Abstract
Dequalinium acetate is taken up rapidly by bacterial cells. Unlike the membrane-active drugs exemplified by cetrimide or chlorhexidine, its capacity for damaging the plasma membrane is low. The drug appears to penetrate quite rapidly into the cytoplasm where its effect seems to be exerted. A review of the evidence obtained in this study suggests that nucleic acid-containing components of the cell may be the prime target of this compound.
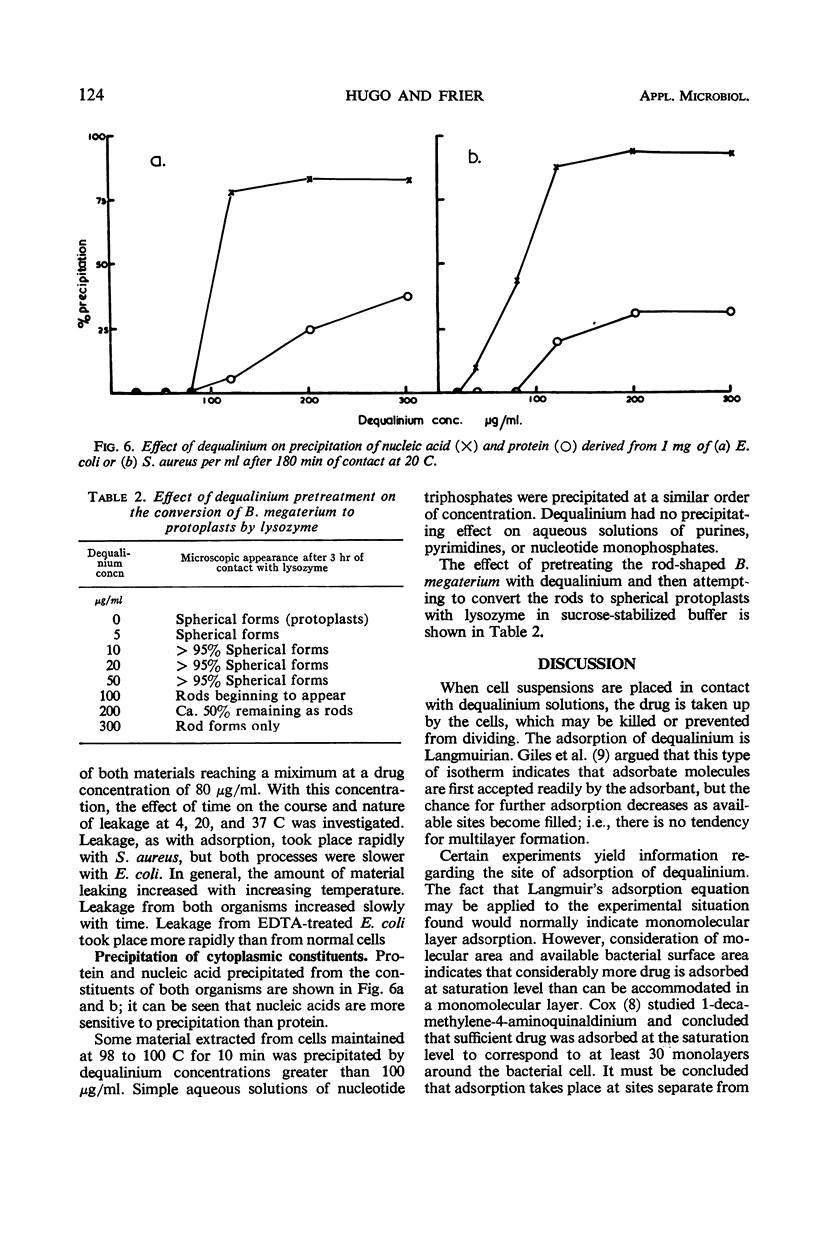
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BABBS M., COLLIER H. O., AUSTIN W. C., POTTER M. D., TAYLOR E. P. Salts of decamethylene-bis-4-aminoquinaldinium (dequadin); a new antimicrobial agent. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1956 Feb;8(2):110–119. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1956.tb12138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALLARD C. W., ISAACS J., SCOTT P. G. The photometric determination of quaternary ammonium salts and of certain amines by compound formation with indicators. I. Quaternary ammonium salts. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1954 Dec;6(12):971–985. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1954.tb11032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERRY H., BEAN H. S. The estimation of bactericidal activity from extinction time data. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1954 Sep;6(9):649–655. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1954.tb10999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox W. A. Site of action of certain antibacterial heterocyclic quaternary ammonium compounds. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Nov;13(6):956–966. doi: 10.1128/am.13.6.956-966.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGO W. B., LONGWORTH A. R. SOME ASPECTS OF THE MODE OF ACTION OF CHLORHEXIDINE. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1964 Oct;16:655–662. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1964.tb07384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGO W. B., RUSSELL A. D. Quantitative aspects of penicillin action on Escherichia coli in hypertonic medium. J Bacteriol. 1960 Oct;80:436–440. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.4.436-440.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugo W. B., Longworth A. R. The effect of chlorhexidine on the electrophoretic mobility, cytoplasmic constituents, dehydrogenase activity and cell walls of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1966 Sep;18(9):569–578. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1966.tb07935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIVE L. A NONSPECIFIC INCREASE IN PERMEABILITY IN ESCHERICHIA COLI PRODUCED BY EDTA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:745–750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERCHE C. Electrophoresis of Micrococcus pyogenes aureus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1953;98:1–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J. BACTERIAL PROTOPLASTS INDUCED BY PENICILLIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):574–577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. Studies on the permeability change produced in coliform bacteria by ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2373–2380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQUILLEN K. The bacterial surface. I. Effect of cetyl-trimethyl-ammonium bromide on the electrophoretic mobility of certain gram-positive bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jun;5(3/4):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90192-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. Site of action of polymyxin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa: antagonism by cations. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Jun;10(3):491–499. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-3-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. The release of soluble constituents from washed cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by the action of polymyxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Aug;9(1):54–64. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-1-54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REPASKE R. Lysis of gram-negative bacteria by lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Oct;22(1):189–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroffe R. C., Wilkinson B. E. The antibacterial action of tetrachlorsalicylanilide. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Sep;44(3):343–352. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-3-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



