Abstract
The two microaerophilic, Fe-oxidizing bacteria (FeOB) Sideroxydans ES-1 and Gallionella ES-2 have single circular chromosomes of 3.00 and 3.16 Mb that encode 3049 and 3006 genes, respectively. Multi-locus sequence analysis (MLSA) confirmed the relationship of these two organisms to one another, and indicated they may form a novel order, the Gallionellalaes, within the Betaproteobacteria. Both are adapted for chemolithoautotropy, including pathways for CO2-fixation, and electron transport pathways adapted for growth at low O2-levels, an important adaptation for growing on Fe(II). Both genomes contain Mto-genes implicated in iron-oxidation, as well as other genes that could be involved in Fe-oxidation. Nearly 10% of their genomes are devoted to environmental sensing, signal transduction, and chemotaxis, consistent with their requirement for growing in narrow redox gradients of Fe(II) and O2. There are important differences as well. Sideroxydans ES-1 is more metabolically flexible, and can utilize reduced S-compounds, including thiosulfate, for lithotrophic growth. It has a suite of genes for nitrogen fixation. Gallionella ES-2 contains additional gene clusters for exopolysaccharide production, and has more capacity to resist heavy metals. Both strains contain genes for hemerythrins and globins, but ES-1 has an especially high numbers of these genes that may be involved in oxygen homeostasis, or storage. The two strains share homology with the marine FeOB Mariprofundus ferrooxydans PV-1 in CO2 fixation genes, and respiratory genes. In addition, ES-1 shares a suite of 20 potentially redox active genes with PV-1, as well as a large prophage. Combined these genetic, morphological, and physiological differences indicate that these are two novel species, Sideroxydans lithotrophicus ES-1T (ATCC 700298T; JCM 14762; DSMZ 22444; NCMA B100), and Gallionella capsiferriformans ES-2T (ATCC 700299T; JCM 14763; DSMZ 22445; NCMA B101).
Keywords: Fe-oxidizing bacteria, Sideroxydans, Gallionellaceae, Gallionella, iron oxidizing bacteria
Introduction
The freshwater Fe-oxidizing bacteria (FeOB) are a group of microbes associated with either natural or technical aqueous environments that contain appreciable concentrations of Fe(II). Because iron is the fourth most abundant element in the Earth's crust, these types of habitats are common and widespread; however due to the rapid chemical oxidation of Fe(II) in fully oxygenated waters they are restricted to redox boundaries where FeOB can flourish in opposing gradients of Fe(II) and O2 (Emerson et al., 2010; Hedrich et al., 2011). Despite historical recognition of the importance of FeOB in mediating Fe-oxidation (Harder, 1919), our detailed knowledge about the physiology and ecology of the FeOB is limited, in part due to the challenge of isolating pure cultures and developing model organisms from the few isolates available.
A number of recent reports have analyzed freshwater communities of FeOB using cultivation-independent approaches, and shown a dominant clade of operational taxonomic units (OTUs) in these communities belong to the Betaproteobacteria (Sahl et al., 2008; Duckworth et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2009; Bruun et al., 2010; Gault et al., 2011; Lin et al., 2011; Johnson et al., 2012). This clade includes the iconic, stalk-forming, Gallionella ferruginea, and other isolates, including Sideroxydans spp. of obligately microaerophilic FeOB (Weiss et al., 2007; Ludecke et al., 2010; Krepski et al., 2012). While prevalent in Fe-rich waters, members of this group are rarely, if ever, reported from other redox stratified habitats. These two lines of evidence suggest members of this lineage of Betaproteobacteria are uniquely adapted for growth on Fe(II) as an energy source.
Genomic analysis has proven useful in the analysis of acidophilic FeOB. Detailed individual analysis of genomes from strains of the well-studied Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, as well as comparative genomics studies, have yielded important insights into how this organism can conserve energy from Fe(II) oxidation for chemolithoautotrophic growth (Valdés et al., 2008). Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, and related species, play a crucial role in Fe-oxidation in acid mine drainage. Metagenomic analysis of communities dominated by Leptospirillum spp. have served as a model for understanding the population biology of naturally occurring microbial communities, and revealed the importance of specific cytochromes for Fe-oxidation (Tyson et al., 2004; Jeans et al., 2008; Singer et al., 2008).
This paper focuses on knowledge gleaned from genomics of two isolates of freshwater, neutrophilic FeOB, Gallionella strain ES-2, and Sideroxydans strain ES-1 (Emerson and Moyer, 1997). These two organisms were isolated from ferrugineous groundwater in Michigan, and described as obligate, microaerobic Fe-oxidizers. The genomic information presented here further develops our understanding of the physiology of these two organisms, and better delineates their respective ecological niches. This analysis also elucidates the taxonomy of these two organisms and the systematics of FeOB, and provides clues as to the mechanism of how they might conserve energy from the oxidation of iron.
Materials and methods
DNA isolation and genome sequencing
Sideroxydans ES-1, and Gallionella ES-2, were grown in the laboratory using standard conditions for the growth of neutrophilic, microaerobic FeOB (Emerson and Floyd, 2005). To produce biomass for DNA sequencing, ~50 FeS gradient plates (15–18 ml each) were harvested for each strain. The cells and iron oxides were harvested by centrifugation and the cell/iron oxide pellet was washed once with phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 8.0) and DNA was extracted using the MoBio PowerSoil DNA kit to a quantity (~70 μg) and quality specified by the JGI.
Genome sequencing, annotation, and analysis
Genome sequencing was done at the JGI using a combination of Illumina (Bennett, 2004) and 454 technologies (Margulies et al., 2005). An Illumina GAii shotgun library with reads of 121 Mb (ES-1) and 244 Mb (ES-2), a 454 Titanium draft library with average read length of 195 bp (ES-1) and 248 bp (ES-2) and a paired end 454 library with average insert size of 12.4 Kb (ES-1) and 11 Kb (ES-2) were generated. Illumina sequencing data was assembled with VELVET (Zerbino and Birney, 2008), and the consensus sequences were shredded into 1.5 kb overlapped fake reads and assembled together with the 454 data. The draft assembly for ES-1 was based on 129.0 Mb of 454 draft data, and 114 kb of 454 paired end data. The ES-2 draft was based on 117.1 Mb 454 draft data, and all of the 454 paired end data. The initial Newbler assembly contained 12 contigs in 1 scaffold for ES-1, and 54 contigs in 2 scaffolds for ES-2. This 454 assembly was converted into a phrap assembly by making fake reads from the consensus, collecting the read pairs in the 454 paired end library. The Phred/Phrap/Consed software package (www.phrap.com) was used for sequence assembly and quality assessment (Ewing and Green, 1998; Ewing et al., 1998; Gordon et al., 1998) in the following finishing process. Illumina data was used to correct potential base errors and increase consensus quality using a software Polisher developed at JGI (Alla Lapidus, unpublished). After the shotgun stage, reads were assembled with parallel phrap (High Performance Software, LLC). Possible mis-assemblies were corrected with gapResolution (Cliff Han, unpublished), Dupfinisher (Han and Chain, 2006), or sequencing cloned bridging PCR fragments with subcloning. Gaps between contigs were closed by editing in Consed, by PCR and by Bubble PCR primer walks. A total of 96 (ES-1) and 297 (ES-2) additional PCR reactions were necessary to close gaps and to raise the quality of the finished sequence for both genomes.
Genes were identified using Prodigal (Hyatt et al., 2010). The predicted CDSs were translated and used to search the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) non-redundant database (nr), UniProt, TIGRFam, Pfam, KEGG, COG, and InterPro databases. The tRNAScan-SE tool (Hacker and Kaper, 2000) was used to find tRNA genes, whereas ribosomal RNA genes were found by searches against models of the ribosomal RNA genes built from SILVA (Pruesse et al., 2007). Other non–coding RNAs such as the RNA components of the protein secretion complex and the RNase P were identified by searching genomes for the corresponding Rfam profiles using INFERNAL (Makarova et al., 1999). Additional gene prediction analysis and manual functional annotation was performed within the Integrated Microbial Genomes (IMG) (Markowitz et al., 2008) platform developed by the JGI (http://img.jgi.doe.gov).
Primary genome analysis was done using the JGI's IMG/ER web-based set of tools for gene comparison and annotation. For the phylogenetic analyses presented, protein sequences were obtained from the NCBI database and aligned with ClustalW using the BLOSUM matrix and further aligned by hand. Maximum likelihood phylogenetic trees were created in MEGA5 (Tamura et al., 2011) using the Poisson Substitution Model and 1000 bootstrap iterations.
Growth studies
Alternative growth substrates to Fe(II) were either tested in gradient tubes, or by inoculating the cells into sealed serum bottles (50 ml in a 125 cc serum bottle) containing liquid MWMM medium amended with the particular growth substrate (Emerson and Floyd, 2005). The headspace contained 2–3% oxygen in a N2-atmosphere, and the pH was buffered to 6.5 with 10 mM MES buffer. For nitrate dependent growth, the MWMM medium was supplemented with 10 mM NaNO3, and the headspace was maintained O2 free. To assess growth on thiosulfate, the MWMM medium in serum bottles was amended with 5 mM thiosulfate and 2–3% O2 was maintained in the headspace. In all cases, growth was assessed by light and epifluorescence microscopy, either qualitatively or quantitatively by direct cell counts as described previously (Emerson and Moyer, 1997).
Fatty acids analysis
Fatty acid methyl esters (FAME) were identified using the procedure recommended by the Microbial Identification System (MIDI, Sherlock Microbial Identification System Version 4.0, MIS Operating Manual, March 2001, Newark, DE). The cells were grown in FeS gradient plates until the late log phase of growth and then harvested by centrifugation. Excess Fe(III) was removed from the cell pellet by treating the sample with 0.33 M oxalic acid for 1 h at 37°C, and then washing it three times by centrifugation with de-ionized water. The extraction of FAMEs and their analysis by gas chromatography was done as previously described (Pikuta et al., 2003).
Results and discussion
Genome properties and phylogeny
Both ES-1 and ES-2 have single circular chromosomes of ~3 Mb as shown in Table 1. The genome sizes are consistent with those of other aerobic, chemolithoautotrophic FeOB, Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans (2.9–3.0 Mb), Mariprofundus ferrooxydans (3.0 Mb), and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans C2–3 (2.56 Mb; Valdés et al., 2008; Singer et al., 2011; Fujimura et al., 2012). Neither genome shows evidence for extrachromosomal elements; nor is there evidence for large blocks of genes (e.g., “pathogenicity islands”) that may have been introduced by horizontal gene transfer (HGT; Gogarten and Townsend, 2005). ES-2 has three SSU rRNA genes that share 100% identity to one another, while ES-1 has two SSU genes, also sharing 100% identity. Gallionella ES-2 and Sideroxydans ES-1 are relatively distant from one another based on comparison of their SSU rRNA genes, sharing 93% similarity, well below the current standard of 98.7% for differentiating species (Stackebrandt and Ebers, 2006). They also differ in G+C content, Table 1. There is limited synteny between the two chromosomes. A phylogeny based on the SSU rRNA gene indicated these two FeOB cluster with numerous environmental clones from freshwater Fe-rich habitats, other isolates of FeOB (Weiss et al., 2007; Ludecke et al., 2010; Krepski et al., 2012), and form a distinct clade within the Betaproteobacteria (data not shown). A more robust multi-locus sequence analysis (MLSA) used six phylogenetically conserved genes (rpoA, rpoB, recA, gyrB, fusA, and ileS) to compare the 10 most closely related members of the Betaproteobacteria that have complete genome sequences (Figure 1). This confirmed the position of these two FeOB as being most closely related to one another and forming a distinct clade in the Betaproteobacteria that could form a novel order, the Gallionellales. Overall the two genomes share significant homology, at a 30% identity ~60% of the genes are homologous (Table 1), and at 60% identity, about 40% of the genes are homologous. This genomics based approach also confirms the phylogenetic distance to the marine Fe-oxidizer M. ferrooxydans, which belongs to the Zetaproteobacteria, a proposed novel class of Proteobacteria (Emerson et al., 2007). Despite this lack of phylogenetic relatedness, the microaerophile M. ferrooxydans shares common physiological traits with ES-1 and ES-2, and common morphological traits with ES-2.
