Abstract
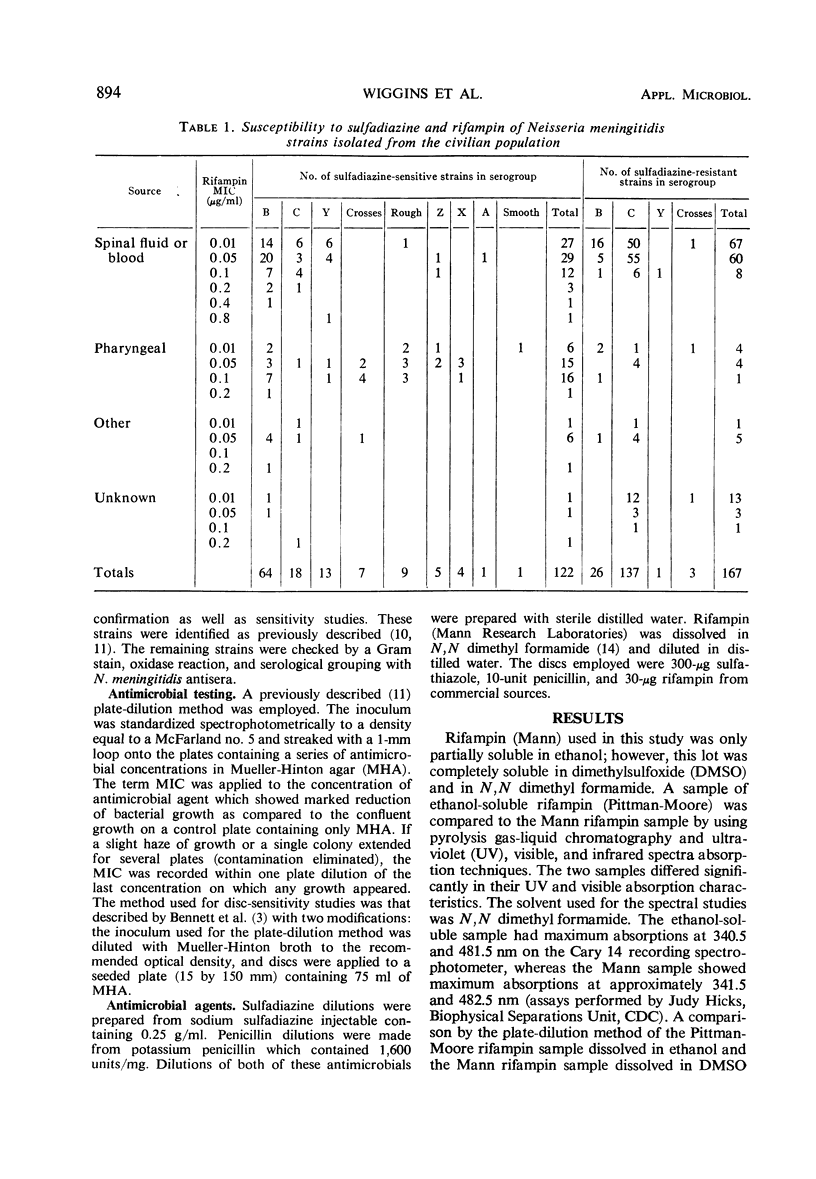
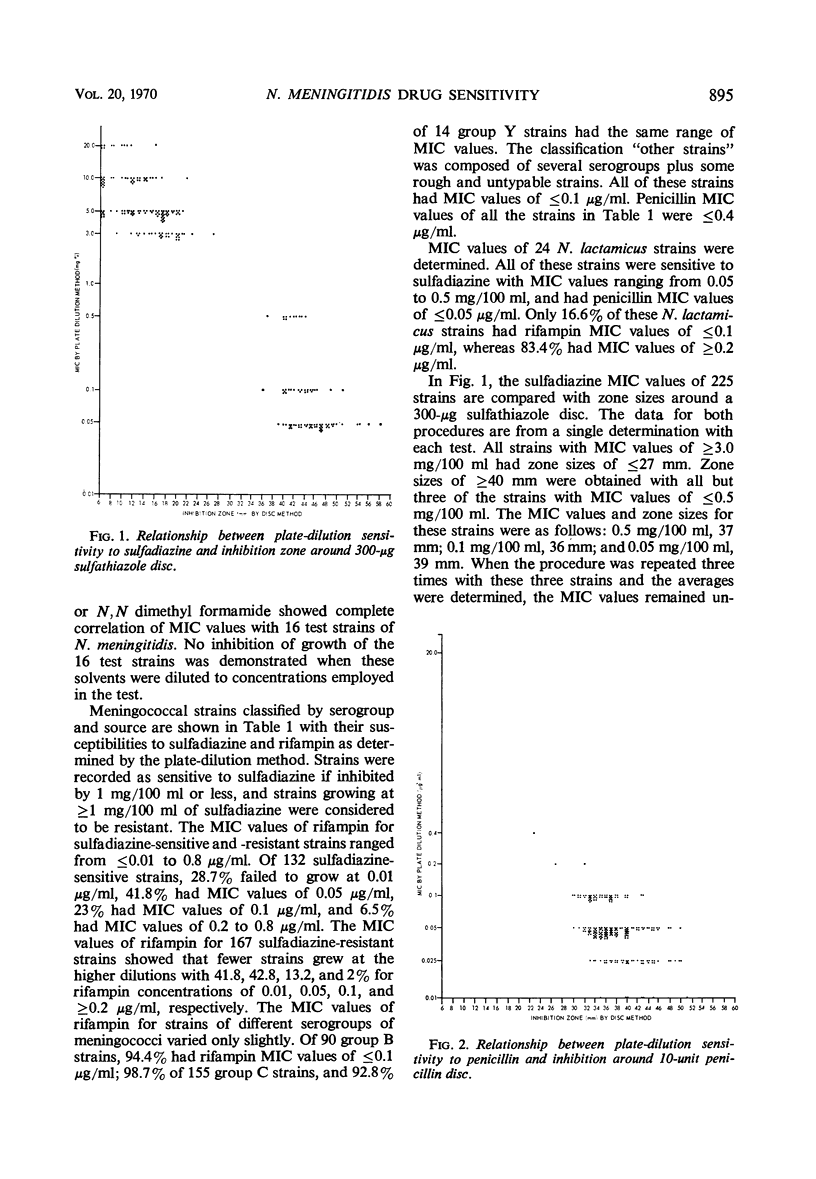
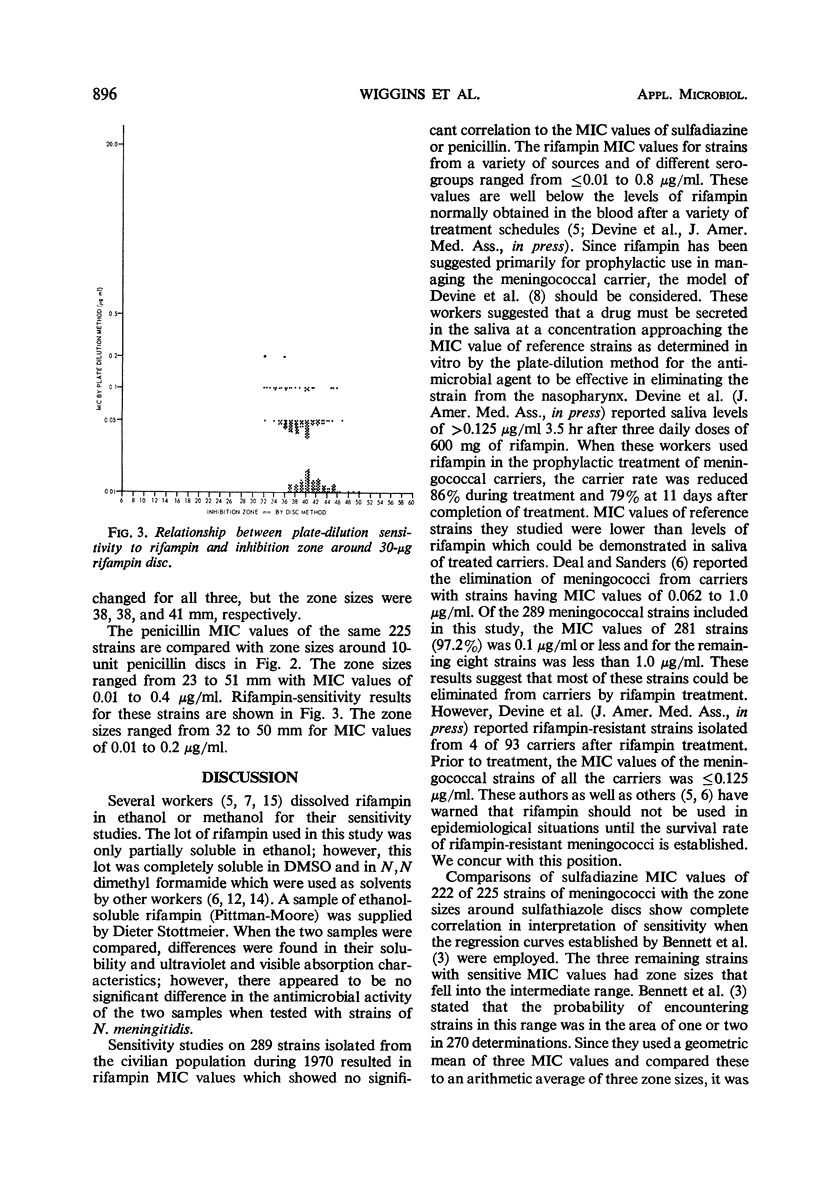
The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of sulfadiazine, penicillin, and rifampin for meningococcal strains isolated from civilians during 1970 were compared. The strains were isolated from various sources and geographical areas and represented several serogroups. The ranges of MIC values were as follows: 0.05 to 20 mg/100 ml for sulfadiazine, 0.01 to 0.4 μg/ml for penicillin, and 0.01 to 0.8 μg/ml for rifampin. There was no significant relationship between MIC values of sensitive or resistant sulfadiazine strains and the MIC values to the other two antimicrobial agents. Comparisons of sulfadiazine MIC values with inhibition zones around sulfathiazole discs showed excellent correlation, provided the strains were separated into sensitive and resistant groups on the basis of growth at 1 mg/100 ml. Regression curves for penicillin and rifampin sensitivity showed homologous sensitive populations with the strains studied.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. V., Camp H. M., Eickhoff T. C. Rapid sulfonamide disc sensitivity test for meningococci. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jul;16(7):1056–1060. doi: 10.1128/am.16.7.1056-1060.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dans P. E., McGehee R. F., Jr, Wilcox C., Finland M. Rifampin: antibacterial activity in vitro and absorption and excretion in normal young men. