 1964 Feb 15;201:704–705. doi: 10.1038/201704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES W. R., GIBBONS N. E. The deoxyribose nucleic acid slime layer of some halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1955 Oct;1(8):614–621. doi: 10.1139/m55-074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON J. F., DUDMAN W. F., ASPINALL G. O. The extracellular polysaccharide of Aerobacter aerogenes A3 (S1) (Klebsiella type 54). Biochem J. 1955 Mar;59(3):446–451. doi: 10.1042/bj0590446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks G., Shapiro M., Burns R. O., Wakil S. J. Control of fatty acid metabolism. I. Induction of the enzymes of fatty acid oxidation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):827–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.827-836.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


