Abstract
In the title compound, C19H14N2O5, the spiro junction links an oxindole moeity and a furan ring, which subtend a dihedral angle of 83.49 (6)°. The molecular structure features an N—H⋯O hydrogen bond, which generates an S(6) ring motif. The crystal packing is governed by two N—H⋯O interactions, one of which generates a centrosymmetric R 2 2(14) dimer. The other N—H⋯O interaction along with a C—H⋯O hydrogen bond contributes to the formation of a C 2 2[R 2 2(9)] dimeric chain running along the b-axis direction.
Related literature
For applications of spiro oxindoles, see: Kornet & Thio (1976 ▶); Kobayashi et al. (1991 ▶). For applications of furans, see: Schoop et al. (2000 ▶). For puckering and asymmetry parameters, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶). For a related structure, see: Gayathri et al. (2006 ▶). For graph-set notation, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).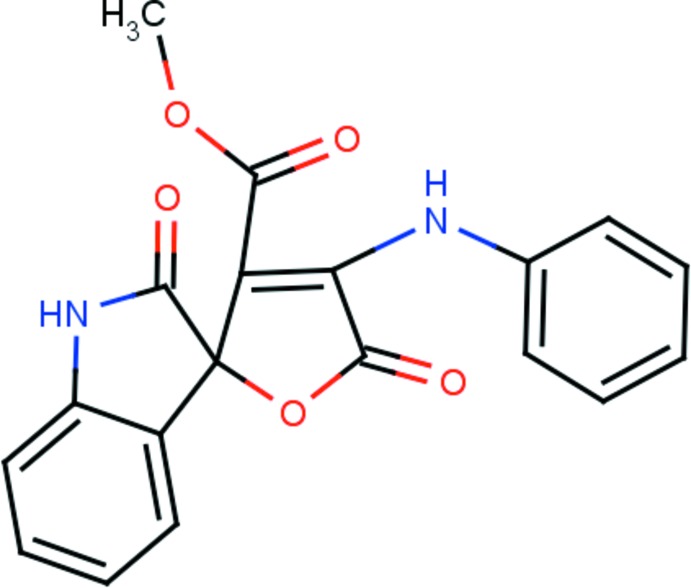
Experimental
Crystal data
C19H14N2O5
M r = 350.32
Monoclinic,

a = 12.1713 (6) Å
b = 13.6144 (7) Å
c = 10.9602 (6) Å
β = 114.813 (2)°
V = 1648.50 (15) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▶) T min = 0.969, T max = 0.979
20901 measured reflections
5167 independent reflections
3502 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.026
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.044
wR(F 2) = 0.132
S = 1.00
5167 reflections
242 parameters
2 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2008 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813014967/rk2403sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813014967/rk2403Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813014967/rk2403Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯O5i | 0.89 (2) | 2.19 (2) | 3.0268 (16) | 157 (2) |
| N2—H2A⋯O1ii | 0.89 (1) | 2.19 (1) | 2.9907 (17) | 149 (1) |
| N2—H2A⋯O5 | 0.89 (1) | 2.39 (2) | 2.9691 (16) | 123 (1) |
| C13—H13A⋯O1iii | 0.96 | 2.41 | 3.2999 (18) | 153 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Babu Varghese, SAIF, IIT, Chennai, India, for the data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Spiro compounds represent an important class of naturally occurring substances characterized by highly pronounced biological properties (Kobayashi et al., 1991). Among them the spiro oxindole is an important structural motif which finds wide applications as antimicrobial and antitumour agents and as inhibitors of the human NK1 receptor (Kornet & Thio, 1976). The construction of polyfunctionalized furans, spiro furans and furan fused cycloalkanes are important from the standpoint of synthesis of biologically active natural products such as aflatoxin, asteltoxin, monensin, panacene etc., (Schoop et al., 2000).
The bond lengths and angles in the title compound are within normal ranges except those at the spiro junction which reflects the presence of bulky subsituents. The dihedral angle between the five (C5/C6/N1/C7/C8) and six membered (C1–C6) rings in the indole group is 4.15 (8)°. The indole moeity is orthogonal to the furan ring as indicated by the dihedral angle of 83.49 (6)° between them.
The furan ring in the structure adopts a twisted conformation with a psuedo–twofold axis passing through the C8 atom and C9–C10 bond. The puckering parameters (Cremer & Pople, 1975) for the furan ring are q2 = 0.0810 (14)Å, φ2 = 310.9 (10)°. The benzene ring is bisectionally oriented to the furan ring, the dihedral angle between them being 52.80 (8)°. The title compound exihibits structural similarities with an already reported related structure (Gayathri et al., 2006.)