Table 1.
Genome characteristics of ES-1 and ES-2.
| Organism | Sideroxydans ES-1 | Gallionella ES-2 |
|---|---|---|
| Genome size | 3.00 Mb | 3.16 Mb |
| Genes | 3049 | 2977 |
| CDS | 2996 (98.26%) | 2917 (97.98%) |
| GC Perc | 58% | 53% |
| 16S genes | 2 | 3 |
| tRNA genes | 44 | 51 |
| Genes w/functional prediction | 2177 (71.4%) | 2297 (77.16%) |
| COGs | 2237 (73.4%) | 2157 (72.5%) |
| Pseudo genes | 16 | 0 |
| CRISPR-related genes | 0 | 0 |
| % homologous genes (1e-5; 30%) | 63.7% | 64.5% |
Figure 1.
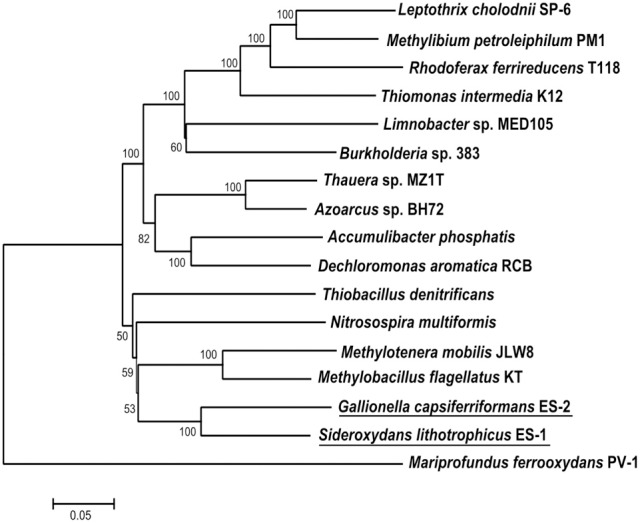
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of 6 concatenated conserved proteins (RpoA, RpoB, RecA, GyrB, FusA, and IleS) within Sideroxydans lithotrophicus ES-1 and Gallionella capsiferriformans ES-2 as well as other Betaproteobacteria. M. ferrooxydans PV-1, a member of the Zetaproteobacteria was used as the outgroup.
Energy transduction from iron
As previously reported, both strains grow on Fe(II) with optimal doubling times in FeS gradient tubes of 8 h (ES-1) to 12 h (ES-2; Emerson and Moyer, 1997). Follow up studies reported here indicated the source of Fe(II) used for growth mattered little. In gradient culture, both strains grew on FeCO3 (siderite), and in liquid culture they grew with FeCl2, Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2, and FeSO4, all with comparable results. Neither strain was able to couple nitrate reduction to iron oxidation, nor were they able to reduce Fe(III) in the presence of acetate under anaerobic conditions. Neither strain could grow on complex media, e.g., R2A, nutrient broth, or peptone, yeast extract, glucose (PYG, ATCC medium #1503), or utilize acetate, pyruvate, succinate, glucose, galactose, ribose, glycerol, aspartate, or glycine as a sole growth substrate in a minimal medium.
Potential candidates for an iron oxidase
In order to capitalize on Fe(II) as an energy source, an organism needs to couple electrons gained through the oxidation of ferrous to ferric iron to the electron transport chain to generate proton motive force (pmf). It is assumed that this initial oxidation is carried out by an iron-oxidizing protein at the cell surface, presumably located at the cell outer membrane, since, at circumneutral pH, Fe(III) reacts almost instantaneously with water to produce insoluble ferric oxyhydroxide (Stumm and Morgan, 1981). Thus, the cell requires a mechanism for extracellular electron transfer from the site of Fe-oxidation to the electron transport chain on the cytoplasmic membrane.
At present, specific mechanisms about how cells conserve energy from oxidation of Fe(II) at circumneutral pH are poorly understood (Emerson, 2012; Ilbert and Bonnefoy, 2013). Recently it has been pointed out that strains ES-1 and ES-2 contain gene homologs to the genes encoding MtrA/B in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1, and the PioA/B genes in Rhodopseudomonas palustris TIE-1 that are involved in Fe-reduction and photoferrotrophy, respectively (Liu et al., 2012). Experimental evidence has shown that the MtrA homolog in ES-1, designated MtoA (metal oxidation), produces a decaheme cytochrome with Fe(II) oxidation activity in vitro. In concert with MtoB (the MtrA homolog) and a CymA homolog found in the same operon, it was proposed these genes could form an Fe-oxidizing pathway in strain ES-1 (Liu et al., 2012). In S. oneidensis, CymA is a tetraheme c-type cytochrome that is thought to reside in the cytoplasmic membrane and mediate electron transfer from the quinone/quinol pool (Gralnick, 2012; Coursolle and Gralnick, 2012; Shi et al., 2012). The relevant gene clusters are shown in Figure 2. ES-2 has MtoA/B (Galf_2004 and Galf_2003) homologs in a gene cluster that shares a c-type cytochrome upstream of MtoA/B with ES-1, but also has an additional multiheme cytochrome, immediately upstream of the c-type cytochrome. This gene (Galf_2006) does not have a homolog in ES-1, but has weak homology (bit score 47; E value 6e-06) to MtrD, a decaheme cytochrome in S. oneidensis MR-1 (Coursolle and Gralnick, 2012). Gallionella strain ES-2 does not have a CymA homolog. These genomic patterns suggest that while ES-1 and ES-2 share the MtoA/B genes, the specific functioning of these genes may be different in the two organisms.
Figure 2.
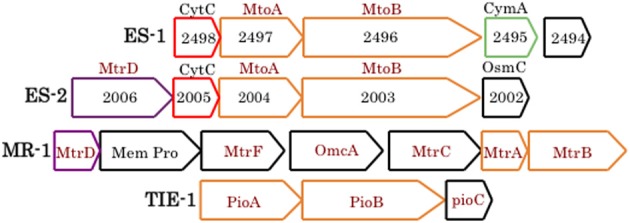
Gene clusters from ES-1, ES-2, S. oneidensis MR-1, and R. palustris TIE-1 that are involved in Fe-oxidation or Fe-reduction (the Mtr cluster in MR-1). The mtoA/B genes are homologs of mtrA/B and pioA/B, all outlined in orange. ES-1 has a cymA homolog (4e-21), green outline, to the cymA gene in MR-1 (not shown), and ES-2 and MR-1 share a weakly homologous mtrD, outlined in purple. Homologous genes between ES-1 and ES-2 that encode a cytochrome C are outlined in red. Genes outlined in black are non-homologous. The numbers refer to the respective Slit_xxxx or Galf_xxxx locus tags in IMG. The respective IMG locus tags for respective genes in MR-1 are SO1782 – SO1776, and for TIE-1, Rpal_0817 – Rpal_0815.
The most well-characterized pathway for aerobic Fe-oxidation is in the acidophile A. ferrooxydans (ATCC 23270); the gene cyc2 encodes a cytochrome located in outer membrane of the cell that catalyzes oxidation of Fe(II) to Fe(III); (Bonnefoy and Holmes, 2011). Electrons released during this oxidation can flow “downhill” to a terminal cytochrome oxidase via a cytochrome encoded by the cyc1 gene, or flow “uphill” to the quinone pool and an the NADH synthase complex. This is, in part, mediated by another cytochrome encoded by the cycA1 gene. It is also thought rusticyanin plays a key role in electron shuttling from the outer membrane to the cytoplasmic membrane, and may also control “uphill” vs. “downhill” flow of electrons (Bird et al., 2011; Bonnefoy and Holmes, 2011). Neither Sideroxydans ES-1 or Gallionella ES-2 contain homologs to rusticyanin, Cyc1, or CycA1. Sideroxydans ES-1 has three weak homologs (E values 8 × 10−9 to 1 × 10−4) to the cyc2 gene that occur in a cluster of three genes (Slit_0263 – Slit_0265); however these genes are not associated with other redox active genes and do not have transmembrane helices. There is one copy of a cyc2 gene homolog in ES-2 (Galf_0431) that shares homology to the genes in ES-1.
A previous report on the genome of M. ferrooxydans PV-1, noted that all three strains of FeOB, PV-1, ES-1, and ES-2 contained molybdopterin oxidoreductase (actB)-containing gene cluster recognized as the alternative complex (AC) III (Pereira et al., 2007; Singer et al., 2011). This was the only homologous multiple gene cluster shared between these three organisms that could play a role in redox reactions directly coupled to Fe-oxidation. PV-1 does not possess Mto homologs. Recent work of Refojo et al. (2012) indicates the actB gene, which was proposed to act as a putative Fe oxidase (Singer et al., 2011), is likely bound to the cytoplasmic membrane in Rhodothermus marinus. If this is the case in the Fe-oxidizers then it is less clear how it would act as an Fe-oxidase, although it may still be involved in electron transport (see below).
In addition to the ACIII complex, Sideroxydans ES-1 and M. ferrooxydans share a suite of 20 genes in common that are organized into three nearly contiguous clusters, with highly conserved gene order (Figure 3). The closest match by BLAST for each of the ES-1 genes is the cognate PV-1 gene (results not shown). Remarkably, 14 of these genes also share homology with the acidophilic Fe-oxidizer Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, in fact in every case, for these homologous genes the next closest match after PV-1 is to a gene from a Leptospirillum spp. The cognate genes in L. ferrooxidans C2–3 do not share the same highly conserved gene order as is found in ES-1 and PV-1 (Fujimura et al., 2012). The majority of these genes are annotated as hypotheticals, although some of them have redox properties, thus their function remains unknown. Gallionella ES-2 does not possess these genes.
Figure 3.
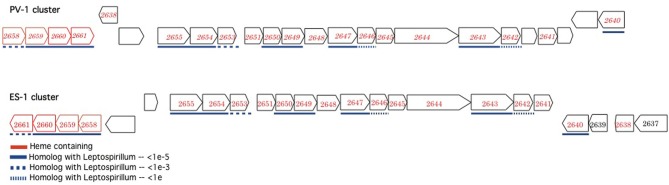
Complementary gene clusters of potentially redox active proteins shared between Sideroxydans ES-1 and M. ferrooxydans PV-1, some of which are also homologous to Leptospirillum spp. The numbers designate the IMG gene locus for the respective genes in Sideroxydans (Slit_xxxx), in the PV-1 gene clusters the homologous ES-1 gene is shown in italics. The genes outlined in red contain hemes.
