Abstract
Background
Yes Associated Protein (YAP) has been implicated in the control of organ size by regulating cell proliferation and survival. YAP is a transcriptional coactivator that controls cellular responses through interaction with TEAD transcription factors in the nucleus, while its transcriptional functions are inhibited by phosphorylation-dependent translocation to the cytosol. YAP overexpression has been associated with different types of cancer, such as lung, skin, prostate, ovary and liver cancer. Recently, YAP was linked to E-cadherin-dependent regulation of contact inhibition in breast cancer cells.
Results
In this study we examined YAP protein expression and cellular localization in 237 cases of human invasive breast cancer by immunohistochemistry and related its expression to clinicopathological features and E-cadherin expression. We observed that invasive lobular carcinoma is characterized by higher expression levels of both nuclear and cytosolic YAP (p < 0.001). Nuclear YAP expression did not associate with other variables such as lymph node involvement, tumor grade, tumor size, mitotic activity or the molecular sub-types of invasive breast cancer. We observed that high nuclear and cytosolic YAP expression are associated with the E-cadherin deficient breast cancer subtype ILC (p < 0.001) and cell lines derived from human breast cancers and conditional mouse models of human lobular breast cancer.
Conclusions
Since our data indicate that nuclear YAP localization is more common in breast cancers lacking functional adherens junctions, it suggests that YAP-mediated transcription may be involved in the development and progression of invasive lobular breast cancer.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s13402-013-0143-7) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Adhesion, Breast cancer, Yap (Hippo) signaling, Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Introduction
Breast cancer prognosis strongly depends on the capacity of tumor cells to invade and colonize foreign tissues, a process that has been linked to the functional loss of cell-cell adhesion. In breast cancer, expression of the tumor suppressor E-cadherin - a key component of the adherens junction (AJ) - is widely used to facilitate differential diagnosis between invasive ductal (IDC) and invasive lobular breast cancer (ILC) [1, 2]. While mutational inactivation of E-cadherin is a causal event in the formation of ILC [4–6], IDC often expresses E-cadherin [3–5]. In IDC, (epigenetic) inactivation of the AJ occurs at later stages, which is thought to induce an epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and subsequent tumor progression [6, 7]. Despite this, little is known regarding the prometastatic downstream molecular processes that are aberrantly regulated upon loss of E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion.
Recently, a transcriptional coactivator named Yorkie was identified in Drosophila as an important regulator of proliferation and apoptosis [8, 9]. Yorkie is a downstream component of the Hippo pathway, consisting of the kinase complexes Hippo-Salvador and Warts-Mats [9–11]. The kinases of the Hippo pathway inhibit Yorkie activity through phosphorylation (Serine 168 in Drosophila) [12]. Subsequent dephosphorylation of Yorkie induces translocation to the nucleus, where it activates transcription to regulate organ size [13, 14]. Yorkie has two homologues in humans, called YAP (Yes Associated Protein) and TAZ (transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif, also known as WWTR1) [15]. Two YAP splice variants can be identified, containing either one or two dual WW domains (YAP1 and YAP2, respectively)[16]. Although Hippo pathway components are conserved in mammals, regulation of YAP signaling seems to be tissue-specific. In mouse liver, Mst1/2 (Hippo in Drosophila) inhibits activation of the YAP orthologue Yorkie [12]. However, in mammalian skin neither Mst1/2 nor Lats1/2 (Hippo and Warts respectively in Drosophila) influence YAP-mediated signaling [13]. Instead, the AJ member αE-catenin appears to regulate YAP activity. In this setting, αE-catenin binds to phosphorylated YAP (Serine 127 in humans) via the 14-3-3 adaptor protein, which prevents YAP binding to and subsequent dephosphorylation by the phosphatase PP2A [13]. Upon disruption of the AJ complex, YAP can be activated by PP2A and subsequently translocate into the nucleus where it drives transcriptional activation [13].
Interestingly, little is known about the regulation mechanism of YAP in breast tissue. Although it is clear that YAP may be differently regulated in breast tissue compared to its orthologue Yorkie, it is still under debate how YAP is phosphorylated and whether this affects YAP activity [17–22]. In breast cancer cell lines, E-cadherin regulates contact-inhibited proliferation through regulation of YAP activation [18, 23]. Here, cell proliferation is inhibited by cell density via α-catenin and αE-catenin-dependent phosphorylation of YAP at serine residue 127 in humans (S112 in mouse) and subsequent translocation of YAP into the cytosol [18, 23]. Moreover, recent data indicate that YAP may also be regulated by the actin and microtubule cytoskeleton [17, 20, 22], although the exact mechanism is largely unknown.
Several observations suggest an oncogenic role for YAP signaling in breast cancer. First, the YAP locus was found amplified in a mammary tumor that developed in a MMTVcre; Brca1 ∆11/co ; Trp53 +/− conditional mouse model [24]. Second, cytosolic YAP was found overexpressed in 31 % of human luminal ductal breast cancers [25]. Also, YAP overexpression resulted in transforming abilities in E-cadherin positive human breast cancer cell lines [22, 24–26]. Finally, YAP/TAZ-mediated transcriptional activity was linked to the maintenance of a cancer stem cell phenotype in breast cancer [27]. In contrast, loss of YAP expression correlated with estrogen receptor α (ERα) and progesterone receptor (PR) negativity in breast cancer [28], suggesting that YAP may also function as a tumor suppressor. Furthermore, loss of heterozygosity (LOH) of the YAP gene locus (located at 11q22.2), was frequently found in sporadic breast cancer [29–33]. Finally, loss of YAP expression was implicated in the induction of anoikis resistance and increased invasiveness [34].
Overall, the current literature indicates a role for YAP in breast cancer and suggests that the AJ and its downstream effectors may regulate YAP. Here, we analyzed 237 invasive human breast cancer samples by relating expression and localization of YAP to clinicopathological features and E-cadherin expression. Our data indicate that high nuclear and cytosolic YAP expression are associated with the E-cadherin deficient breast cancer subtype ILC. Furthermore, using human breast cancer cell lines and conditional mouse models of human ILC, we substantiate that nuclear localization of YAP is linked to loss of E-cadherin expression. Our data thus indicate that nuclear YAP is a feature of invasive breast cancers lacking a functional AJ, which suggests a role for YAP signaling in ILC.