The molecular structure is stabilized by intramolecular N2—H2A···O5 bond which generates S(6) ring motif. Atom N2 acts as a donor to O1ii generating a centrosymmetric dimer with graph set descriptor of R22(14) (Bernstein et al., 1995). The bifurcated H bond at O1 facilitates the C13—H13···O1iii bond, which together with a N1—H1(A)···O5i interaction forms a non–centrosymmetric R22(9) dimer. These non–centrosymmetric dimers aggregate to form C22[R22(9)] supramolecular chains running along the b axis. The symmetry codes for the interactions are: (i) 1-x, -1/2+y, 3/2-z; (ii) 1-x, 1-y, 2-z; (iii) 1-x, 1/2+y, 3/2-z.
Experimental
Isatin (1 mmol), aromatic amine (1 mmol), and dimethyl acetylene dicarboxylate (1 mmol) were stirred at room temperature in methanol in the presence of triethylamine (20 mol%) for 4 hrs to give the spirolactones which was filtered out and recrystallized from methanol to afford the pure product (85% yield) as yellow solid.
Refinement
Positions of the H atoms were localized from the difference electron density maps and their distances were geometrically constrained. The H atoms of amine groups were refined freely with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(N). The atoms bound to the C atoms were treated as riding atoms with d(C—H) = 0.93Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for aromatic H; d(C—H) = 0.96Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H. The rotation angle methyl group was optimized by least squares.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at 30% probability level. H atoms are present as small spheres of arbitary radius.
Fig. 2.
Part of crystal structure of the title compound, showing the formation the intramolecular S(6) ring motif, R22(14) centrosymmetric and the R22(9) non–centrosymmetric dimers as viewed along the b–axis.
Crystal data
| C19H14N2O5 | F(000) = 728 |
| Mr = 350.32 | Dx = 1.411 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 3502 reflections |
| a = 12.1713 (6) Å | θ = 2.4–31.0° |
| b = 13.6144 (7) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| c = 10.9602 (6) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 114.813 (2)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 1648.50 (15) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD diffractometer | 5167 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine–focus sealed tube | 3502 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.026 |
| ω– and φ–scans | θmax = 31.0°, θmin = 2.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −17→17 |
| Tmin = 0.969, Tmax = 0.979 | k = −19→19 |
| 20901 measured reflections | l = −15→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.132 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.00 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0665P)2 + 0.2325P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 5167 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 242 parameters | Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R–factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R–factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R–factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R–factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R–factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.20517 (13) | 0.35795 (13) | 0.37822 (16) | 0.0565 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.2233 | 0.3054 | 0.3355 | 0.068* | |
| C2 | 0.13329 (14) | 0.43504 (14) | 0.30526 (17) | 0.0602 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.1041 | 0.4347 | 0.2121 | 0.072* | |
| C3 | 0.10387 (14) | 0.51262 (13) | 0.36769 (17) | 0.0573 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.0555 | 0.5635 | 0.3164 | 0.069* | |
| C4 | 0.14643 (12) | 0.51452 (11) | 0.50668 (16) | 0.0494 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.1265 | 0.5660 | 0.5494 | 0.059* | |