Electron transport complexes
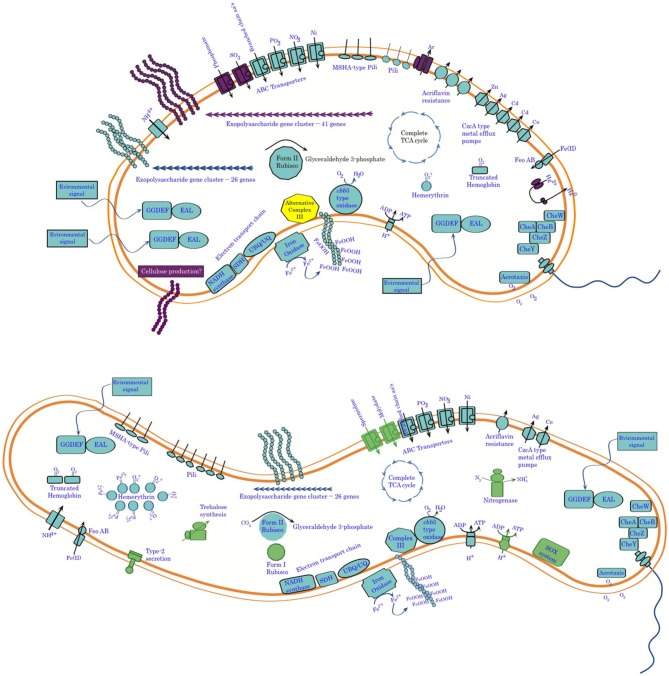
The electron transport chain responsible for generation of pmf and ATP generation consists of five separate complexes (Nicholls and Ferguson, 2002). Both ES-1 and ES-2 have complete gene complements for the NADH dehydrogenase (synthase; Complex I), as well as complex II, succinate dehydrogenase, Figure 4. Both organisms have quinones that couple electron transport from the NADH dehydrogenase to complex III type cytochromes; however here the pathways between ES-1 and ES-2 show divergence. ES-1 has genes (Slit_130 – Slit_132) for a canonical cytochrome bc1 complex; however ES-2 does not contain such homologs. As discussed above, both organisms do contain an eight gene cluster that includes a molybdopterin oxidoreductase. This ACIII complex is capable of interacting with the quinone pool and passing electrons to a terminal oxidase (Refojo et al., 2012). If this is the case, then ES-2 may utilize this in place of the bc1 complex. Both ES-1 and ES-2 also encode a cbb3 type terminal cytochrome oxidase (C-family heme-copper oxidoreductases), but lack the cytochrome aa3 or bo3 terminal oxidases (A-family) that have low affinity for O2 (Gennis and Stewart, 1996). This is consistent with these organisms being obligate microaerophiles, since the cbb3 cytochrome oxidase has a very high affinity for oxygen, while bo type oxidases are thought to be most efficient in more oxic conditions (Han et al., 2011; Morris and Schmidt, 2013). Both ES-1 and ES-2 also encode cytochrome bd oxidases, which also have a high oxygen affinity, and could serve as terminal oxidases coupled directly to the quinone pool (Borisov et al., 2011). Finally, ES-1 and ES-2 both encode genes for a canonical bacterial ATP synthase coded in contiguous 8 gene clusters (Slit_2980 – Slit_2987 and Galf_2932 – Galf_2939, respectively). ES-1, alone, has a second bacteria/archaea ATP synthase. The subunits for this ATPase are in a contiguous gene cluster (Slit_2558 – Slit_2550). The genes for this latter ATPase share highest homology with an ammonia-oxidizing Nitrococcus spp. The advantage of having this second ATP synthase is not known.
Figure 4.
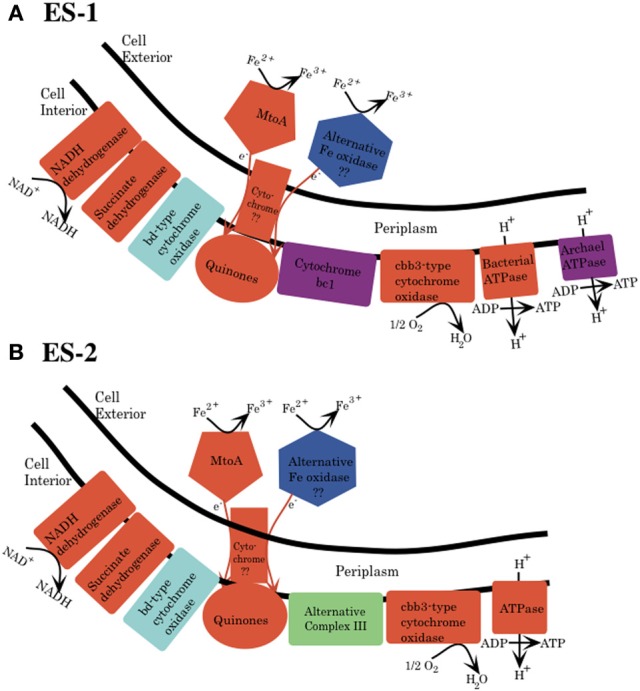
Schematic for electron transport from Fe(II) to the electron transport chain in the cytoplasmic membrane for both Sideroxydans ES-1 (A) and Gallionella ES-2 (B). This is based solely on genomic analysis. MtoA is shown as one possible protein that initiates oxidation of Fe(II) to Fe(III), and an alternative oxidase is also shown, but there is no specific candidate for this protein yet. The mechanism for transfer of electrons from the outer membrane to the cytoplasmic membrane is also unknown. (A) Cytochrome bc1 (purple) and archaeal type ATPase are found only in ES-1. (B) ES-2 lacks cytochrome bc1, and it is proposed that the ACIII could substitute this function. Both organisms have a bd-type cytochrome oxidase, which could interact directly with the quinones. The specific stoichiometry of proton flux across the cytoplasmic membrane is not understood and is not shown.
Sulfur oxidation
Sideroxydans ES-1 has a soxXYZAB gene cluster (Slit_1700 – Slit_1696), these genes share significant homology and gene order to the soxXYZAB genes in Thiobacillus denitrificans (Figure 5), and are generally thought to be involved in growth on sulfide or thiosulfate (Ghosh and Dam, 2009). In the same genomic region are 15 contiguous genes (Slit_1671 – Slit_1686) that encode for the alpha and beta-subunits of dissimilatory sulfite reductase, the dsrEFHC genes, and other genes that appear to be involved in lithotrophic S-metabolism (Ghosh and Dam, 2009). These genes share the same order and are highly homologous to a gene cluster in T. denitrificans, as well as sharing the same gene order with Allochromatium vinosum (DSM 180). The presence of these suites of S-oxidation genes suggest ES-1 should be able to grow by utilizing reduced S-compounds.
Figure 5.
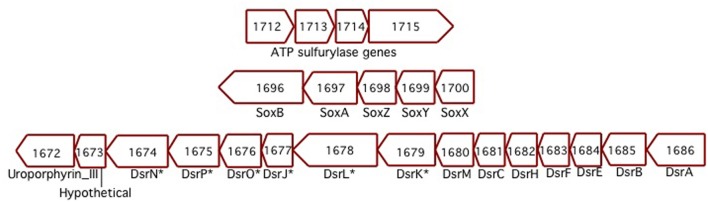
Three separate clusters of sulfur-oxidizing genes found in ES-1. The Dsr-homologs that are denoted with an * are respective gene designations that are listed only in Allochromatium. The numbers designate the IMG gene locus for ES-1, Slit_xxxx.
Although initial attempts to grow ES-1 on thiosulfate or sulfide were unsuccessful (Emerson and Moyer, 1997), a subsequent attempt to grow ES-1 on 5 mM thiosulfate in a mineral salts medium was successful (Figure 6). The doubling time (approximately 8 h) of cells growing on thiosulfate was about the same as cells grown on FeCl2, which is surprising since the free energy available from thiosulfate is several times greater than for Fe(II); (White et al., 2012). This implies Sideroxydans ES-1 is better adapted for growth on Fe(II) than reduced S-compounds; however the ability to grow on these compounds would give it a competitive advantage in ecosystems where reduced S-compounds were also present. Gallionella ES-2 does not possess S-oxidation pathways, nor does it show evidence for growth on reduced S compounds. A search of the literature and analysis of Genbank records did not reveal any evidence for Sideroxydans or Gallionellales environmental 16S sequences from S-rich freshwater habitats, e.g., caves or freshwater sulfureta, again suggesting S-oxidation is not a preferred metabolism for this group of organisms.
Figure 6.
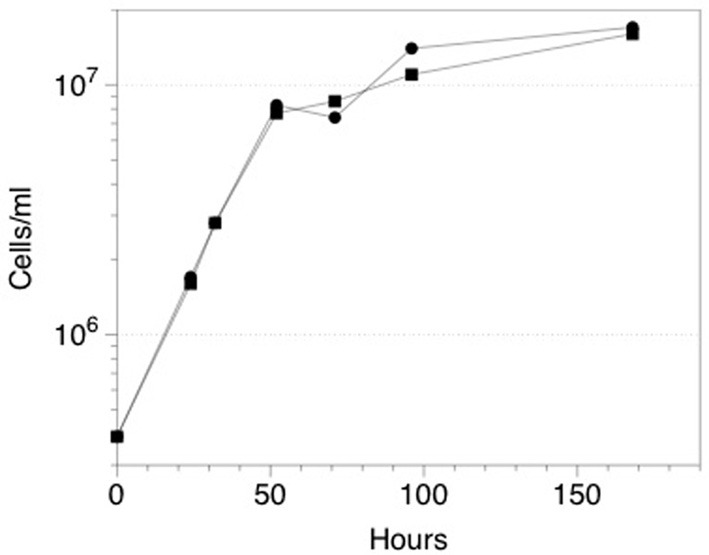
Growth of Sideroxydans ES-1 on 5 mM thiosulfate (•), or FeCl2 (▪). Each time point is the result of a duplicate sample, the standard error was 10–15% for each of the values; error bars are not shown to maintain clarity.
CO2 fixation
Both strains ES-1 and ES-2 contain ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (RubisCO) genes. Strain ES-1 has two large subunit RubisCO genes. One of these genes (Slit_0022) is in a 7 gene cluster with cbbQ, cbbO, fructose-1-6-bisphosphatase, and a carbonate dehydratase (likely a carbonic anhydrase). This 7 gene cluster is identical in gene order and composition to one in strain ES-2 (Galf_0034 – Galf_0040). This is the only RubisCO gene cluster in ES-2. While these Form II RubisCO proteins are homologous to other close relatives within the Betaproteobacteria, such as Thiobacillus denitrificans, they also share significant similarities to non-related microorganisms such as Hydrogenovibrio marinus and Mariprofundus ferrooxydans PV-1 (Figure 7).
Figure 7.
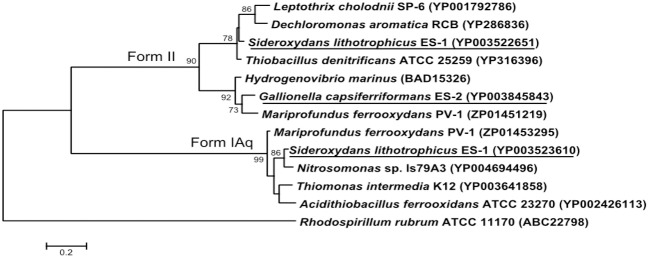
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of the Form II Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (RubisCO) large subunit proteins within S. lithotrophicus ES-1 (Slit_0022), and G. capsiferriformans ES-2 (Galf_0034), and the small subunit Form IAq gene from ES-1 (Slit_0968). Related Betaproteobacteria are also shown, but both RubisCO genes also share a closer than expected relationship with M. ferrooxydans PV-1. The Alphaproteobacteria Rhodospirillum rubrum represents the out-group and only bootstrap values above 50% are reported.
Sideroxydans ES-1 possesses a second large subunit RubisCO (Slit_0985) in a 5 gene cluster (Slit_0985 – Slit_0989) that includes a small subunit RubisCO (Slit_0986), cbbQ, cbbO, and a small (100aa) hypothetical protein. The large subunit of this RubisCO operon is most homologous with other chemolithoautotrophs including Nitrosomonas spp., Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, and M. ferrooxydans PV-1. The small subunit RubisCO is in the Form IAq RubisCO group (Badger and Bek, 2007), and is homologous to Thiobacillus spp., Nitrosomonas spp. and M. ferroxydans (Figure 7). This type of RubisCO is not known to be associated with carboxysomes, consistent with there being no evidence for carboxysome genes in ES-1, nor has transmission electron microscopy revealed any obvious carboxysome-like structures in these cells (Emerson and Moyer, 1997).