Materials and methods
Patients
The study population was derived from the archives of the Departments of Pathology of the University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, and the Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre, Nijmegen, The Netherlands. These comprised 237 cases of invasive breast cancer (operated between 2003 and 2007). Histological grade was assessed according to the Nottingham scheme [35], and mitotic activity index (MAI) was assessed as before [36]. The clinicopathologic characteristics are shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Clinicopathological characteristics of the 237 invasive breast cancer patients studied for the expression of YAP
| Feature | Grouping | N or value | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | Mean | 60 | |
| Range | 28 to 88 | ||
| Histologic type | IDC | 187 | 78.9 |
| ILC | 50 | 21.1 | |
| Tumor size (cm) | ≤2 | 108 | 45.6 |
| >2 and ≤5 | 98 | 41.4 | |
| >5 | 30 | 12.7 | |
| Not available | 1 | 0.4 | |
| Histologic grade | 1 | 36 | 15.2 |
| 2 | 76 | 32.1 | |
| 3 | 125 | 52.7 | |
| MAI | ≤ 12 | 103 | 43.5 |
| ≥ 13 | 134 | 56.5 | |
| Lymph node status | Negative* | 98 | 41.4 |
| Positive** | 125 | 52.7 | |
| Not available | 14 | 5.9 |
#per 2 mm2
*negative = N0 or N0(i+)
**positive = ≥N1mi (according to TNM 7th edition, 2010)
From representative donor paraffin blocks of the primary tumors, tissue microarrays were constructed by transferring tissue cylinders of 0.6 mm (3 cylinders per tumor) from the tumor area, determined by a pathologist based on haematoxylin-eosin stained slides, using a tissue arrayer (Beecher Instruments, Sun Prairie, WI, USA) as described before [37]. Normal breast tissue was obtained from patients that underwent mammoplasty, and was thus tumor-free. The use of anonymous or coded left over material for scientific purposes is part of the standard treatment contract with patients in The Netherlands [38], and no ethical approval is required according to Dutch legislation (as is stated by the Dutch committee for research on patient material ‘Centrale Commissie Mensgebonden Onderzoek’).
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry was carried out on 4 μm thick sections. After deparaffination and rehydration, endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked for 15 min in a 46 mM citric acid-100 mM sodium phosphate buffer solution (pH5.8) containing 0.3 % hydrogen peroxide. After antigen retrieval, i.e. boiling for 20 min in 10 mM citrate pH6.0 (PR, YAP), Tris/EDTA pH9.0 (E-cadherin, ERα, HER2), a cooling period of 30 min preceded the primary antibody incubation. Primary antibodies against E-cadherin (clone 4A2C7, Zymed, Invitrogen, Breda, The Netherlands) 1:200; ERα (clone ID5, DAKO, Glostrup Denmark) 1:80; PR (clone PgR636, DAKO) 1:25; HER2 (SP3, Neomarkers, Duiven, The Netherlands) 1:100 were diluted in PBS containing 2%BSA and incubated for 1 h at room temperature. Primary antibodies against YAP (1:50, cat 4912, Cell Signaling), (YAP-IHC) were incubated over night at 4 °C. The signal was amplified using Powervision poly-HRP anti-mouse, -rabbit, -rat (DPVO-HRP, Immunologic, Duiven, The Netherlands), followed by counterstaining with haematoxylin, dehydration in alcohol, and mounting.
Scoring of immunohistochemistry
All scoring was done blinded to patient characteristics and results of other stainings by two individual observers. E-cadherin expression was scored using the DAKO/HER2 scoring system for membranous staining. Membranous scores 1+, 2+, and 3+ were considered positive, except for HER2 where only a score of 3+ was considered positive. Percentages of cells with nuclear YAP staining were estimated, and samples with more than 20 % positive tumor nuclei were considered positive. Intensity of cytosolic YAP expression was semi-quantitatively scored as 0, 1, 2 or 3, regarding scores 2 and 3 as high. Based on ER, PR, and HER2 immunohistochemistry, tumors were classified as luminal (ERα and/or PR positive), HER2-driven (ER-, PR-, HER2+), or basal-like/triple negative (ER-, PR-, HER2- with or without EGFR expression), the immunohistochemical surrogate [39] of the original Sorlie/Perou classification [40].
Statistics
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS Statistics version 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Associations between categorical variables were examined using the Pearson’s Chi-square test. P-values <0.05 were considered to be statistically significant.
Cell culture
Origin and culture of the mouse cell lines Trp53∆/∆-4, Trp53∆/∆-7, mILC-1 and mILC-3 were described before [41]. ILC cell line IPH-926 was a kind gift from Dr. M. Christgen (Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany) and cultured as described [42]. Human breast cancer cell line MCF10A was obtained from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC), while T47D and SKBR-3 were a kind gift from Dr. J. Martens (Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands) and originate from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). These cell lines were cultured in DMEM-F12 (Sigma), and validated by Short Tandem Repeat (STR) profiling. All media contained 10 % fetal calf serum, 100 IU/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin, and all cell lines were maintained at 37 °C in a 5 % CO2 humidified atmosphere.
Western blotting
Samples were lysed in sample buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 0.5 % β-mercaptoethanol, 2 % SDS, 0.005 % bromophenolblue, and 10 % glycerol (all Sigma-Aldrich). Samples were heated for 10 min at 100 °C and proteins were separated using standard PAGE protocols and blotting as described previously [43].
Nuclear fractionation
Cells were grown to confluence, washed with PBS containing Mg2+ and Ca2+ (PBS+), scraped from the plate and suspended in buffer A (10 mM HEPES pH 7.9, 1.5 mM MgCL2, 10 mM KCl and freshly added 1 mM DTT, 0.5 mM PMSF, 5ug/ml leupeptin, 5ug/ml aprotinin). Cells were centrifuged at 400 g at 4 °C for 5 min, resuspended in 1 ml PBS+, and centrifuged. Cells were resuspended in buffer A, centrifuged and resuspended again in buffer A. Cells were incubated for 10 min on ice, centrifuged, resuspended in buffer A and mechanically lysed with 50–75 strokes in a glass 2 mL-douncer. Cell lysates were centrifuged for 10 min at 500 g at 4 °C. Cell pellets (nuclear fraction) were separated from the supernatant (cytosolic fraction). Both fractions were submitted to another round of washing and centrifugation (10 min, 500 g at 4 °C) and used for western blotting. Rabbit anti-TAF5, [44], was used as a nuclear marker, and goat anti-AKT (1:1000; cat sc-1618, Santa Cruz Biotechnology) was used as a cytosolic marker. The primary antibody against YAP was mouse anti-YAP (1:200; cat sz101199, Santa Cruz), (YAP-IF).
