Abstract
Natural killer (NK) cells are classically viewed as lymphocytes that provide innate surveillance against virally-infected cells and tumor cells through release of cytolytic mediators and IFN-γ. In humans, blood CD56dim NK cells specialize in lysis of cell targets1. In lymph nodes, CD56bright NK cells secrete IFN-γ cooperating with dendritic cells (DC) and T cells in the generation of adaptive responses1, 2. Here we report the characterization of a human NK cell subset located in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues (MALT), such as tonsils and Payer’s patches, which is hard-wired to secrete interleukin (IL)-22, IL-26, and leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF). These NK cells, which we refer to as NK-22 cells, are triggered by acute exposure to IL-23. In vitro, NK-22-secreted cytokines stimulate epithelial cells to secrete IL-10, proliferate and express a variety of mitogenic and anti-apoptotic molecules. NK-22 cells are also found in mouse MALT and appear in the small intestine lamina propria during bacterial infection suggesting that NK-22 cells provide an innate source of IL-22 that may help constrain inflammation and protect mucosal sites.
Human NK cells have been dissected into CD56dim and CD56bright subsets possessing either lytic or IFN-γ secretory functions1. Recently, a subset of tonsil NK cells was shown to express the receptor NKp442, which is not present on blood NK cells unless they are activated in vitro with IL-2 or IL-153. We noticed that NKp44+ NK cells are present in tonsils, but not in lymph nodes (Supplementary Fig. 1). Immunohistochemical and immunofluorescent analyses revealed that NKp44+ NK cells are predominantly located in the mucosa surrounding the lymphoid follicles (Fig. 1a-c), with only a few in the interfollicular area (not shown). Because tonsils are associated with the oral mucosa, we hypothesized that NKp44 identifies a subset of NK cells preferentially situated in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues (MALT). Indeed, we also found NKp44+ cells in the Peyer’s patches of the ileum and the appendix (Fig. 1d, e).
Figure 1. NKp44+ NK cells are prominently found within MALT.
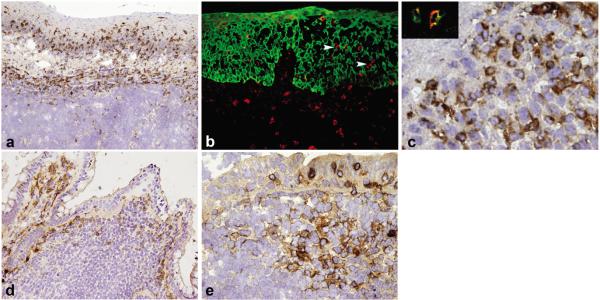
a, Immunohistochemical analysis of tonsil sections with anti-NKp44 shows NKp44+ NK cells residing within the tonsil epithelium and the lamina propria. b, Double immunofluorescence confirms that NKp44+ cells (red) are either in the lamina propria, or within the surface epithelium in close contact with cytokeratin-5+ (green) epithelial cells (white arrowheads). c, At high power view, NKp44+ NK cells show a round to oval morphology and co-express CD56 (inset). d,e, Numerous NKp44+ NK cells are present in the dome region of ileum Peyer's patches (d) and in the luminal epithelium, dome and interfollicular regions of the appendix (e).
