Abstract
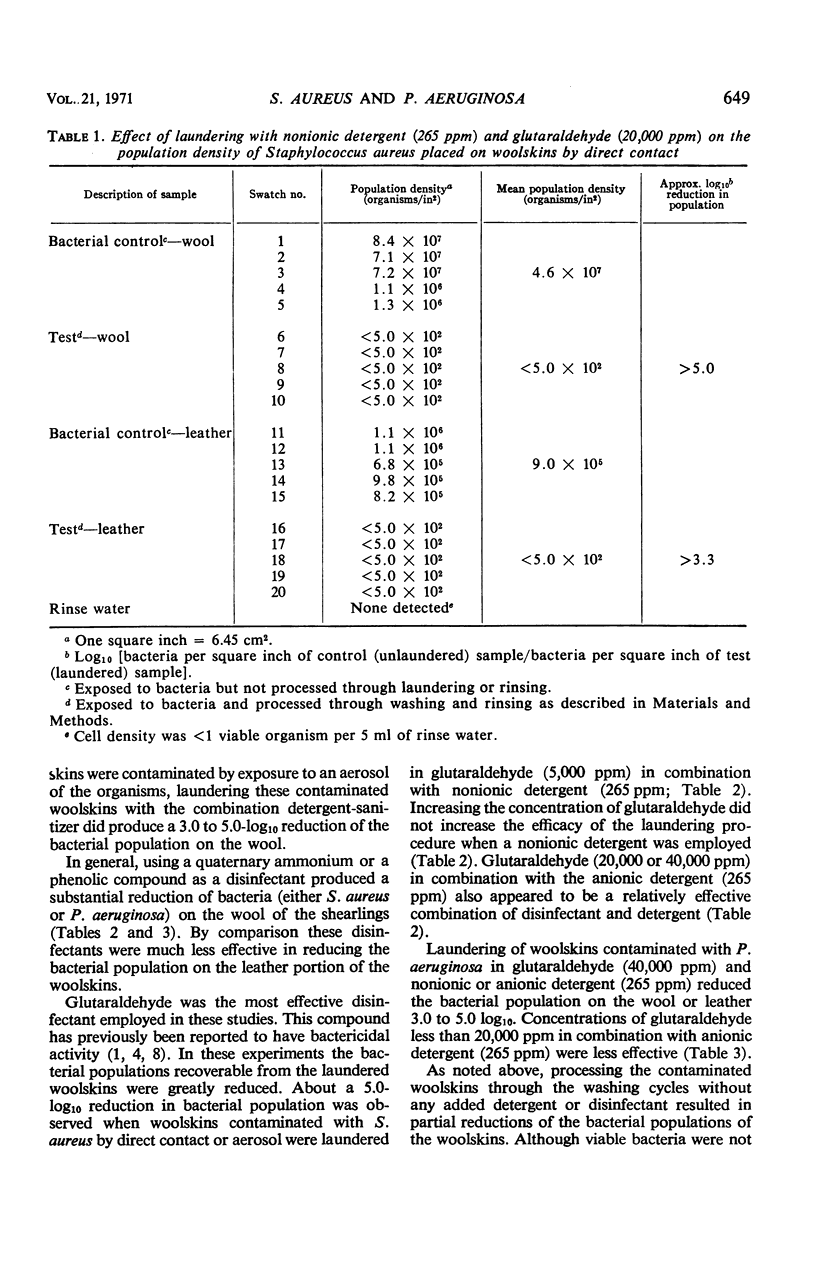
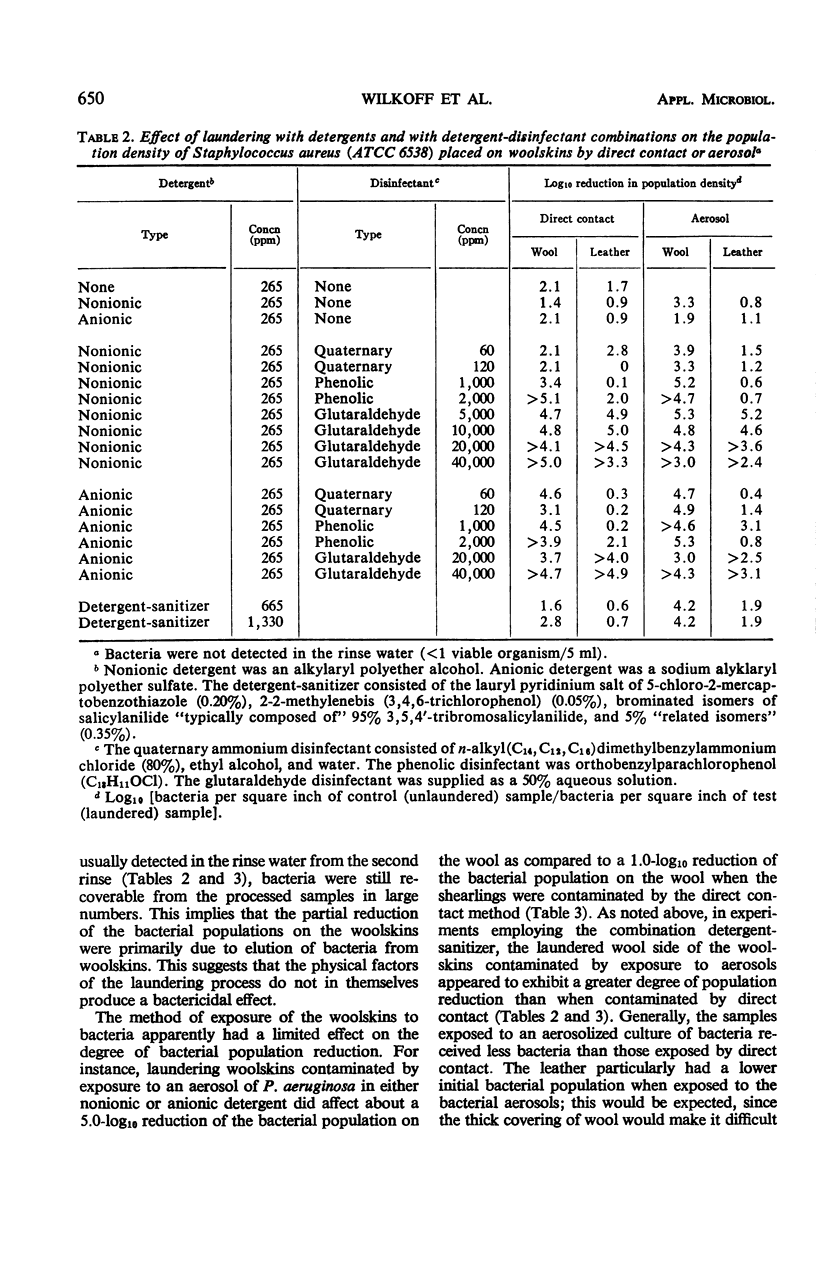
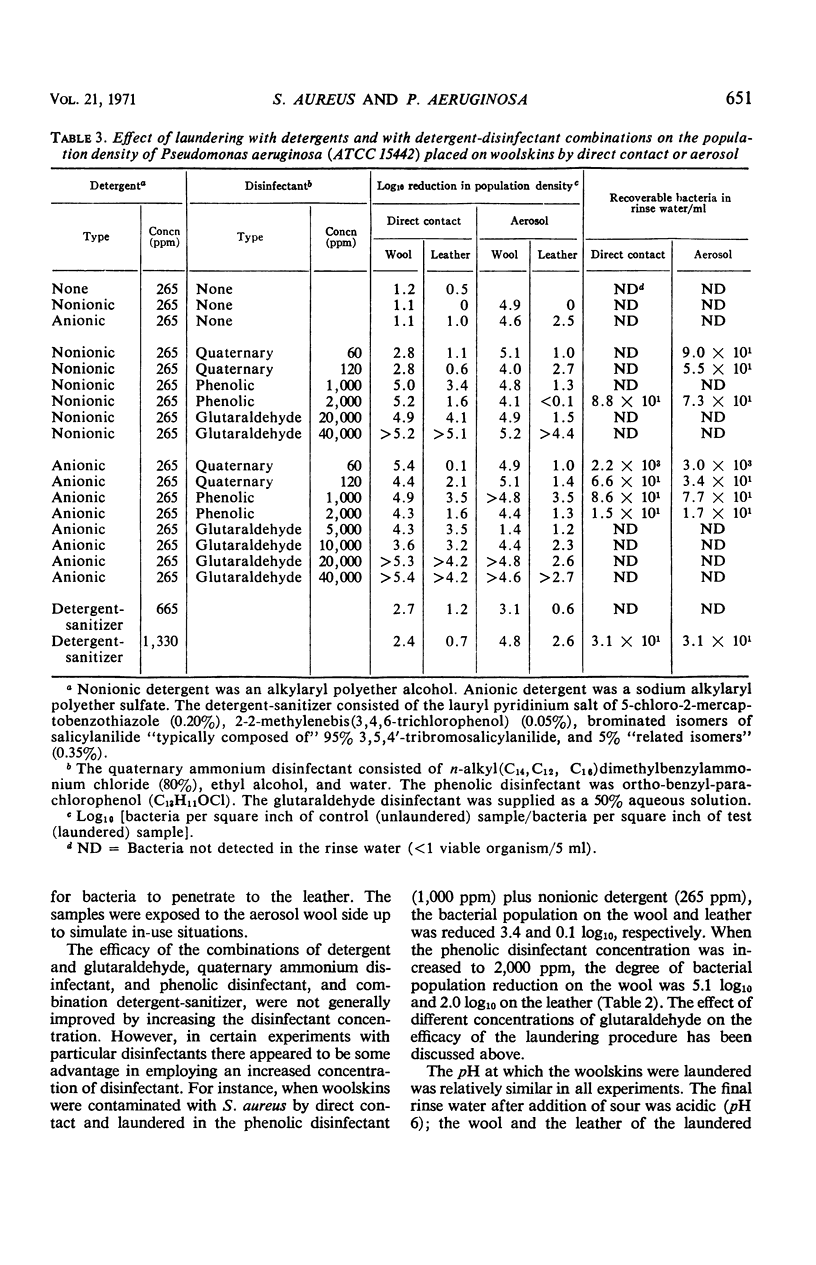
Glutaraldehyde-tanned woolskins which are used as bedpads to prevent decubitus ulcers were contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 15442). Two methods of exposure, direct contact and aerosol, were used in separate experiments. Attempts were made to decrease the bacterial population placed on the woolskins by laundering them in a quaternary ammonium disinfectant, a phenolic disinfectant, or alkalinized glutaraldehyde, in combination with an anionic or nonionic detergent. The effect of a commercial detergent-sanitizer was also studied. Bacterial populations were significantly reduced in all experiments, but only laundering in glutaraldehyde in combination with either detergent resulted in maximum removal of bacteria. Viable bacteria were usually not detected in the rinse water (<1 viable organism/5 ml of rinse water).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORICK P. M., DONDERSHINE F. H., CHANDLER V. L. ALKALINIZED GLUTARALDEHYDE, A NEW ANTIMICROBIAL AGENT. J Pharm Sci. 1964 Oct;53:1273–1275. