Abstract
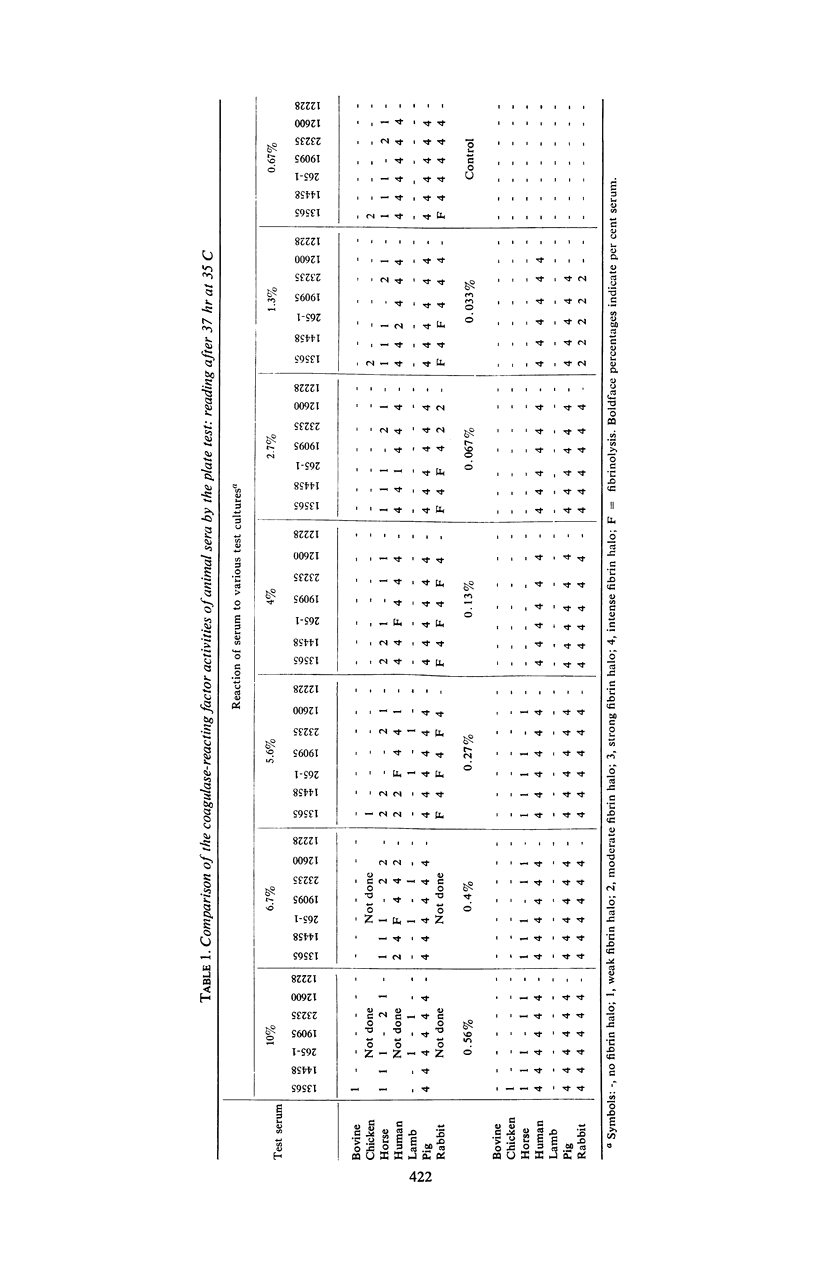
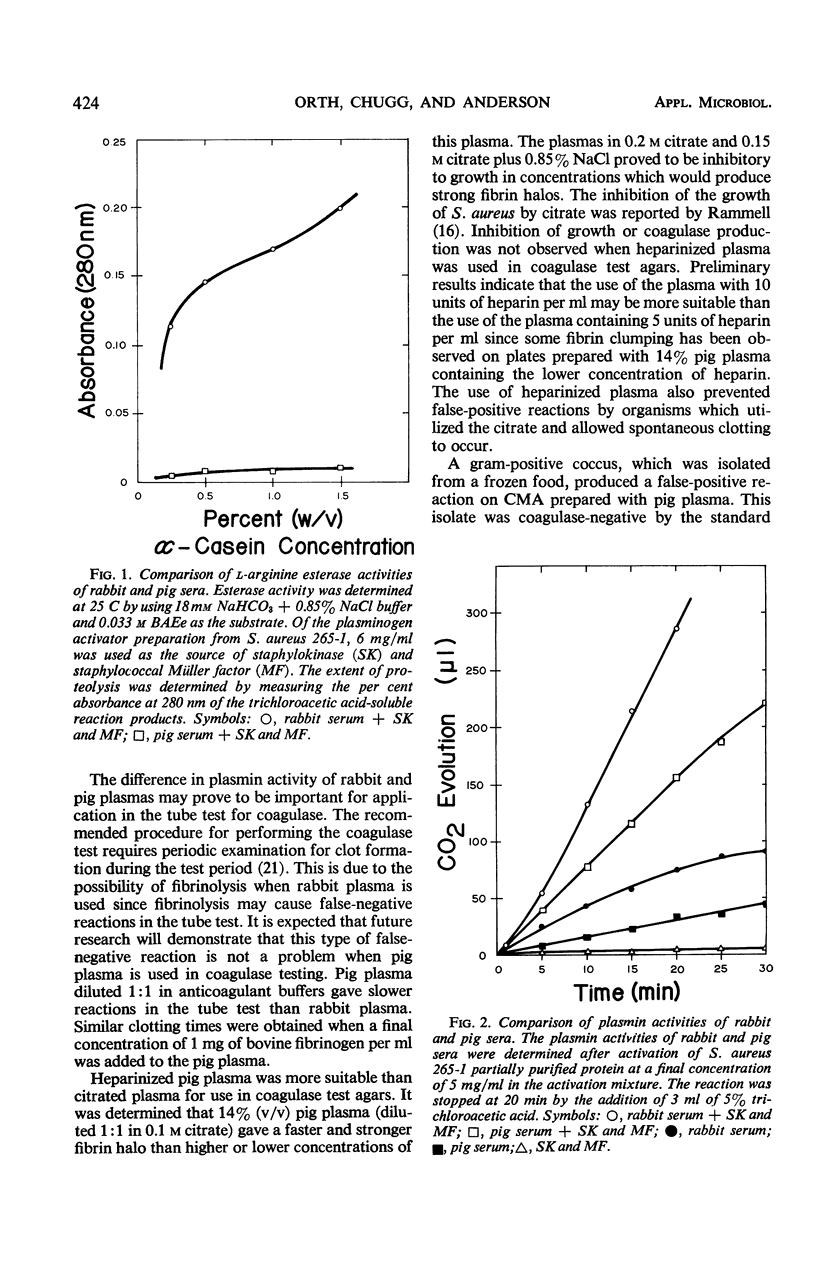
The sera of several animals were examined for suitability in coagulase testing. The assay for coagulase-reacting factor (CRF) activities of the whole sera indicated the following relative concentrations of CRF: human > pig > rabbit > horse > bovine, chicken, and lamb. Human, pig, and rabbit sera had adequate amounts of CRF for coagulase testing. The plasmin activities of the different sera, arranged from the strongest to the weakest, were as follows: rabbit > human > lamb > horse > bovine, chicken, and pig. Fibrinolysis was observed when rabbit, human, lamb, or horse sera were incorporated into coagulase test agars. Pig serum was superior to the other sera for use in the plate test for coagulase since it had adequate amounts of CRF and the plasminogen-plasmin system was not activated by staphylokinase or staphylococcal Müller factor. Heparinized pig plasma was more suitable than citrated pig plasma since citrate interfered with the growth of Staphylococcus aureus, and the use of heparinized plasma prevented false-positive coagulase reactions due to citrate utilization.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLIFFTON E. E., CANNAMELA D. A. Variations in proteolytic activity of serum of animals including man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Jun;77(2):305–308. doi: 10.3181/00379727-77-18760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS N. A., DAVIS G. H. SELECTIVE CULTURE OF COAGULASE-POSITIVE STAPHYLOCOCCI. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:380–386. doi: 10.1002/path.1700890145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE E. S., LORENZ L. L. Staphylococcal coagulase; mode of action and antigenicity. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Feb;6(1-2):95–107. doi: 10.1099/00221287-6-1-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESBER R. J., FAULCONER R. J. A medium for initial visual demonstration of production of coagulase and fermentation of mannitol by pathogenic staphylococci. Tech Bull Regist Med Technol. 