Abstract
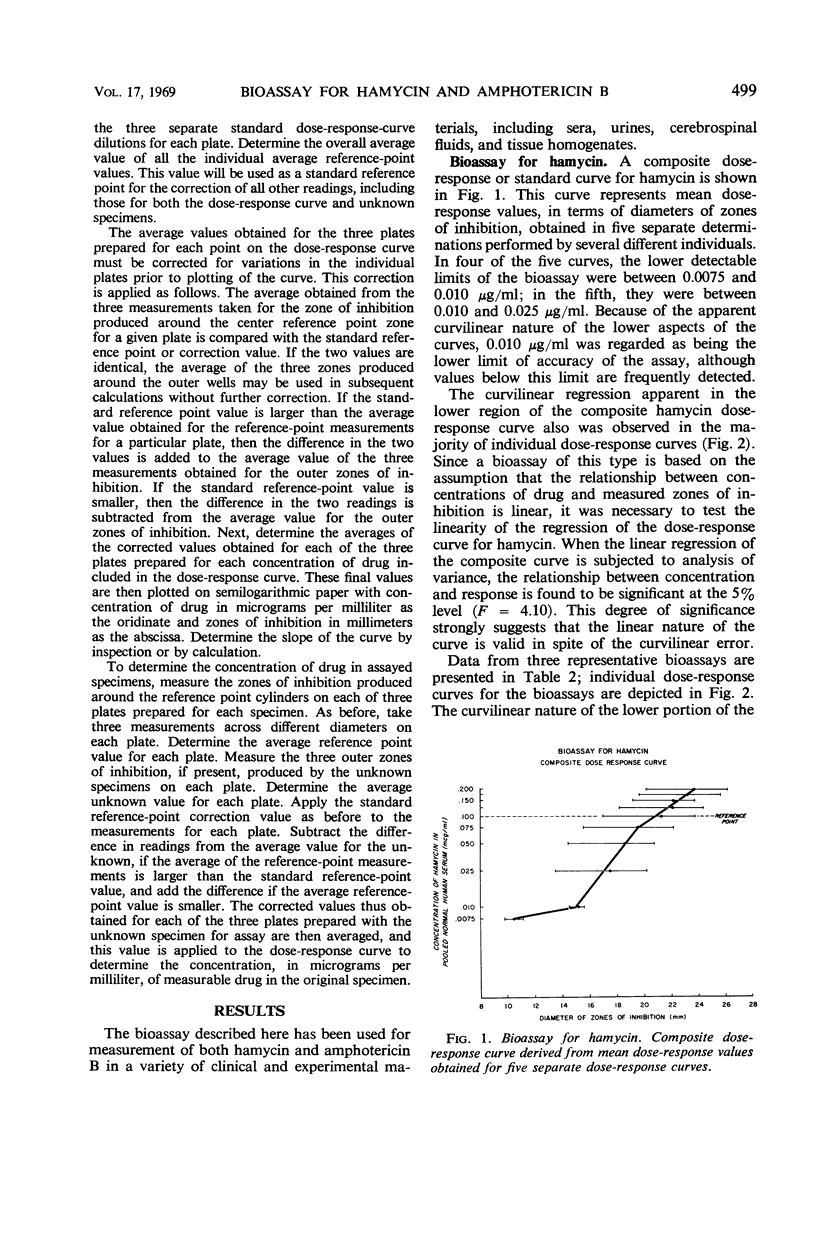
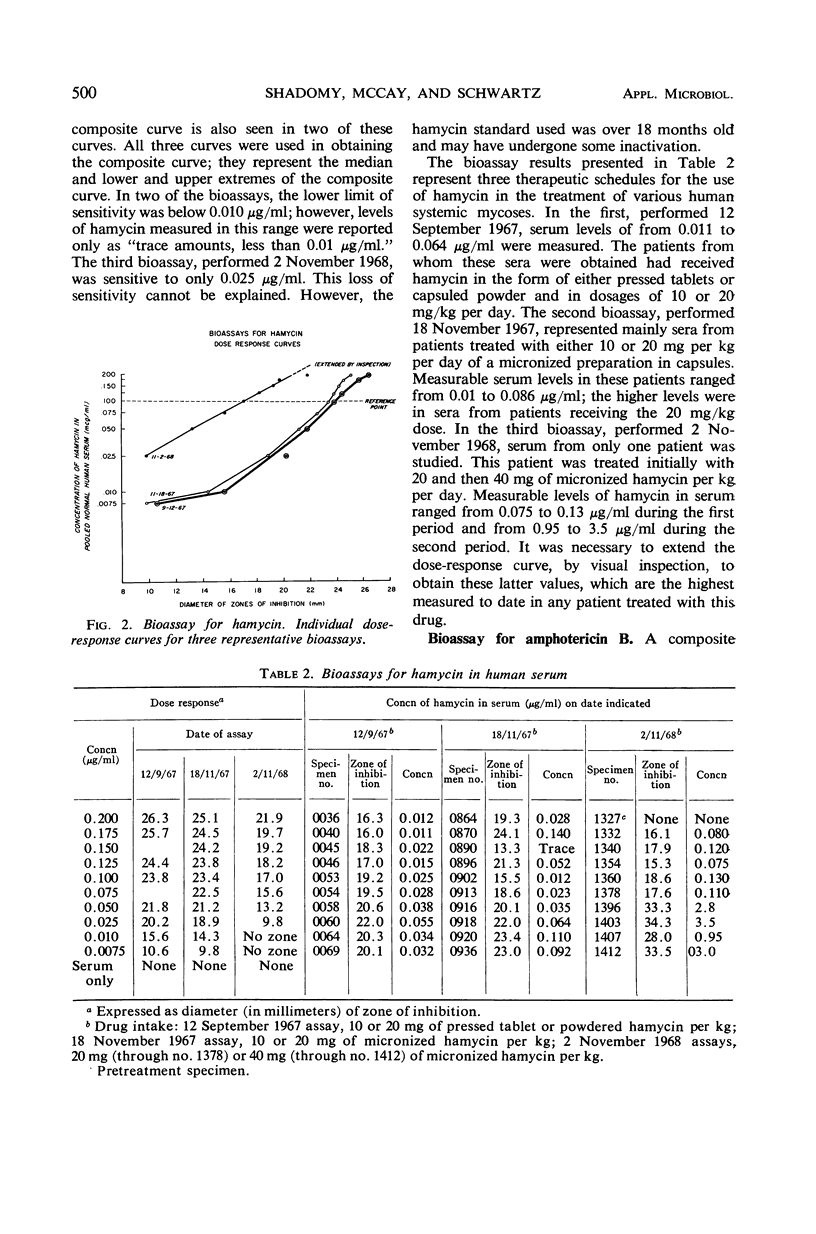
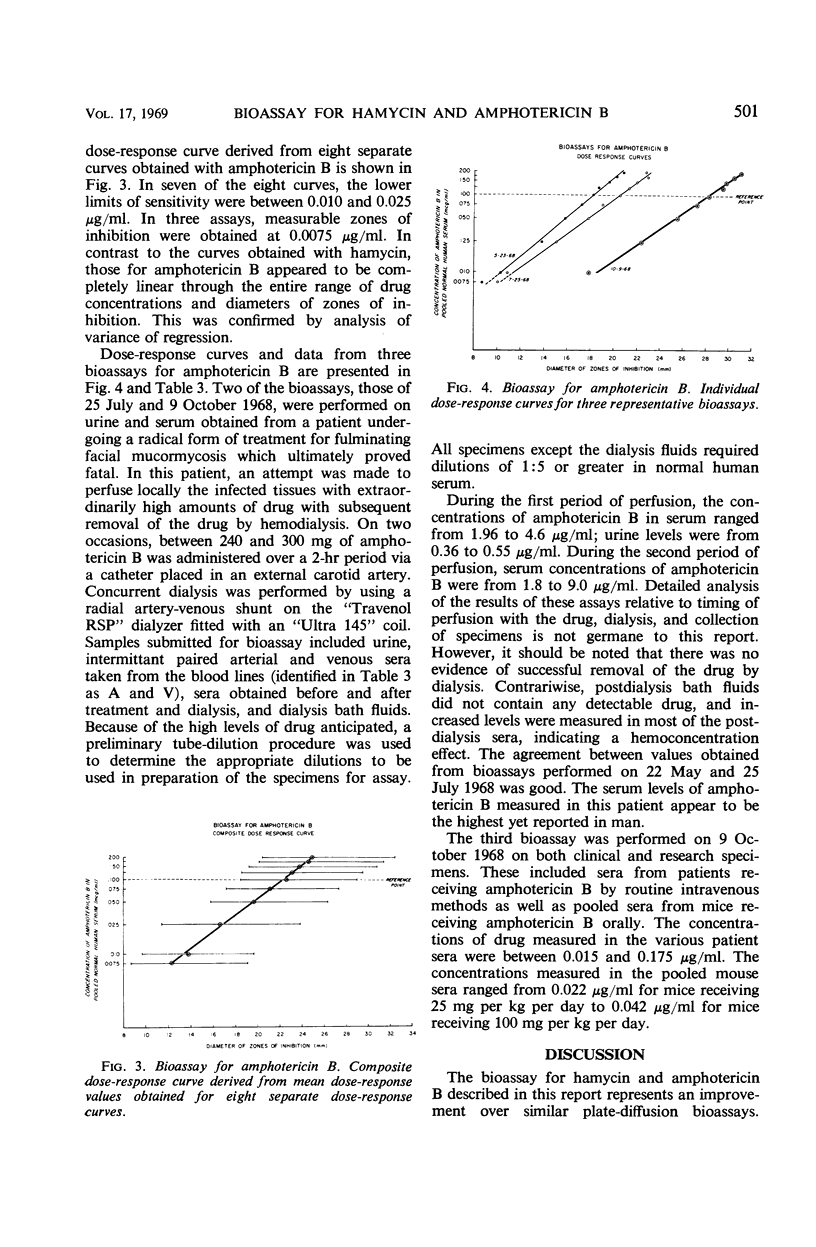
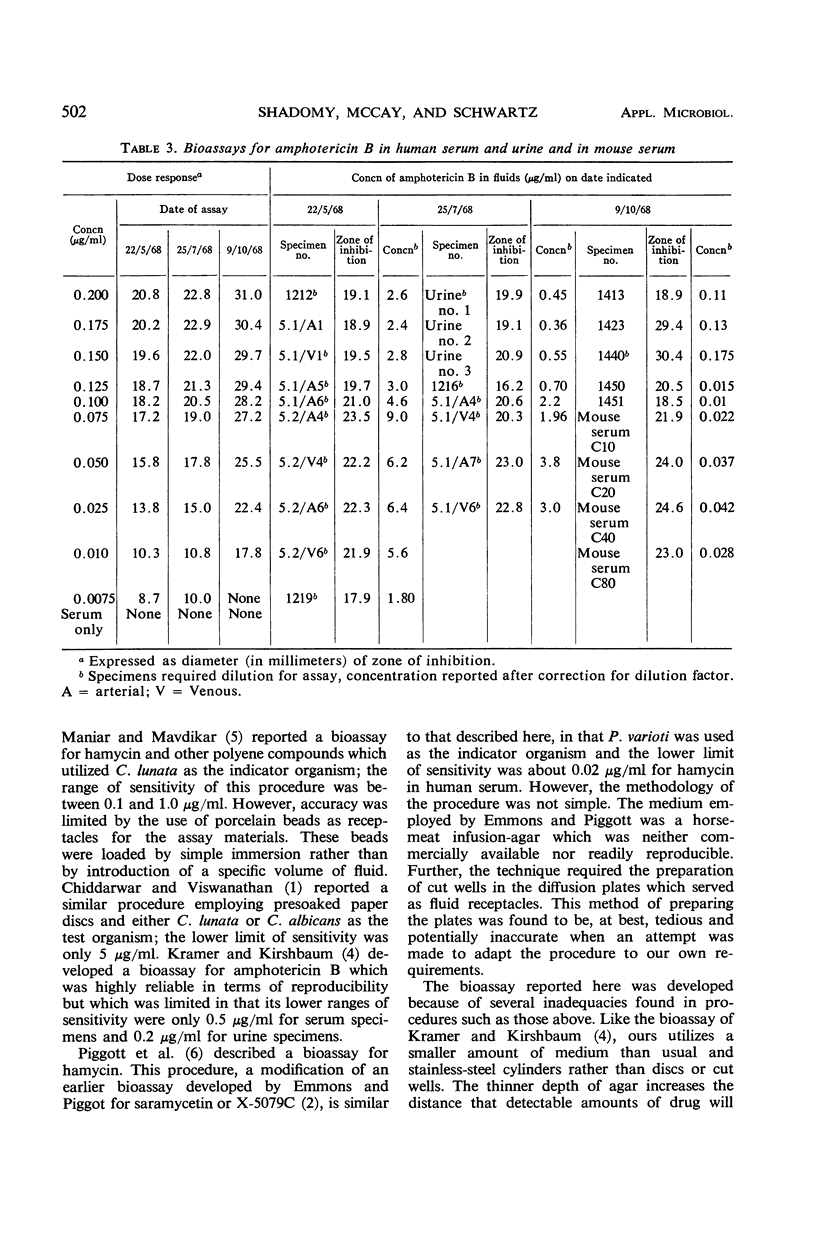
A bioassay suitable for measuring concentrations of the polyene antifungal agents hamycin and amphotericin B in biological fluids is described. By using Paecilomyces varioti as the indicator organism, sensitivity of the bioassay was found to be in the range of 0.01 to 0.02 μg/ml. A linear dose-response curve was obtained with amphotericin B; the curve for hamycin was curvilinear. In a series of assays, hamycin serum levels in the range of 0.01 to 3.5 μg/ml were measured; with amphotericin B, serum levels in the range of 0.015 to 0.175 μg/ml were measured in patients receiving orthodox intravenous medication and as high as 9.0 μg/ml in one patient treated with extraordinarily high doses of the drug.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EMMONS C. W., PIGGOTT W. R. Bioassay of the antifungal agent X-5079C in serum of patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Oct;84:534–537. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.84.4.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERKE J. R., MADIGAN M. E. Amphotericin B and other polyene antifungal antibiotics: photometric assay and factors influencing activity. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1961 Apr;11:227–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAMER J., KIRSHBAUM A. Cylinder plate assays for amphotericin B in dosage forms and body fluids. Antibiot Chemother. 1960 Mar;10:188–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggott W. R., Williams T. W., Jr, Emmons C. W. Bioassay for hamycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:353–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