The Form I enzymes have a higher affinity for CO2 compared to O2, which would allow them to fix CO2 at higher O2 partial pressures than organisms with Form II only (Badger and Bek, 2007). In strictly microaerophilic microorganisms, Form II RubisCO may rarely see oxygen levels high enough to stimulate the oxygenase reaction compared to the CO2 fixation pathway. The fact that strain ES-1 has both Form I and Form II RubisCO, suggests it is more tolerant of fluctuating, and overall higher O2 levels, than strain ES-2.
Hemerythrins and globins
Hemerythrin and globin genes are found in many bacteria, and can be involved in oxygen-sensing and oxygen-binding. They may be also be involved in oxygen storage, oxygen-sensing, detoxification, or even the binding of iron or other metals (French et al., 2008). Both ES-1 and ES-2 have single-domain and multi-domain hemerythrin genes; however strain ES-1 has significantly more total hemerythrin genes than strain ES-2 (14 and 3, respectively; Table 2). This difference is attributed to the 11 single-domain hemerythrins that ES-1 possesses (ES-2 has only one). More specifically, ES-1 has 10 metal-binding hemerythrins, one type of single-domain hemerythrin, while ES-2 has none. Strain ES-1 also has significantly more total hemerythrin genes when compared to other circumneutral pH FeOB such as Leptothrix cholodnii SP-6 and Mariprofundus ferrooxydans PV-1 (5 and 2, respectively), Table 2. The only other organisms known to have as many metal-binding single-domain hemerythrins as ES-1 are magnetotactic bacteria such as Magnetospirillum magneticum, where these genes are believed to be important in aerotaxis (Bailly et al., 2008; French et al., 2008). Hemerythrins involved in the binding of oxygen typically have 6 specific hydrophobic amino acid residues that line the oxygen-binding pocket (French et al., 2008). Of the 10 metal-binding hemerythrins found in strain ES-1, 8 of them have all 6 of these conserved hydrophobic residues, suggesting they bind to O2. The HHE cation-binding single-domain hemerythrin genes (another type of single-domain hemerythrin) found in ES-1 and ES-2 does not have these conserved hydrophobic residues suggesting they may not bind O2, but could instead bind iron, or another metal. ES-1 and ES-2 also contain three and two multi-domain hemerythrins, respectively. These also contain conserved hydrophobic residues. Many of the multi-domain hemerythrins are found in gene clusters with large numbers of chemotactic and environmental sensing genes (see Table 2) suggesting they may likely be involved in oxygen-sensing in the environment.
Table 2.
Summary of hemerythrin-like protein types in circumneutral iron-oxidizing bacteria.
| Organism | Single-domain | Multi-domain | Total hemerythrin-like genes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metal-binding | HHE cation-binding | PAS/PAC | GGDEF | Histidine Kinase | Methyl-accepting chemotaxis | ||
| Sideroxydans lithotrophicus ES-1 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 14 |
| Gallionella capsiferriformans ES-2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Mariprofundus ferrooxydans PV-1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Leptothrix cholodnii SP6 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
Both strains ES-1 and ES-2 also contain genes for truncated hemoglobins (trHb), a short length hemoglobin often found in bacteria, which binds to O2. Strain ES-1 possesses a total of 4 trHb genes which is greater than the single globin gene found in most organisms with similar genome sizes (Vinogradov et al., 2006). The average genome size for organisms with four globin genes is 6.5 ± 1.9 Mb, more than double the genome size of strain ES-1 suggesting these globins are important for strain ES-1's survival. The four trHbs found in ES-1 represent two major types: trHbO (Slit_1261) and trHbN (Slit_1217, Slit_2374, Slit_2830). Strain ES-2 contains only one trHbO gene (Galf_2494). Due to differences in O2 binding efficiencies, it has been proposed that trHbO proteins are involved in O2 transport under microaerophilic conditions in other organisms while trHbN proteins may be part of a terminal oxidase or involved in nitric oxide detoxification (Pathania et al., 2002; Lama et al., 2006; Niemann and Tisa, 2008). Both strain ES-1 and ES-2 may use trHbO for improving O2 transfer efficiency of aerobic respiration under microaerophilic conditions. Interestingly, the trHbN proteins of strain ES-1 are more highly similar to those of M. ferrooxydans PV-1 (which also has three copies of trHbN and one copy of trHbO) than to other related Betaproteobacteria, suggesting either a common ancestor, or a strong common selective pressure for the genes from ES-1 and PV-1 (Figure 8). Both ES-1 and ES-2 have nitric oxide reductases suggesting the trHbN found in strain ES-1 is more likely a part of a terminal oxidase rather than involved in NO detoxification. Similarly, the trHbO protein from ES-1, ES-2, and PV-1 are all most similar to each other (~60% amino acid similarity), further demonstrating the potential importance of these oxygen-binding proteins for FeOB that live under microaerophilic conditions with high concentrations of Fe(II).
Figure 8.
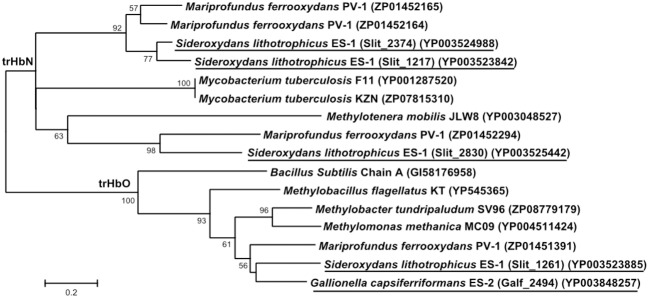
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of truncated hemoglobin (trHb) proteins showing the close relationship of Sideroxydans lithotrophicus ES-1, Gallionella capsiferriformans ES-2, to Mariprofundus ferrooxydans PV-1, and compared to reference organisms, and other related Betaproteobacteria. Only bootstrap values above 50% are reported.
Why strain ES-1 has so many hemerythrin and globin genes remains unknown. It is quite likely that these genes are involved in oxygen-sensing in the environment as has been suggested for magnetotactic bacteria (Bailly et al., 2008; French et al., 2008). Another intriguing hypothesis is that ES-1 could use these proteins to store oxygen and then grow by Fe-oxidation under anoxic conditions. This would allow it to access higher Fe(II) concentrations in anoxic water, or continue to oxidize Fe(II) under conditions where O2 concentrations fluctuated between oxic and anoxic. Alternatively, these genes may play a part in the overall strategy that ES-1 utilizes to protect itself from significant fluctuations in environmental oxygen concentrations, by either binding excess O2 in the cytoplasm or Fe(II) and limiting the production of reactive oxygen species. If it is more commonly exposed to these types of fluctuations or is just more sensitive to them is unclear; however, in either case this could explain why ES-1 has so many more of these genes compared to ES-2.
Motility, chemotaxis, and environmental sensing mechanisms
Both Sideroxydans ES-1 and Gallionella ES-2 have significant percentages of genes involved in environmental sensing and signal transduction. ES-1 has 9.3% of its genes in the COG category, signal transduction mechanisms, while ES-2 has 11.6% of its COGs in this category. These numbers are higher than for other Betaproteobacteria like the methylotrophs, Methylotenera spp. (8%), and Methylobacillus flagellatus (6.4%), or ammonia-oxidizing Nitrosomonas spp. (5%) They are also substantially higher than the 7% average for signal transduction genes estimated for marine copiotrophs, and nearly triple the 3.6% average for oligotrophic marine microbes as reported by Lauro et al. (2009). These COG percentages are similar to the Fe-reducing Geobacter spp. (around 10%), and a little lower than some magnetotactic bacteria (around 12.5%) that live in redox stratified environments.
The 10 most abundant COGs in ES-1 and ES-2 are listed in Table 3. In ES-1 seven of these COGs are involved in signal transduction, chemotaxis, or some type of environmental sensory response, while in ES-2, eight of the top 10 COGs are related to these activities. They share six of these top 10 COGs in common, all related to sensory genes. COGs 5002 and 2199 that encode for GGDEF and EAL domains in sensory proteins account for 43 genes in ES-1, and 46 genes in ES-2. Of the 2366 genomes listed in IMG at the time of this study that contain COG 2199, only 42 genomes have a greater number of these genes than ES-2; 19 of these are from Vibrio spp. that all have significantly larger genomes than ES-2. Other genomes with high numbers of COG2199 include sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in the Epsilonproteobacteria, including Campylobacterales sp. GD1 (54 genes), and Sulfuricurvum kujiense YK-1 (38 genes). These chemolithoautotrophic S-oxidizers also thrive in redoxicline habitats. GGDEF domains control synthesis of the secondary messenger cyclic di-GMP (C-di-GMP) by diguanylate cyclase, while the EAL domain is responsible for degradation of C-di-GMP through phosphodiesterase activity (Römling, 2011). Through their actions with C-di-GMP these domains are involved in eliciting physiological responses to a variety of external signals including oxygen, and nutrient starvation, as well as controlling cellular behavior and differentiation between sessile, e.g., biofilm formation, and motile states (Jenal and Malone, 2006). The majority of work on these signaling systems has been done on a few model organisms, mostly in relation to virulence, and it is likely they respond to many more environmental signals that have yet to be identified (Jenal and Malone, 2006).
Table 3.
Ten most abundant COGs in ES-1 and ES-2.
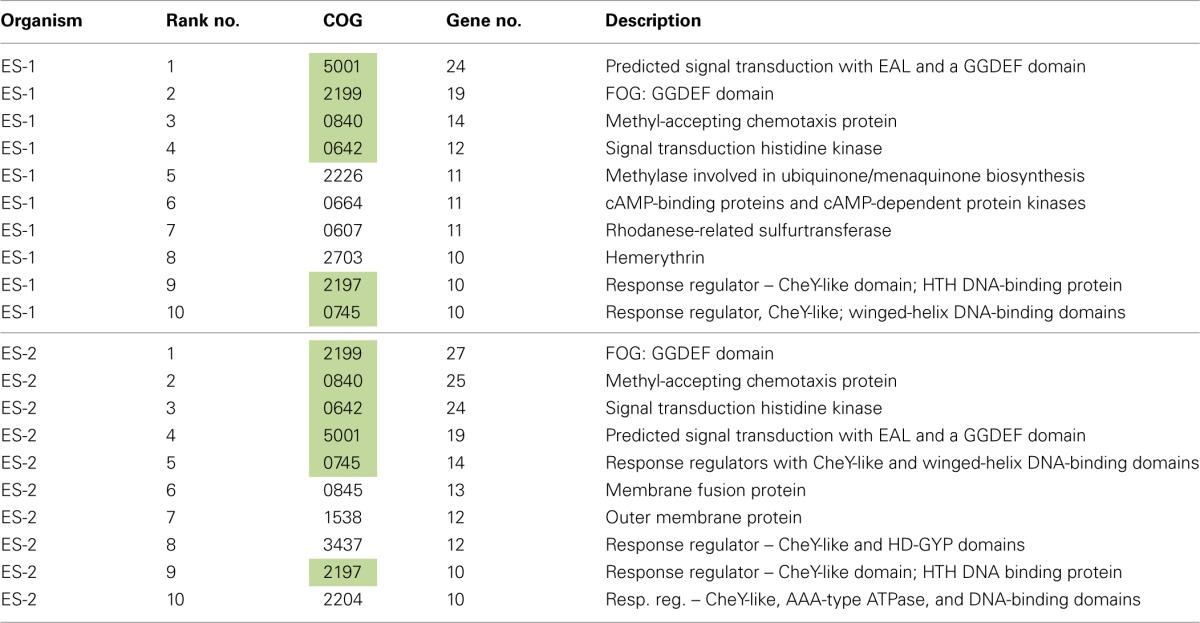
Shaded COGs are present in both organisms.