Constructs, viral production and transduction
Cos-7 cells were transfected using X-tremeGene9 (cat 06365809001, Roche), and lentiviral particles were produced using third-generation packaging constructs as described [41]. For knockdown of YAP we used pLKO1-shYAP1 (cat 27368 addgene). Supernatant containing viral particles was harvested 48 h after transfection, passed through a 45-μm filter, and concentrated 15- to 20-fold by centrifugation (175,000 g; 150 min). Cells were transduced overnight in the presence of 4 μg/ml polybrene (Sigma-Aldrich).
Immunofluorescence
Cells were cultured on glass coverslips and fixed in 1 % paraformaldehyde in PBS for 10 min on ice, permeabilized using 0.3 % Triton-X100/PBS and subsequently blocked with 4 % BSA in PBS (Roche, Woerden, The Netherlands). Formalin fixed and paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissue slides were treated as described for immunohistochemistry staining. Blocking was done with 4 % BSA in PBS after antigen retrieval. FFPE slides were incubated with rabbit anti-YAP (1:50; cat 4912, Cell Signaling), (YAP-IHC), at 4 °C overnight. The mouse anti-p63 antibody (1:400; MS-115-P, Neomarkers) was incubated for 1 h at room temperature. Directly conjugated antibodies against E-cadherin (1:150, 612130 BD and 560062 BD Biosciences) were incubated for 1–3 h at room temperature. All antibodies were diluted in 4 % BSA/PBS. Secondary antibodies were incubated in 4 % BSA/PBS for 1 h (goat anti-rabbit Alexa-555, cat A21428, goat anti-mouse highly cross-adsorbed Alexa-488 and Alexa-568, cat A11029 and A11031, and goat anti-rabbit highly cross-adsorbed Alexa-488 and Alexa-568, cat A11036 and A11034, all from Invitrogen). Cell lines grown on glass coverslips were incubated with mouse anti-YAP (1:50; cat sz101199, Santa Cruz), (YAP-IF), in 4 % BSA at 4 °C over night. Subsequently, cells were incubated in 4 % BSA with goat anti-mouse Alexa-555 (1:600; cat A21422, Invitrogen) for 1 h. DNA was stained with DAPI (1:1000; cat D1306, Invitrogen) for 5 min at room temperature. Cover slips were mounted using Vectashield (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, USA) and analyzed either by a Zeiss LSM 510 Meta confocal laser microscope using a 63 × 1.4 objective or by using the Zeiss LSM 700 confocal laser microscope using the 63X 1.4 objective.
Results
YAP expression in human and mouse normal breast tissue
In normal human breast tissue, we found YAP to be predominantly expressed in the outer layer of the ducts, the myoepithelium (Fig. 1a and Online Resource Fig. 1). While YAP was expressed at low levels in the cytosol, we detected prominent nuclear YAP staining using immunofluorescence in this cell type (Fig. 1a, arrowheads and Online Resource Fig. 1). In contrast, E-cadherin-expressing luminal cells showed low YAP expression that was mainly localized to the apical snouts (Fig. 1a, arrow and and Online Resource Fig. 1). Next, we assessed YAP expression and localization in mouse mammary epithelium. As in the human tissue, mouse myoepithelial cells showed a stronger nuclear YAP localization pattern (arrowheads), whereas luminal mammary epithelial cells mostly expressed cytoplasmic YAP (Fig. 1b). Specificity of the YAP-IF antibody used was confirmed by performing shRNA-mediated knock-down (Online Resource Fig. 2, middle panel).
Fig. 1.
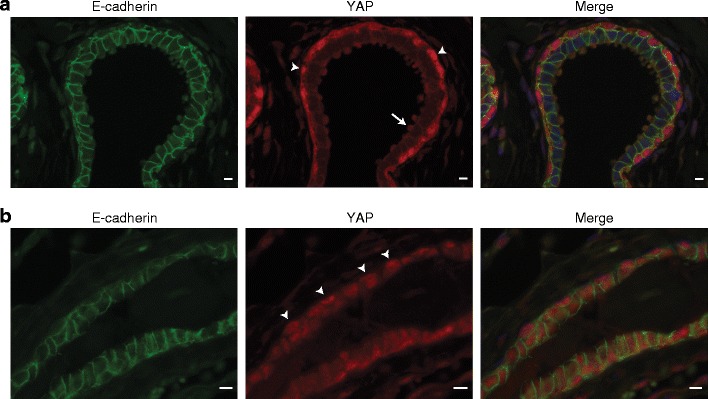
YAP expression in human and mouse normal breast tissue. a YAP expression in normal human breast tissue. Shown are immunofluorescence for YAP (middle panel, red) and E-cadherin (left panel, green). Nuclei were visualized using DAPI. Right panel depicts the merged image. Luminal epithelial cells form clear AJ and are characterized by low cytosolic YAP expression. Note the predominant nuclear YAP localization in myoepithelial cells (arrowheads) and expression of YAP in apical snouts (arrow). Size bar = 5 μm. b. YAP expression in mouse mammary glands. Shown are immunofluorescence for YAP (middle panel, red) and E-cadherin (left panel, green). Arrowheads depict nuclear YAP expression in mouse myoepithelial cells. Nuclei were visualized using DAPI. Right panel depicts the merged image. Size bar = 5 μm
Nuclear YAP localization in invasive lobular carcinoma
To investigate the expression pattern of YAP in invasive breast cancer, we stained a tissue micro array (TMA) containing 237 invasive breast cancer samples using immunohistochemistry (IHC). The clinicopathological characteristics of these tumors are shown in Table 1. Because YAP functions as a mediator of transcriptional activation, we based our score on an estimation of the percentage of YAP positive nuclei. Representative pictures of nuclear YAP staining are shown in Figure 2A. Moreover, since YAP shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, we scored the intensity of cytoplasmic YAP as well (Fig 2b). Since a different antibody was used for IHC (YAP-IHC), we also confirmed specificity for this antibody by using a YAP knock-down approach (Online Resource Fig. 2, top panel). Analysis of the YAP expression patters showed that both high cytoplasmic levels and nuclear YAP localization correlated with the histological type of breast cancer invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) (p = 0.002 and p < 0.001, respectively; Table 2 and 3). We used 20 % as cut-off value for positive nuclear YAP staining, although 5 % and 10 % cut-off were also statistically significant (p < 0.001 for both 5 % and 10 %). Neither cytosolic nor nuclear YAP expression correlated with histological grade, mitotic activity or lymph node status (Tables 2 and 3). We also analyzed the relationship between YAP expression and tumor size. Because ILC tumors were significantly larger compared to the IDC tumors, we corrected for this and found that nuclear YAP expression was not correlated with tumor size (odd ratio 1.451, 95 % confidence interval of 0.790 to 2.667), while high nuclear YAP localization remained significantly correlated with ILC tumors (odds ratio 8.829, 95 % confidence interval of 4.208 to 18.523) (Table 3). In contrast to previously published data [28], we did not find a correlation between nuclear or cytosolic YAP localization and hormone receptor status, HER2 expression or molecular breast cancer subtypes (Online Resource Table 1 and Table 2). In conclusion, increased cytosolic YAP expression and nuclear YAP localization are associated with ILC.
