Abstract
In the title compound, C12H9BrN4O, the N′-methylidenepyrazine-2-carbohydrazide and 4-bromobenzene groups are oriented at a dihedral angle of 10.57 (7)°. The hydrazide N—H group is involved in intramolecular N—H⋯N interaction, which generates an S(5) motif. A short C—H⋯O interaction is formed between the methylidene H atom and the carbonyl O atom. It connects molecules into chains extending along [100]. In addition, molecules are arranged into stacks extending along [010] via π–π interactions between pyrazine and benzene rings, with centroid–centroid distances of 3.837 (2) and 3.860 (2) Å.
Related literature
For a related crystal structure and related studies, see: Hearn & Cynamon (2004 ▶); Jin et al. (2006 ▶); Yuan et al. (2006 ▶). For graph-set notation, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).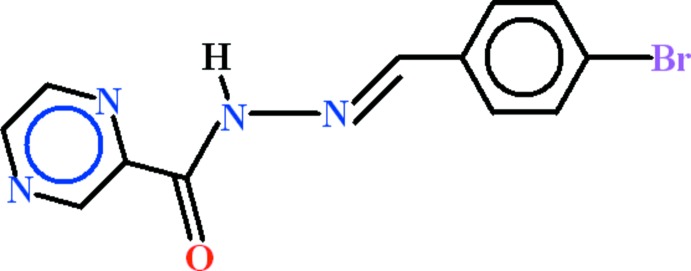
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H9BrN4O
M r = 305.14
Triclinic,
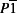
a = 5.8947 (9) Å
b = 7.6941 (12) Å
c = 14.029 (2) Å
α = 83.273 (7)°
β = 80.086 (7)°
γ = 72.440 (6)°
V = 596.11 (16) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 3.44 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.26 × 0.22 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.425, T max = 0.503
7382 measured reflections
2529 independent reflections
1403 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.074
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.039
wR(F 2) = 0.084
S = 0.94
2529 reflections
163 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 2012 ▶) and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813016917/gk2580sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813016917/gk2580Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813016917/gk2580Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6—H6⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.24 | 3.132 (4) | 161 |
| N3—H3A⋯N1 | 0.86 | 2.27 | 2.671 (3) | 108 |
Symmetry code: (i) 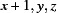 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the provision of funds for the purchase of a diffractometer and encouragement by Dr Muhammad Akram Chaudhary, Vice Chancellor, University of Sargodha, Pakistan. The authors are also thankful to the Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan for financial support. MA is also thankful to the Pakistan Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (PCSIR) Laboratories of Pakistan for financial support throughout his study leave.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound (Fig. 1) was prepared to study biological activities of hydrazone compounds (Hearn & Cynamon, 2004; Jin et al., 2006).
Crystals of the earlier reported 4-chlorobenzaldehyde(pyrazine-2-carbonyl) hydrazone (Yuan et al., 2006) are practically isostructural with the title compound.
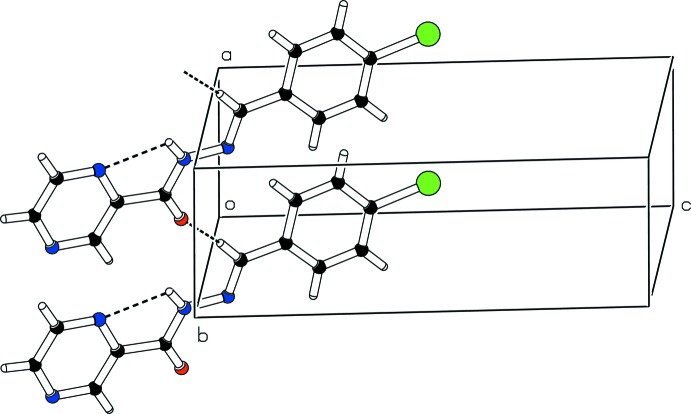
In the title compound the N'-methylidenepyrazine-2-carbohydrazide (A) (C1–C6/N1–N4/O1) and 4-bromophenyl (B) (C7–C12/Br1) moieties are almost planar with r. m. s. deviations of 0.061 Å and 0.009 Å, respectively. The dihedral angle between A/B is 10.57 (7)°. There exists intramolecular N—H···.N hydrogen bond (Table 1, Fig. 2) forming S(5) motif (Bernstein et al., 1995). The intermolecular hydrogen bonds of C—H···.O type (Table 1, Fig. 2) generate C(6) chains (Bernstein et al., 1995) along the crystallographic a-axis. There exist π–π interactions with a distance of 3.838 (2) Å [Cg1—Cg2i & Cg2— Cg1i: i = -x, 2 - y, -z] and 3.860 (2) Å [Cg1—Cg2ii & Cg2—Cg1ii: ii = -x, 1 - y, -z], between the centroids of pyrazine (Cg1) and benzene (Cg2) rings.