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600531041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon G. J., Sidwell R. W., McNeil E. Quantitative studies on fabrics as disseminators of viruses. II. Persistence of poliomyelitis virus on cotton and wool fabrics. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):183–188. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.183-188.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubbo S. D., Gardner J. F., Webb R. L. Biocidal activities of glutaraldehyde and related compounds. J Appl Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;30(1):78–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1967.tb00277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Dixon G. J., McNeil E. Quantitative studies on fabrics as disseminators of viruses. I. Persistence of vaccinia virus on cotton and wool fabrics. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Jan;14(1):55–59. doi: 10.1128/am.14.1.55-59.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Dixon G. J., Westbrook L., Dulmadge E. A. Procedure for the evaluation of the virucidal effectiveness of an ethylene oxide gas sterilizer. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):790–796. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.790-796.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Westbrook L., Dixon G. J., Happich W. F. Potentially infectious agents associated with shearling bedpads. I. Effect of laundering with detergent-disinfectant combinations on polio and vaccinia viruses. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):53–59. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.53-59.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkoff L. J., Westbrook L., Dixon G. J. Factors affecting the persistence of Staphylococcus aureus on fabrics. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Feb;17(2):268–274. doi: 10.1128/am.17.2.268-274.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkoff L. J., Westbrook L., Dixon G. J. Persistence of Salmonella typhimurium on fabrics. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Aug;18(2):256–261. doi: 10.1128/am.18.2.256-261.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


