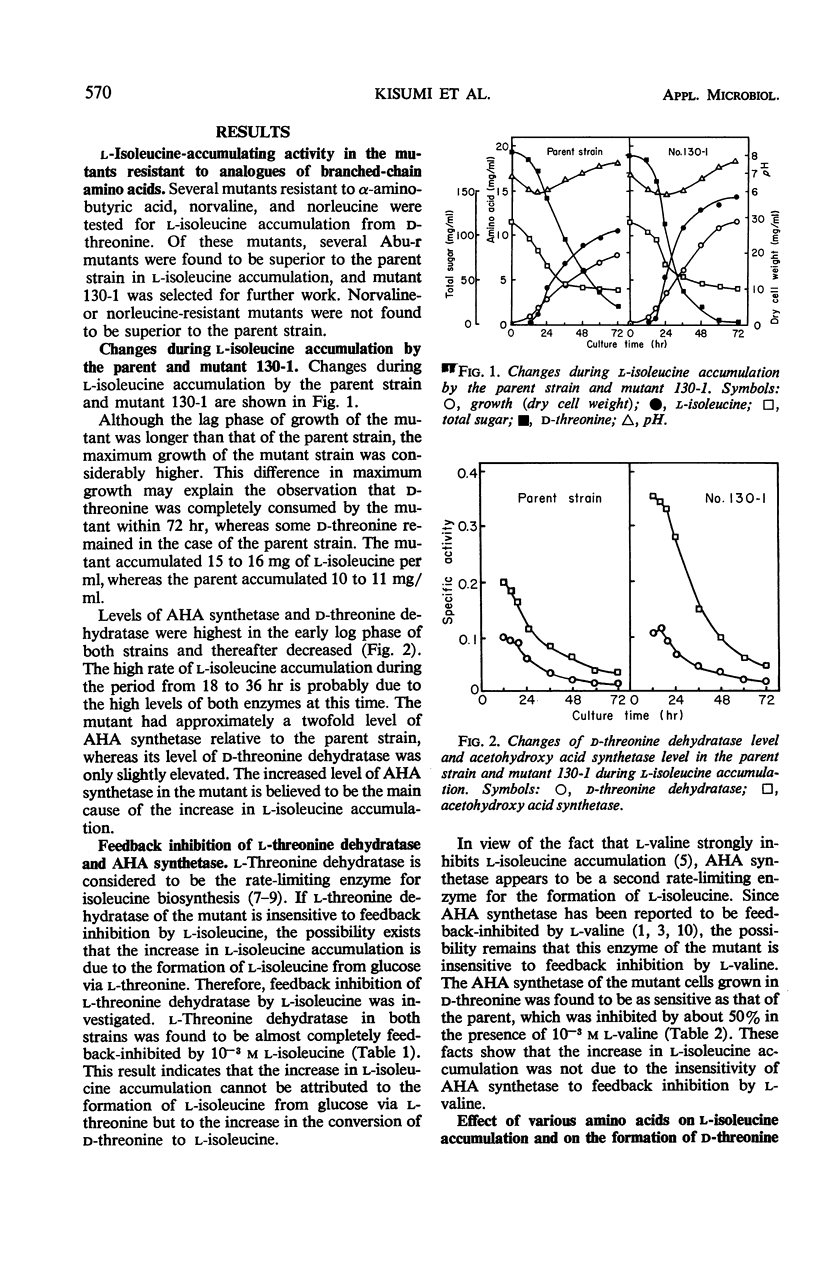
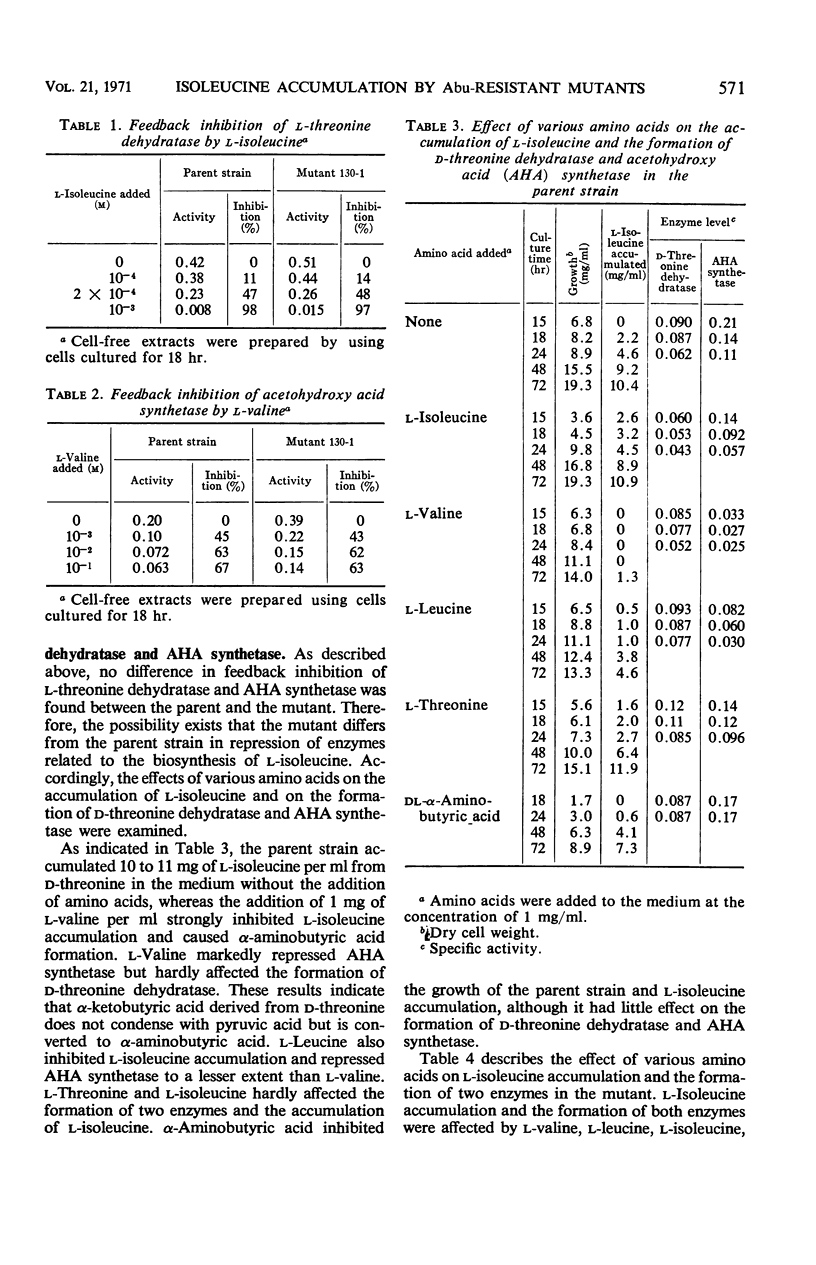
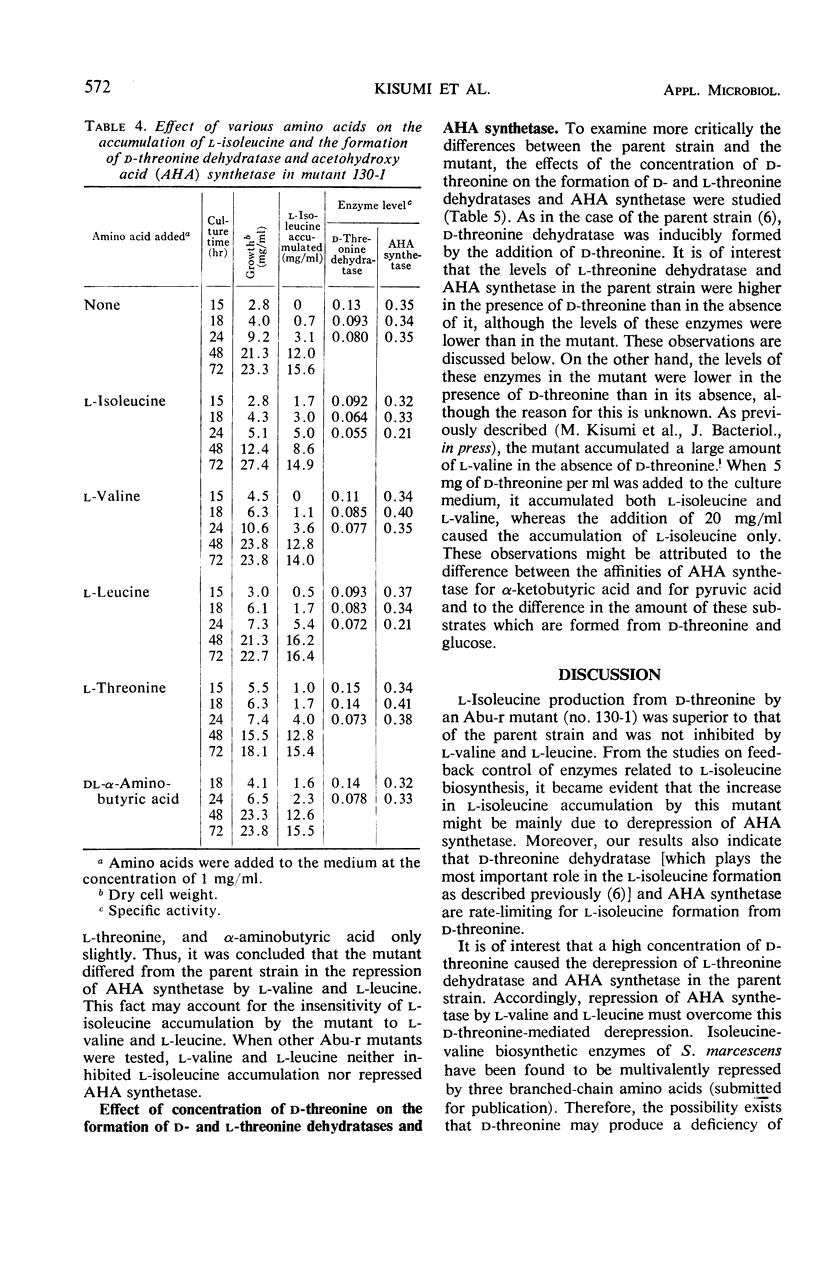
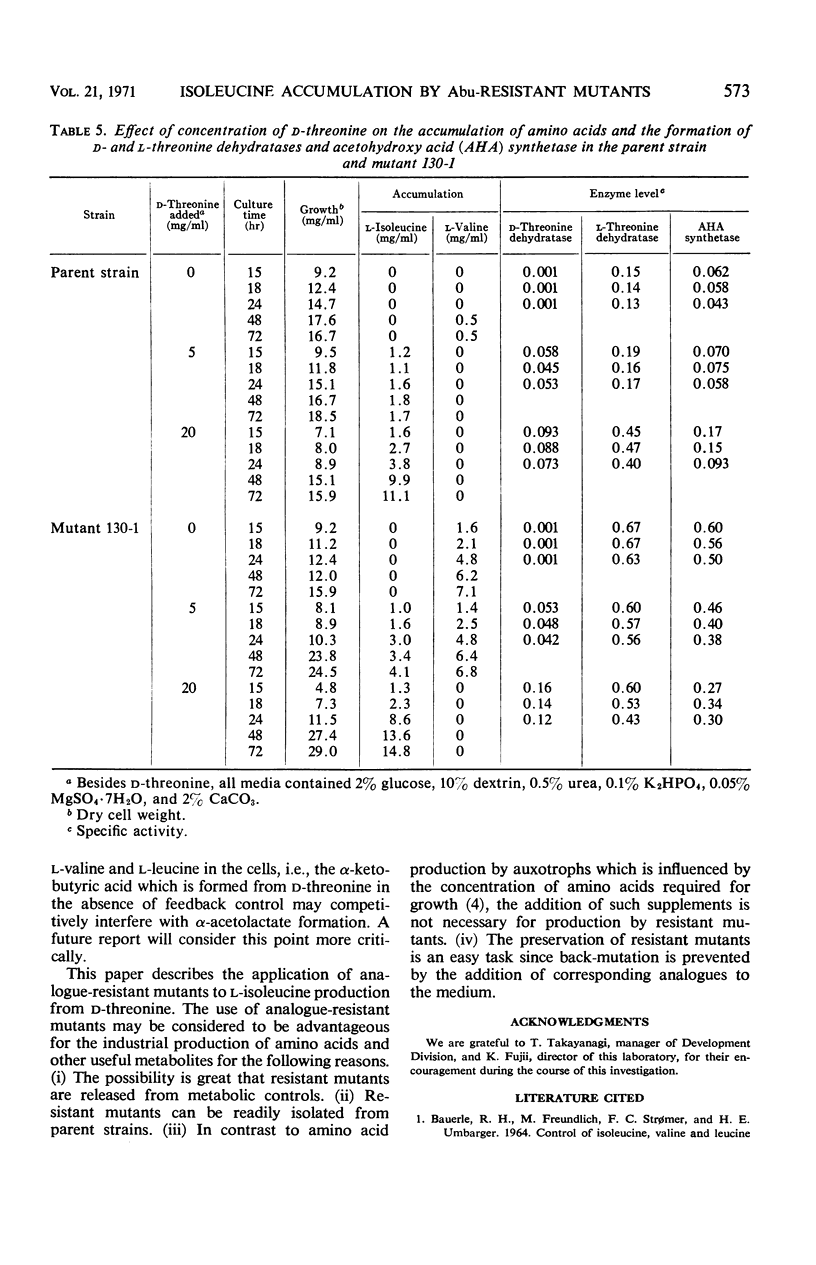
Abstract
Several α-aminobutyric acid-resistant (Abu-r) mutants of Serratia marcescens were found to be superior to the parent strain in converting d-threonine to l-isoleucine. One of them accumulated 1.5 times more l-isoleucine that the parent strain. The level of acetohydroxy acid (AHA) synthetase in this mutant increased twofold above that of the parent strain. In the parent strain, AHA synthetase was repressed and l-isoleucine accumulation was decreased by either l-valine or l-leucine, whereas in the mutant the AHA synthetase level and l-isoleucine accumulation were not affected by these amino acids. AHA synthetase of the Abu-r mutant was feedback-inhibited by l-valine to the same