Histidine kinases (HK) are another class of enzymes that are known to play an important role in environmental signaling and gene regulation (White et al., 2012). ES-1 has 37 HK genes, and ES-2 has 47. These numbers place them in the top 10% for HK gene abundance among currently sequenced bacterial genomes. While there is overlap in their HK genes, there are also differences in the types of HKs the two organisms possess. ES-1 has 17 (46%) of its HK genes associated with two component regulatory systems, including 7 luxR family proteins, as well as three CheA HK's. ES-2 has five CheA HK's, but only 30% (14 genes) of its HK's are associated with two component regulatory systems, with three of these belonging to the LuxR family. For ES-2, 38% of its HK's are associated with other types of sensor elements that include unidentified regulatory response receivers, PAS/PAC type sensors, and others. Thus, it appears that while HK's must play an important role in extracellular sensing and gene regulation for both organisms, different signaling mechanisms and types of response may be elicited by the HK's.
The most well-understood behavioral trait among bacteria is the ability to produce flagella, and control motility to track gradients of chemo-attractants or chemo-repellents (Hazelbauer et al., 2008). In growing cultures of Sideroxydans ES-1 and Gallionella ES-2 motility is a variable trait, at certain times motile cells are observed; but are not always present, and as yet, motility has not been shown to correspond with any particular phase of growth for either organism. Consistent with the observation of motile cells, both strains contain nearly complete sets of flagellar genes. In ES-2 these are encoded in contiguous gene clusters (Galf_1042 – Galf_1079), while in ES-1 there are two separate clusters (Slit_0562 – Slit_0575 and Slit_0568 – Slit_0599) in close proximity to one another.
Both ES-1 and ES-2 will grow as distinct bands in opposing gradients of oxygen and Fe(II), and appear to be able to track these gradients (Druschel et al., 2008), suggesting they are tactic to O2 and/or Fe(II). Specific chemotaxis assays have not been done for either strain, however both organisms contain full complements of chemotaxis genes. ES-2 has redundant copies of most chemotaxis genes, including five cheA histidine kinase genes; six cheW genes, four cheZ genes, and 2 cheY genes that control flagellar switching (Porter et al., 2011). ES-1 has fewer total chemotaxis genes, but still has redundant copies of cheA(2), and cheY(2). ES-2 has 25 methyl-accepting chemotaxis genes (MCPs), while ES-1 has 14 MCPs. The MCPs are known to act as chemoreceptors that bind specific attractants or repellents and initiate a tactic response through coordination with Che genes (Hazelbauer et al., 2008). These are relatively large numbers of MCPs, for example, Escherichia coli has 5 chemoreceptors while Pseudomonas aeruginosa has 26 receptors, but its genome is twice the size of ES-2 (Porter et al., 2011). In terms of responding tactically to oxygen (Taylor et al., 1999), ES-2 has three aerotaxis (aer) genes (Galf_0774, Galf_1969, and Galf_2093), while ES-1 has one aer gene (Slit_0546).
Overall, both organisms have a rich complement of genes for environmental sensing, motility, and chemotaxis, indicating that they are capable of an array of behavioral and physiological responses for adapting to a dynamic environment. The signaling pathways implied by these families of genes are complex, and based on studies of model organisms could include chemotaxis-like pathways that are involved in processes like biofilm formation or other behaviors (Porter et al., 2011). Members of the Fe-reducing Geobacteraceae also contain large numbers of MCPs as well as redundant sets of chemotaxis genes that are thought to play multiple roles in how these organisms sense and metabolize iron (Tran et al., 2008).
Pilin- related genes
Pili are proteinaceous extracellular filaments that are attached as hair-like projections to the cell surface. They are found in a wide variety of bacteria and archaea, and have diverse functions that include: colonization and attachment to surfaces (including to other bacteria), secretion of exoproteins, as well as twitching motility, which allows bacteria to “crawl” along surfaces (Giltner et al., 2012). Pili contain a central pilin protein and suite of other proteins involved in processing and anchoring the structures in the membrane (Pelicic, 2008; Giltner et al., 2012). Both ES-1 and ES-2 have the genetic capacity to produce Type IVa pili. Both encode a PilMNOPQ inner membrane complex that is immediately upstream of three additional conserved genes found in this gene cluster (Pelicic, 2008), and immediately downstream of a penicillin binding protein that is also conserved (Figure 9). A second cluster of six pilin genes, pilM/fimT/pilVWXY, is found in both organisms. The chromosomal arrangement of the gene clusters is different between ES-1 and ES-2. In ES-2, both pilin gene clusters are adjacent to one another, but transcribed in opposite directions (Figure 9) while in ES-1, the two gene clusters are in different regions of the chromosome. Furthermore, ES-1 contains a second pilM/fimT/pilVWXY gene cluster that is not present in ES-2. This cluster is only weakly paralogous to the cognate gene cluster in ES-1, and is most homologous to pilin genes in Cupriavirdis spp. and Ralstonia spp. (in the Burkholderiales), Figure 9.
Figure 9.
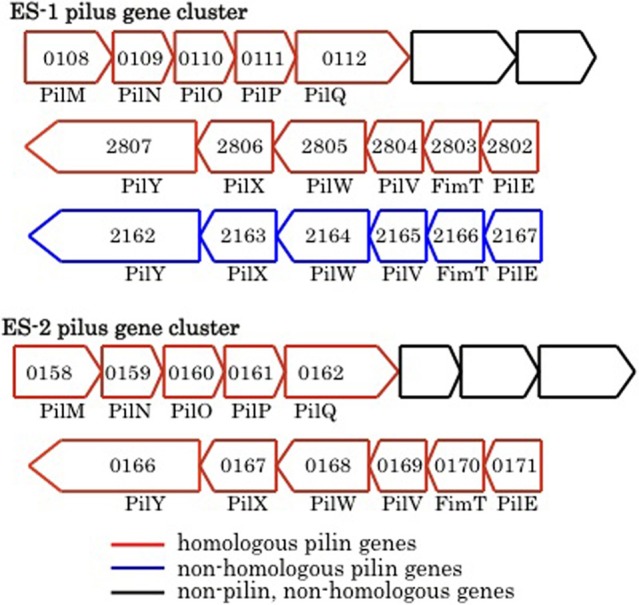
Major groups of pilin-related genes found in ES-1 and ES-2. The numbers inside the arrows are the IMG locus tags only for the respective genes that are homologs of pilin genes.
Both ES-1 and ES-2 contain homologous gene clusters to the MSH genes that encode another Type IVa pilus structure (Taylor and Marsh, 1999). These two gene clusters are well-conserved between the two organisms, but have undergone a significant gene rearrangement compared to the homologous gene clusters in Pseudoalteromonas tunicata and Vibrio cholera (data not shown). In P. tunicata, it is proposed that this set of pilin genes allows for attachment to eukaryotic algal cells (Dalisay et al., 2006); however their function in the FeOB is unknown. In addition, both ES-1 and ES-2 contain PilT (Slit_1759 and Galf_2682) and PilU (Slit_1760 and Galf_1683) that encode for pili known to be involved in twitching motility (Jarrell and McBride, 2008).
The role of pili in ES-1 and ES-2 maybe multifaceted. They could help in colonizing surfaces as a way to maintain spatial position within gradients of Fe(II) and O2, or promote cell–cell contact. A motility mechanism like twitching could also help the cells escape encrustation from Fe-oxides that are deposited around the cells as a result of their metabolism. In Geobacter spp. type IVa pili have been shown to be conductive via associated cytochromes, and play a role in extracellular electron transfer during anaerobic respiration coupled to Fe-reduction or transfer of electrons to the solid surface of an anode (Lovley, 2011). The pili-related proteins, including the primary pilin protein formed by the FeOB, are only weakly homologous to the pili proteins formed by Geobacter. At present it is not known if they could play any role in energy conservation from Fe-oxidation.
Nitrogen fixation (nif) genes
Sideroxydans possesses three clusters of nif genes. These have the potential to encode for an FeMo type nitrogenase (White et al., 2012). The first cluster (Slit_0832 – Slit_0837) includes nifB and nifQ that are involved in biosynthesis of the iron-molybdenum cofactor in the active site of nitrogenase. The second cluster (Slit_0881 – Slit_0888) includes the nifH, nifD, and nifK genes that encode the major subunits of nitrogenase, as well as nifT (aka fixT), a short polypeptide thought to be involved in biosynthesis (Dixon and Kahn, 2004). The third cluster (Slit_0903 – Slit_0910) contains genes involved in synthesis of Fe-Mo cofactor in active nitrogenase and includes nifE, nifN, and nifX. Immediately adjacent to this gene cluster are five genes (Slit_0895 – Slit_0899) that are involved in molybdenum transport via the molybdate ABC transporter. While ES-1 is capable of growth in medium with no added N-source; its ability to fix N2 or express nitrogenase genes under N-limited conditions has not been tested. Gallionella ES-2 does not possess nitrogen fixation genes. The capacity to fix N2 would provide ES-1 with the ability to occupy niches depleted in N and provide a competitive advantage over organisms like ES-2 that cannot fix N2.
Oxygen defense
A potentially significant problem for bacteria growing in an oxygenated environment with high Fe(II) concentrations is that the reaction of hydrogen peroxide with Fe(II) (often referred to as Fenton chemistry) can produce highly reactive oxygen species (Imlay, 2008). The production of catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) are common defense mechanisms microbes employ to prevent production of reactive oxygen species. Sideroxydans ES-1 has a single catalase gene (Slit_0713). ES-2 has a heme-peroxidase (Galf_1411) that can presumably act as either a catalase or peroxidase. In addition ES-2 has a di-haem cytochrome c peroxidase (Galf_1894) and a second di-haem peroxidase (Galf_2287). None of these genes have homologs in ES-1. Both strains have a single manganese/iron type SOD gene (Galf_2442; Slit_2312) that share high homology to one another. Many aerobic bacteria have multiple forms of SOD, so it is perhaps a little surprising that these FeOB seem to have a fairly minimal defense against toxic oxygen species. As observed above, it is also possible the abundance of hemerythrins and truncated hemoglobins could help reduce or control intracellular O2 concentrations.
Metal sensitivity
Environments that have the high Fe(II) concentrations required to support the growth of FeOB, may also have relatively high concentrations of other metals and metalloids, including those that may be toxic. Gallionella ES-2 has a suite of mercury resistance genes, merTPF (Galf_1897-99) and merA (Galf_1900), indicating it is resistant to mercury (Barkay et al., 2003). The mercury resistance genes are not present in ES-1. ES-2 also has a cluster of five genes involved in arsenic resistance arsRCDA and the arsenical resistance protein ACR3 (Galf_2398 – Galf_2394; Rosen, 2002). ES-1 has arsR (Slit_0995), an arsC homolog (Slit_0996), and an ACR3 (Slit_0997) homolog, but lacks arsA and arsD. In terms of metal efflux capacity, ES-2 has 8 genes listed as members of the CzcA family of heavy metal efflux pumps. These are members of the cation diffusion facilitator (CDF) family of proteins that are responsible for removal of toxic metals like cadmium, cobalt, silver, zinc, and copper from the cytoplasm (Haney et al., 2005). In addition, ES-2 has five gene products related to acriflavin resistance genes, these are broad substrate efflux systems for the removal of antibiotics, detergents, and other potentially deleterious small organic molecules. All of these genes (both CDFs and acriflavin resistance) are associated with genes for the energy-dependent RND family of efflux transporters (Haney et al., 2005). In ES-1 there are only two czcA genes and two acriflavin resistance genes. Thus, it appears that Gallionella ES-2 is better equipped to deal with metals and other environmental toxicants in its environment, which would provide it with an advantage in waters with higher overall concentrations of metals, metalloids, or organic compounds that are hazardous to the cell.
