Abstract
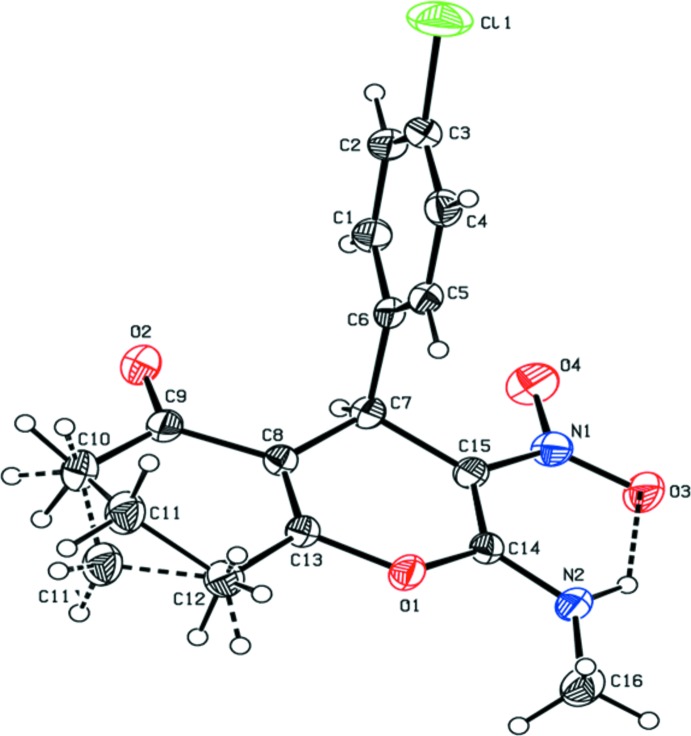
The title compound, C16H15ClN2O4, contains a chiral centre and crystallizes as a racemate. The methylene group β-positioned to the carbonyl group is partially (21%) disordered. It flips to the opposite sides of the corresponding six-membered carbocycle by −0.304 (3) and 0.197 (11) Å, producing alternative envelope conformations. The planes of the pyran and chlorophenyl rings form a dihedral angle of 86.25 (9)°. The molecular structure is characterized by an intramolecular N—H⋯O interaction, which generates an S(6) ring motif. The corresponding amino N atom deviates from the plane of the pyran ring by 0.1634 (19) Å. In the crystal, molecules are linked via C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming C(8) chains running parallel to the b-axis direction. The crystal structure also features C—H⋯π interactions.
Related literature
For the uses and biological importance of chromene, see: Ercole et al. (2009 ▶); Geen et al. (1996 ▶) Khan et al. (2010 ▶); Raj et al. (2010 ▶). For related structures, see: Sun et al., (2012 ▶). For graph-set notation, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶). 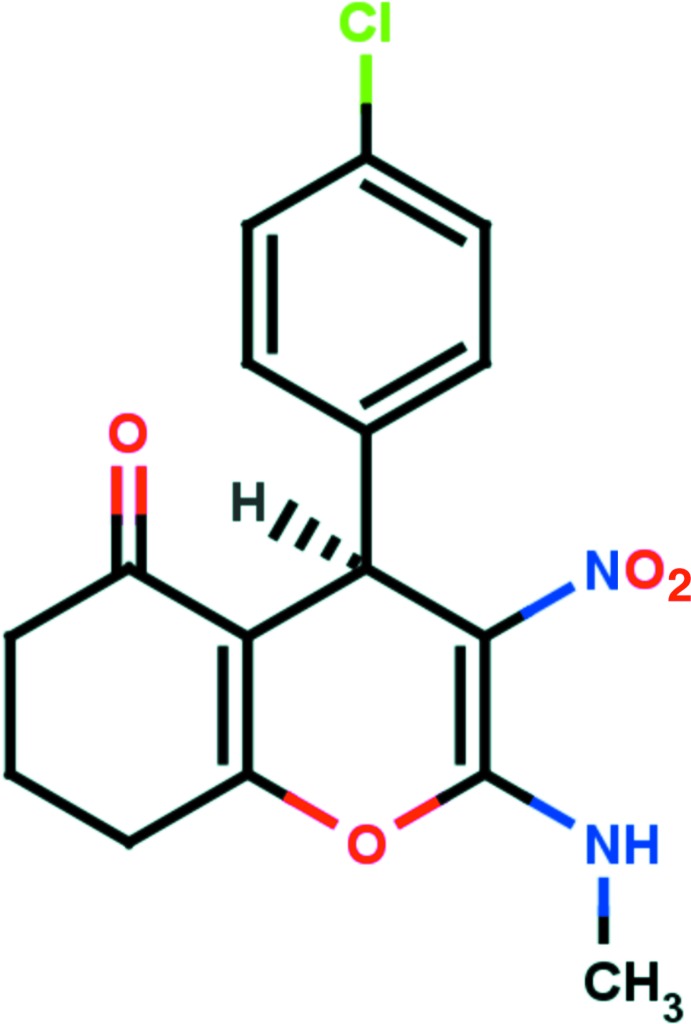
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H15ClN2O4
M r = 334.75
Monoclinic,
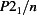
a = 8.0285 (4) Å
b = 10.8460 (5) Å
c = 18.2337 (9) Å
β = 94.067 (2)°
V = 1583.74 (13) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.26 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.35 × 0.30 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▶) T min = 0.912, T max = 0.924
11848 measured reflections
2786 independent reflections
2208 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.029
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.119
S = 1.09
2786 reflections
218 parameters
4 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2; data reduction: SAINT (Bruker, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 2012 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813014530/ld2104sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813014530/ld2104Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813014530/ld2104Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the pyran ring C7/C8/C13/O1/C14/C15.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2A⋯O3 | 0.90 (2) | 1.86 (2) | 2.599 (2) | 137 (2) |
| C2—H2⋯O4i | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.420 (3) | 160 |
