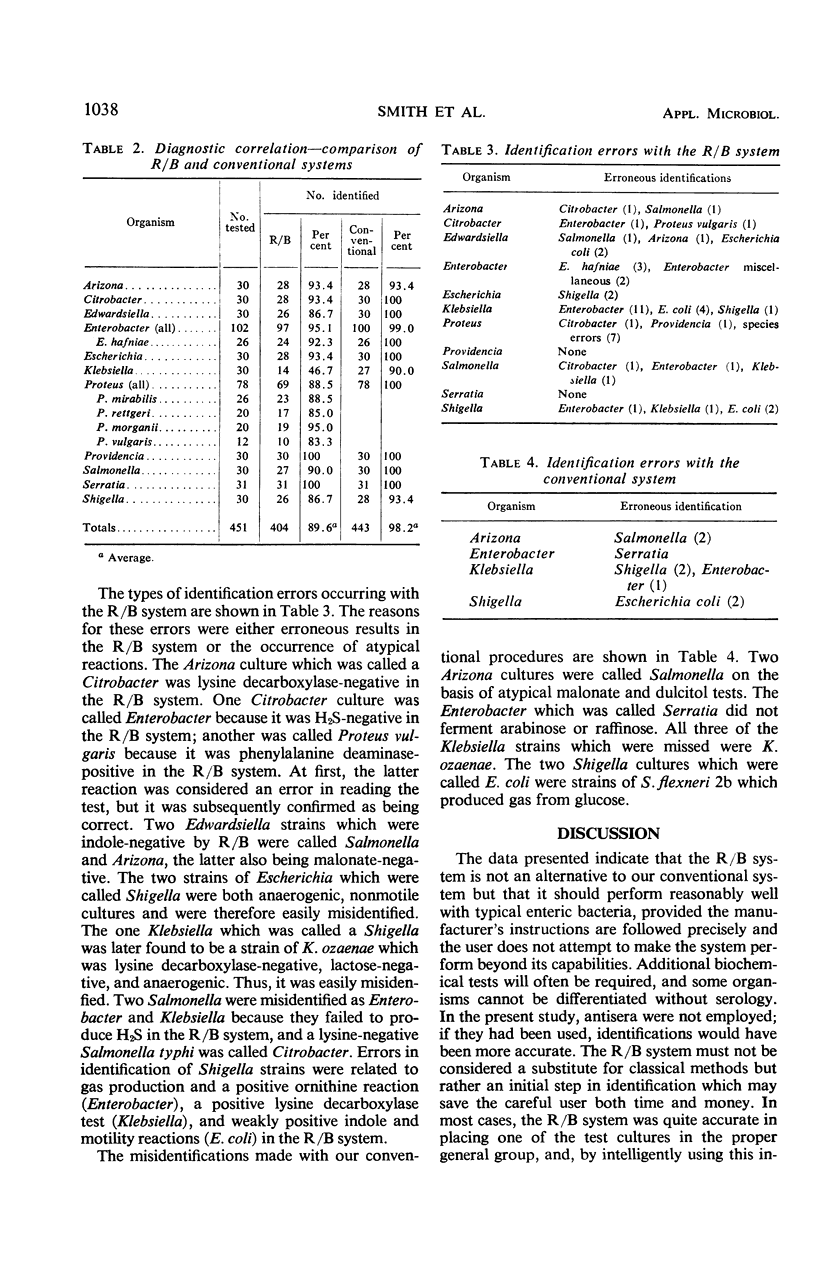
Abstract
The R/B Enteric Differential System for identifying enteric bacteria has been evaluated with 451 “unknown” cultures from the stock culture collection of the Center for Disease Control. An average of 89.6% of these cultures were correctly identified by the R/B system, when used as recommended by the manufacturer but without the assistance of serology. This percentage ranged, however, from 47% for Klebsiella to 100% for Serratia and Providencia. Of 11 groups or genera of Enterobacteriaceae tested, only three (Enterobacter, Serratia, and Providencia) were identified with 95% or better accuracy. Four groups (Arizona, Citrobacter, Escherichia, and Salmonella) attained 90 to 95% accuracy of identification, and three groups (Edwardsiella, Proteus, and Shigella) scored between 85 and 90% accuracy. We recommend the R/B system as a screening device which is reasonably successful in grouping bacteria but not as a substitute for more exacting conventional procedures.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Martin W. J., Birk R. J., Yu P. K., Washington J. A., 2nd Identification of members of the family Enterobacteriaceae by the R-B system. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Dec;20(6):880–883. doi: 10.1128/am.20.6.880-883.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell E. D., Kaufman F. J., Longo E. D., Ellner P. D. Evaluation of the R-B system for the identification of enterobacteriacease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Feb;53(2):145–148. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.2.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