Fig. 2.
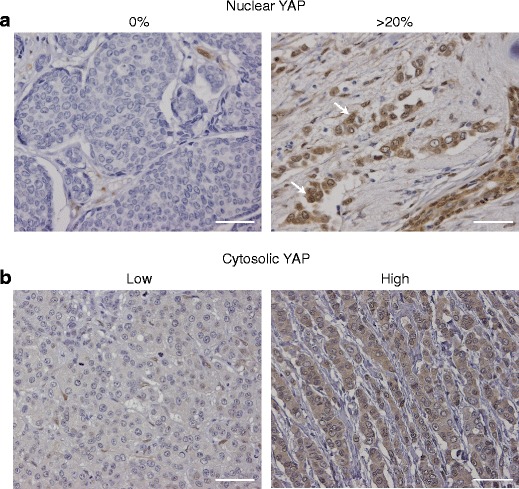
YAP expression in human invasive breast cancer. a Nuclear YAP expression patterns. Shown are representative examples of immunohistochemistry of YAP (IHC). The percentage of nuclei that showed YAP expression was determined and scored as 0 % (left panel) or more than 20 % (right panel). Arrows denote nuclear staining. b Cytosolic intensities of YAP expression. Shown are representative examples of immunohistochemistry of YAP (IHC). Cytosolic YAP expression was scored as either low YAP (left panel) or high YAP (right panel). The sample shown in the right panel was also scored <20 % (15–20 %) for nuclear YAP localization. Size bar = 25 μm
Table 2.
Correlations of cytosolic YAP with clinicopathological features in invasive breast cancer
| Feature | N | Cytosolic YAP expression Negative N (%) | Positive N (%) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histologic type | ||||
| IDC | 187 | 126 (67.4) | 61 (32.6) | 0.002 |
| ILC | 49 | 21 (42.9) | 28 (57.1) | |
| Histologic grade | ||||
| 1 | 36 | 25 (69.4) | 11 (30.6) | 0.626 |
| 2 | 76 | 46 (60.5) | 30 (39.5) | |
| 3 | 124 | 76 (61.3) | 48 (38.7) | |
| Tumor size (cm) | ||||
| ≤ 2 | 108 | 67 (62.0) | 41 (38.0) | 0.240 |
| > 2 and ≤5 | 97 | 65 (67.0) | 32 (33.0) | |
| > 5 | 30 | 15 (50.0) | 15 (50.0) | |
| MAI (per 2 mm2) | ||||
| ≤ 12 | 103 | 64 (62.1) | 39 (37.9) | 0.966 |
| ≥ 13 | 133 | 83 (62.4) | 50 (37.6) | |
| Lymph node status | ||||
| Negative | 97 | 57 (58.8) | 40 (41.2) | 0.426 |
| Positive | 125 | 80 (64.0) | 45 (36.0) | |
Table 3.