| C10—H10A⋯Cg1ii | 0.97 | 2.75 | 3.515 (2) | 136 |
| C16—H16B⋯Cg1iii | 0.96 | 2.76 | 3.577 (3) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 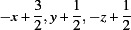 ; (ii)
; (ii) 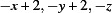 ; (iii)
; (iii) 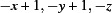 .
.
Acknowledgments
PN and KS thank Dr Babu Varghese, Senior Scientific Officer, SAIF, IIT Madras, Chennai, India, for the X-ray intensity data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Chromene derivatives are very important heterocyclic compounds that have a variety of industrial, biological and chemical synthesis applications (Geen et al., 1996; Ercole et al., 2009). They exhibit a number of pharmacological activities such as anti-HIV, anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, anti-allergic, anti-cancer etc. (Khan et al., 2010, Raj et al., 2010). Against this backround, X-ray analysis of the title compound has been carried out to study its structural aspects.
X-ray analysis confirms the molecular structure and atom connectivity. The molecular structure is stabilized by intramolecular N2—H2A···O3 interaction, which generates S(6) ring motif as illustrated in Fig. 1. The methelene group carbon atom C11 of the chromene moiety is disordered over two positions, with an occupancy factor of 0.787 (5):0.213 (5). The pyrane ring (C7/C8/C13/C14/C15/O1) is almost orthogonal to the chlorophenyl ring (C1–C6), with a dihedral angle of 86.25 (9)° between their mean planes.
The pyrane ring is almost coplanar with the least-square planes of the nitro and methylene groups, making dihedral angles of 5.19 (14) and 5.01 (16)°, with them, respectively.
The six-membered carbocyclic rings (C8/C9/C10/C11/C12/C13) and (C8/C9/C10/C11'/C12/C13) of the chromene moiety adopt envelope conformations on the atoms C11 and C11', with puckering paramaters: Q2 = 0.366 (3) Å, Q3 = 0.229 (3) Å and φ2 = 178.1 (2)°, and Q2 = 0.211 (7) Å, Q3 = -0.185 (5) Å and φ2 = 3.1 (2)°, respectively. Also, the atoms C11 and C11' deviate from their respective mean planes of the rest of the ring atoms by -0.304 (3) and 0.197 (11) Å, respectively. The amine group nitrogen atom N2 deviates by 0.1634 (19) Å from the mean plane of the pyran ring. The chlorine atom Cl1 deviates from the phenyl ring (C1–C6) by 0.0571 (9) Å. The title compound exihibits structural similarities with an already reported related structure (Sun et al., 2012).
