Abstract
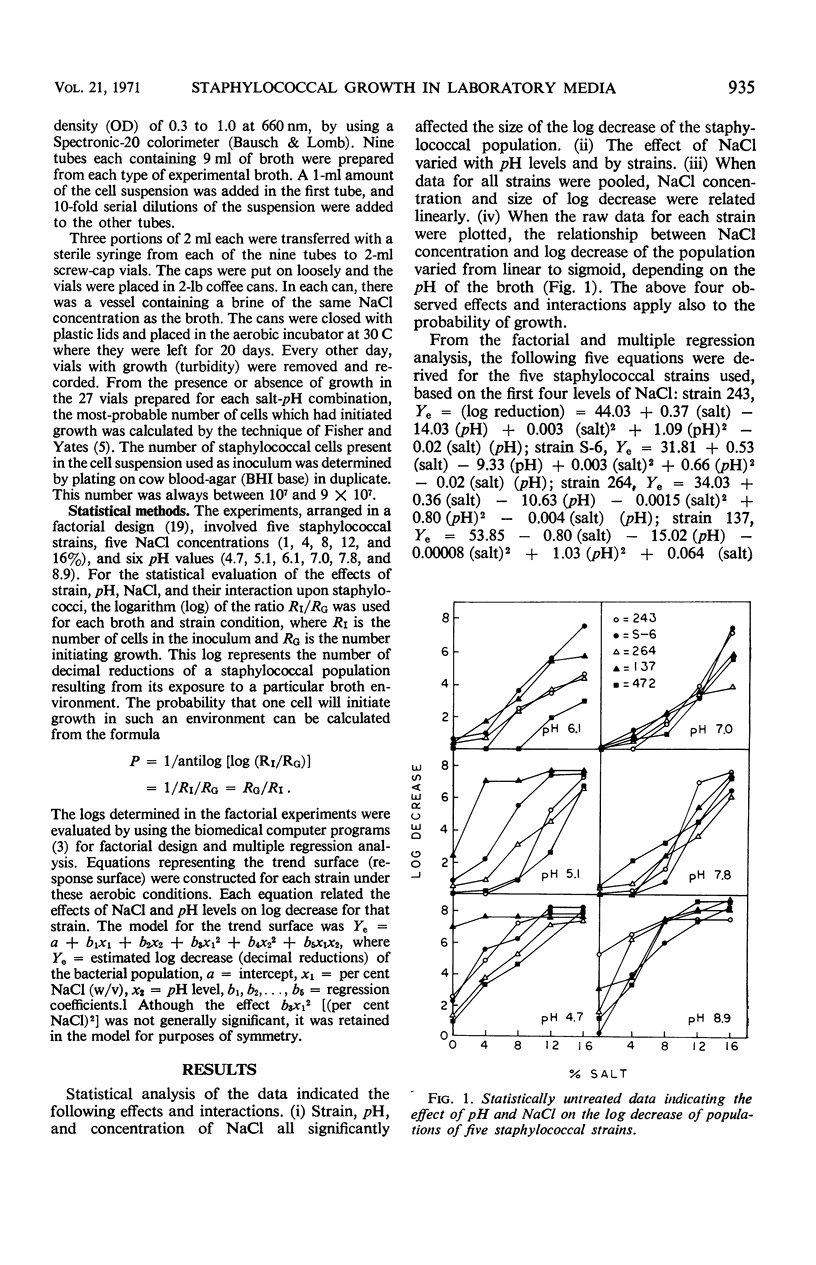
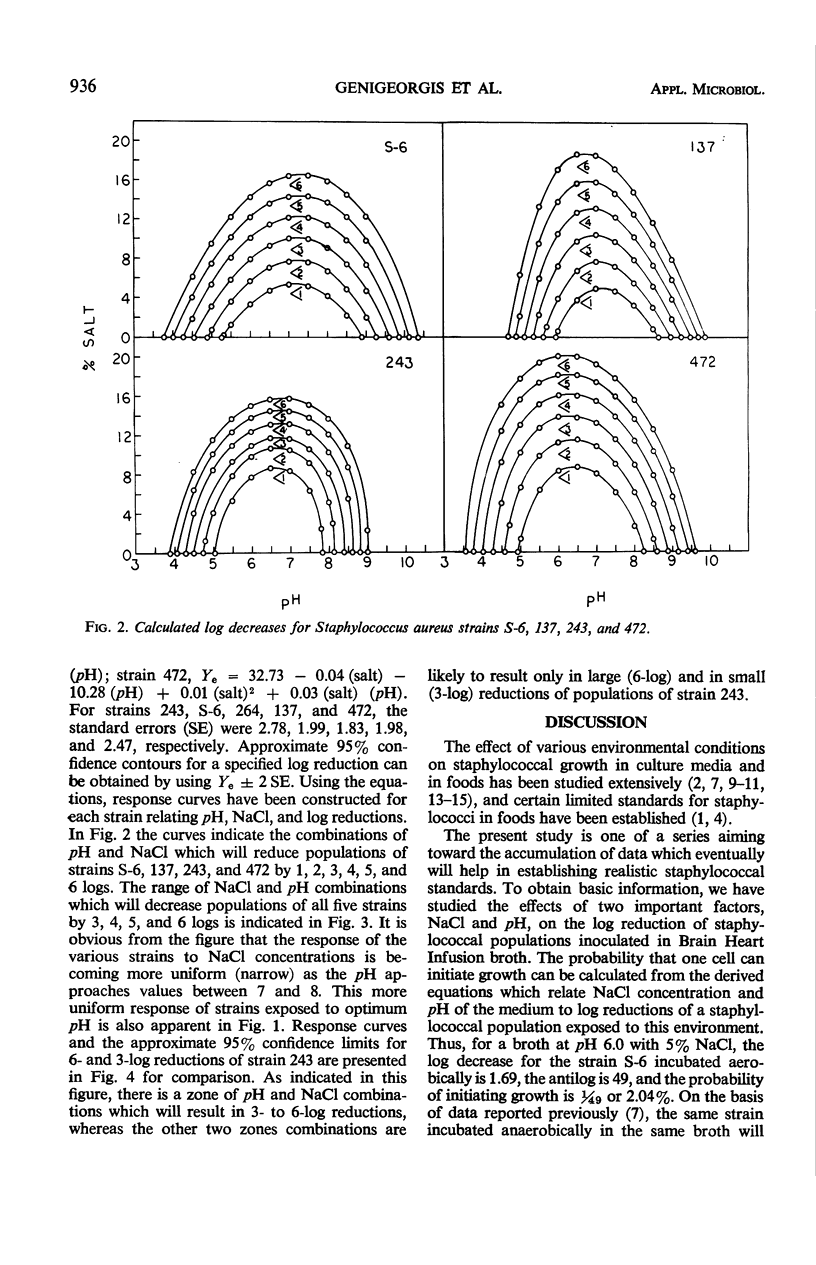
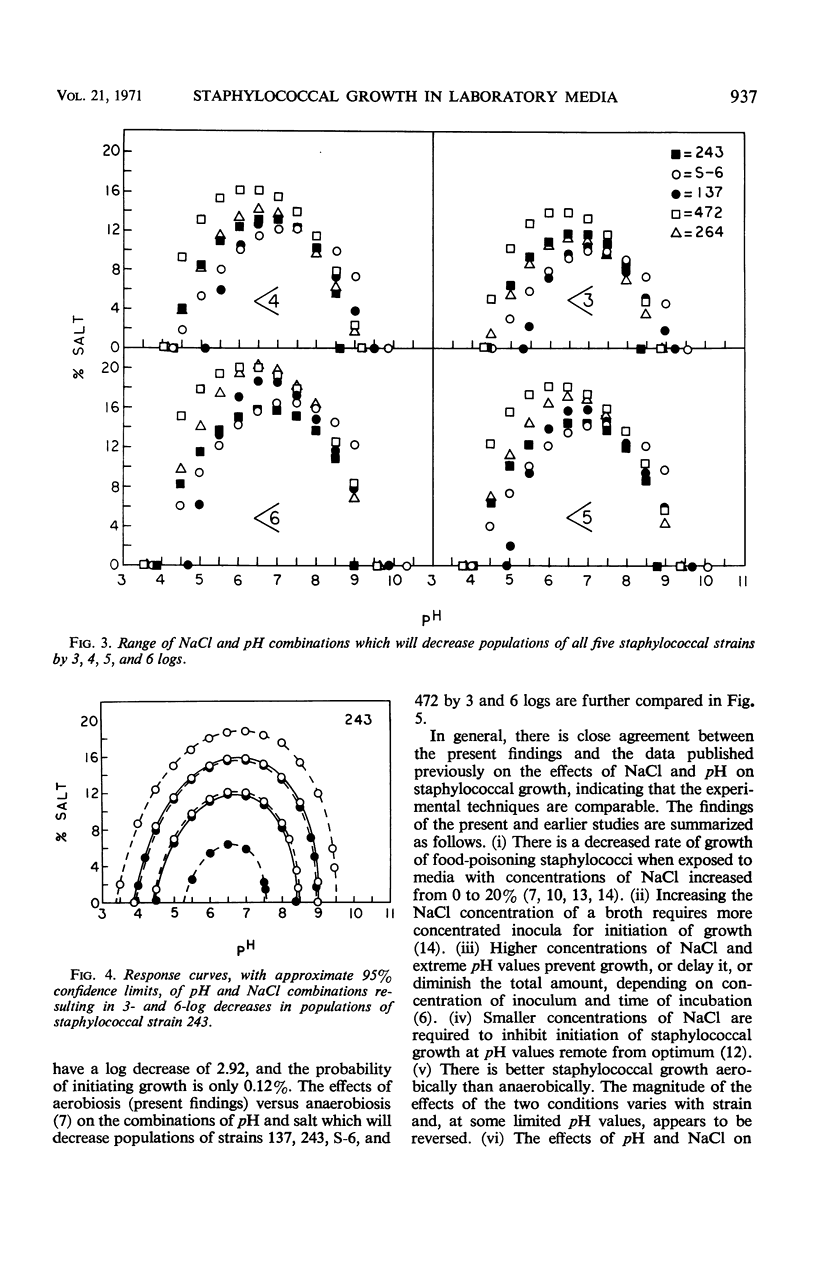
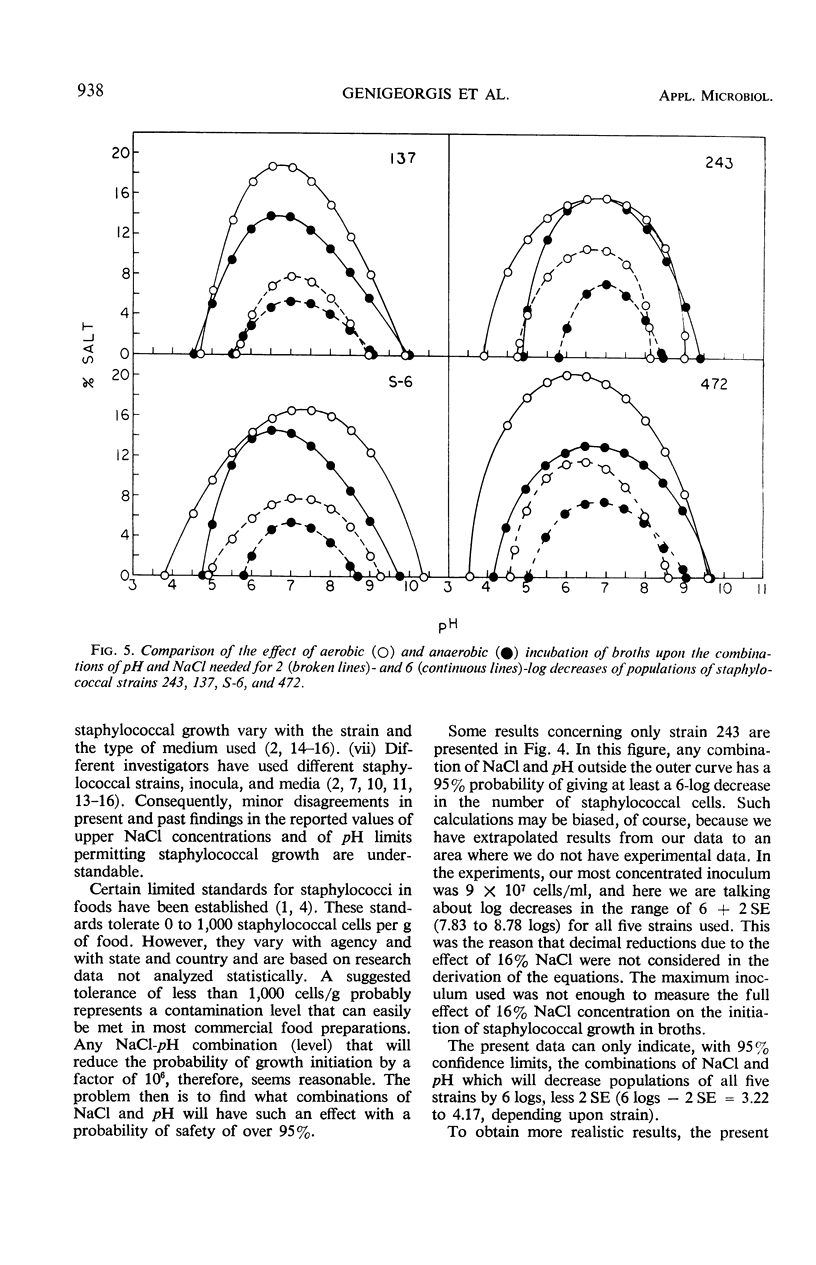
The effects of pH and NaCl concentration on the probability of aerobic growth initiation in Brain Heart Infusion broth at 30 C by five staphylococcal strains producing enterotoxins A, B, C, and D were studied in a factorial design experiment. Statistical analysis of the data indicated: (i) significant effects of pH, NaCl, and strain on the probability of growth; (ii) diverse effects of NaCl with various pH levels and strains; (iii) essentially a linear relationship between NaCl concentration and probability of growth initiation when data for all strains were pooled; (iv) the relationship between NaCl concentration and probability of growth initiation varies from linear to sigmoid, depending on the pH of the broth, when the statistically