Experimental
The title compound was prepared by the condensation of equimolar ratio of pyrazine-2-carbohydrazide (0.50 g, 3.6 mmol) and 4-bromobenzaldehyde (0.67 g, 3.6 mmol) in methanol by the reflux of 5 h. The resulting reaction mixture was allowed to cool over night. The precipitated solid was filtered, washed with petroleum ether and recrystalized from chloroform in petroleum ether and dried under reduced pressure over CaCl2 to give white prisms. Rf: 0.40 (30% acetone in petroleum ether): Yield: 83%, soluble in chloroform; m.p. 546–547 K.
Refinement
The H atoms were positioned geometrically (N–H = 0.86 Å, C–H = 0.93 Å) and refined as riding on their carriers with Uiso(H) = xUeq(C, N), where x = 1.2 for all H-atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
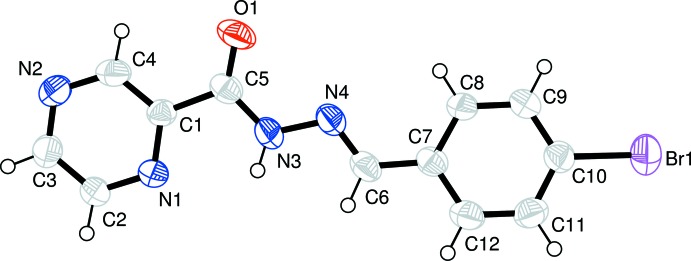
View of the title compound with the displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are shown by small circles of arbitrary radii.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of the title compound showing S(5) motif and C(6) chains along [1 0 0].
Crystal data
| C12H9BrN4O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 305.14 | F(000) = 304 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.700 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 5.8947 (9) Å | Cell parameters from 1403 reflections |
| b = 7.6941 (12) Å | θ = 2.1–25.5° |
| c = 14.029 (2) Å | µ = 3.44 mm−1 |
| α = 83.273 (7)° | T = 296 K |
| β = 80.086 (7)° | Prism, white |
| γ = 72.440 (6)° | 0.26 × 0.22 × 0.20 mm |
| V = 596.11 (16) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2529 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1403 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.074 |
| Detector resolution: 8.10 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.1°, θmin = 1.5° |
| ω scans | h = −7→6 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | k = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.425, Tmax = 0.503 | l = −17→17 |
| 7382 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.084 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.94 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0355P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2529 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 163 parameters | Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.36405 (7) | 0.25644 (5) | 0.47485 (3) | 0.07332 (19) | |
| O1 | −0.4594 (4) | 0.8146 (3) | −0.03918 (16) | 0.0633 (7) | |
| N1 | −0.0274 (4) | 0.9547 (3) | −0.21291 (18) | 0.0486 (7) | |
| N2 | −0.4307 (5) | 1.1093 (4) | −0.3071 (2) | 0.0599 (8) | |
| N3 | −0.0701 (5) | 0.7949 (3) | −0.03380 (18) | 0.0523 (7) | |
| H3A | 0.0565 | 0.8198 | −0.0649 | 0.063* | |
| N4 | −0.0613 (5) | 0.7038 (3) | 0.05682 (19) | 0.0508 (7) | |
| C1 | −0.2458 (5) | 0.9456 (4) | −0.1727 (2) | 0.0401 (8) | |
| C2 | −0.0148 (6) | 1.0405 (4) | −0.3008 (2) | 0.0538 (9) | |
| H2 | 0.1337 | 1.0501 | −0.3321 | 0.065* | |
| C3 | −0.2126 (6) | 1.1151 (4) | −0.3467 (2) | 0.0549 (9) | |
| H3 | −0.1927 | 1.1724 | −0.4084 | 0.066* | |
| C4 | −0.4426 (6) | 1.0230 (4) | −0.2191 (3) | 0.0540 (9) | |
| H4 | −0.5918 | 1.0148 | −0.1877 | 0.065* | |
| C5 | −0.2732 (6) | 0.8455 (4) | −0.0745 (2) | 0.0476 (8) | |
| C6 | 0.1460 (6) | 0.6511 (4) | 0.0827 (2) | 0.0496 (9) | |