In the crystal, the molecules are linked via intermolecular C2—H2···O4i hydrogen-bond interaction, which generates C(8) chains running parallel to b axis (Bernstein et al.,1995). The crystal structure is further stabilized by C10—H10A···Cg1ii and C16—H16B···Cg1iii intermolecular interactions, where Cg1 is the center of gravity of the pyran ring (C7/C8/C13/O1/C14/C15). The symmetry codes: (i) 3/2 - x, 1/2 + y, 1/2 - z (ii) 2 - x, 2 - y, -z (iii) 1 - x, 1 - y, -z. The packing view of the title compound is shown in Fig. 2.
Experimental
A solution of 4-chlorobenzaldehyde (0.14 g, 1.0 mmol), cyclic 1,3-dicarbonyl compound (1.0 mmol), NMSM (0.15 g, 1.0 mmol) and piperidine (0.2 equivalents) in EtOH (2 ml) was stirred for 3.5 h. After the reaction was complete as indicated by TLC, the product was filtered and washed with EtOH (2 ml) to remove the excess base and other impurities. Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were prepared by slow evaporation of a solution of the title compound in ethanol at room temperature.
Refinement
Positions of the H atoms were localized from the difference electron-density maps and their distances were geometrically constrained. The H atoms of the amine group were constrained to distances of N—H = 0.901 (10) Å with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(N). The H atoms bound to the C atoms were treated as riding atoms, with C—H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for aromatic, C—H = 0.97 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for methelene, C—H = 0.98 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for methiene, and C—H = 0.96 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(C) for methyl groups. The rotation angles for methyl groups were optimized by least squares. The bond distances of the disordered components were restrained using standard similarity restraint SADI (SHELXL97; Sheldrick, 2008) with an s.u. of 0.01 Å. The atomic displacement parameters of the major and minor components were made similar using the constraint EADP.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with the atom-numbering scheme. The intramolecular hydrogen bond is shown. The displacement ellipsoids are drawn at 30% probability level. H atoms are shown as spheres of arbitary radius.
Fig. 2.
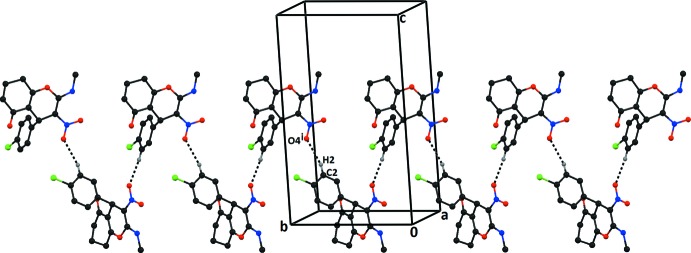
The crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along c axis, showing C2—H2···O4i hydrogen bonds producing C(8) chains parallel to b axis. H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonding have been excluded for clarity. The symmetry code: (i) 3/2 - x, 1/2 + y, 1/2 - z.
