Abstract
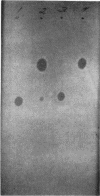
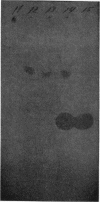
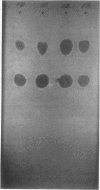
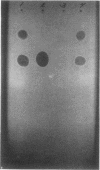
Paper chromatographic procedures may be used to detect cephalothin and its metabolite desacetylcephalothin in urine, plasma, synovial fluid, and cerebrospinal fluid. Protein-bound antibiotics are released from plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, and synovial fluid by dilution with an equal volume of dimethylformamide. Data are presented on the sample preparation, paper chromatographic system, and other specific techniques.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hoehn M. M., Pugh C. T. Method for the detection and quantitative assay of cephaloglycin and its biologically active metabolites. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Aug;16(8):1132–1133. doi: 10.1128/am.16.8.1132-1133.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE C. C., HERR E. B., Jr, ANDERSON R. C. Pharmacological and toxicological studies on cephalotin. Clin Med (Northfield) 1963 Jun;70:1123–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens V. C., Pugh C. T., Davis N. E., Hoehn M. M., Ralston S. A study of the behavior of propionyl erythromycin in blood by a new chromatographic method. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1969 Nov;22(11):551–557. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.22.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]