Abstract
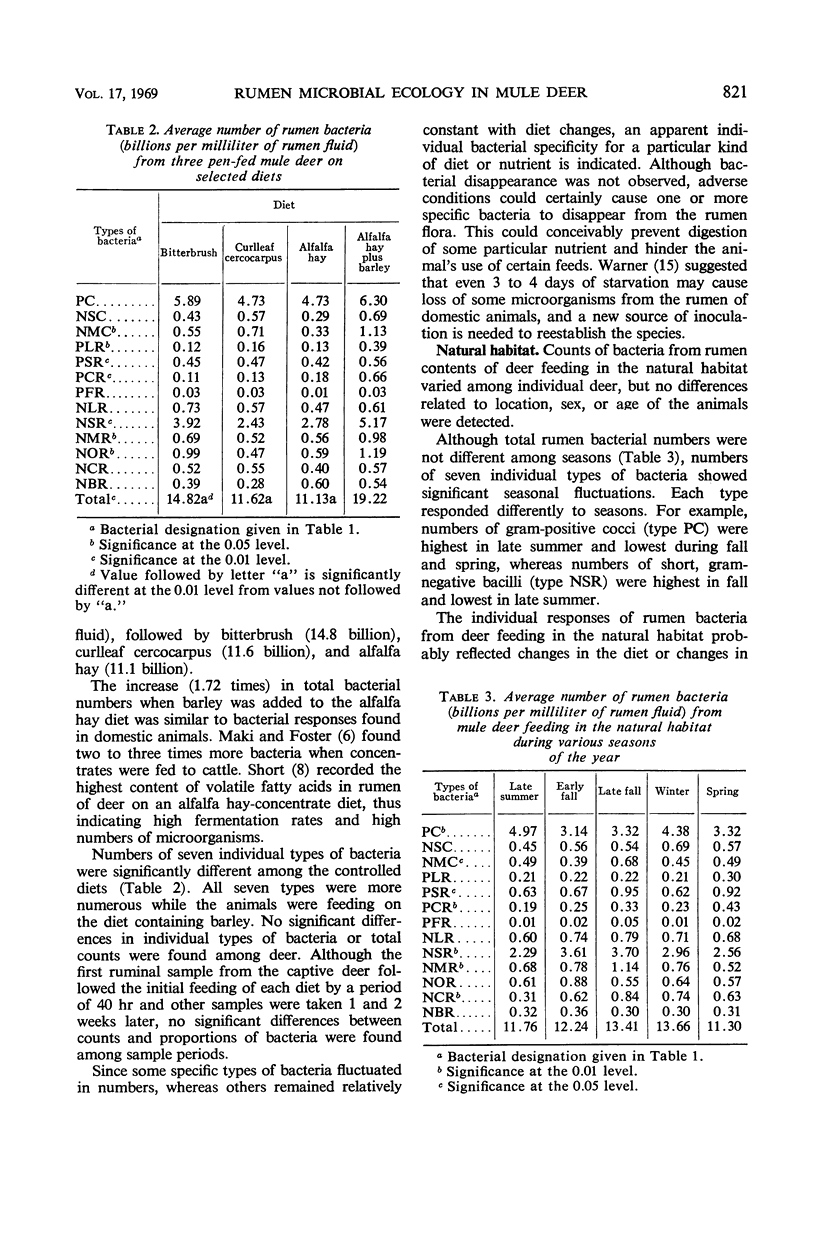
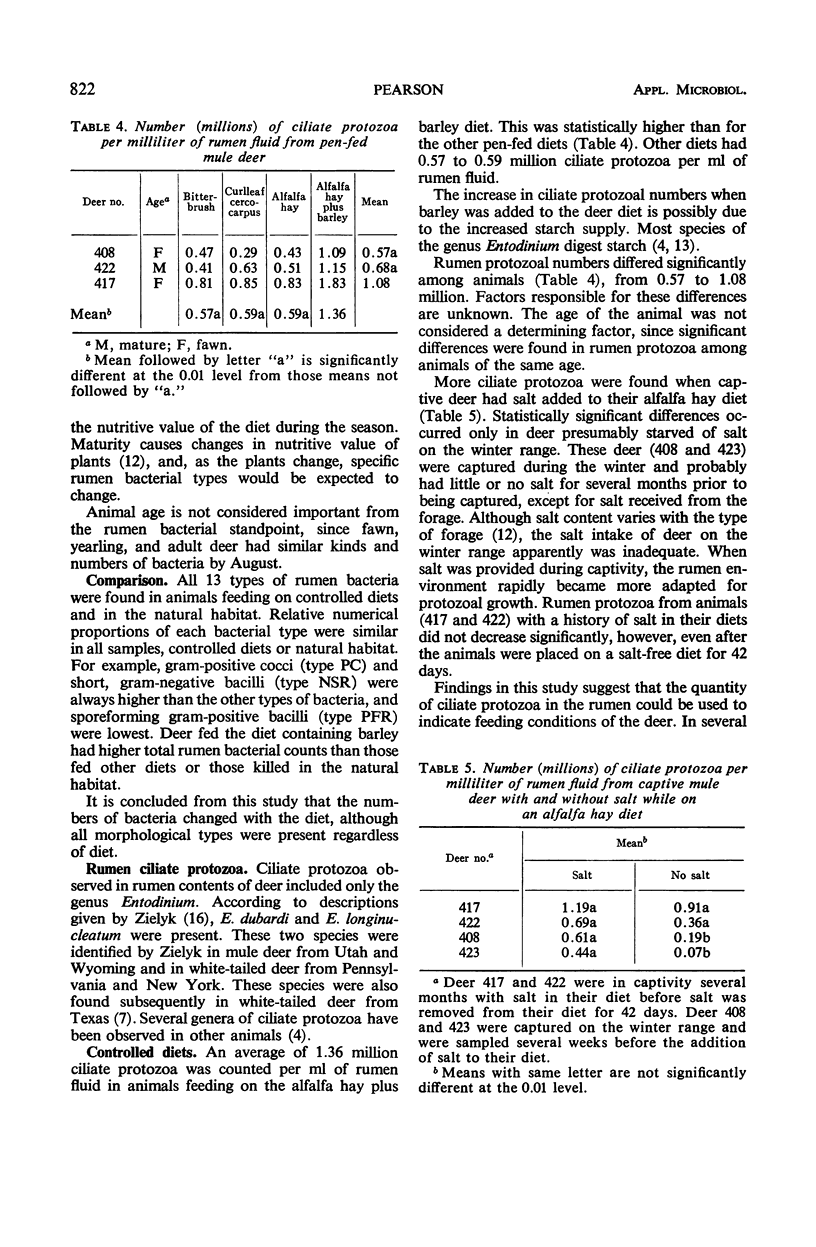
Mule deer rumen microbial populations from animals in the natural habitat in Utah and from captive deer fed various rations were studied. The microorganisms were characterized on the basis of morphology and Gram reaction. Rumen samples contained 13 identifiable types of bacteria and one genus of ciliate protozoa (Entodinium). Highest rumen bacterial populations were produced on rations containing barley. No differences in proportions of ruminal bacteria in the various morphological groups could be detected when animals were fed either natural browse plants or alfalfa hay. The total numbers of bacteria were similar for animals feeding on controlled diets of browse or hay and those in the natural habitat. Numbers of some bacterial types were directly related to ciliate protozoal numbers, whereas others were inversely related. Highest rumen ciliate protozoal populations were observed on rations containing barley. No differences in protozoal populations were noted between diets containing only browse or hay. Seasonal variations were noted in ciliate protozoal numbers from deer feeding in the natural habitat. The total number of ciliate protozoa decreased in the fall and winter and remained low until spring. There were indications that salt in the deer diet favorably affected rumen ciliate protozoa. Rather than revealing direct deer management applications, this study serves to stimulate and illuminate new approaches to research in range and wildlife nutrition.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P. Bacterial species of the rumen. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Sep;23(3):125–153. doi: 10.1128/br.23.3.125-153.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E., BRYANT M. P., MAH R. A. THE RUMEN BACTERIA AND PROTOZOA. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1964;18:131–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.18.100164.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. Symposium: selected topics in microbial ecology. I. Microbial ecology of the rumen. Bacteriol Rev. 1960 Dec;24(4):353–364. doi: 10.1128/br.24.4.353-364.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGDEN B. The cultivation and metabolism of oligotrich Protozoa from the sheep's rumen. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Aug;9(1):44–53. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-1-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