Crystal data
| C16H15ClN2O4 | F(000) = 696 |
| Mr = 334.75 | Dx = 1.404 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 2208 reflections |
| a = 8.0285 (4) Å | θ = 2.2–25.0° |
| b = 10.8460 (5) Å | µ = 0.26 mm−1 |
| c = 18.2337 (9) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 94.067 (2)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1583.74 (13) Å3 | 0.35 × 0.30 × 0.30 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2786 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2208 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.029 |
| ω and φ scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −9→8 |
| Tmin = 0.912, Tmax = 0.924 | k = −12→12 |
| 11848 measured reflections | l = −15→21 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.119 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.09 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0482P)2 + 0.9511P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2786 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 218 parameters | Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3 |
| 4 restraints | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| C1 | 0.8013 (3) | 0.7871 (2) | 0.15451 (11) | 0.0393 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.8934 | 0.7510 | 0.1798 | 0.047* | |
| C2 | 0.7070 (3) | 0.8723 (2) | 0.19018 (12) | 0.0440 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.7358 | 0.8944 | 0.2387 | 0.053* | |
| C3 | 0.5699 (3) | 0.9234 (2) | 0.15224 (13) | 0.0443 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.5244 (3) | 0.8923 (2) | 0.08060 (13) | 0.0426 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.4302 | 0.9271 | 0.0561 | 0.051* | |
| C5 | 0.6215 (2) | 0.80814 (19) | 0.04556 (11) | 0.0359 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.5927 | 0.7870 | −0.0031 | 0.043* | |
| C6 | 0.7614 (2) | 0.75474 (18) | 0.08203 (11) | 0.0321 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.8702 (2) | 0.66430 (18) | 0.04219 (11) | 0.0333 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.9648 | 0.6402 | 0.0761 | 0.040* | |
| C8 | 0.9376 (2) | 0.72565 (18) | −0.02368 (11) | 0.0340 (5) | |
| C9 | 1.0653 (3) | 0.8231 (2) | −0.01071 (13) | 0.0408 (5) | |
| C10 | 1.1262 (3) | 0.8872 (2) | −0.07623 (15) | 0.0568 (7) | |
| H10A | 1.1514 | 0.9722 | −0.0631 | 0.068* | 0.787 (5) |
| H10B | 1.2293 | 0.8485 | −0.0888 | 0.068* | 0.787 (5) |
| H10C | 1.0732 | 0.9676 | −0.0794 | 0.068* | 0.213 (5) |
| H10D | 1.2450 | 0.9012 | −0.0664 | 0.068* | 0.213 (5) |
| C11 | 1.0072 (4) | 0.8859 (3) | −0.14166 (18) | 0.0539 (9) | 0.787 (5) |
| H11A | 1.0619 | 0.9181 | −0.1834 | 0.065* | 0.787 (5) |
| H11B | 0.9140 | 0.9397 | −0.1331 | 0.065* | 0.787 (5) |
| C11' | 1.1015 (14) | 0.8288 (11) | −0.1501 (5) | 0.0539 (9) | 0.213 (5) |
| H11C | 1.1949 | 0.7744 | −0.1572 | 0.065* | 0.213 (5) |
| H11D | 1.1009 | 0.8925 | −0.1874 | 0.065* | 0.213 (5) |
| C12 | 0.9406 (3) | 0.7556 (2) | −0.16027 (13) | 0.0488 (6) | |
| H12A | 0.8457 | 0.7608 | −0.1962 | 0.059* | 0.787 (5) |
| H12B | 1.0268 | 0.7070 | −0.1813 | 0.059* | 0.787 (5) |
| H12C | 0.9528 | 0.6925 | −0.1972 | 0.059* | 0.213 (5) |
| H12D | 0.8519 | 0.8105 | −0.1787 | 0.059* | 0.213 (5) |
| C13 | 0.8893 (3) | 0.69552 (19) | −0.09213 (11) | 0.0360 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.7355 (2) | 0.52214 (18) | −0.05564 (11) | 0.0344 (5) | |
| C15 | 0.7772 (2) | 0.54932 (18) | 0.01722 (11) | 0.0329 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.6240 (4) | 0.3970 (3) | −0.15987 (14) | 0.0699 (9) | |
| H16A | 0.5475 | 0.4562 | −0.1823 | 0.105* | |
| H16B | 0.5771 | 0.3158 | −0.1655 | 0.105* | |
| H16C | 0.7275 | 0.4004 | −0.1831 | 0.105* | |
| N1 | 0.7340 (2) | 0.46946 (16) | 0.07175 (10) | 0.0408 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.6539 (2) | 0.42483 (17) | −0.08263 (10) | 0.0442 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.77966 (19) | 0.59923 (14) | −0.10937 (8) | 0.0436 (4) | |