| H6 | 0.2748 | 0.6734 | 0.0398 | 0.060* | |
| C7 | 0.1898 (6) | 0.5575 (4) | 0.1764 (2) | 0.0449 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.0083 (6) | 0.5360 (4) | 0.2494 (2) | 0.0496 (8) | |
| H8 | −0.1509 | 0.5833 | 0.2386 | 0.060* | |
| C9 | 0.0571 (6) | 0.4466 (4) | 0.3372 (2) | 0.0524 (9) | |
| H9 | −0.0679 | 0.4339 | 0.3853 | 0.063* | |
| C10 | 0.2919 (6) | 0.3757 (4) | 0.3537 (2) | 0.0500 (8) | |
| C11 | 0.4775 (6) | 0.3941 (4) | 0.2827 (2) | 0.0555 (9) | |
| H11 | 0.6361 | 0.3455 | 0.2939 | 0.067* | |
| C12 | 0.4264 (6) | 0.4854 (4) | 0.1945 (2) | 0.0543 (9) | |
| H12 | 0.5516 | 0.4989 | 0.1467 | 0.065* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.0815 (3) | 0.0777 (3) | 0.0601 (3) | −0.0224 (2) | −0.0225 (2) | 0.01461 (19) |
| O1 | 0.0580 (15) | 0.0762 (17) | 0.0622 (15) | −0.0398 (13) | 0.0071 (13) | 0.0006 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0420 (16) | 0.0576 (17) | 0.0482 (17) | −0.0216 (13) | −0.0063 (13) | 0.0069 (13) |
| N2 | 0.0479 (18) | 0.070 (2) | 0.064 (2) | −0.0208 (15) | −0.0186 (16) | 0.0107 (15) |
| N3 | 0.0564 (19) | 0.0604 (18) | 0.0429 (16) | −0.0271 (14) | −0.0057 (15) | 0.0106 (13) |
| N4 | 0.0555 (19) | 0.0552 (17) | 0.0433 (17) | −0.0238 (14) | −0.0035 (14) | 0.0059 (13) |
| C1 | 0.0373 (19) | 0.0392 (18) | 0.0455 (19) | −0.0143 (15) | −0.0058 (16) | −0.0009 (14) |
| C2 | 0.048 (2) | 0.066 (2) | 0.050 (2) | −0.0259 (17) | −0.0076 (18) | 0.0125 (17) |
| C3 | 0.057 (2) | 0.061 (2) | 0.051 (2) | −0.0225 (18) | −0.0159 (19) | 0.0060 (17) |
| C4 | 0.041 (2) | 0.062 (2) | 0.062 (2) | −0.0221 (17) | −0.0034 (18) | −0.0014 (18) |
| C5 | 0.052 (2) | 0.047 (2) | 0.048 (2) | −0.0234 (17) | −0.0001 (18) | −0.0048 (16) |
| C6 | 0.055 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.045 (2) | −0.0293 (17) | −0.0008 (18) | 0.0027 (16) |
| C7 | 0.048 (2) | 0.0429 (18) | 0.048 (2) | −0.0225 (15) | −0.0039 (17) | −0.0031 (15) |
| C8 | 0.0401 (19) | 0.053 (2) | 0.057 (2) | −0.0192 (16) | −0.0062 (17) | 0.0068 (17) |
| C9 | 0.048 (2) | 0.059 (2) | 0.051 (2) | −0.0221 (17) | −0.0024 (18) | 0.0051 (17) |
| C10 | 0.052 (2) | 0.049 (2) | 0.051 (2) | −0.0199 (16) | −0.0092 (18) | 0.0019 (15) |
| C11 | 0.043 (2) | 0.060 (2) | 0.065 (2) | −0.0157 (17) | −0.0119 (19) | −0.0025 (18) |
| C12 | 0.048 (2) | 0.064 (2) | 0.054 (2) | −0.0247 (17) | 0.0008 (18) | −0.0048 (18) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C10 | 1.886 (3) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C5 | 1.204 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C2 | 1.329 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.447 (4) |
| N1—C1 | 1.332 (3) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C3 | 1.322 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.383 (4) |
| N2—C4 | 1.332 (4) | C7—C12 | 1.393 (4) |
| N3—C5 | 1.346 (4) | C8—C9 | 1.370 (4) |
| N3—N4 | 1.379 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| N3—H3A | 0.8600 | C9—C10 | 1.376 (4) |
| N4—C6 | 1.268 (4) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C4 | 1.370 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.377 (4) |
| C1—C5 | 1.506 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.382 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.368 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C2—N1—C1 | 115.4 (3) | N4—C6—C7 | 122.5 (3) |