Correlations of nuclear YAP with clinicopathological features in invasive breast cancer
| Feature | N | Nuclear YAP expression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (<20 %) N (%) | High (≥20 %) N (%) | p-value | ||
| Histologic type | ||||
| IDC | 187 | 140 (74.9) | 47 (25.1) | <0.001* |
| ILC | 50 | 12 (24.0) | 38 (76.0) | |
| Histologic grade | ||||
| 1 | 36 | 19 (52.8) | 17 (47.2) | 0.297 |
| 2 | 76 | 51 (67.1) | 25 (32.9) | |
| 3 | 125 | 82 (65.6) | 43 (34.4) | |
| Tumor size (cm) | ||||
| ≤2 | 108 | 79 (73.1) | 29 (26.9) | 1.451* |
| >2 and ≤5 | 98 | 60 (61.2) | 38 (38.8) | |
| >5 | 30 | 13 (43.3) | 17 (56.7) | |
| MAI (per 2 mm2) | ||||
| ≤12 | 103 | 61 (59.2) | 42 (40.8) | 0.167 |
| ≥13 | 134 | 91 (67.9) | 43 (32.1) | |
| Lymph node status | ||||
| Negative | 98 | 65 (66.3) | 33 (33.7) | 0.544 |
| Positive | 125 | 78 (62.4) | 47 (37.6) | |
*these data have been corrected for the difference in tumor size between IDC and ILC tumors
High YAP expression is correlated with human and mouse ILC
Since E-cadherin has been implicated in the regulation of YAP activity in human breast cell lines [17, 18, 23], we analyzed whether E-cadherin expression was correlated with YAP expression in our invasive breast cancer samples. Indeed, we found that high cytoplasmic as well as high nuclear YAP expression inversely correlated with E-cadherin expression (p = 0.024 and p < 0.001, respectively, Table 4, Table 5 and Fig. 3). We substantiated the correlation between E-cadherin loss and nuclear YAP localization in ILC by analyzing YAP expression in a set of E-cadherin expressing and E-cadherin mutant (lobular) breast cancer cell lines. In agreement with the findings in our invasive breast cancer cohort we observed that the E-cadherin positive cell lines T47D and MCF10A showed cytosolic YAP staining (Fig 4a), whereas the E-cadherin mutant cell lines SKBR-3 and lobular breast cancer cell line IPH-926 [42, 45], showed predominately nuclear YAP localization (Fig 4c). Next, we used tumor cell lines generated from mammary tumors that developed in conditional mouse models based on tissue-specific and conditional inactivation of E-cadherin and/or p53. In these mice, inactivation of E-cadherin is causal to the formation of invasive and metastatic tumors that mimic human ILC [4, 5]. Using immunofluorescence we compared YAP localization in Trp53∆/∆ (E-cadherin positive, p53 negative) and mouse ILC (mILC) (E-cadherin and p53 negative) cell lines. Similar to their human counterparts, mILC cells showed an increase in nuclear YAP localization. Furthermore, while both mILC and Trp53∆/∆ cells showed cytosolic YAP, YAP expression in Trp53∆/∆ cell lines was mainly cytoplasmic (Fig 4b and d). In order to corroborate our finding that nuclear YAP expression is a hallmark of E-cadherin mutant breast cancer, we performed nuclear fractionation of human and mouse cell lines, which were compared using western blot analyses. Indeed, using TAF5 as a nuclear marker we observed that in both species E-cadherin negative cell lines showed an enrichment of nuclear YAP when compared to their E-cadherin expressing counterparts (Online Resource Fig. 3). In conclusion, our data indicate that YAP localization is inversely correlated with E-cadherin expression, since nuclear YAP is a characteristic of E-cadherin negative ILC from mice and man.
Table 4.
Correlation between E-cadherin expression and cytosolic YAP expression in invasive breast cancer
| Feature | N | Cytosolic YAP expression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative N (%) | Positive N (%) | p-value | ||
| E-cadherin | ||||
| Positive | 176 | 114 (64.8) | 62 (35.2) | 0.024 |
| Negative | 49 | 23 (46.9) | 26 (53.1) | |
Table 5.
Correlation between E-cadherin expression and nuclear YAP expression in invasive breast cancer
| Feature | N | Nuclear YAP expression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (<20 %) N (%) | High (≥20 %) N (%) | p-value | ||
| E-cadherin | ||||
| Positive | 176 | 127 (72.2) | 49 (27.8) | <0.001 |
| Negative | 50 | 15 (30.0) | 35 (70.0) | |
Fig. 3.
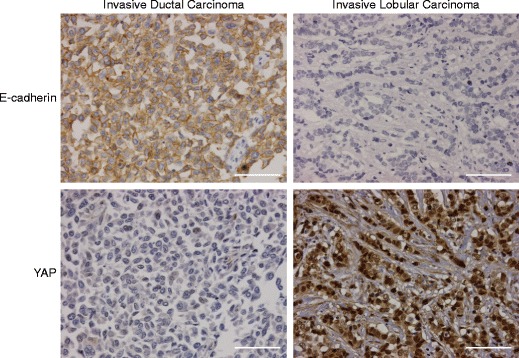
Nuclear YAP expression is a feature of E-cadherin negative ILC. E-cadherin status correlates with nuclear YAP expression. IDC (left panels) and ILC (right panels) samples were stained for E-cadherin (top panels) and YAP (IHC) (bottom panels). Note the striking correlation between nuclear YAP and absence of E-cadherin expression. Size bar = 50 μm
Fig. 4.
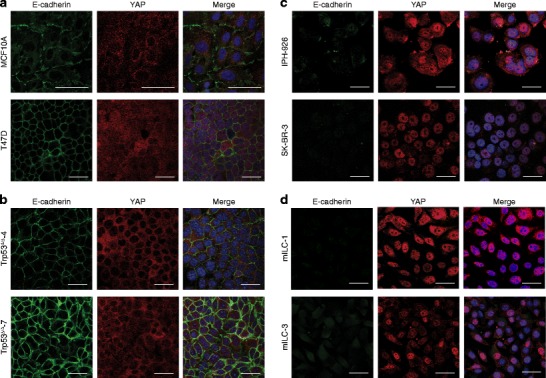
Nuclear localization of YAP in human and mouse ILC. Immunofluorescence for E-cadherin (left panels, green) and YAP (YAP-IF, middle panels, red). Nuclei were visualized using DAPI (blue). Right panels depict the merged image. In E-cadherin positive human (a) and mouse (b) cell lines YAP expression is predominantly cytosolic. E-cadherin negative human (c) and mouse ILC (d) cell lines are characterized by prominent nuclear YAP expression. Size bar = 15 μm
Discussion
This study demonstrates for the first time that nuclear and cytosol YAP localization are correlated with E-cadherin negative invasive lobular breast cancer. As YAP is a transcriptional coactivator that shuttles between the cytosol and nucleus, we analyzed cytosolic intensity of YAP expression and the number of YAP positive nuclei. Our results suggest that YAP does not only translocate into the nucleus of E-cadherin negative breast cancer, but also that total YAP levels are increased in this situation. While we have not tested whether YAP expression levels correlate with YAP activity, it was recently demonstrated that YAP signaling may also be regulated through YAP degradation [21]. It is currently unknown whether E-cadherin expression regulates YAP degradation. A possibility might be that loss of E-cadherin inhibits YAP phosphorylation and subsequent ubiquitin-mediated degradation, leading to increased levels of YAP. However, while we observed a correlation between membranous E-cadherin expression and cytoplasmic YAP localization, total YAP protein levels did not seem to correlate with E-cadherin status in the human breast cell lines (data not shown). This discrepancy may reflect differences between cultured cell lines and clinical breast cancer specimens.
In contrast to previous studies [19, 28], we did not find a correlation between YAP expression/localization and overall survival of breast cancer patients. We did not observe a statistically significant correlation between YAP expression/localization and overall survival (data not shown). We think that the lack of correlation in our cohort is not surprising, since YAP is strongly linked to ILC, and differences in survival rates for ILC and IDC patients are only observed when comparing large numbers of patients over long time periods of more than 10 years [46].