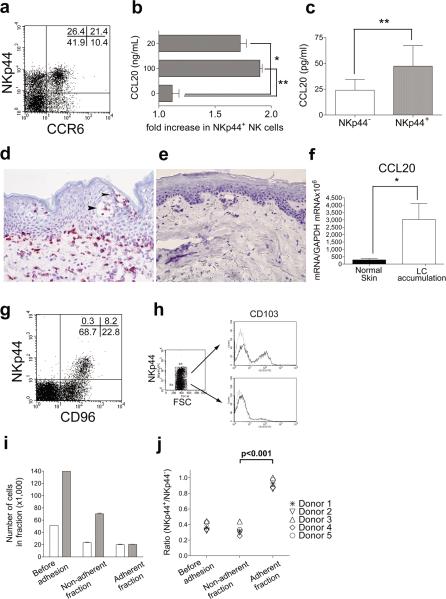
Gene expression profiles of tonsil NKp44+ and NKp44− NK cells (Supplementary Fig. 2 and Table 1) revealed that NKp44+ NK cells preferentially express the chemokine receptor CCR6 and its ligand CCL20 (Supplementary Table 1), which are known to direct mucosal migration of memory CD4+ T cells, B cells, DC and, TH17 T cells4, 5. Flow cytometry and migration assays confirmed that a large fraction of NKp44+ NK cells express functional CCR6 (Fig. 2a, b). Moreover, NKp44+ NK cells secreted more CCL20 than NKp44− NK cells (Fig. 2c). Thus, NKp44+ NK cells can contribute to CCL20 production in the mucosa, promoting their own accumulation and attracting other immune cells. That the CCR6-CCL20 axis has a major role in driving localization of NKp44+ NK cells was corroborated by analysis of human dermatitis with proliferation and retention of Langerhans cell (LC) in the skin6. LC accumulation caused abnormal production of CCL20, resulting in extensive infiltration of NKp44+ NK cells (Fig. 2d-f). Consistent with their localization in MALT, NKp44+ NK cells also expressed multiple proteins known to promote lymphocyte adhesion to epithelial cells, including CD967 and CD1038 (Supplementary Table 1). Flow cytometric analysis confirmed higher levels of CD96 on all NKp44+ NK cells than on NKp44− NK cells (Fig. 2g) as well as expression of CD103 on a significant percentage of NKp44+ NK cells (Fig. 2h). Moreover, NKp44+ NK cells adhered to epithelial cells better than NKp44− NK cells (Fig. 2i, j).
Figure 2. A subset of tonsil NKp44+ NK cells express CCR6, respond to CCL20 in vitro and in vivo, produce CCL20, and adhere to epithelial cells.
a, Approximately 50% of NKp44+ NK cells express CCR6. b, Tonsil NK cells migrate in response to CCL20. Bars indicate the ratio between the percentage of input NKp44+ NK cells versus the percentage of migrated NKp44+ NK cells. c, PMA/ionomycin treated NKp44+ NK cells produce significantly more CCL20 than NKp44− NK cells. d, e, A case of dermatitis with pathological LC accumulation shows extensive skin infiltration of NKp44+ NK cells as compared to a normal skin. Arrows indicate pseudo-Pautrier abscesses indicative of LC accumulation6. f, Real time PCR shows that skin with LC accumulation produces more CCL20 than normal skin. g, NKp44+ NK cells express higher levels of CD96 than NKp44− NK cells. h, A discrete subset of NKp44+ NK cells expresses CD103. i, NKp44+ NK cells firmly adhere to epithelial cells. The ratio of NKp44+ to NKp44− cells within non-adherent and adherent CD3−CD56+ cells was determined by flow cytometry. j, The adhesiveness of NKp44+ NK cells to epithelial cells is consistent in different donors. All error bars indicate s.d. with n=3
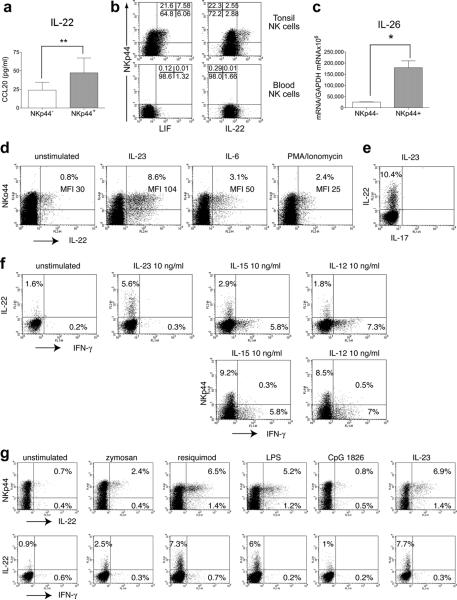
Next we evaluated function of NKp44+ NK cells. Previous studies demonstrated that tonsil NK cells have limited cytotoxic capacity2. Indeed, no intracellular perforin and little intracellular granzyme B were detected in NKp44+ NK cells (Supplementary Fig. 3). Moreover, intracellular IFN-γ was barely detectable in NKp44+ NK cells (Supplementary Fig. 4). Intriguingly, gene chip analysis of NKp44+ NK cells revealed production of IL-22, which is involved in mucosal defense9-13. IL-26 and leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF), which activate epithelial cells14, were also elevated (Supplementary Table 1). To corroborate these data, we measured IL-22 secretion by tonsil NK cells stimulated with PMA/ionomycin and assessed the intracellular content of IL-22 and LIF in activated tonsil NK cell subsets. Both assays confirmed augmented IL-22 and LIF secretion by NKp44+ NK cells (Fig. 3a and 3b). Preferential IL-26 expression by NKp44+ NK cells was validated by realt-time-PCR (Fig. 3c). Although IL-22 and IL-26 are part of the TH17 CD4+ T cell cytokine profile13, 15-19, NKp44+ NK cells did not produce IL-17 (data not shown). Thus, we will refer to NKp44+ NK cells that secrete IL-22 as NK-22 cells.