Polysaccharide synthesis
Neither Sideroxydans ES-1 or Gallionella ES-2 produce unique extracellular structures, such as sheaths or stalks that are often associated with neutrophilic FeOB, and are thought to help prevent the cells from becoming encrusted in Fe-oxyhydroxides. In order to help prevent encrustation, it is speculated that these cells may produce an uncoordinated exopolymer, most likely composed of a polysaccharide (Emerson and Moyer, 1997; Chan et al., 2009). Analysis of the two genomes reveals that in ES-2 there are two large clusters of genes that may be involved in polysaccharide synthesis and exopolymer production. One cluster has 41 contiguous genes (Galf_2851 – Galf_2817) that includes 9 glycosyl transferases and 6 epimerase/dehydratases and two genes annotated as homologs of polysaccharide biosynthesis genes (CapD; Galf_2833 and Galf_2823). Another cluster of 26 genes (Galf_1266 – Galf_1292) have the potential to be involved in exopolymer synthesis. This includes a polysaccharide export gene (Galf_1266), 6 glycosyl transferases, as well as a sulfotransferase (Galf_1285) suggesting the possibility for substituated polysaccharides. By comparison, ES-1 has one large cluster of 26 contiguous genes that appear to be involved in exopolymer synthesis (Slit_2879 – Slit_2904). There are 8 glycosyl transferase genes, at least 3 epimerase/dehydratase genes, and 2 polysaccharide biosynthesis genes in addition to other genes consistent with polysaccharide production. Interestingly, despite encoding for genes that may share functional overlap, the overall gene homology between the ES-1 and ES-2 gene clusters is low. ES-2 and ES-1 have other gene clusters/pathways involved in biosynthesis of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and peptidoglycan, so it seems likely that these gene clusters may be involved in EPS production rather than production of cell wall structural glycosides.
In addition to the EPS gene clusters described above, Gallionella ES-2 has at least 15 genes that are associated with cellulose production that are not present in ES-1. The cellulose genes are organized into two separate clusters. One cluster, starting with Galf_0480 has seven genes identified as involved in cellulose biosynthesis, and also includes two genes (Galf_0486 and Galf_0487) that are homologs of algJ and algF, genes involved in alginate biosynthesis. A second cluster (Galf_2424 – Galf_2435) has 10 genes involved in cellulose biosynthesis; however one of these (Galf_2432), an 1179aa cellulose synthase gene is interrupted by a transposon that could disrupt the functionality of cellulose production. Direct testing of cellulose production by ES-2 has not been done.
Secretion and transporters
The Sideroxydans ES-1 genome encodes a type II secretion system (Douzi et al., 2012). The first three genes of this 15 gene cluster (Slit_0506 – Slit_0489), starting with a TonB-like gene share homology and gene order with three genes in ES-2 that encode for an ABC-type transporter; the remaining genes encode for type II secretion proteins CDEFGHIJMN. ES-2 does not possess these type II secretion homologs. Nitrospira multiformis has a cognate set of genes that, on average, share the greatest homology with the genes in ES-1. Neither ES-1 nor ES-2 have evidence of Type III, IV, V, or VI secretion systems based on analysis of KEGG pathways.
Both organisms have the iron transport genes feoA (Slit_2291 and Galf_2202) and feoB (Slit_2292 and Galf_2203) (Kammler et al., 2003). FeoA is a small soluble SH3-domain protein, probably located in cytosol, while FeoB is a large inner membrane bound protein thought to act as a permease for Fe(II) (Cartron et al., 2006). Homologs of FeoC, a transcriptional repressor, are not found in either strain; however both strains do possess the Fur-type iron regulatory genes. ES-1 has one Fur family gene (Slit_2531) and ES-2 has three Fur genes (Galf_0862, Galf_2181, and Galf_2385) that are all paralogs.
ABC transporters are present in both ES-1 and ES-2 for sulfonate/nitrate/taurine, phosphate, branched-chain amino acids, and nickel. ES-2 has an ABC transport systems for sulfate and phosphonate that are not present in ES-1, and ES-1 has transporters for molybdate and spermidine/putrescine that are not present in ES-2. Neither organism has ABC transporters identified for any types of sugars, consistent with their inability to utilize carbohydrates for growth.
Genes for phage and genetic recombination
There are two large clusters of phage genes within the chromosome of Sideroxydans ES-1 that presumably encode for a prophage. The first cluster (Slit_0188 – Slit_0249; 39.7 kb) has a putative phage repressor gene followed by 63 genes all transcribed in the same direction; 37 are either hypotheticals or proteins of unknown function. This cluster ends with a Mu-like prophage protein coupled with a DNA methyltransferase. Remarkably, within this cluster are 28 genes that share homology with genes in a putative prophage in M. ferrooxydans PV-1 (Figure 10). Sixteen of these genes are hypotheticals, or are of unknown function, and 12 are identified as phage related, most often belonging to the broad host-range Mu family of phage. The overall relatedness, both by homology and gene order, suggests that it is possible that phage-mediated gene exchange between Mariprofundus and Sideroxydans occurred at some point in the past. It is unlikely that a freshwater Fe-oxidizer from Michigan and a marine Fe-oxidizer from the central Pacific have been in close proximity in the recent past. Nonetheless, a recent study looking at the distribution of marine and freshwater Fe-oxidizers along a salinity gradient did find that Sideroxydans-related freshwater FeOB did overlap with members of the Zetaproteobacteria that include M. ferrooxydans, suggesting ancestors of these organisms could have overlapped in the past (McBeth et al., 2013).
Figure 10.
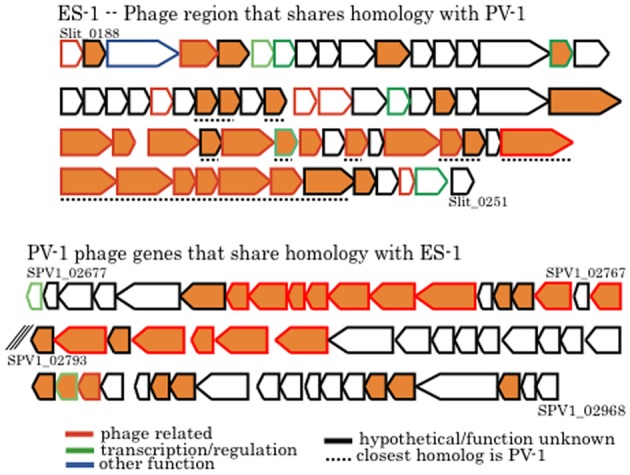
Comparison of phage genes between Sideroxydans ES-1 and M. ferrooxydans PV-1. The line outlining the arrow is color coded to designate putative gene function as denoted. All orange colored genes share homology between the two organisms. Numbers denote IMG gene loci; the back slashes in the PV-1 gene cluster indicate a break between two contigs.
The 2nd cluster of phage-related genes in ES-1 (Slit_1888 – Slit_1969; 54.3 kb) begins with a hypothetical, adjacent to a 16S–23S rRNA gene cluster, and has 82 genes, 67 of which are hypothetical or of unknown function. None of these phage genes have homologs with either PV-1 or ES-2, nor do they share identity with the Mu phage. ES-2 appears to have one putative prophage with 22 genes (Galf_2020 – Galf_2041; 18.9 kb) composed mostly of hypotheticals as well as several phage-related genes. None of these genes share significant identity with ES-1 or PV-1, nor do they appear to be in the phage Mu family. Neither of the two strains have identified CRISPR sequences.
The ES-2 genome has 21 genes listed as either integrase family proteins or phage integrases, and 25 transposase genes, in contrast the ES-1 genome has only three integrases and three transposases. ES-2 has a cluster of seven genes (Galf_0939 – Galf_0945) that include the tra genes encoding, TraF, TraI, TraU, TrbC, and TraN that are involved in synthesis of the sex pilus; however there is no evidence that ES-2 contains a conjugative plasmid. ES-1 does not possess any cognate tra genes. Together these results suggest there is greater plasticity in ES-2 genome for genetic exchange and recombination events than in ES-1.
Summary of genomics
Comparative genomics of these two organisms confirms their overall phylogenetic relatedness and reveals functional similarities, in terms of both physiology and behavior (Figure 11). This work provides further clues for the activity of cytochrome systems being involved in conservation of energy from Fe(II) oxidation by these organisms. It also confirms the unlikelihood of there being a universally conserved set of proteins involved in Fe-oxidation among lithotrophic Fe-oxidizing bacteria. It also points up important differences between these two organisms in terms of potential niche separation, and raises intriguing questions about possible mechanisms they may use to oxidize Fe(II). Important differences include the capacity of Sideroxydans ES-1 to grow on thiosulfate, and to fix nitrogen. These physiological adaptations would give it an advantage over Gallionella ES-2 under N-limiting conditions, or in the presence of reduced S-compounds. On the other hand, ES-2 appears to be more tolerant of potentially toxic metals, which may be relatively common in high iron environments. It also is capable of producing a more varied array of exopolymers than ES-1, although the function of these is unknown they could confer advantages in preventing the cells from encrustation in Fe-oxides, or help it establish and maintain position within a gradient. Perhaps related to this is the even greater number of sensory genes that ES-2 has compared to ES-1. ES-2 may be more restricted to low O2 conditions than ES-1 based on its possessing fewer hemerythrins and globins, as well as the lack of a Form I type RubisCO. Nonetheless, both of these organisms are uniquely adapted for growth on Fe(II) in freshwater redoxicline habitats.
Figure 11.
Summary of genomic analysis of Sideroxydans ES-1 and Gallionella ES-2. Features shown in purple in ES-2 are for functions only found in ES-2, while functions shown in green in ES-1 are not found in ES-2. In some cases, e.g., metal efflux systems, the number of features is representative of the relative abundance of the genes in the two organisms.
Taxonomic descriptions
While Sideroxydans ES-1 and Gallionella ES-2 share a common metabolism in Fe-oxidation, and were isolated from the same habitat (Emerson and Moyer, 1997), the comparative analysis presented here indicates they are very different organisms that warrant separate genus and species designations. In addition to the characteristics described above that differentiate them, they are distinguished by morphology; Sideroxydans ES-1 is a thin, often vibrio shaped cell, while Gallionella ES-2 is a thicker and shorter, bean-shaped cell. Interestingly, although both organisms have gram-negative cell walls when viewed by TEM (Emerson and Moyer, 1997), they both stained gram positive when treated by conventional gram reagents following removal of Fe-oxides by treatment with either hydroxylamine or oxalic acid. To confirm this a fluorescent dye method (Mason et al., 1998) was employed on live cells (both log and stationary phase) with the same gram-positive result. The results of FAME analysis for the two strains are included in Table 4, where primary differences are in the relative abundances of the 16:0 and 18:1 w9c fatty acids.
Table 4.
Comparison of FAME profiles for Sideroxydans ES-1, and Gallionella ES-2.
| Fatty acid | ES-1Ta | ES-2T |
|---|---|---|
| 10:0 3OH | 5.6% | 3.5% |
| 12:0 | 4.0 | 0 |
| 14:0 | 3.2 | 3.2 |
| 16:0 | 30.8 | 15 |
| 18:1 w9c | 5.0 | 11.4 |
| 18:1 w7c | 4.2 | 0 |
| 18:0 | 7.1 | 11.7 |
| 15:0 ISO 2OH/16:1w7cb | 32.6 | 55.2 |
Fatty acids that comprised <3% of total are not shown; total shown = 92.5%.
The FAME analysis could not distinguish between these two fatty acids; they are reported together as “summed in feature 3”.
