Abstract
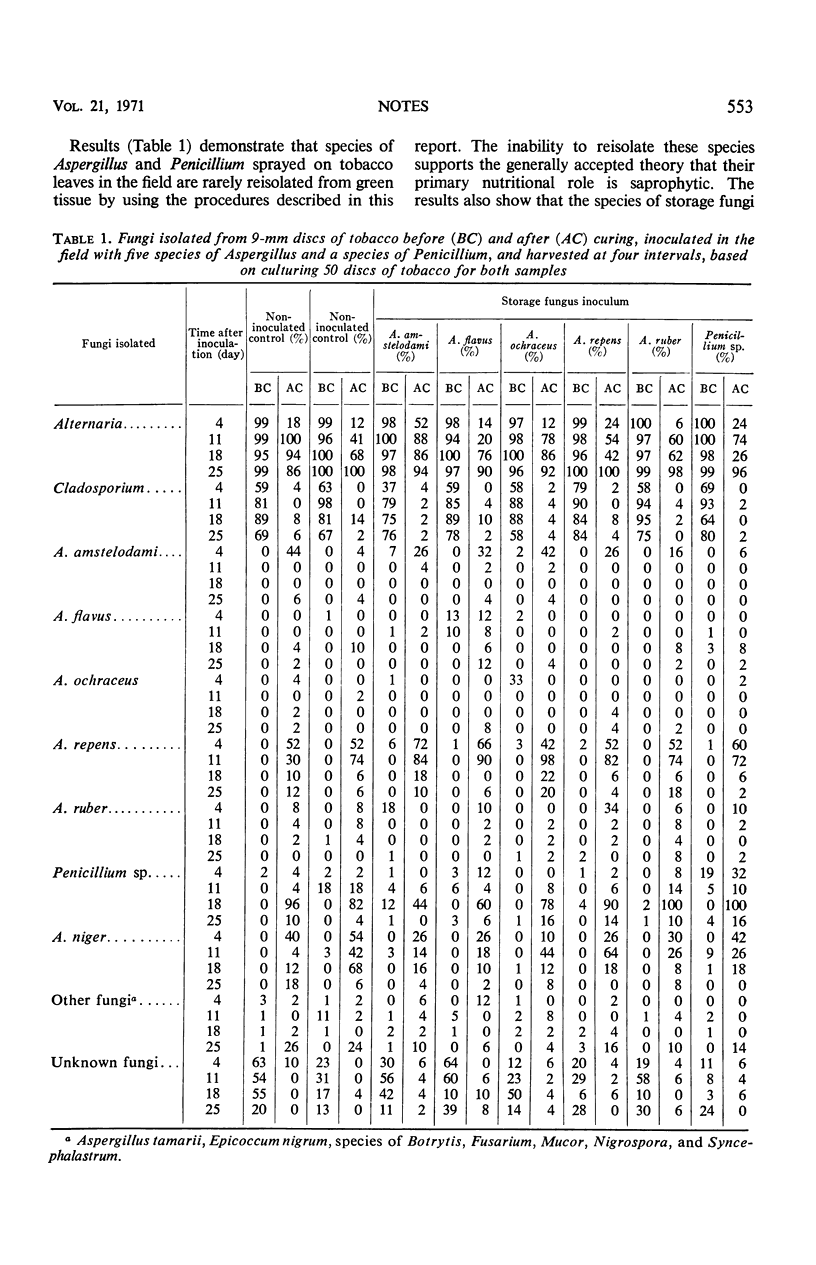
Flue-cured tobacco inoculated in the field with A. amstelodami, A. flavus, A. ochraceus, A. repens, A. ruber, and a species of Penicillium was rarely invaded by these fungi. Regardless of inoculum, the predominant fungi reisolated from green tissue were species of Alternaria and Cladosporium. After curing, A. repens, A. niger, and species of Alternaria and a species of Penicillium were the most commonly isolated fungi. The fungus used as inoculum was not the predominant fungus reisolated from green or cured tissue. Conditions during handling and storage prior to marketing probably determine when storage fungi become associated with the leaf and which species becomes predominant.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Welty R. E., Lucas G. B., Fletcher J. T., Yang H. Fungi isolated from tobacco leaves and brown-spot lesions before and after flue-curing. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1309–1313. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1309-1313.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welty R. E., Lucas G. B. Fungi Isolated from Flue-cured Tobacco at Time of Sale and After Storage. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Mar;17(3):360–365. doi: 10.1128/am.17.3.360-365.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