Figure 3. Tonsil NKp44+ NK cells produce IL-22, IL-26 and LIF. IL-23 and TLR-activated monocytes trigger IL-22 secretion.
a, IL-22 concentration in supernatants of NKp44+ and NKp44− tonsil NK cells stimulated with PMA/ionomycin. b, Intracellular IL-22 and LIF content of tonsil NKp44+ cells and blood NK cells stimulated with PMA/ionomycin. c, NKp44+ NK cells express higher levels of IL-26 mRNA than NKp44− NK cells. d-e, IL-23 triggers secretion of IL-22 (d, e) but not IL-17 (e) by NK-22 cells. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. f, NKp44+ NK cells produce IL-22 in response to IL-23 and, to some extent, IL-15. NKp44− NK cells release IFN-γ in response to IL-12 or IL-15. g, Monocytes stimulated with resiquimod and LPS induce IL-22 secretion in NK-22 cells. All error bars indicate s.d. with n=3
While PMA/ionomycin stimulation exposed the unique NK-22 cytokine profile, the physiological stimuli that activate NK-22 cells were not clear. Engagement of NKp44 or other receptors with specific antibodies had no effect (data not shown). However, stimulation of tonsil NKp44+ NK cells with a variety of inflammatory cytokines revealed that NK-22 cells are selectively and acutely responsive to IL-23 (Fig. 3d and Supplementary Fig. 5a). Similar results were observed for Peyer's patch NK cells (Supplementary Fig. 5b). Of all NKp44+ NK cells, only those expressing CCR6 responded to IL-23 (Supplementary Fig 5c), revealing that NK-22 cells are a discrete subset within NKp44+ NK cells. IL-23 did not elicit IL-17 (Fig. 3e). NK-22 cells were also slightly responsive to IL-6 and IL-15 (Fig. 3d and 3f). IL-12, which induces IFN-γ in blood NK cells, induced neither IL-22 nor IFN-γ in NK-22 cells (Fig. 3f).
In contrast, tonsilar NKp44− NK cells did not respond to IL-23, but did react to IL-12, secreting IFN-γ rather than IL-22 (Fig. 3f). In addition, IL-15 and IL-12 induced IFN-γ in NKp44− NK cells almost equally well (Fig. 3f). Neither IL-23 nor IL-15 induced IL-22 by peripheral blood NK cells (data not shown). Together, these results indicate that MALT NK-22 cells are hard-wired to secrete IL-22, particularly in response to IL-23. In contrast, NKp44− NK cells are programmed to secrete IFN-γ after stimulation with IL-12 or IL-15. Thus, NKp44− NK cells most likely correspond to the tonsilar NK cells recently shown to inhibit Epstein-Barr virus-induce B cell transformation through IFN-γ secretion20.
