Abstract
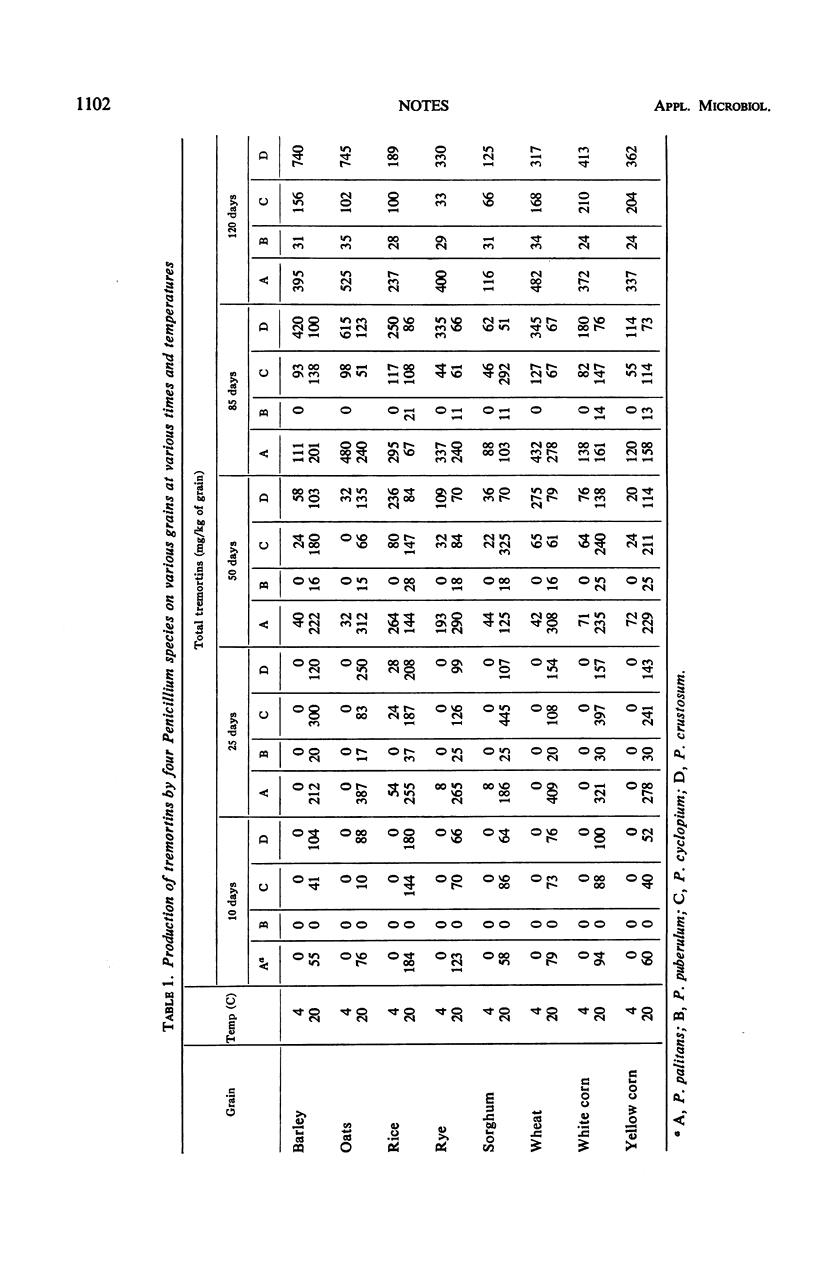
A low temperature (4 C) favors the accumulation of the mycotoxin tremortin when tremortin-producing molds are grown on various agricultural commodities. However, the rate of toxin formation is more rapid at a high temperature (20 C).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ciegler A., Pitt J. I. Survey of the genus Penicillium for tremorgenic toxin production. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1970 Dec 28;42(1):119–124. doi: 10.1007/BF02051832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciegler A. Tremorgenic toxin from Penicillium palitans. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jul;18(1):128–129. doi: 10.1128/am.18.1.128-129.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou C. T., Ciegler A., Hesseltine C. W. Tremorgenic toxins from Penicillia. I. Colorimetric determination of tremortins A and B. Anal Biochem. 1970 Oct;37(2):422–428. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde M. B. New storage systems in relation to infestation problems. Chem Ind. 1969 Oct 11;41:1448–1451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. J., Wilson C. H., Hayes A. W. Tremorgenic toxin from Penicillium cyclopium grown on food materials. Nature. 1968 Oct 5;220(5162):77–78. doi: 10.1038/220077b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