| C5 | 0.21853 (11) | 0.43880 (9) | 0.57979 (14) | 0.0401 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.24886 (11) | 0.36182 (10) | 0.51613 (15) | 0.0444 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.35751 (11) | 0.32910 (9) | 0.73933 (15) | 0.0440 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.28153 (11) | 0.42334 (9) | 0.72866 (14) | 0.0383 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.21736 (12) | 0.45201 (9) | 0.89615 (14) | 0.0416 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.30798 (11) | 0.53001 (8) | 0.90518 (13) | 0.0355 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.35077 (10) | 0.50798 (8) | 0.81357 (13) | 0.0346 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.45130 (11) | 0.55592 (8) | 0.79841 (13) | 0.0347 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.57815 (14) | 0.55042 (11) | 0.68384 (18) | 0.0541 (4) | |
| H13A | 0.5593 | 0.6150 | 0.6455 | 0.081* | |
| H13B | 0.5951 | 0.5079 | 0.6240 | 0.081* | |
| H13C | 0.6477 | 0.5537 | 0.7686 | 0.081* | |
| C14 | 0.26345 (11) | 0.64409 (9) | 1.05174 (13) | 0.0383 (3) | |
| C15 | 0.30989 (14) | 0.68008 (11) | 1.18109 (15) | 0.0512 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.3924 | 0.6758 | 1.2355 | 0.061* | |
| C16 | 0.23301 (17) | 0.72265 (13) | 1.22943 (18) | 0.0649 (5) | |
| H16 | 0.2643 | 0.7472 | 1.3167 | 0.078* | |
| C17 | 0.11072 (16) | 0.72924 (13) | 1.1501 (2) | 0.0646 (5) | |
| H17 | 0.0594 | 0.7565 | 1.1844 | 0.077* | |
| C18 | 0.06501 (14) | 0.69548 (12) | 1.02087 (18) | 0.0592 (4) | |
| H18 | −0.0174 | 0.7007 | 0.9665 | 0.071* | |
| C19 | 0.14097 (12) | 0.65364 (11) | 0.97084 (15) | 0.0482 (3) | |
| H19 | 0.1097 | 0.6318 | 0.8823 | 0.058* | |
| N1 | 0.32908 (11) | 0.29741 (8) | 0.61328 (14) | 0.0520 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.3634 (15) | 0.2457 (10) | 0.5943 (17) | 0.062* | |
| N2 | 0.34264 (10) | 0.60019 (8) | 1.00166 (11) | 0.0393 (2) | |
| H2A | 0.4110 (10) | 0.6321 (10) | 1.0165 (15) | 0.047* | |
| O1 | 0.42614 (9) | 0.29188 (7) | 0.84405 (12) | 0.0569 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.19725 (8) | 0.39643 (6) | 0.78561 (10) | 0.0445 (2) | |
| O3 | 0.17129 (11) | 0.43426 (8) | 0.96977 (12) | 0.0624 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.47595 (8) | 0.51218 (7) | 0.70423 (10) | 0.0448 (2) | |
| O5 | 0.50692 (8) | 0.62507 (6) | 0.86606 (9) | 0.0437 (2) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0449 (8) | 0.0651 (9) | 0.0649 (10) | −0.0106 (7) | 0.0283 (8) | −0.0261 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0438 (8) | 0.0854 (12) | 0.0511 (8) | −0.0129 (8) | 0.0197 (7) | −0.0146 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0410 (7) | 0.0686 (10) | 0.0575 (9) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0160 (7) | 0.0021 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0405 (7) | 0.0483 (7) | 0.0580 (9) | 0.0048 (6) | 0.0193 (7) | −0.0054 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0299 (6) | 0.0394 (6) | 0.0516 (7) | −0.0037 (5) | 0.0176 (5) | −0.0109 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0326 (6) | 0.0419 (6) | 0.0606 (8) | −0.0062 (5) | 0.0214 (6) | −0.0156 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0325 (6) | 0.0304 (6) | 0.0668 (9) | −0.0038 (5) | 0.0186 (6) | −0.0062 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0319 (6) | 0.0315 (5) | 0.0542 (8) | −0.0026 (4) | 0.0206 (6) | −0.0058 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0381 (6) | 0.0368 (6) | 0.0533 (8) | −0.0040 (5) | 0.0224 (6) | 0.0004 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0325 (5) | 0.0308 (5) | 0.0442 (7) | −0.0012 (4) | 0.0172 (5) | 0.0022 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0321 (5) | 0.0280 (5) | 0.0444 (7) | −0.0020 (4) | 0.0167 (5) | −0.0012 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0330 (5) | 0.0303 (5) | 0.0428 (6) | −0.0001 (4) | 0.0180 (5) | 0.0019 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0546 (8) | 0.0540 (8) | 0.0706 (10) | −0.0117 (7) | 0.0429 (8) | −0.0084 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0401 (6) | 0.0340 (6) | 0.0454 (7) | −0.0037 (5) | 0.0224 (6) | −0.0024 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0463 (7) | 0.0529 (8) | 0.0534 (8) | −0.0050 (6) | 0.0199 (7) | −0.0145 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0698 (11) | 0.0678 (10) | 0.0635 (10) | −0.0082 (8) | 0.0344 (9) | −0.0273 (8) |
