Abstract
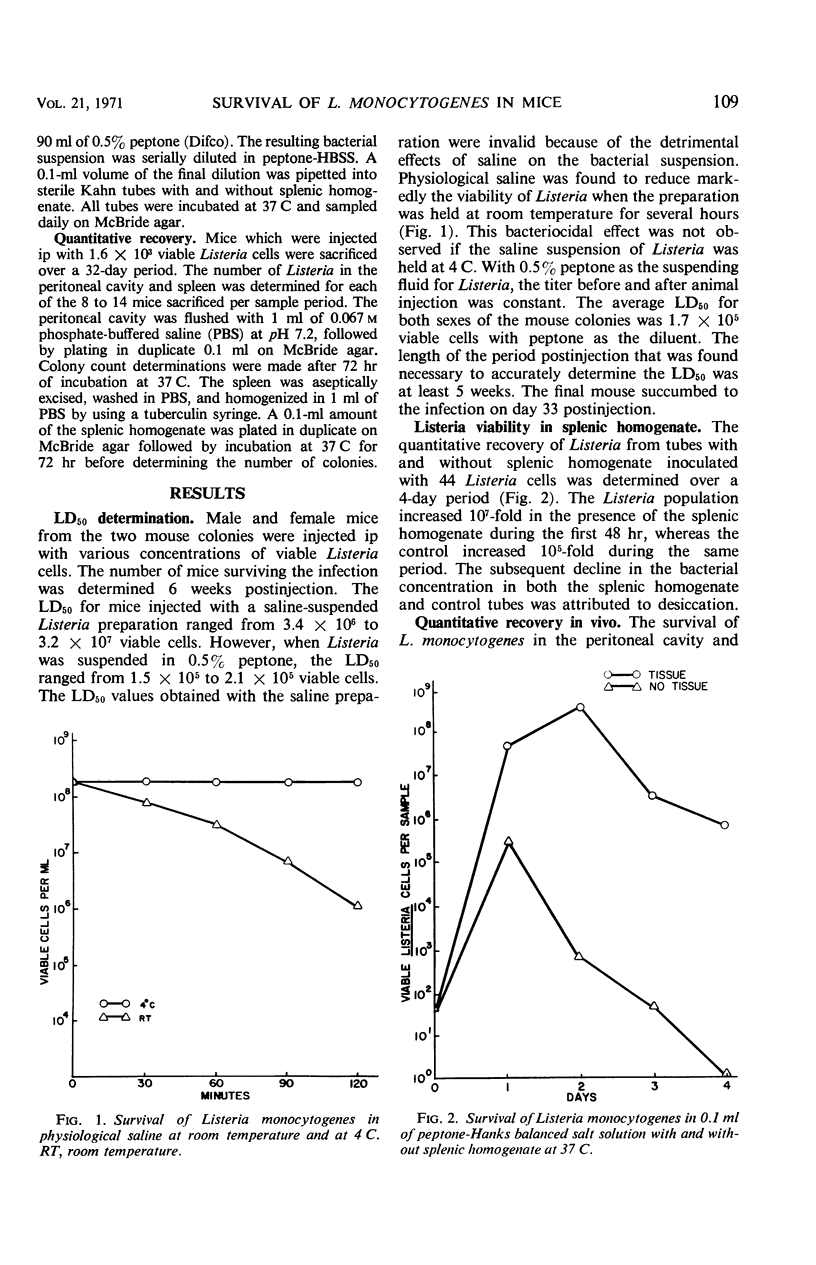
Physiological saline was found to be very detrimental to the viability of Listeria monocytogenes. The LD50 value was substantially reduced when peptone was used as the suspending fluid rather than saline. Normal splenic tissue was not inhibitory to the survival of Listeria. In experimentally infected mice, L. monocytogenes survived for 8 days in the peritoneal cavity and for at least 11 days in the spleen.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coppel S., Youmans G. P. Specificity of Acquired Resistance Produced by Immunization with Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria Fractions. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):121–126. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.121-126.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel S., Youmans G. P. Specificity of the anamnestic response produced by Listeria monocytogenes or Mycobacterium tuberculosis to challenge with Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):127–133. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.127-133.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. L., Killinger A. H. Listeria monocytogenes and listeric infections. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):309–382. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.309-382.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. L., Stafseth H. J., Thorp F., Sholl L. B., Riley W. F. A New Technique for Isolating Listerellae from the Bovine Brain. J Bacteriol. 1948 Apr;55(4):471–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman B., Cherry W. B. Isolation of Listeria monocytogenes from brains of rabies-negative animals. Am J Vet Res. 1967 May;28(124):779–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