Monocytes, DC and macrophages produce IL-23 in response to microbial stimuli21 and hence may provide a major intramucosal source of stimuli for NK-22 cell activation. To test this hypothesis, tonsilar NK cells were co-cultured with either unstimulated or activated human allogeneic monocytes. As predicted, activated monocytes induced IL-22 production by NK-22 cells (Fig. 3g). Culture supernatants from activated monocytes contained IL-23 and induced IL-22 secretion just like monocytes (Supplementary Fig. 6).
To assess the impact of NK-22 cell-secreted cytokines on epithelial cell function, we measured proliferation and cytokine secretion of colon epithelial cells after stimulation with culture supernatant harvested from activated NK-22 cells. NK-22 cell-conditioned medium induced proliferation of epithelial cells (Fig. 4a) and secretion of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 (Fig. 4b). Importantly, NK-22 cell-conditioned medium was more effective than recombinant IL-22 alone, consistent with a concerted action of IL-22, IL-26 and possibly yet unknown factors. IL-22, IL-26 and LIF have been shown to activate signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)10, 22, a known inducer of cell survival and proliferation, as well as STAT1. Robust STAT3 and STAT1 phosphorylation was observed in epithelial cells following stimulation with NK-22 cell-conditioned medium (Fig. 4c). To further define downstream signalling mediators induced by NK-22-derived cytokines, we obtained gene expression profiles of colon epithelial cells treated with recombinant IL-22 (Supplementary Table 2). IL-22-induced genes were subsequently verified in epithelial cells stimulated with NK-22 cell-conditioned medium by immunoblot and real-time PCR analyses. Remarkably, NK-22 cell-conditioned medium strongly induced the proto-oncogenes Bcl-3 and Bcl-6 (Supplementary Fig. 7). Bcl-3 interaction with NF-κB promotes transcription of proliferation genes in response to growth signals while Bcl-6 may favour proliferation by preventing terminal differentiation23. Furthermore, we detected transcriptional activation of genes involved in cell growth (PBEF1), cell cycle progression (c-Myc) and protection from apoptotic stimuli (kinase SGK1, serine protease inhibitors SerpinA1 and A3 and the protein Gadd45γ) (Supplementary Fig. 7). Thus, NK-22 cytokines stimulate epithelial cell proliferation, secretion of IL-10 and activate a variety of mitogenic and antiapoptotic pathways.
Figure 4. NK-22 cell-secreted cytokines stimulate epithelial cells to proliferate, release IL-10 and activate STAT1 and STAT3.
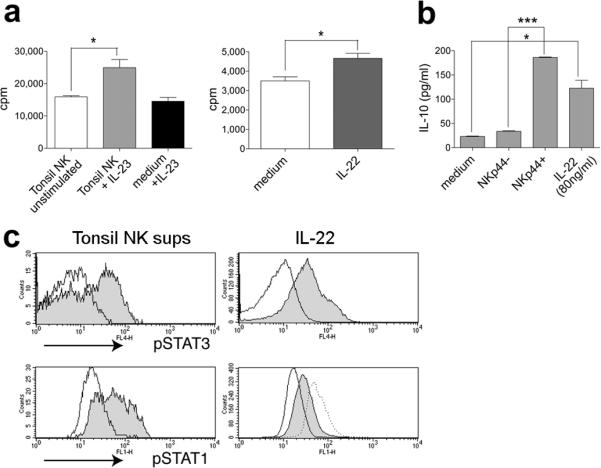
a, Colo205 proliferation in response to supernatants derived from resting or IL-23-stimulated tonsil NK cells (left panel) or IL-22 (right panel). b, IL-10 secretion by Colo205 stimulated with supernatants from activated NKp44+ or NKp44− tonsil NK cells or IL-22. c, STAT3 and STAT1 phosphorylation in Colo205 stimulated with supernatants of IL-23-activated NKp44+ NK cells (left panels, grey histograms), NKp44− NK cells (left panels, empty histograms), IL-22 (right panels, grey histograms) or medium (right panels, empty histograms). As an additional control for STAT1 phosphorylation, cells were stimulated with IFN-γ (dotted line). All error bars indicate s.d. with n=3