An interesting yet unanswered question is the possible link between YAP localization/function and E-cadherin negative IDC. In contrast to early mutational inactivation of E-cadherin in ILC, IDC tends to show loss of E-cadherin by epigenetic mechanisms during later stages of tumor progression [1, 47, 48]. Since almost all our IDC cases showed membranous expression of E-cadherin (97 %), this prevented an in-depth survey into the localization of YAP in E-cadherin negative IDC.
Our current findings are in line with recent data that addressed a scenario whereby stress fiber formation resulted in a reduction of YAP phosphorylation and subsequent nuclear localization [17, 20, 22]. Although the impact of cell-cell adhesion was not directly addressed in these studies, it was recently shown that E-cadherin-dependent contact inhibition and a resulting reduction in proliferation may be regulated through Lats-dependent phosphorylation of YAP [18]. Cell-type specific differences may play a role, as morphology-dependent F-actin bundling can also regulate YAP in a Lats-independent manner [17]. Regardless of the exact mechanism, a common denominator in the nuclear localization of YAP seems the activation of Rho-Rock-driven actin polymerization. As such, both cellular morphology and cadherin-mediated cell-cell binding may regulate YAP-mediated transcriptional activity in a tension-dependent manner. Interestingly, YAP overexpression can also cause transformation of E-cadherin expressing breast cancer cells, which is accompanied by loss of epithelial characteristics, expression of mesenchymal markers and acquisition of invasiveness and anchorage-independence [22, 24, 49]. Thus, irrespective of the upstream signaling cascade, nuclear YAP may play a central role in the regulation of breast cancer invasiveness.
We have previously demonstrated that loss of junctional integrity through mutational inactivation of E-cadherin leads to a p120-catenin and MRIP-dependent activation of the Rho-Rock pathway in metastatic ILC [41]. In this setting, the functional consequence of active Rock signaling is the regulation of anchorage-independent tumor growth and metastasis. Because activation of Rock directs actin polymerization, this may result in dephosphorylation and subsequent nuclear membranous expression of E-cadherin and nuclear localization of YAP appear to be largely mutually exclusive in mouse and human breast cancer. We think that actin-dependent nuclear translocation of YAP is a plausible mode of action since several Hippo pathway components bind actin and recent data indicated that F-actin may regulate YAP downstream of cell morphology [20, 50–53]. Our recent finding that p120 controls anchorage independence through MRIP-dependent F-actin bundling [41], may provide an alternative mode of regulation. Whether p120 links actin polymerization to subsequent nuclear YAP expression in ILC, and how these events contribute to ILC development and metastasis, is subject of further research.
To summarize, our results show that nuclear YAP localization and overall YAP expression levels significantly correlate with the ILC breast cancer subtype, a malignancy that is causally related to mutational inactivation of E-cadherin. These findings were validated in human and mouse E-cadherin mutant cell lines, which showed an increase in nuclear YAP localization compared to E-cadherin expressing cell lines. We hypothesize that upon loss of E-cadherin and subsequent inactivation of the AJ complex, YAP translocates to the nucleus where it may induce a transcriptional program favoring ILC tumor development and progression. In conclusion, our data suggest that YAP translocation to the nucleus is a consequence of early mutational inactivation of E-cadherin and subsequent p120-mediated activation of Rock-dependent actin polymerization. As such, YAP and its target genes hold promise for the development of novel intervention strategies to better treat metastatic ILC.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
(DOCX 20 kb)
(DOCX 21 kb)
Myoepithelial cells express nuclear YAP. Normal human breast tissue was sectioned and triple-stained using immunofluorescence for YAP, E-cadherin and p63 to determine YAP expression in luminal and myoepithelial mammary cells. DAPI depicts the nuclei (left panel). The right panel shows a merged image of YAP (red), E-cadherin (blue), and p63 (green) signals. (PDF 2191 kb)
Validation of the YAP antibodies. YAP knock down in the T47D cell line. The YAP-IHC and the YAP-IF antibody were used to analyze YAP expression levels. Both antibodies clearly show a reduction of YAP expression upon shRNA-mediated knock down and thereby establish specificity for the antibodies used (PDF 148 kb)
E-cadherin mutant breast cancer cells are characterized by nuclear YAP localization. Biochemical fractionation to study YAP localization in breast cancer cell lines. Nuclear (N) and cytosolic (C) compartments from E-cadherin expressing (left panels) and E-cadherin mutant (right panels) human (a) and mouse (b) breast cancer cell lines were western blotted and probed with the YAP-IF antibody. TAF5 was used as a nuclear marker. Note the enrichment of YAP in the nuclear fractions of E-cadherin mutant breast cancer cell lines SKBR-3 (a) and mILC-1 (b) compared to their E-cadherin expressing counterparts. AKT was used as cytosolic marker (PDF 1284 kb)
Acknowledgements
We thank Petra van der Groep and Nathalie ter Hoeve for excellent assistance with immunohistochemistry, and Matthias Christgen for IPH-926. Pascal Jansen and Michiel Vermeulen for sharing their glass douncer. The Timmers and Roeder laboratories that kindly provided the TAF5 antibody. The Cell Microscopy Centre (CMC) of the Department of Cell Biology of the University Medical Centre (UMC) Utrecht, The Netherlands, for providing the microscopy service of the Zeiss LSM 700. We thank Corlinda ten Brink for confocal microscopy support. All members of the Derksen and Van Diest laboratories are acknowledged for support and discussions.
Financial Disclosure
This work was supported by a grant from The Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO-VIDI 917.96.318). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Footnotes
Author contributions
Experiments were conceived and designed by EJV and PWBD. EJV, RvdV and JFV performed the experiments. EJV, PB and PVD performed the pathological analyses and scoring of human tumor samples. EJV and PWBD wrote the paper.