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Feb;259(2):120–132. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197002000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deal W. B., Sanders E. Efficacy of rifampin in treatment of meningococcal carriers. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 18;281(12):641–645. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909182811203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine L. F., Hagerman C. R. Spectra of susceptibility of Neisseria meningitidis to antimicrobial agents in vitro. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Feb;19(2):329–334. doi: 10.1128/am.19.2.329-334.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine L. F., Knowles R. C., Pierce W. E., Peckinpaugh R. O., Hagerman C. R., Lytle R. I. Proposed model for screening antimicrobial agents for potential use in eliminating meningococci from the nasopharynx of healthy carriers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:307–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowd J. M., Blink D., Miller C. H., Frank P. F., Pierce W. E. Antibiotic prophylaxis of carriers of sulfadiazine-resistant meningococci. J Infect Dis. 1966 Oct;116(4):473–480. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.4.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis D. G., Wiggins G. L., Schubert J. H. Serological studies of ungroupable Neisseria meningitidis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.1-4.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis D. G., Wiggins G. L., Weaver R. E. Neisseria lactamicus sp. n., a lactose-fermenting species resembling Neisseria meningitidis. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jan;17(1):71–77. doi: 10.1128/am.17.1.71-77.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlson A. G., Ulrich J. A. Stability of rifampin in dimethylsulfoxide. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Oct;18(4):692–693. doi: 10.1128/am.18.4.692-693.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLAR J. W., SIESS E. E., FELDMAN H. A., SILVERMAN C., FRANK P. IN VIVO AND IN VITRO RESISTANCE TO SULFADIAZINE IN STRAINS OF NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS. JAMA. 1963 Oct 12;186:139–141. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.63710020008016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallanza R., Arioli V., Furesz S., Bolzoni G. Rifampicin: a new rifamycin. II. Laboratory studies on the antituberculous activity and preliminary clinical observations. Arzneimittelforschung. 1967 May;17(5):529–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stottmeier K. D., Kubica G. P., Woodley C. L. Antimycobacterial activity of rifampin under in vitro and simulated in vivo conditions. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):861–865. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.861-865.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



