Abstract
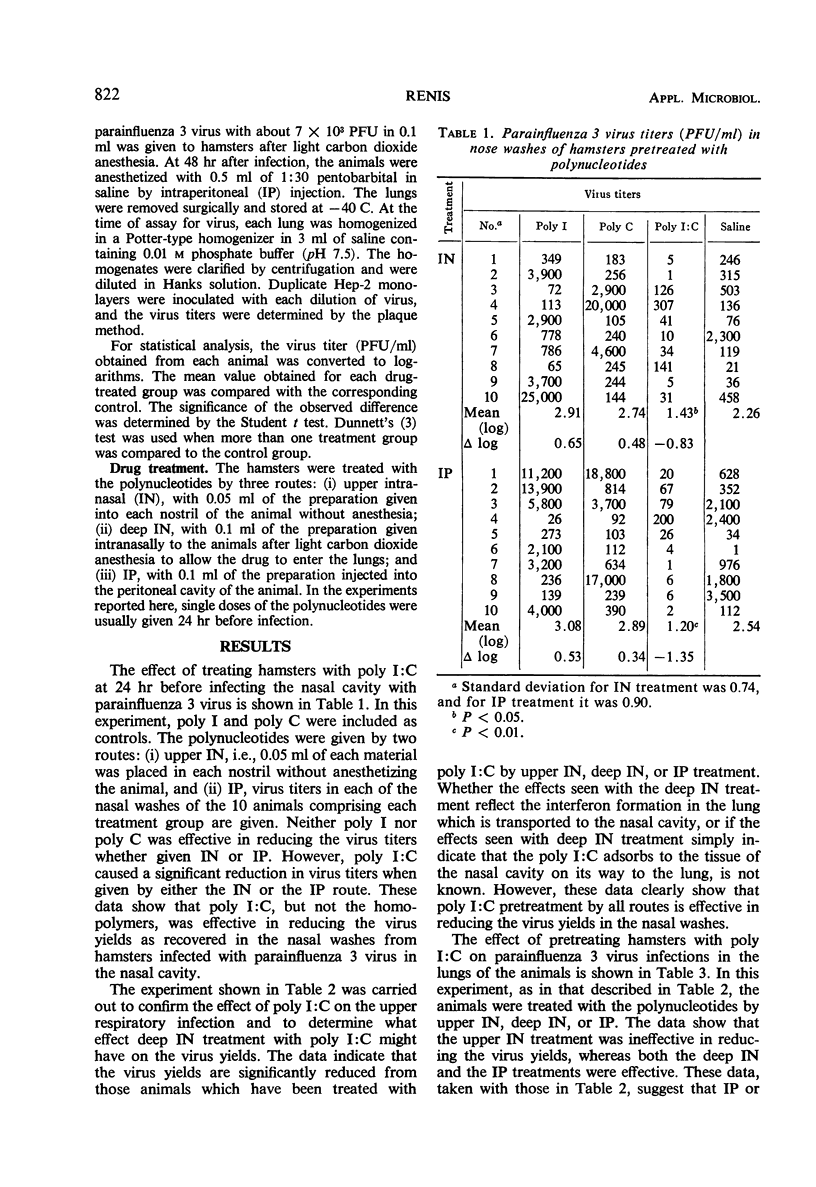
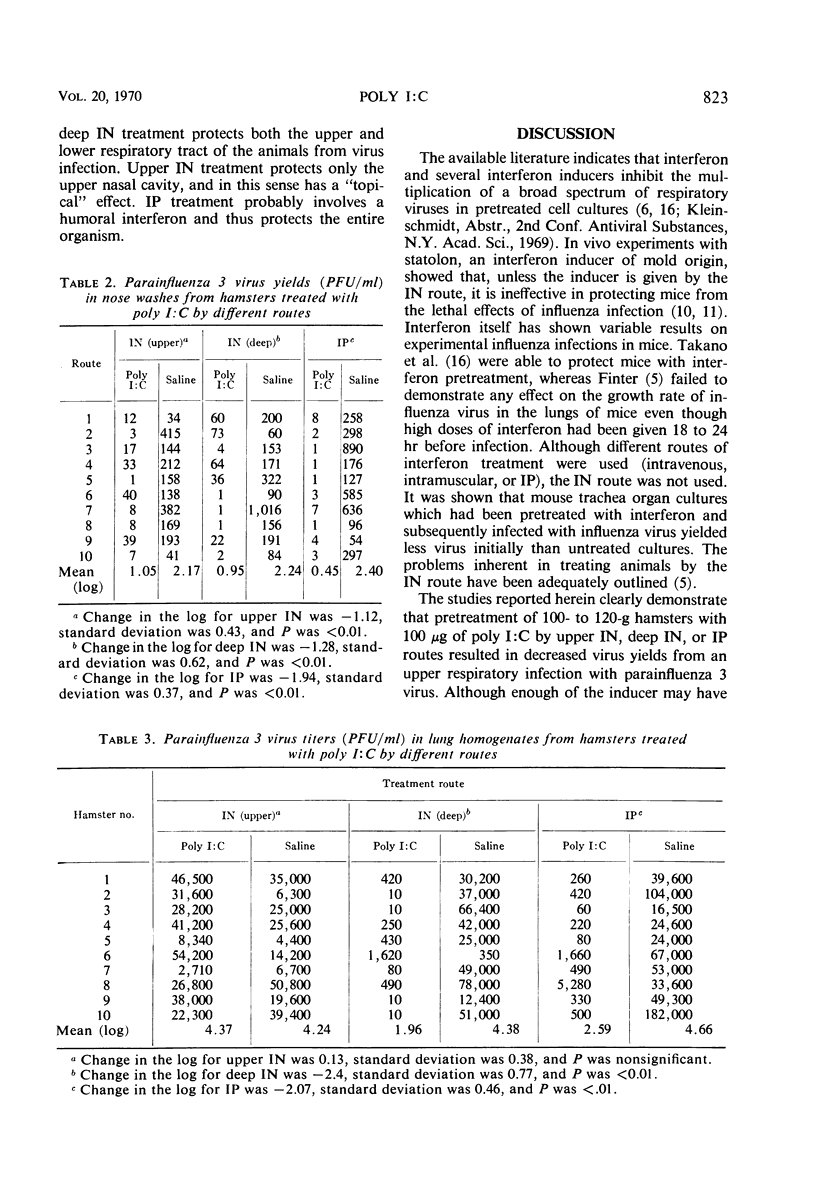
The interferon inducer double-stranded polyinosinic acid and polycytidylic acid (poly I:C) was studied in hamsters experimentally infected with parainfluenza 3 virus. Upper intranasal, deep intranasal, or intraperitoneal treatment of hamsters with poly I:C (100 μg/100- to 120-g animal) 24 hr before an upper respiratory infection significantly reduced the virus yields taken 28 hr after infection. Deep intranasal and intraperitoneal treatment with poly I:C greatly decreased the virus titers in the lungs, as measured 48 hr after a deep lung infection with parainfluenza 3 virus; however, the upper respiratory poly I:C treatment was ineffective.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTHALA D. A., SORET M. G. PARAINFLUENZA TYPE 3 VIRUS INFECTION IN HAMSTERS: VIROLOGIC, SEROLOGIC, AND PATHOLOGIC STUDIES. J Infect Dis. 1964 Jun;114:226–234. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.3.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAIGHEAD J. E., COOK M. K., CHANOCK R. M. Infection of hamsters with para influenza 3 virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jun;104:301–304. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. II. Multistranded synthetic polynucleotide complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. A., Baron S., Chanock R. M. Sensitivity of common respiratory viruses to an interferon inducer in human cells. Lancet. 1969 Jul 26;2(7613):187–188. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91425-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindh H. F., Lindsay H. L., Mayberry B. R., Forbes M. Polyinosinic-cytidylic acid complex (poly I:C) and viral infections in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Oct;132(1):83–87. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C., Sharp E., Collins J. Studies on the pathogenesis of parainfluenza type 3 virus infection in hamsters. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1968;24(3):203–219. doi: 10.1007/BF01241293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemes M. M., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Field A. K., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. VI. Antiviral efficacy of poly I:C in animal models. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):776–783. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pindak F. F., Schmidt J. P., Kendrick J. Z. Influence of statolon on resistance of mice to influenza. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Aug;18(2):147–151. doi: 10.1128/am.18.2.147-151.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince H. N., Grunberg E. Nature of the antiviral activity of statolon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:588–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renis H. E. In vitro antiviral activity of calcium elenolate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1969;9:167–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soret M. G. Antiviral activity of calcium elenolate on parainfluenza infection of hamsters. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1969;9:160–166. doi: 10.1128/AAC.9.1.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soret M. G. System for antiviral drug evaluation in hamsters infected with HA-1 virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:220–224. doi: 10.1128/AAC.8.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Scott W. D., Sulkin S. E. Relative sensitivities of viruses to different species of interferon. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):147–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.147-153.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKANO K., JENSEN K. E., WARREN J. PASSIVE INTERFERON PROTECTION IN MOUSE INFLUENZA. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Nov;114:472–475. doi: 10.3181/00379727-114-28706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