| C3—N2—C4 | 114.6 (3) | N4—C6—H6 | 118.7 |
| C5—N3—N4 | 121.3 (3) | C7—C6—H6 | 118.7 |
| C5—N3—H3A | 119.4 | C8—C7—C12 | 117.9 (3) |
| N4—N3—H3A | 119.4 | C8—C7—C6 | 123.3 (3) |
| C6—N4—N3 | 114.5 (3) | C12—C7—C6 | 118.7 (3) |
| N1—C1—C4 | 121.5 (3) | C9—C8—C7 | 121.6 (3) |
| N1—C1—C5 | 118.5 (3) | C9—C8—H8 | 119.2 |
| C4—C1—C5 | 119.9 (3) | C7—C8—H8 | 119.2 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 122.4 (3) | C8—C9—C10 | 119.7 (3) |
| N1—C2—H2 | 118.8 | C8—C9—H9 | 120.2 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 118.8 | C10—C9—H9 | 120.2 |
| N2—C3—C2 | 122.8 (3) | C9—C10—C11 | 120.4 (3) |
| N2—C3—H3 | 118.6 | C9—C10—Br1 | 120.6 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 118.6 | C11—C10—Br1 | 119.0 (3) |
| N2—C4—C1 | 123.2 (3) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.5 (3) |
| N2—C4—H4 | 118.4 | C10—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| C1—C4—H4 | 118.4 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| O1—C5—N3 | 125.4 (3) | C11—C12—C7 | 120.9 (3) |
| O1—C5—C1 | 121.7 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| N3—C5—C1 | 112.9 (3) | C7—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C5—N3—N4—C6 | 174.4 (3) | C4—C1—C5—N3 | −173.2 (3) |
| C2—N1—C1—C4 | −1.1 (4) | N3—N4—C6—C7 | 178.3 (3) |
| C2—N1—C1—C5 | 178.2 (3) | N4—C6—C7—C8 | −7.6 (5) |
| C1—N1—C2—C3 | 0.3 (5) | N4—C6—C7—C12 | 172.5 (3) |
| C4—N2—C3—C2 | −0.7 (5) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | −0.1 (5) |
| N1—C2—C3—N2 | 0.7 (5) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −180.0 (3) |
| C3—N2—C4—C1 | −0.1 (5) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.1 (5) |
| N1—C1—C4—N2 | 1.0 (5) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.0 (5) |
| C5—C1—C4—N2 | −178.2 (3) | C8—C9—C10—Br1 | 178.7 (2) |
| N4—N3—C5—O1 | −1.9 (5) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.4 (5) |
| N4—N3—C5—C1 | 179.1 (2) | Br1—C10—C11—C12 | −178.3 (2) |
| N1—C1—C5—O1 | −171.5 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −0.6 (5) |
| C4—C1—C5—O1 | 7.8 (5) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | 0.5 (5) |
| N1—C1—C5—N3 | 7.6 (4) | C6—C7—C12—C11 | −179.7 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C6—H6···O1i | 0.93 | 2.24 | 3.132 (4) | 161 |
| N3—H3A···N1 | 0.86 | 2.27 | 2.671 (3) | 108 |
Symmetry code: (i) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: GK2580).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2005). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Hearn, M. J. & Cynamon, M. H. (2004). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 53, 185–191. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Jin, L., Chen, J., Song, B., Chen, Z., Yang, S., Li, Q., Hu, D. & Xu, R. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16, 5036–5040. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.-C., Wu, L., Xing, Z.-Y. & Shi, X.-F. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o3274–o3275.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813016917/gk2580sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813016917/gk2580Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813016917/gk2580Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report