extent as that of the parent strain. The level of d-threonine dehydratase in both strains was only slightly affected by several amino acids tested. l-Threonine dehydratase of the parent strain and of the mutant was almost completely inhibited by l-isoleucine. These results indicate that the increase in l-isoleucine accumulation by Abu-r mutants is due to the genetic derepression of AHA synthetase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAUERLE R. H., FRUENDLICH M., STORMER F. C., UMBARGER H. E. CONTROL OF ISOLEUCINE, VALINE AND LEUCINE BIOSYNTHESIS. II. ENDPRODUCT INHIBITION BY VALINE OF ACETOHYDROXY ACID SYNTHETASE IN SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Oct 23;92:142–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERN Y. S., UMBARGER H. E. Evidence for two distinct enzyme systems forming acetolactate in Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3067–3071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. T. Microbial production of amino acids. Prog Ind Microbiol. 1964;5:55–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISUMI M. Studies on the isoleucine fermentation. I. Screening of organisms and investigation of cultural conditions. J Biochem. 1962 Dec;52:390–399. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMAKRISHNAN T., ADELBERG E. A. REGULATORY MECHANISMS IN THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF ISOLEUCINE AND VALINE. 3. MAP ORDER OF THE STRUCTURAL GENES AND OPERATOR GENES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:661–664. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.661-664.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMAKRISHNAN T., ADELBERG E. A. REGULATORY MECHANISMS IN THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF ISOLEUCINE AND VALINE. I. GENETIC DEREPRESSION OF ENZYME FORMATION. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:566–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.566-573.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMAKRISHNAN T., ADELBERG E. A. REGULATORY MECHANISMS IN THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF ISOLEUCINE AND VALINE. II. IDENTIFICATION OF TWO OPERATOR GENES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:654–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.654-660.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UMBARGER H. E., BROWN B. Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli. VIII. The formation of acetolactate. J Biol Chem. 1958 Nov;233(5):1156–1160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