References
- 1.Berx G, Cleton-Jansen AM, Nollet F, de Leeuw WJ, van de Vijver M, et al. E-cadherin is a tumour/invasion suppressor gene mutated in human lobular breast cancers. EMBO J. 1995;14:6107–6115. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moll R, Mitze M, Frixen UH, Birchmeier W. Differential loss of E-cadherin expression in infiltrating ductal and lobular breast carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1993;143:1731–1742. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vos CB, Cleton-Jansen AM, Berx G, de Leeuw WJ, ter Haar NT, et al. E-cadherin inactivation in lobular carcinoma in situ of the breast: an early event in tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 1997;76:1131–1133. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1997.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Derksen PW, Liu X, Saridin F, van der Gulden H, Zevenhoven J, et al. Somatic inactivation of E-cadherin and p53 in mice leads to metastatic lobular mammary carcinoma through induction of anoikis resistance and angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2006;10:437–449. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Derksen PW, Braumuller TM, van der Burg E, Hornsveld M, Mesman E, et al. Mammary-specific inactivation of E-cadherin and p53 impairs functional gland development and leads to pleomorphic invasive lobular carcinoma in mice. Dis Model Mech. 2011;4:347–358. doi: 10.1242/dmm.006395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lombaerts M, van Wezel T, Philippo K, Dierssen JW, Zimmerman RM, et al. E-cadherin transcriptional downregulation by promoter methylation but not mutation is related to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer. 2006;94:661–671. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kalluri R, Weinberg RA. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:1420–1428. doi: 10.1172/JCI39104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Edgar BA. From cell structure to transcription: Hippo forges a new path. Cell. 2006;124:267–273. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huang J, Wu S, Barrera J, Matthews K, Pan D. The Hippo signaling pathway coordinately regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by inactivating Yorkie, the Drosophila Homolog of YAP. Cell. 2005;122:421–434. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wu S, Huang J, Dong J, Pan D. hippo encodes a Ste-20 family protein kinase that restricts cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in conjunction with salvador and warts. Cell. 2003;114:445–456. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00549-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wei X, Shimizu T, Lai ZC. Mob as tumor suppressor is activated by Hippo kinase for growth inhibition in Drosophila. EMBO J. 2007;26:1772–1781. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dong J, Feldmann G, Huang J, Wu S, Zhang N, et al. Elucidation of a universal size-control mechanism in Drosophila and mammals. Cell. 2007;130:1120–1133. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Schlegelmilch K, Mohseni M, Kirak O, Pruszak J, Rodriguez JR, et al. Yap1 acts downstream of alpha-catenin to control epidermal proliferation. Cell. 2011;144:782–795. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Saucedo LJ, Edgar BA. Filling out the Hippo pathway. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:613–621. doi: 10.1038/nrm2221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kanai F, Marignani PA, Sarbassova D, Yagi R, Hall RA, et al. TAZ: a novel transcriptional co-activator regulated by interactions with 14-3-3 and PDZ domain proteins. EMBO J. 2000;19:6778–6791. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.24.6778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Komuro A, Nagai M, Navin NE, Sudol M. WW domain-containing protein YAP associates with ErbB-4 and acts as a co-transcriptional activator for the carboxyl-terminal fragment of ErbB-4 that translocates to the nucleus. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:33334–33341. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305597200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dupont S, Morsut L, Aragona M, Enzo E, Giulitti S, et al. Role of YAP/TAZ in mechanotransduction. Nature. 2011;474:179–183. doi: 10.1038/nature10137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kim NG, Koh E, Chen X, Gumbiner BM. E-cadherin mediates contact inhibition of proliferation through Hippo signaling-pathway components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:11930–11935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1103345108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Matallanas D, Romano D, Yee K, Meissl K, Kucerova L, et al. RASSF1A elicits apoptosis through an MST2 pathway directing proapoptotic transcription by the p73 tumor suppressor protein. Mol Cell. 2007;27:962–975. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.08.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wada K, Itoga K, Okano T, Yonemura S, Sasaki H. Hippo pathway regulation by cell morphology and stress fibers. Development. 2011;138:3907–3914. doi: 10.1242/dev.070987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhao B, Li L, Tumaneng K, Wang CY, Guan KL. A coordinated phosphorylation by Lats and CK1 regulates YAP stability through SCF(beta-TRCP) Genes Dev. 2010;24:72–85. doi: 10.1101/gad.1843810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhao B, Li L, Wang L, Wang CY, Yu J, et al. Cell detachment activates the Hippo pathway via cytoskeleton reorganization to induce anoikis. Genes Dev. 2012;26:54–68. doi: 10.1101/gad.173435.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Perrais M, Chen X, Perez-Moreno M, Gumbiner BM. E-cadherin homophilic ligation inhibits cell growth and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling independently of other cell interactions. Mol Biol Cell. 2007;18:2013–2025. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E06-04-0348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Overholtzer M, Zhang J, Smolen GA, Muir B, Li W, et al. Transforming properties of YAP, a candidate oncogene on the chromosome 11q22 amplicon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:12405–12410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605579103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.X. Wang, L. Su, Q. Ou, Yes-associated protein promotes tumour development in luminal epithelial derived breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer. (2011) [DOI] [PubMed]
- 26.Zhang J, Ji JY, Yu M, Overholtzer M, Smolen GA, et al. YAP-dependent induction of amphiregulin identifies a non-cell-autonomous component of the Hippo pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:1444–1450. doi: 10.1038/ncb1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cordenonsi M, Zanconato F, Azzolin L, Forcato M, Rosato A, et al. The Hippo transducer TAZ confers cancer stem cell-related traits on breast cancer cells. Cell. 2011;147:759–772. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tufail R, Jorda M, Zhao W, Reis I, Nawaz Z. Loss of Yes-associated protein (YAP) expression is associated with estrogen and progesterone receptors negativity in invasive breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;131:743–750. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1435-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hampton GM, Mannermaa A, Winqvist R, Alavaikko M, Blanco G, et al. Loss of heterozygosity in sporadic human breast carcinoma: a common region between 11q22 and 11q23.3. Cancer Res. 1994;54:4586–4589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gudmundsson J, Barkardottir RB, Eiriksdottir G, Baldursson T, Arason A, et al. Loss of heterozygosity at chromosome 11 in breast cancer: association of prognostic factors with genetic alterations. Br J Cancer. 1995;72:696–701. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Carter SL, Negrini M, Baffa R, Gillum DR, Rosenberg AL, et al. Loss of heterozygosity at 11q22-q23 in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1994;54:6270–6274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tomlinson IP, Strickland JE, Lee AS, Bromley L, Evans MF, et al. Loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 11 q in breast cancer. J Clin Pathol. 1995;48:424–428. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.5.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Winqvist R, Hampton GM, Mannermaa A, Blanco G, Alavaikko M, et al. Loss of heterozygosity for chromosome 11 in primary human breast tumors is associated with poor survival after metastasis. Cancer Res. 1995;55:2660–2664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yuan M, Tomlinson V, Lara R, Holliday D, Chelala C, et al. Yes-associated protein (YAP) functions as a tumor suppressor in breast. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15:1752–1759. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2008.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chen YY, Hwang ES, Roy R, DeVries S, Anderson J, et al. Genetic and phenotypic characteristics of pleomorphic lobular carcinoma in situ of the breast. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33:1683–1694. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181b18a89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.van der Groep P, Bouter A, van der Zanden R, Siccama I, Menko FH, et al. Distinction between hereditary and sporadic breast cancer on the basis of clinicopathological data. J Clin Pathol. 2006;59:611–617. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2005.032151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Packeisen J, Korsching E, Herbst H, Boecker W, Buerger H. Demystified…tissue microarray technology. Mol Pathol. 2003;56:198–204. doi: 10.1136/mp.56.4.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.van Diest PJ. No consent should be needed for using leftover body material for scientific purposes. BMJ. 2002;325:648–651. doi: 10.1136/bmj.325.7365.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tirkkonen M, Tanner M, Karhu R, Kallioniemi A, Isola J, et al. Molecular cytogenetics of primary breast cancer by CGH. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1998;21:177–184. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2264(199803)21:3<177::AID-GCC1>3.0.CO;2-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:10869–10874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191367098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schackmann RC, van Amersfoort M, Haarhuis JH, Vlug EJ, Halim VA, et al. Cytosolic p120-catenin regulates growth of metastatic lobular carcinoma through Rock1-mediated anoikis resistance. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:3176–3188. doi: 10.1172/JCI41695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Christgen M, Bruchhardt H, Hadamitzky C, Rudolph C, Steinemann D, et al. Comprehensive genetic and functional characterization of IPH-926: a novel CDH1-null tumour cell line from human lobular breast cancer. J Pathol. 2009;217:620–632. doi: 10.1002/path.2495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Derksen PW, Tjin E, Meijer HP, Klok MD, MacGillavry HD, et al. Illegitimate WNT signaling promotes proliferation of multiple myeloma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:6122–6127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0305855101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Christova R, Oelgeschlager T. Association of human TFIID-promoter complexes with silenced mitotic chromatin in vivo. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:79–82. doi: 10.1038/ncb733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.van de Wetering M, Barker N, Harkes IC, van der Heyden M, Dijk NJ, et al. Mutant E-cadherin breast cancer cells do not display constitutive Wnt signaling. Cancer Res. 2001;61:278–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Pestalozzi BC, Zahrieh D, Mallon E, Gusterson BA, Price KN, et al. Distinct clinical and prognostic features of infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: combined results of 15 International Breast Cancer Study Group clinical trials. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3006–3014. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.9336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zhao H, Langerod A, Ji Y, Nowels KW, Nesland JM, et al. Different gene expression patterns in invasive lobular and ductal carcinomas of the breast. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15:2523–2536. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E03-11-0786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lehr HA, Folpe A, Yaziji H, Kommoss F, Gown AM. Cytokeratin 8 immunostaining pattern and E-cadherin expression distinguish lobular from ductal breast carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2000;114:190–196. doi: 10.1309/CPUX-KWEH-7B26-YE19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhao B, Ye X, Yu J, Li L, Li W, et al. TEAD mediates YAP-dependent gene induction and growth control. Genes Dev. 2008;22:1962–1971. doi: 10.1101/gad.1664408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Densham RM, O’Neill E, Munro J, Konig I, Anderson K, et al. MST kinases monitor actin cytoskeletal integrity and signal via c-Jun N-terminal kinase stress-activated kinase to regulate p21Waf1/Cip1 stability. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29:6380–6390. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00116-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.McCartney BM, Kulikauskas RM, LaJeunesse DR, Fehon RG. The neurofibromatosis-2 homologue, Merlin, and the tumor suppressor expanded function together in Drosophila to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. Development. 2000;127:1315–1324. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.6.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ernkvist M, Aase K, Ukomadu C, Wohlschlegel J, Blackman R, et al. p130-angiomotin associates to actin and controls endothelial cell shape. FEBS J. 2006;273:2000–2011. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gagne V, Moreau J, Plourde M, Lapointe M, Lord M, et al. Human angiomotin-like 1 associates with an angiomotin protein complex through its coiled-coil domain and induces the remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009;66:754–768. doi: 10.1002/cm.20405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(DOCX 20 kb)
(DOCX 21 kb)
Myoepithelial cells express nuclear YAP. Normal human breast tissue was sectioned and triple-stained using immunofluorescence for YAP, E-cadherin and p63 to determine YAP expression in luminal and myoepithelial mammary cells. DAPI depicts the nuclei (left panel). The right panel shows a merged image of YAP (red), E-cadherin (blue), and p63 (green) signals. (PDF 2191 kb)
Validation of the YAP antibodies. YAP knock down in the T47D cell line. The YAP-IHC and the YAP-IF antibody were used to analyze YAP expression levels. Both antibodies clearly show a reduction of YAP expression upon shRNA-mediated knock down and thereby establish specificity for the antibodies used (PDF 148 kb)
E-cadherin mutant breast cancer cells are characterized by nuclear YAP localization. Biochemical fractionation to study YAP localization in breast cancer cell lines. Nuclear (N) and cytosolic (C) compartments from E-cadherin expressing (left panels) and E-cadherin mutant (right panels) human (a) and mouse (b) breast cancer cell lines were western blotted and probed with the YAP-IF antibody. TAF5 was used as a nuclear marker. Note the enrichment of YAP in the nuclear fractions of E-cadherin mutant breast cancer cell lines SKBR-3 (a) and mILC-1 (b) compared to their E-cadherin expressing counterparts. AKT was used as cytosolic marker (PDF 1284 kb)