untreated (raw) data are plotted for each strain. Equations were derived which relate the decimal reductions of the number of cells of a staphylococcal population to the concentration of NaCl and pH of broth to which the population was exposed. From the equations, the probability that one cell is capable of initiating growth can be calculated. The impact of these types of studies on the development of realistic staphylococcal standards in foods is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ELLIOTT R. P., MICHENER H. D. Microbiological standards and handling codes for chilled and frozen foods. A review. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Sep;9:452–468. doi: 10.1128/am.9.5.452-468.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS J. B., LECHOWICH R. V., NIVEN C. F., Jr Effect of curing ingredients and procedures on the survival and growth of staphylococci in and on cured meats. Appl Microbiol. 1956 Nov;4(6):360–363. doi: 10.1128/am.4.6.360-363.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genigeorgis C., Sadler W. W. Effect of sodium chloride and pH on enterotoxin B production. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1383–1387. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1383-1387.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genigeorgis C., Savoukidis M., Martin S. Initiation of staphylococcal growth in processed meat environments. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):940–942. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.940-942.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucker G. J., Haynes W. C. Certain Factors Affecting the Growth of Food Poisoning Micrococci. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1937 Jun;27(6):590–594. doi: 10.2105/ajph.27.6.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IANDOLO J. J., ORDAL Z. J., WITTER L. D. THE EFFECT OF INCUBATION TEMPERATURE AND CONTROLLED PH ON THE GROWTH OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS MF 31 AT VARIOUS CONCENTRATIONS OF NACL. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Oct;10:808–811. doi: 10.1139/m64-104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunheimer T. D., Fabian F. W. Influence of Organic Acids, Sugars, and Sodium Chloride upon Strains of Food Poisoning Staphylococci. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1940 Sep;30(9):1040–1049. doi: 10.2105/ajph.30.9.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARFENTJEV I. A., CATELLI A. R. TOLERANCE OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS TO SODIUM CHLORIDE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:1–3. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.1-3.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