| O2 | 1.1201 (2) | 0.84650 (17) | 0.05139 (10) | 0.0574 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.6480 (2) | 0.37405 (14) | 0.05646 (9) | 0.0529 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.7809 (3) | 0.49375 (16) | 0.13643 (9) | 0.0593 (5) | |
| Cl1 | 0.45353 (11) | 1.03329 (9) | 0.19602 (5) | 0.0864 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.621 (3) | 0.377 (2) | −0.0458 (10) | 0.058 (8)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0421 (12) | 0.0421 (12) | 0.0334 (11) | −0.0032 (10) | 0.0014 (9) | 0.0005 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0523 (13) | 0.0468 (13) | 0.0341 (12) | −0.0107 (11) | 0.0099 (10) | −0.0078 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0439 (12) | 0.0403 (12) | 0.0510 (14) | −0.0058 (10) | 0.0186 (10) | −0.0095 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0342 (11) | 0.0407 (12) | 0.0533 (14) | −0.0023 (9) | 0.0048 (10) | 0.0005 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0362 (11) | 0.0359 (11) | 0.0354 (11) | −0.0074 (9) | 0.0023 (8) | −0.0038 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0334 (10) | 0.0292 (10) | 0.0342 (11) | −0.0072 (8) | 0.0056 (8) | −0.0008 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0329 (10) | 0.0325 (11) | 0.0342 (11) | −0.0016 (8) | −0.0002 (8) | 0.0004 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0325 (10) | 0.0301 (11) | 0.0401 (12) | −0.0018 (8) | 0.0065 (8) | −0.0025 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0336 (11) | 0.0371 (12) | 0.0520 (14) | −0.0031 (9) | 0.0066 (10) | −0.0091 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0599 (15) | 0.0415 (14) | 0.0707 (17) | −0.0169 (12) | 0.0173 (13) | −0.0015 (12) |
| C11 | 0.062 (2) | 0.0432 (19) | 0.0571 (19) | −0.0125 (14) | 0.0095 (16) | 0.0095 (15) |
| C11' | 0.062 (2) | 0.0432 (19) | 0.0571 (19) | −0.0125 (14) | 0.0095 (16) | 0.0095 (15) |
| C12 | 0.0615 (15) | 0.0446 (13) | 0.0417 (13) | −0.0119 (11) | 0.0136 (11) | 0.0021 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0379 (11) | 0.0303 (11) | 0.0405 (12) | −0.0044 (9) | 0.0084 (9) | −0.0011 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0345 (10) | 0.0297 (10) | 0.0399 (12) | −0.0027 (8) | 0.0081 (8) | −0.0001 (9) |
| C15 | 0.0360 (10) | 0.0271 (10) | 0.0358 (11) | −0.0005 (8) | 0.0044 (8) | 0.0014 (8) |
| C16 | 0.087 (2) | 0.076 (2) | 0.0483 (16) | −0.0372 (16) | 0.0119 (14) | −0.0187 (14) |
| N1 | 0.0514 (11) | 0.0311 (10) | 0.0404 (11) | 0.0013 (8) | 0.0063 (8) | 0.0047 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0542 (11) | 0.0378 (11) | 0.0416 (11) | −0.0144 (9) | 0.0102 (9) | −0.0070 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0555 (9) | 0.0415 (9) | 0.0341 (8) | −0.0178 (7) | 0.0051 (7) | −0.0012 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0482 (10) | 0.0634 (11) | 0.0606 (12) | −0.0179 (8) | 0.0035 (8) | −0.0148 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0695 (11) | 0.0331 (9) | 0.0572 (11) | −0.0129 (8) | 0.0109 (8) | 0.0050 (7) |
| O4 | 0.0923 (14) | 0.0494 (10) | 0.0353 (10) | −0.0065 (9) | −0.0008 (9) | 0.0095 (8) |
| Cl1 | 0.0797 (5) | 0.0901 (6) | 0.0916 (6) | 0.0240 (4) | 0.0224 (4) | −0.0350 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C6 | 1.383 (3) | C10—H10D | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.386 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.540 (4) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.375 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C11'—C12 | 1.516 (8) |
| C3—C4 | 1.373 (3) | C11'—H11C | 0.9700 |
| C3—Cl1 | 1.742 (2) | C11'—H11D | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.386 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.487 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C12—H12A | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.390 (3) | C12—H12B | 0.9700 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C12—H12C | 0.9700 |
| C6—C7 | 1.531 (3) | C12—H12D | 0.9700 |
| C7—C8 | 1.507 (3) | C13—O1 | 1.387 (2) |
| C7—C15 | 1.507 (3) | C14—N2 | 1.319 (3) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9800 | C14—O1 | 1.354 (2) |