The comparative phylogenetic analysis presented here lend further support to the proposal that these two organisms and related lithotrophic FeOB belong in a novel order of the Betaproteobacteria, the Gallionellales (Weiss et al., 2007). A summary of the primary taxonomic characteristics of both strains is compared in Table 5 along with the other isolates of FeOB that belong to the Gallionellales.
Table 5.
Characteristics of Fe-oxidizers in the Gallionellalesa.
| Sideroxydans ES-1 | Gallionella ES-2 | Sideroxydans R-1 | S. paludicola | G. ferruginea | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolation source: | Groundwater | Groundwater | Wetland | Rhizosphere | Groundwater | |||||
| Geographic location: | Michigan, USA | Michigan, USA | Delaware, USA | Virginia, USA | Sweden | |||||
| Morphology: | Helical rod | Curved rod | Curved rod | Helical rod | Curved rod | |||||
| Biogenic oxide type: | Particulate | Particulate | Stalk | Particulate | Stalk | |||||
| Cell diameter: | 0.32 μm | 0.73 μm | 0.35 μm | 0.42 μm | ||||||
| Motile: | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Microaerophilic: | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Substrate utilization: | ||||||||||
| Fe(II) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Thiosulfate | Yes | No | No | No | No | |||||
| Other lithotrophy | No | No | No | No | No | |||||
| Organic matter | No | No | No | No | Yesb | |||||
| Fe(II) doubling time | 8 | 12 | 15 | 15.8 | 10 | |||||
| Growth Temperature: | ||||||||||
| 6°C | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | |||||
| 30°C | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | |||||
| pH optimum | 6.0–6.5 | 6.0-6.5 | 5.6–6.1 | 6.0–6.5 | Unknown | |||||
| pH range | 5.5–7.0 | 5.5–7.0 | 5.6–7.0 | 4.5–7.0 | 5.0–6.5 | |||||
| Reference | This work | This work | Krepski et al., 2012 | Weiss et al., 2007 | Hallbeck et al., 1993 | |||||
This table only includes isolates separated by ≥3% DNA sequence divergence in the SSU rRNA gene.
Based on uptake of 14C-labled glucose (Hallbeck and Pedersen, 1991).
Description of Sideroxydans lithotrophicus sp. nov.
Sideroxydans lithotrophicus (li.tho.tro'phi.cus. Gr. n. lithos stone; Gr. adj. trophikos consuming; Gr. masc. adj. lithotrophicus one that feeds on inorganic substrates).
This organism was isolated from an iron-mat formed in Fe(II)-containing groundwater in Michigan. The cell morphology is that of a short to medium length curved rod with a diameter of 0.2–0.3 μm that exhibits a gram-negative cell-wall by TEM, but stains gram-positive. Ferrous iron is the preferred growth substrate for this organism, although growth was also observed on thiosulfate as sole electron donor; no growth was observed on H2, or NH3, and heterotrophic growth was not observed. During growth particulate iron oxyhydroxides of no determinate shape are precipitated; the cells are associated with these oxides and are often only visible by epifluorescence microscopy. The pH range for growth is between 5.5 and 7.5 with an optimum between pH 6.0 and 6.5. The temperature range for growth was between 10°C and 35°C; the optimal growth temperature is 30°C. The cells are oxidase and catalase negative based on spot tests. The major fatty acids are 10:0 3OH, 16:0, 18:1 w9c, 18:0. The G+C content was 57.5%, and the genome size is 3.0 Mb. The type strain ES-1T (=ATCC 700298T; JCM 14762; DSMZ 22444; NCMA B100) was isolated from Michigan groundwater.
Description of Gallionella capsiferriformans sp. nov.
(cap.si.ferri.for.mans L. n. capsa, a box, and in bacteriology a capsule; L. n. ferrum, iron; L. part. adj. formans, forming, building; N.L. part. adj. capsiferriformans, an organism that forms a capsular-like precipitate of Fe-oxide).
This organism was isolated from an iron-mat formed in Fe(II)-containing groundwater in Michigan. Cells are curved or bean-shaped (~0.8 μm in diameter) and exhibit a gram-negative cell wall by TEM, but stain gram-positive. The cells are motile. The only confirmed energy source is ferrous iron; no growth was observed on reduced S species, H2, or NH3. Heterotrophic growth was not observed. During growth particulate iron oxyhydroxides of no determinate shape are precipitated; the cells are typically associated with these oxides and are often only visible by epifluorescence microscopy. This distinguishes this species from Gallionella ferruginea which forms a distinctive helical-shaped stalk. Growth on Fe(II) is O2-dependent and the cells are microaerophilic and appear to be aerotactic. The pH range for growth is between 5.5 and 7.5 with an optimum between pH 6.0 and 6.5. The temperature range for growth was between 4°C and 30°C. The major fatty acids are 16:0, 18:1 w7c, and 18:0. The G+C content was 52.7%, and the genome size is 3.0 Mb. The type strain for the species is ES-2T (=ATCC 700299T; JCM 14763; DSMZ 22445; NCMA B101).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Cynthia Lydell and Melissa Floyd for preparation of DNA from the two strains, and Dr. Jeremy Rentz for help with some of the taxonomic work, and Paul Krader for performing FAME analysis. Eleanora French and Audrey Lyman are appreciated for help with gene annotation. This work was supported in part by NASA EPSCoR funding to the Maine Space Grant Consortium and the NSF (IOS 0951077). The work conducted by the U.S. Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231.
References
- Badger M. R., Bek E. J. (2007). Multiple rubisco forms in proteobacteria: their functional significance in relation to CO2 acquisition by the cbb cycle. J. Exp. Bot. 59, 1525–1541 10.1093/jxb/erm297 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly X., Vanin S., Chabasse C., Mizuguchi K., Vinogradov S. N. (2008). A phylogenomic profile of hemerythrins, the nonheme diiron binding respiratory proteins. BMC Evol. Biol. 8:244 10.1186/1471-2148-8-244 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkay T., Miller S. M., Summers A. O. (2003). Bacterial mercury resistance from atoms to ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 27, 355–384 10.1016/S0168-6445(03)00046-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett S. (2004). Solexa Ltd. Pharmacogenomics 5, 433–438 10.1517/14622416.5.4.433 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird L., Bonnefoy V., Newman D. K. (2011). Bioenergetic challenges of microbial iron metabolisms. Trends Microbiol. 19, 330–340 10.1016/j.tim.2011.05.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy V., Holmes D. S. (2011). Genomic insights into microbial iron oxidation and iron uptake strategies in extremely acidic environments. Environ. Microbiol. 14, 1597–1611 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02626.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisov V. B., Gennis R. B., Hemp J., Verkhovsky M. I. (2011). The cytochrome bd respiratory oxygen reductases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1807, 1398–1413 10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.06.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruun A. M., Finster K., Gunnlaugsson H., Nornberg P., Friedrich M. W. (2010). A comprehensive investigation on iron cycling in a freshwater seep including microscopy, cultivation and molecular community analysis. Geomicrobiol. J. 27, 15–34 10.1080/01490450903232165 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cartron M. L., Maddocks S., Gillingham P., Craven C. J., Andrews S. C. (2006). Feo - transport of ferrous iron into bacteria. Biometals 19, 143–157 10.1007/s10534-006-0003-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. S., Fakra S., Edwards D. C., Emerson D., Banfield J. F. (2009). Iron oxyhydroxide mineralization on microbial polymers. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 73, 3807–3818 10.1016/j.gca.2009.02.036 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Coursolle D., Gralnick J. A. (2012). Reconstruction of extracellular respiratory pathways for iron(III) reduction in Shewanella oneidensis strain MR-1. Front. Microbiol. 3:56 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00056 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalisay D. S., Webb J. S., Scheffel A., Svenson C., James S., Holmstrom C., et al. (2006). A mannose-sensitive haemagglutinin (MSHA)-like pilus promotes attachment of Pseudoalteromonas tunicata cells to the surface of the green alga Ulva australis. Microbiology 152, 2875–2883 10.1099/mic.0.29158-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R., Kahn D. (2004). Genetic regulation of biological nitrogen fixation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2, 621–631 10.1038/nrmicro954 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douzi B., Filloux A., Voulhoux R. (2012). On the path to uncover the bacterial type II secretion system. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 367, 1059–1072 10.1098/rstb.2011.0204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druschel G. K., Emerson D., Sutka R., Suchecki P., Luther G. W., 3rd. (2008). Low oxygen and chemical kinetic constraints on the geochemical niche of neutrophilic iron(II) oxidizing microorganisms. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 72, 3358–3370 10.1016/j.gca.2008.04.035 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth O. W., Holmstrom S. J. M., Pena J., Sposito G. (2009). Biogeochemistry of iron oxidation in a circumneutral habitat. Geology 260, 149–158 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.027 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson D. (2012). Biogeochemistry and microbiology of microaerobic Fe(II) oxidation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 40, 1211–1216 10.1042/BST20120154 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson D., Fleming E. J., McBeth J. M. (2010). Iron-oxidizing bacteria: an environmental and genomic perspective. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 64, 561–583 10.1146/annurev.micro.112408.134208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson D., Floyd M. M. (2005). Enrichment and isolation of iron-oxidizing bacteria at neutral pH. Methods Enzymol. 397, 112–124 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)97006-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson D., Moyer C. L. (1997). Isolation and characterization of novel iron-oxidizing bacteria that grow at circumneutral pH. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 4784–4792 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson D., Rentz J. A., Lilburn T. G., Davis R. E., Aldrich H., Chan C., et al. (2007). A novel lineage of proteobacteria involved in formation of marine Fe-oxidizing microbial mat communities. PLoS ONE 2:e667 10.1371/journal.pone.0000667 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing B., Green P. (1998). Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res. 8, 186–194 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing B., Hillier L., Wendl M. C., Green P. (1998). Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res. 8, 175–185 10.1101/gr.8.3.175 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French C. E., Bell J. M., Ward F. B. (2008). Diversity and distribution of hemerythrin-like proteins in prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 279, 131–145 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.01011.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura R., Sato Y., Nishizawa T., Oshima K., Kim S. W., Hattori M., et al. (2012). Complete genome sequence of Leptospirillum ferrooxidans strain c2-3, isolated from a fresh volcanic ash deposit on the island of Miyake, Japan. J. Bacteriol. 194, 4122–4123 10.1128/JB.00696-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gault A. G., Ibrahim A., Langley S., Renaud R., Takahashi Y., Boothman C., et al. (2011). Microbial and geochemical features suggest iron redox cycling within bacteriogenic iron oxide-rich sediments. Chem. Geol. 281, 41–51 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.11.027 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gennis R. B., Stewart V. (1996). Respiration, in Escherichia coli and Salmonella Cellular and Molecular Biology, eds Neihardt F. C., Curtiss R., Ingraham J. L., Lin E. C. C., Low K. B., Magasanik B., et al. (Washington, DC: ASM Press; ), 217–261 [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh W., Dam B. (2009). Biochemistry and molecular biology of lithotrophic sulfur oxidation by taxonomically and ecologically diverse bacteria and archaea. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 33, 999–1043 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00187.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giltner C. L., Nguyen Y., Burrows L. L. (2012). Type IV pilin proteins: versatile molecular modules. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 76, 740–772 10.1128/MMBR.00035-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogarten J., Townsend J. (2005). Horizontal gene transfer, genome innovation and evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3, 679–687 10.1038/nrmicro1204 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D., Abajian C., Green P. (1998). Consed: a graphical tool for sequence finishing. Genome Res. 8, 195–202 10.1101/gr.8.3.195 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick J. A. (2012). On conducting electron traffic across the periplasm. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 40, 1178–1180 10.1042/BST20120129 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker J., Kaper J. B. (2000). Pathogenicity islands and the evolution of microbes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 54, 641–679 10.1146/annurev.micro.54.1.641 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallbeck L., Pedersen K. (1991). Autotrophic and mixotrophic growth of Gallionella ferruginea. J. Gen. Microbiol. 137, 2657–2661 10.1099/00221287-137-11-2657 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hallbeck L., Stahl F., Pedersen K. (1993). Phylogeny and phenotypic characterization of the stalk-forming and iron-oxidizing bacterium Gallionella ferruginea. J. Gen. Microbiol. 139, 1531–1535 10.1099/00221287-139-7-1531 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Chain P. (2006). Finishing repeat regions automatically with dupfinisher, in Proceeding of the International Conference on Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, eds Arabnia H. R., Valaform H. (CSREA Press; ), 141–146 [Google Scholar]
