Abstract
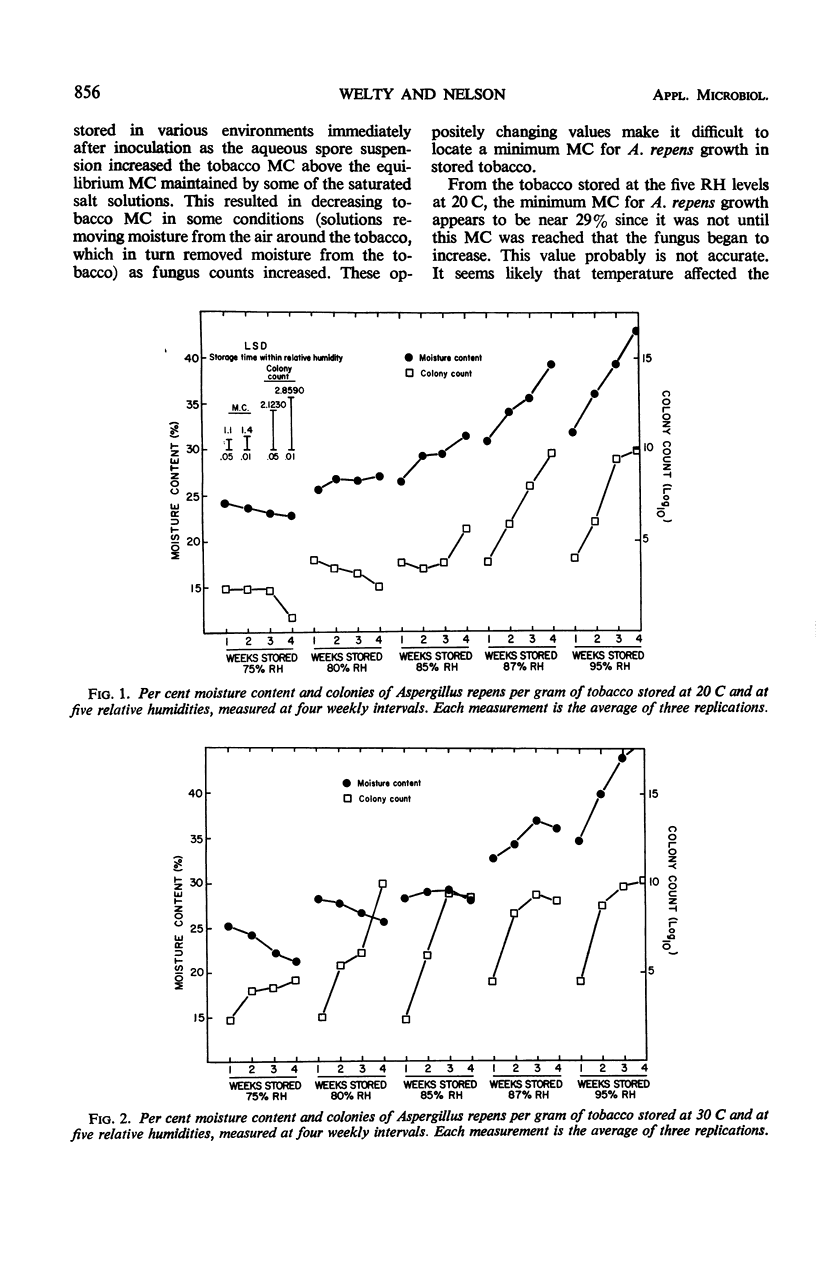
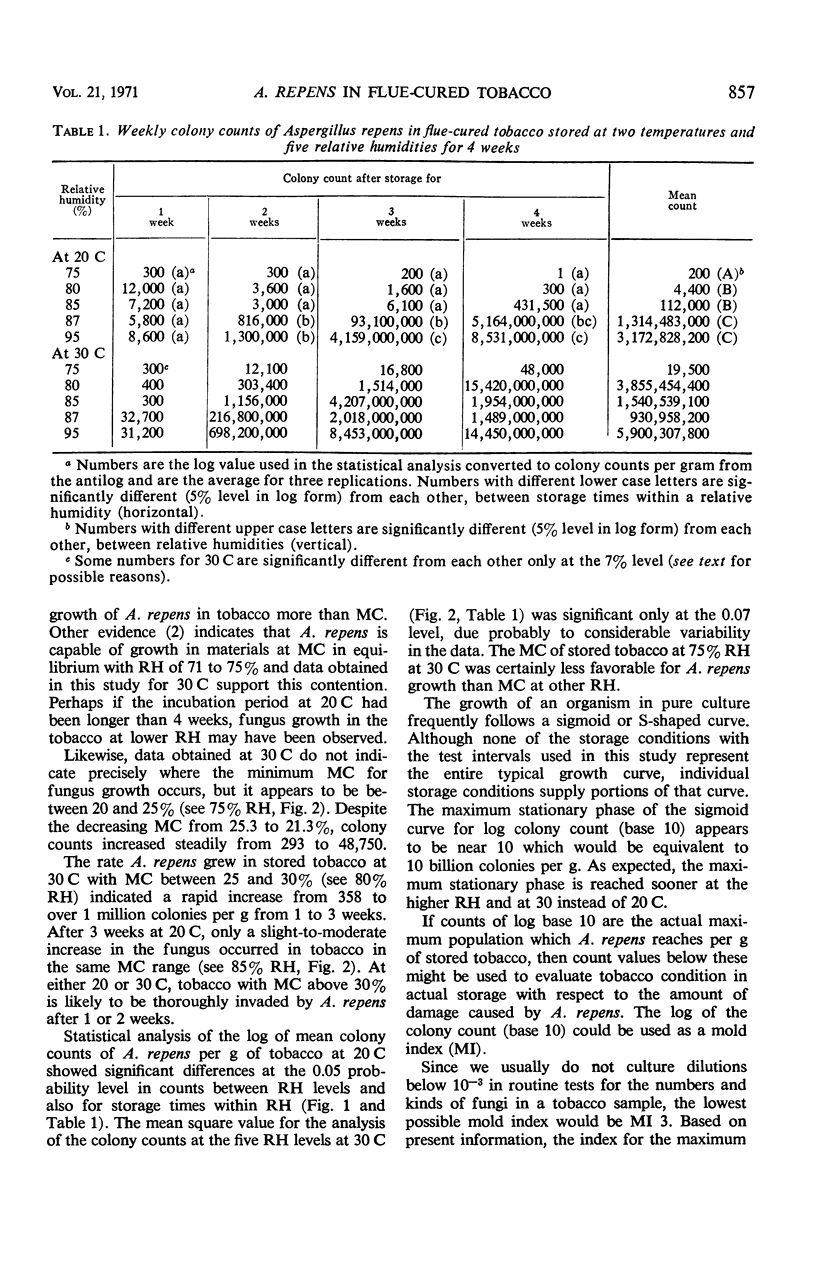
In laboratory tests, flue-cured tobacco inoculated with Aspergillus repens was stored at 75, 80, 85, 87, and 95% relative humidity at 20 and 30 C. Samples were taken weekly for 4 weeks and evaluated for mold growth (colony count) and moisture content (MC). The weekly rate of fungus increase was slower at 20 C than at 30 C. Tobacco at 20 C with MC between 25 to 30% supported a slight to moderate increase in A. repens after 3 weeks of storage. However, tobacco at the same MC stored at 30 C was subject to rapid invasion by the fungus in as few as 1 to 2 weeks. Tobacco with MC above 30% stored at either 20 or 30 C became moldy in about 1 week. A mold index is proposed for evaluating populations of A. repens in tobacco.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Welty R. E. Fungi isolated from flue-cured tobacco inoculated in the field with storage fungi. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Mar;21(3):552–554. doi: 10.1128/am.21.3.552-554.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welty R. E., Lucas G. B., Fletcher J. T., Yang H. Fungi isolated from tobacco leaves and brown-spot lesions before and after flue-curing. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1309–1313. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1309-1313.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welty R. E., Lucas G. B. Fungi Isolated from Damaged Flue-cured Tobacco. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jun;16(6):851–854. doi: 10.1128/am.16.6.851-854.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welty R. E., Lucas G. B. Fungi Isolated from Flue-cured Tobacco at Time of Sale and After Storage. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Mar;17(3):360–365. doi: 10.1128/am.17.3.360-365.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