| C8—C13 | 1.321 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.379 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.480 (3) | C15—N1 | 1.381 (3) |
| C9—O2 | 1.212 (3) | C16—N2 | 1.444 (3) |
| C9—C10 | 1.494 (3) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C10—C11 | 1.475 (4) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C10—C11' | 1.489 (8) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C10—H10A | 0.9700 | N1—O4 | 1.241 (2) |
| C10—H10B | 0.9700 | N1—O3 | 1.264 (2) |
| C10—H10C | 0.9700 | N2—H2A | 0.901 (10) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 121.4 (2) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.1 |
| C6—C1—H1 | 119.3 | C10—C11—H11B | 109.1 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.3 | C12—C11—H11B | 109.1 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 118.5 (2) | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.8 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.7 | C10—C11'—C12 | 113.0 (6) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.7 | C10—C11'—H11C | 109.0 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 122.0 (2) | C12—C11'—H11C | 109.0 |
| C4—C3—Cl1 | 119.25 (19) | C10—C11'—H11D | 109.0 |
| C2—C3—Cl1 | 118.77 (18) | C12—C11'—H11D | 109.0 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.7 (2) | H11C—C11'—H11D | 107.8 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.7 | C13—C12—C11' | 114.3 (4) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.7 | C13—C12—C11 | 109.3 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.05 (19) | C13—C12—H12A | 109.8 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C11'—C12—H12A | 132.3 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 | C11—C12—H12A | 109.8 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.42 (19) | C13—C12—H12B | 109.8 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 120.98 (18) | C11'—C12—H12B | 72.9 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.58 (17) | C11—C12—H12B | 109.8 |
| C8—C7—C15 | 108.83 (16) | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.3 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 110.16 (16) | C13—C12—H12C | 108.6 |
| C15—C7—C6 | 112.73 (16) | C11'—C12—H12C | 109.1 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 108.3 | C11—C12—H12C | 138.6 |
| C15—C7—H7 | 108.3 | H12A—C12—H12C | 71.7 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 108.3 | C13—C12—H12D | 108.6 |
| C13—C8—C9 | 118.77 (19) | C11'—C12—H12D | 108.6 |
| C13—C8—C7 | 123.07 (18) | C11—C12—H12D | 75.4 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 118.15 (18) | H12B—C12—H12D | 136.4 |
| O2—C9—C8 | 120.0 (2) | H12C—C12—H12D | 107.5 |
| O2—C9—C10 | 122.1 (2) | C8—C13—O1 | 122.63 (18) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 117.8 (2) | C8—C13—C12 | 126.9 (2) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 114.4 (2) | O1—C13—C12 | 110.45 (18) |
| C11'—C10—C9 | 119.7 (4) | N2—C14—O1 | 111.88 (18) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 108.7 | N2—C14—C15 | 127.66 (19) |
| C11'—C10—H10A | 129.7 | O1—C14—C15 | 120.45 (18) |
| C9—C10—H10A | 108.7 | C14—C15—N1 | 120.21 (18) |
| C11—C10—H10B | 108.7 | C14—C15—C7 | 123.32 (18) |
| C11'—C10—H10B | 70.3 | N1—C15—C7 | 116.47 (17) |
| C9—C10—H10B | 108.7 | N2—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 107.6 | N2—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—H10C | 72.8 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C11'—C10—H10C | 107.4 | N2—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10C | 107.4 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| H10B—C10—H10C | 138.8 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—H10D | 136.3 | O4—N1—O3 | 120.52 (18) |
| C11'—C10—H10D | 107.4 | O4—N1—C15 | 118.43 (18) |
| C9—C10—H10D | 107.4 | O3—N1—C15 | 121.05 (18) |
| H10A—C10—H10D | 67.7 | C14—N2—C16 | 125.1 (2) |
| H10C—C10—H10D | 106.9 | C14—N2—H2A | 110.2 (17) |
| C10—C11—C12 | 112.5 (2) | C16—N2—H2A | 124.7 (17) |
| C10—C11—H11A | 109.1 | C14—O1—C13 | 119.69 (16) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.9 (3) | C10—C11'—C12—C13 | −33.1 (11) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.1 (3) | C10—C11'—C12—C11 | 57.6 (6) |