- Han H., Hemp J., Pace L., Ouyang H., Ganesan K., Roh J. H., et al. (2011). Adaptation of aerobic respiration to low O2 environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 14109–14114 10.1073/pnas.1018958108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haney C. J., Grass G., Franke S., Rensing C. (2005). New developments in the understanding of the cation diffusion facilitator family. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32, 215–226 10.1007/s10295-005-0224-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder E. C. (1919). Iron-depositing bacteria and their geologic relations. U.S. Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 113, 7–89 [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Falke J. J., Parkinson J. S. (2008). Bacterial chemoreceptors: high-performance signaling in networked arrays. Trends Biochem. Sci. 33, 9–19 10.1016/j.tibs.2007.09.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrich S., Schlomann M., Johnson D. B. (2011). The iron-oxidizing Proteobacteria. Microbiology 157, 1551–1564 10.1099/mic.0.045344-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyatt D., Chen G.-L., LoCascio P., Land M., Larimer F., Hauser L. J. (2010). Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinformatics 11:119 10.1186/1471-2105-11-119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilbert M., Bonnefoy V. (2013). Insight into the evolution of the iron oxidation pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1827, 161–175 10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.10.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A. (2008). Cellular defenses against superoxide and hydrogen peroxide. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 77, 755–776 10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.061606.161055 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrell K. F., McBride M. J. (2008). The surprisingly diverse ways that prokaryotes move. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 466–476 10.1038/nrmicro1900 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeans C., Singer S. W., Chan C. S., Verberkmoes N. C., Shah M., Hettich R. L., et al. (2008). Cytochrome 572 is a conspicuous membrane protein with iron oxidation activity purified directly from a natural acidophilic microbial community. ISME J. 2, 542–550 10.1038/ismej.2008.17 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenal U., Malone J. (2006). Mechanisms of cyclic-di-gmp signaling in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Genet. 40, 385–407 10.1146/annurev.genet.40.110405.090423 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. W., Carmichael M. J., McDonald W., Rose N., Pitchford J., Windelspecht M., et al. (2012). Increased abundance of Gallionella spp., Leptothrix spp. and total bacteria in response to enhanced Mn and Fe concentrations in a disturbed Southern Appalachian high elevation wetland. Geomicrobiol. J. 29, 124–138 10.1080/01490451.2011.558557 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kammler M., Schon C., Hantke K. (2003). Characterization of the ferrous iron uptake system of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 175, 6212–6219 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krepski S. T., Hanson T. E., Chan C. S. (2012). Isolation and characterization of a novel biomineral stalk-forming iron-oxidizing bacterium from a circumneutral groundwater seep. Environ. Microbiol. 14, 1671–1680 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02652.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lama A., Pawaria S., Dikshit K. L. (2006). Oxygen binding and no scavenging properties of truncated hemoglobin hbn of Mycobacterium smegmatis. FEBS Lett. 580, 4031–4041 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.06.037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauro F. M., McDougald D., Thomas T., Williams T. J., Egan S., Rice S., et al. (2009). The genomic basis of trophic strategy in marine bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 15527–15533 10.1073/pnas.0903507106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C., Larsen E. I., Grace P. R., Smith J. J. (2011). Occurrence of iron and associated bacterial populations in soils of a forested subtropical coastal catchment. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 47, 322–332 10.1016/j.ejsobi.2011.07.008 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Wang Z., Belchik S. M., Edwards M. J., Liu C., Kennedy D. W., et al. (2012). Identification and characterization of MtoA: a decaheme c-type cytochrome of the neutrophilic Fe(II)-oxidizing bacterium Sideroxydans lithotrophicus ES-1. Front. Microbiol. 3:37 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R. (2011). Electromicrobiology. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 66, 391–409 10.1146/annurev-micro-092611-150104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludecke C., Reiche M., Eusterhues K., Nietzsche S., Küsel K. (2010). Acid-tolerant microaerophilic Fe(II)-oxidizing bacteria promote Fe(III)-accumulation in a fen. Environ. Microbiol. 12, 2814–2825 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02251.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makarova K. S., Aravind L., Galperin M. Y., Grishin N. V., R., Tatusov R. L., Wolf Y. I., et al. (1999). Comparative genomics of the Archaea (Euryarchaeota): evolution of conserved protein families, the stable core, and the variable shell. Genome Res. 9, 608–628 10.1101/gr.9.7.608 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies M., Egholm M., Altman W. E., Attiya S., Bader J. S., Bemben L. A., et al. (2005). Genome sequencing in microfabricated high-density picolitre reactors. Nature 437, 376–380 10.1038/nature03959 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz V. M., Ivanova N. N., Szeto E., Palaniappan K., Chu K., et al. (2008). IMG/M: a data management and analysis system for metagenomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D534–D538 10.1093/nar/gkm869 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. J., Shanmuganathan S., Mortimer F. C., Gant V. A. (1998). A fluorescent gram stain for flow cytometry and epifluorescence microscopy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 2681–2685 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBeth J. M., Fleming E. J., Emerson D. (2013). The transition from freshwater to marine iron-oxidizing bacterial lineages along a salinity gradient on the Sheepscot river, Maine, USA. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 5, 453–463 10.1111/1758-2229.12033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. L., Schmidt T. M. (2013). Shallow breathing: bacterial life at low O2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 11, 205–212 10.1038/nrmicro2970 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G., Ferguson S J. (2002). Bioenergetics 3. London: Academic Press [Google Scholar]
- Niemann J., Tisa L. S. (2008). Nitric oxide and oxygen regulate truncated hemoglobin gene expression in Frankia strain cci3. J. Bacteriol. 190, 7864–7867 10.1128/JB.01100-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathania R., Navani K. N., Rajamohan G., Dikshit K. L. (2002). Mycobacterium tuberculosis hemoglobin hbo associates with membranes and stimulates cellular respiration recombinant Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 15293–15302 10.1074/jbc.M111478200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicic V. (2008). Type IV pili: e pluribus unum? Mol. Microbiol. 68, 827–837 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06197.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. M., Refojo P. N., Hreggvidsson G. O., Hjorleifsdottir S., Teixeira M. (2007). The alternative complex III from Rhodothermus marinus–a prototype of a new family of quinol: electron acceptor oxidoreductases. FEBS Lett. 581, 4831–4835 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.09.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikuta E., Hoover R. B., Bej A. K., Marsic D., Detkova E. N., Whitman W. B., et al. (2003). Tindallia californiensis sp. nov., a new anaerobic, haloalkalophilic, spore-forming acetogen isolated from mono lake in california. Extremophiles 7, 327–334 10.1007/s00792-003-0326-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter S. L., Wadhams G. H., Armitage J. P. (2011). Signal processing in complex chemotaxis pathways. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 9, 153–165 10.1038/nrmicro2505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruesse E., Quast C., Knittel K., Fuchs B. M., Ludwig L., Peplies J., et al. (2007). SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 7188–7196 10.1093/nar/gkm864 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refojo P. N., Teixeira M., Pereira M. M. (2012). The alternative complex III: properties and possible mechanisms for electron transfer and energy conservation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1817, 1852–1859 10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römling U. (2011). Cyclic di-gmp, an established secondary messenger still speeding up. Environ. Microbiol. 14, 1817–1829 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02617.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P. (2002). Biochemistry of arsenic detoxification. FEBS Lett. 529, 86–92 10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03186-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahl J. W., Schmidt R., Swanner E. D., Mandernack K. W., Templeton A. S., Kieft T. L., et al. (2008). Subsurface microbial diversity in deep-grantic-fracture water in Colorado. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74, 143–152 10.1128/AEM.01133-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi L., Rosso K. M., Clarke T. A., Richardson D. J., Zachara J. M., Frederickson J. K. (2012). Molecular underpinnings of Fe(III) oxide reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Front. Microbiol. 3:50 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00050 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer E., Emerson D., Webb E. A., Ferriera S., Johnson J., Kuenen J. G., et al. (2011). Genomic insights into the Fe-oxidizing bacterium Mariprofundus ferrooxydans PV-1 – the first genome from the Zetaproteobacteria. PLoS ONE 6:e25386 10.1371/journal.pone.0025386 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S., Chan C., Zemla A., Verberkmoes N., Hwang M., Hettich R., et al. (2008). Characterization of cytochrome 579, an unusual cytochrome isolated from an iron-oxidizing microbial community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74, 4454–4462 10.1128/AEM.02799-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stackebrandt E., Ebers J. (2006). Taxonomic parameters revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol. Today 33, 152–155 [Google Scholar]
- Stumm W., Morgan J. J. (1981). Aquatic Chemistry, 2nd Edn. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Peterson D., Peterson N., Stecher G., Nei M., Kumar S. (2011). MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 28, 2731–2739 10.1093/molbev/msr121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L., Zhulin I. B., Johnson M. S. (1999). Aerotaxis and other energy-sensing behavior in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 53, 103–128 10.1146/annurev.micro.53.1.103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Marsh J. W. (1999). Genetic and transcriptional analyses of the Vibrio cholerae mannose-sensitive hemagglutinin type 4 pilus gene locus. J. Bacteriol. 181, 1110–1117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran H., Krushkal J., Antommattei F., Lovley D. R., Weis R. M. (2008). Comparative genomics of Geobacter chemotaxis genes reveals diverse signaling function. BMC Genomics 9:471 10.1186/1471-2164-9-471 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson G. W., Chapman J., Hugenholtz P., Allen E. E., Ram R. J., Richardson P. M., et al. (2004). Community structure and metabolism through reconstructino of microbial genomes from the environment. Nature 428, 37–43 10.1038/nature02340 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdés J., Pedroso I., Quatrini R., Dodson R., Tettelin H., Blake R., et al. (2008). Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans metabolism: from genome sequence to industrial applications. BMC Genomics 9:597 10.1186/1471-2164-9-597 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov S. N., Hoogewiis D., Bailly X., Arredondo-Peter R., Gough J., Dewilde S., et al. (2006). A phylogenomic profile of globins. BMC Evol. Biol. 6:31 10.1186/1471-2148-6-31 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Muyzer G., Bodelier P., Laanbroek H. (2009). Diversity of iron oxidizers in wetland soils revealed by novel 16s rRNA primers targeting Gallionella-related bacteria. ISME J. 3, 715–725 10.1038/ismej.2009.7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. V., Rentz J. A., Plaia T., Neubauer S. C., Floyd M. M., Lilburn T. G., et al. (2007). Characterization of neutrophilic Fe(II)-oxidizing bacteria isolated from the rhizosphere of wetland plants and description of Ferritrophicum radicicola gen. nov. sp. nov., and Sideroxydans paludicola sp. nov. Geomicrobiol. J. 24, 559–570 10.1080/01490450701670152 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- White D., Drummond J., Fuqua C. (2012). The Physiology and Biochemistry of Prokaryotes, 4th Edn. New York, NY: Oxford University Press [Google Scholar]
- Zerbino D. R., Birney E. (2008). Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 18, 821–829 10.1101/gr.074492.107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]