To identify NK-22 cells in mouse MALT, we examined NK cells in Peyer’s patches of C57/BL6 mice and found two subsets: NKp46+NK1.1+ (40-50% of total NKp46+ cells) and NKp46+NK1.1− (Supplementary Fig. 8). Acute in vitro stimulation with IL-23 elicited production of IL-22 in both subsets (Fig. 5a, b). No NK-22 cells were detectable in the lamina propria (LP) or within the intestinal epithelium (IEL) under homeostatic conditions (Supplementary Fig. 9a). Since IL-22 has been shown to be essential for the early host defense against Citrobacter rodentium (C. rodentium)11, we infected mice with C. rodentium and observed the appearance of NK-22 cells in the lamina propria 6 days after oral inoculation (Fig. 5c and Supplementary Fig. 9b). In recombination activating gene-2 (RAG-2)-deficient mice, which lack T cell sources of IL-22, NK-22 were detected in IELs before and after infection with C. rodentium (Supplementary Fig. 10a) and spontaneously secreted IL-22 ex-vivo after infection. Moreover, depletion of RAG2−/− mice with NK1.1 at early stages of infection resulted in accelerated mortality of infected mice (Supplementary Fig. 10b), suggesting that NK-22 may provide an innate source of IL-22 that contributes to mucosal immunity.
Figure 5. Identification of mouse NK-22 cells.
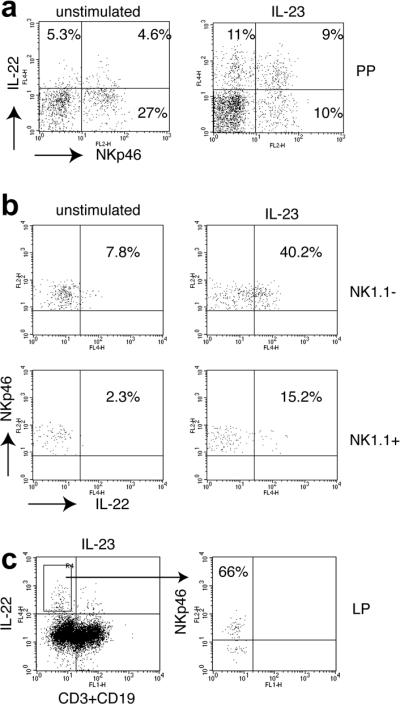
a, In vitro stimulation of Peyer’s patches cells with IL-23 induces production of IL-22 by NKp46+ NK cells. A gate was applied to exclude CD3+CD19+ cells; b, NKp46+ IL-22-producing cells are in part NK1.1− and, to a lower degree, NK1.1+. c, NK-22 cell appear in the small intestine lamina propria of C. rodentium-infected mice. A large proportion (55-80% in different experiments) of cells producing IL-22 in the lamina propria express NKp46.
Finally, we investigated the developmental pathway of NK-22 cells. Multiple similarities between NK-22 and TH17 cells suggest similar differentiation requirements, further supported by NK-22 expression of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), RORα, RORγ and IRF4 (Supplementary Fig. 11 and Supplementary Table 1), all transcription factors recognized as being required for TH17 differentiation and/or IL-22 secretion24-26. However, culture of peripheral blood or cord blood NK cells under various TH17 polarizing conditions4, 5, 15, 27-29 with or without various AHR ligands24, 25 did not yield any IL-22-producing NK cells. Thus, NK-22 cells may develop from local progenitors, perhaps lymphoid tissue inducer (LTi) cells, which also express RORγ30, under the influence of microenvironmental factors such as intestinal microbiota.
In conclusion, we propose that NK-22 cells are an innate cell type that contributes to mucosal homeostasis. Although NK-22 and TH17 cells share several features, NK-22 cells are unique in several respects. First, because they do not secrete IL-17, NK-22 cells are unlikely to have pro-inflammatory activity. Second, while TH17 cells are triggered through the TCR and require IL-23 for expansion17-19, NK-22 cells are directly and acutely stimulated by IL-23. Third, blood NK cells cultured in TH17 polarizing cytokines and AHR agonists do not acquire the ability to secrete IL-22, perhaps reflecting a distinct differentiation pathway. We envision that upon microbial challenge of mucosal barriers and subsequent release of IL-23 by antigen-presenting cells, NK-22 cells provide a source of IL-22 and other cytokines that may help constrain inflammation and protect mucosal sites.