| C1—C2—C3—Cl1 | −178.49 (17) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 46.9 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.9 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C11' | −58.2 (6) |
| Cl1—C3—C4—C5 | 177.67 (16) | C9—C8—C13—O1 | 175.11 (18) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.7 (3) | C7—C8—C13—O1 | −4.1 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.1 (3) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | −4.8 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 177.64 (19) | C7—C8—C13—C12 | 176.0 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.3 (3) | C11'—C12—C13—C8 | 20.5 (7) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.48 (18) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −20.3 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −119.8 (2) | C11'—C12—C13—O1 | −159.3 (6) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 58.9 (2) | C11—C12—C13—O1 | 159.8 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—C15 | 118.4 (2) | N2—C14—C15—N1 | 0.5 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C15 | −62.8 (2) | O1—C14—C15—N1 | −179.05 (18) |
| C15—C7—C8—C13 | 13.3 (3) | N2—C14—C15—C7 | −179.6 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C13 | −110.8 (2) | O1—C14—C15—C7 | 0.9 (3) |
| C15—C7—C8—C9 | −166.00 (17) | C8—C7—C15—C14 | −11.7 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 69.9 (2) | C6—C7—C15—C14 | 110.8 (2) |
| C13—C8—C9—O2 | −174.9 (2) | C8—C7—C15—N1 | 168.27 (17) |
| C7—C8—C9—O2 | 4.4 (3) | C6—C7—C15—N1 | −69.2 (2) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | 3.3 (3) | C14—C15—N1—O4 | 176.39 (19) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −177.4 (2) | C7—C15—N1—O4 | −3.6 (3) |
| O2—C9—C10—C11 | −156.9 (3) | C14—C15—N1—O3 | −3.9 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 24.9 (3) | C7—C15—N1—O3 | 176.11 (18) |
| O2—C9—C10—C11' | 159.0 (6) | O1—C14—N2—C16 | 4.2 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11' | −19.1 (7) | C15—C14—N2—C16 | −175.4 (2) |
| C11'—C10—C11—C12 | 57.4 (6) | N2—C14—O1—C13 | −169.49 (18) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −50.4 (4) | C15—C14—O1—C13 | 10.1 (3) |
| C11—C10—C11'—C12 | −59.2 (7) | C8—C13—O1—C14 | −8.7 (3) |
| C9—C10—C11'—C12 | 33.9 (11) | C12—C13—O1—C14 | 171.21 (19) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the pyran ring C7/C8/C13/O1/C14/C15.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2A···O3 | 0.90 (2) | 1.86 (2) | 2.599 (2) | 137 (2) |
| C2—H2···O4i | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.420 (3) | 160 |
| C10—H10A···Cg1ii | 0.97 | 2.75 | 3.515 (2) | 136 |
| C16—H16B···Cg1iii | 0.96 | 2.76 | 3.577 (3) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+3/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x+2, −y+2, −z; (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LD2104).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Ercole, F., Davis, T. P. & Evans, R. A. (2009). Macromolecules, 42, 1500–1511.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Geen, G. R., Evans, J. M. & Vong, A. K. (1996). Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry, 1st ed., edited by A. R. Katrizky, Vol. 3, pp. 469–500. New York: Pergamon.
- Khan, K. M., Ambreen, N., Mughal, U. R., Jalil, S., Perveen, S. & Choudhary, M. I. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 4058–4064. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Raj, T., Bhatia, R. K., Kapur, A., Sharma, M., Saxena, A. K. & Ishar, M. P. S. (2010). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 45, 790–794. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sun, R., Wang, K., Wu, D.-D., Huang, W. & Ou, Y.-B. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813014530/ld2104sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813014530/ld2104Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813014530/ld2104Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report