1959 Jul;29(7):108–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEMPERER R., HAUGHTON G. A medium for the rapid recognition of penicillin-resistant coagulase-positive staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1957 Feb;10(1):96–99. doi: 10.1136/jcp.10.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSEN M. The esterase activity of the fibrinolytic system. Biochem J. 1958 Jul;69(3):360–366. doi: 10.1042/bj0690360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer W. Uber die Brauchbarkeit des Koagulasetestes mit verschiedenen Plasmaarten zur Differenzierung von Staphylococcus aureus-Stämmen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1966 Nov;201(3):331–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orth D. S., Anderson A. W., Montgomery M. W. Activation of coagulase clotting by trypsin inhibitor. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):906–910. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.906-910.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orth D. S., Anderson A. W. Polymyxin-coagulase-mannitol-agar. I. A selective isolation medium for coagulase-positive Staphylococci. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):73–75. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.73-75.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMMELL C. G. Inhibition by citrate of the growth of coagulase-positive Staphylococci. J Bacteriol. 1962 Nov;84:1123–1124. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.5.1123-1124.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROLL W., SHERRY S. The activation of human plasminogen by streptokinase. J Biol Chem. 1955 Apr;213(2):881–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROLL W., SHERRY S., WACHMAN J. The action of plasmin on synthetic substrates. J Biol Chem. 1954 May;208(1):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterberg O., Wadström T., Vesterberg K., Svensson H., Malmgren B. Studies on extracellular PROTEINS FROM Staphylococcus aureus. I. Separation and characterization of enzymes and toxins by isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 11;133(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