Methods Summary
Isolation of tonsil NK cells
Tonsils were mechanically disrupted and NK cells were pre-enriched by magnetic purification with CD56 microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec). For many experiments cells were further stained with a combination of -CD56, -CD3, -CD19 (Pharmingen) and -NKp44 antibodies and sorted either on a Moflo cell sorter (Cytomation) or a FACSVantage sorter (BD).
Reagents
Human and mouse IL-22 ELISA kits were obtained from Antigenix America. CCL20 ELISA kit, recombinant CCL20, IL-23 ELISA kit, anti-human IL-22 antibody for intracellular staining and anti-mouse NKp46 were obtained by R&D. IL-22 and IL-1β were purchased from Peprotec. IL-22 was used at 80 ng/ml for stimulation of epithelial cells. IL-23 was used at 40ng/ml for stimulation of NK cells, unless otherwise stated. IL-6, IL-15, IL-26, mouse and human IL-23 were purchased from R&D. Anti-IL-17A antibody was obtained from eBioscience. IL-12p70 and anti-IFN-γ, -TNF-α, -GM-CSF, -LIF, -perforin, -granzyme, -CCR6, -CD103, -pSTAT3, -pSTAT1, -NK1.1, -mouse CD3 and -mouse CD19 antibodies were purchased from Pharmingen. Anti-BCL-3, -BCL-6, -MCL-1 and -actin antibodies for immunoblotting were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. IL-10 was quantified in cell culture supernatants with the CBA human inflammation kit (Pharmingen). Anti-NKp44 and -CD96 antibodies were produced and conjugated in our laboratory.
Full Methods and any associated references are available in the online version of the paper at www.nature.com/nature.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Jackie Hughes, Bill Eades (High Speed Cell Sorter Core, Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center) and Suzanne Schloehmann (Department of Pathology and Immunology Sorting Core Facility, Washington University School of Medicine) for expert cell sorting; Dr. Randall Clary and the nursing staff (Children’s Hospital, Washington University School of Medicine) for providing tonsil specimens; Silvia Lonardi (University of Brescia) for excellent assistance in immunohistochemistry; John Pfeifer (Department of Pathology and Immunology, Washington University School of Medicine) for providing gut specimens; Aaron Rapaport and Steve McCartney for help in gene chip analysis. Susan Gilfillan for critically reading the manuscript. This work was supported by NIH grants R01AI056139-05 and R21AI067748-02 (to M. Co.) and NIDDK R01 DK079798 (to J. C. M.).
References
- 1.Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Caligiuri MA. The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol. 2001;22:633–40. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4906(01)02060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ferlazzo G, Munz C. NK cell compartments and their activation by dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2004;172:1333–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.3.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vitale M, et al. NKp44, a novel triggering surface molecule specifically expressed by activated natural killer cells, is involved in non-major histocompatibility complex-restricted tumor cell lysis. J Exp Med. 1998;187:2065–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.12.2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Acosta-Rodriguez EV, et al. Surface phenotype and antigenic specificity of human interleukin 17-producing T helper memory cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:639–46. doi: 10.1038/ni1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Manel N, Unutmaz D, Littman DR. The differentiation of human T(H)-17 cells requires transforming growth factor-beta and induction of the nuclear receptor RORgammat. Nat Immunol. 2008 doi: 10.1038/ni.1610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Candiago E, Marocolo D, Manganoni MA, Leali C, Facchetti F. Nonlymphoid intraepidermal mononuclear cell collections (pseudo-Pautrier abscesses): a morphologic and immunophenotypical characterization. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000;22:1–6. doi: 10.1097/00000372-200002000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fuchs A, Cella M, Giurisato E, Shaw AS, Colonna M. Cutting edge: CD96 (tactile) promotes NK cell-target cell adhesion by interacting with the poliovirus receptor (CD155) J Immunol. 2004;172:3994–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.7.3994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cepek KL, et al. Adhesion between epithelial cells and T lymphocytes mediated by E-cadherin and the alpha E beta 7 integrin. Nature. 1994;372:190–3. doi: 10.1038/372190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Aujla SJ, et al. IL-22 mediates mucosal host defense against Gram-negative bacterial pneumonia. Nat Med. 2008;14:275–81. doi: 10.1038/nm1710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zheng Y, et al. Interleukin-22, a T(H)17 cytokine, mediates IL-23-induced dermal inflammation and acanthosis. Nature. 