| C17 | 0.0623 (10) | 0.0629 (10) | 0.0865 (12) | −0.0056 (8) | 0.0489 (10) | −0.0207 (9) |
| C18 | 0.0431 (8) | 0.0626 (9) | 0.0763 (11) | −0.0004 (7) | 0.0293 (8) | −0.0091 (8) |
| C19 | 0.0426 (7) | 0.0546 (8) | 0.0484 (8) | −0.0004 (6) | 0.0200 (6) | −0.0041 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0444 (6) | 0.0364 (6) | 0.0737 (8) | 0.0024 (5) | 0.0234 (6) | −0.0171 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0356 (5) | 0.0399 (5) | 0.0455 (6) | −0.0056 (4) | 0.0200 (5) | −0.0062 (4) |
| O1 | 0.0459 (5) | 0.0375 (5) | 0.0743 (7) | 0.0017 (4) | 0.0126 (5) | −0.0019 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0383 (5) | 0.0376 (4) | 0.0634 (6) | −0.0096 (4) | 0.0268 (5) | −0.0070 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0679 (7) | 0.0621 (7) | 0.0739 (7) | −0.0214 (5) | 0.0460 (6) | −0.0051 (6) |
| O4 | 0.0443 (5) | 0.0417 (5) | 0.0575 (6) | −0.0095 (4) | 0.0304 (5) | −0.0116 (4) |
| O5 | 0.0456 (5) | 0.0371 (4) | 0.0523 (5) | −0.0115 (4) | 0.0245 (4) | −0.0072 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C6 | 1.377 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.4564 (16) |
| C1—C2 | 1.385 (2) | C12—O5 | 1.2137 (14) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C12—O4 | 1.3304 (15) |
| C2—C3 | 1.385 (2) | C13—O4 | 1.4498 (16) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.388 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3729 (19) | C14—C15 | 1.3773 (19) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C14—C19 | 1.3842 (19) |
| C5—C6 | 1.3920 (17) | C14—N2 | 1.4253 (16) |
| C5—C8 | 1.4981 (19) | C15—C16 | 1.381 (2) |
| C6—N1 | 1.4083 (19) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C7—O1 | 1.2112 (17) | C16—C17 | 1.376 (3) |
| C7—N1 | 1.3466 (19) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C8 | 1.5571 (17) | C17—C18 | 1.366 (2) |
| C8—O2 | 1.4537 (15) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C11 | 1.4986 (16) | C18—C19 | 1.380 (2) |
| C9—O3 | 1.1847 (16) | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C9—O2 | 1.3607 (17) | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C10 | 1.5041 (17) | N1—H1A | 0.887 (9) |
| C10—C11 | 1.3448 (17) | N2—H2A | 0.890 (9) |
| C10—N2 | 1.3545 (16) | ||
| C6—C1—C2 | 117.66 (14) | O5—C12—O4 | 124.86 (11) |
| C6—C1—H1 | 121.2 | O5—C12—C11 | 123.91 (11) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 121.2 | O4—C12—C11 | 111.20 (10) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.61 (15) | O4—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.2 | O4—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.2 | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.11 (16) | O4—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.64 (14) | C15—C14—C19 | 119.50 (12) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.7 | C15—C14—N2 | 119.60 (12) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.7 | C19—C14—N2 | 120.88 (12) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.78 (13) | C14—C15—C16 | 119.51 (14) |
| C4—C5—C8 | 130.60 (12) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.2 |
| C6—C5—C8 | 108.54 (11) | C16—C15—H15 | 120.2 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 121.17 (14) | C17—C16—C15 | 120.83 (15) |
| C1—C6—N1 | 129.20 (13) | C17—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| C5—C6—N1 | 109.60 (12) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| O1—C7—N1 | 128.04 (12) | C18—C17—C16 | 119.66 (14) |
| O1—C7—C8 | 124.58 (13) | C18—C17—H17 | 120.2 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 107.35 (12) | C16—C17—H17 | 120.2 |
| O2—C8—C11 | 103.98 (10) | C17—C18—C19 | 120.11 (15) |
| O2—C8—C5 | 111.85 (10) | C17—C18—H18 | 119.9 |
| C11—C8—C5 | 117.76 (11) | C19—C18—H18 | 119.9 |
| O2—C8—C7 | 105.30 (10) | C18—C19—C14 | 120.34 (14) |
| C11—C8—C7 | 115.18 (10) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.8 |
| C5—C8—C7 | 102.35 (10) | C14—C19—H19 | 119.8 |