2007;445:648–51. doi: 10.1038/nature05505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zheng Y, et al. Interleukin-22 mediates early host defense against attaching and effacing bacterial pathogens. Nat Med. 2008;14:282–9. doi: 10.1038/nm1720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sugimoto K, et al. IL-22 ameliorates intestinal inflammation in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:534–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI33194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zenewicz LA, et al. Interleukin-22 but not interleukin-17 provides protection to hepatocytes during acute liver inflammation. Immunity. 2007;27:647–59. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.07.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hor S, et al. The T-cell lymphokine interleukin-26 targets epithelial cells through the interleukin-20 receptor 1 and interleukin-10 receptor 2 chains. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:33343–51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405000200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wilson NJ, et al. Development, cytokine profile and function of human interleukin 17-producing helper T cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:950–7. doi: 10.1038/ni1497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Liang SC, et al. Interleukin (IL)-22 and IL-17 are coexpressed by Th17 cells and cooperatively enhance expression of antimicrobial peptides. J Exp Med. 2006;203:2271–9. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Weaver CT, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Harrington LE. IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:821–52. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stockinger B, Veldhoen M, Martin B. Th17 T cells: linking innate and adaptive immunity. Semin Immunol. 2007;19:353–61. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ouyang W, Kolls JK, Zheng Y. The biological functions of T helper 17 cell effector cytokines in inflammation. Immunity. 2008;28:454–67. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.03.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Strowig T, et al. Tonsilar NK cells restrict B cell transformation by the Epstein-Barr virus via IFN-gamma. PLoS Pathog. 2008;4:e27. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0040027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Acosta-Rodriguez EV, Napolitani G, Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F. Interleukins 1beta and 6 but not transforming growth factor-beta are essential for the differentiation of interleukin 17-producing human T helper cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:942–9. doi: 10.1038/ni1496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nagalakshmi ML, Rascle A, Zurawski S, Menon S, de Waal Malefyt R. Interleukin-22 activates STAT3 and induces IL-10 by colon epithelial cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2004;4:679–91. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2004.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kusam S, Dent A. Common mechanisms for the regulation of B cell differentiation and transformation by the transcriptional repressor protein BCL-6. Immunol Res. 2007;37:177–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02697368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Veldhoen M, et al. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor links TH17-cell-mediated autoimmunity to environmental toxins. Nature. 2008;453:106–9. doi: 10.1038/nature06881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Quintana FJ, et al. Control of T(reg) and T(H)17 cell differentiation by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nature. 2008;453:65–71. doi: 10.1038/nature06880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brustle A, et al. The development of inflammatory T(H)-17 cells requires interferon-regulatory factor 4. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:958–66. doi: 10.1038/ni1500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Volpe E, et al. A critical function for transforming growth factor-beta, interleukin 23 and proinflammatory cytokines in driving and modulating human T(H)-17 responses. Nat Immunol. 2008 doi: 10.1038/ni.1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhou L, et al. TGF-beta-induced Foxp3 inhibits T(H)17 cell differentiation by antagonizing RORgammat function. Nature. 2008;453:236–40. doi: 10.1038/nature06878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yang L, et al. IL-21 and TGF-beta are required for differentiation of human T(H)17 cells. Nature. 2008 doi: 10.1038/nature07021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mebius RE. Organogenesis of lymphoid tissues. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:292–303. doi: 10.1038/nri1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.