| O3—C9—O2 | 122.23 (12) | C7—N1—C6 | 111.98 (11) |
| O3—C9—C10 | 130.00 (13) | C7—N1—H1A | 123.5 (11) |
| O2—C9—C10 | 107.70 (11) | C6—N1—H1A | 124.2 (11) |
| C11—C10—N2 | 130.46 (11) | C10—N2—C14 | 123.85 (10) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 107.25 (11) | C10—N2—H2A | 116.6 (10) |
| N2—C10—C9 | 121.93 (11) | C14—N2—H2A | 117.1 (10) |
| C10—C11—C12 | 126.32 (11) | C9—O2—C8 | 110.27 (9) |
| C10—C11—C8 | 110.00 (10) | C12—O4—C13 | 116.51 (10) |
| C12—C11—C8 | 123.66 (11) | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.3 (2) | C5—C8—C11—C10 | 122.03 (12) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.1 (2) | C7—C8—C11—C10 | −117.01 (12) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.6 (2) | O2—C8—C11—C12 | 176.23 (10) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.3 (2) | C5—C8—C11—C12 | −59.41 (15) |
| C3—C4—C5—C8 | 176.78 (13) | C7—C8—C11—C12 | 61.55 (16) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 2.1 (2) | C10—C11—C12—O5 | −2.4 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—N1 | −175.49 (13) | C8—C11—C12—O5 | 179.27 (12) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.7 (2) | C10—C11—C12—O4 | 175.70 (12) |
| C8—C5—C6—C1 | −178.88 (12) | C8—C11—C12—O4 | −2.62 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | 176.37 (12) | C19—C14—C15—C16 | 1.8 (2) |
| C8—C5—C6—N1 | −0.85 (14) | N2—C14—C15—C16 | 179.97 (14) |
| C4—C5—C8—O2 | 73.88 (17) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.2 (3) |
| C6—C5—C8—O2 | −109.27 (11) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −1.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—C8—C11 | −46.46 (18) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 1.0 (3) |
| C6—C5—C8—C11 | 130.39 (11) | C17—C18—C19—C14 | 1.1 (2) |
| C4—C5—C8—C7 | −173.86 (13) | C15—C14—C19—C18 | −2.5 (2) |
| C6—C5—C8—C7 | 2.99 (12) | N2—C14—C19—C18 | 179.41 (13) |
| O1—C7—C8—O2 | −65.30 (15) | O1—C7—N1—C6 | −177.92 (13) |
| N1—C7—C8—O2 | 112.83 (12) | C8—C7—N1—C6 | 4.03 (15) |
| O1—C7—C8—C11 | 48.61 (18) | C1—C6—N1—C7 | 175.69 (14) |
| N1—C7—C8—C11 | −133.26 (12) | C5—C6—N1—C7 | −2.14 (15) |
| O1—C7—C8—C5 | 177.64 (12) | C11—C10—N2—C14 | 151.63 (13) |
| N1—C7—C8—C5 | −4.23 (13) | C9—C10—N2—C14 | −36.17 (18) |
| O3—C9—C10—C11 | 167.68 (15) | C15—C14—N2—C10 | 152.11 (13) |
| O2—C9—C10—C11 | −9.33 (14) | C19—C14—N2—C10 | −29.79 (18) |
| O3—C9—C10—N2 | −6.1 (2) | O3—C9—O2—C8 | −169.38 (13) |
| O2—C9—C10—N2 | 176.87 (11) | C10—C9—O2—C8 | 7.91 (14) |
| N2—C10—C11—C12 | 1.5 (2) | C11—C8—O2—C9 | −3.79 (13) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −171.60 (11) | C5—C8—O2—C9 | −131.88 (11) |
| N2—C10—C11—C8 | 179.99 (12) | C7—C8—O2—C9 | 117.71 (11) |
| C9—C10—C11—C8 | 6.91 (14) | O5—C12—O4—C13 | 0.81 (19) |
| O2—C8—C11—C10 | −2.33 (13) | C11—C12—O4—C13 | −177.27 (11) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···O5i | 0.89 (2) | 2.19 (2) | 3.0268 (16) | 157 (2) |
| N2—H2A···O1ii | 0.89 (1) | 2.19 (1) | 2.9907 (17) | 149 (1) |
| N2—H2A···O5 | 0.89 (1) | 2.39 (2) | 2.9691 (16) | 123 (1) |
| C13—H13A···O1iii | 0.96 | 2.41 | 3.2999 (18) | 153 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2; (iii) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+3/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: RK2403).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, U.S.A.
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Gayathri, D., Velmurugan, D., Ravikumar, K., Savitha, G. & Perumal, P. T. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o5947–o5949.
- Kobayashi, J., Tsuda, M., Agemi, K., Shigemori, H., Ishibashi, M., Sasaki, T. & Mikami, Y. (1991). Tetrahedron, 47, 6617–6622.
- Kornet, M. J. & Thio, A. P. (1976). J. Med. Chem. 19, 892–898. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Schoop, A., Grieving, H. & Gohrt, A. (2000). Tetrahedron Lett. 41, 1913–1916.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813014967/rk2403sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813014967/rk2403Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813014967/rk2403Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




