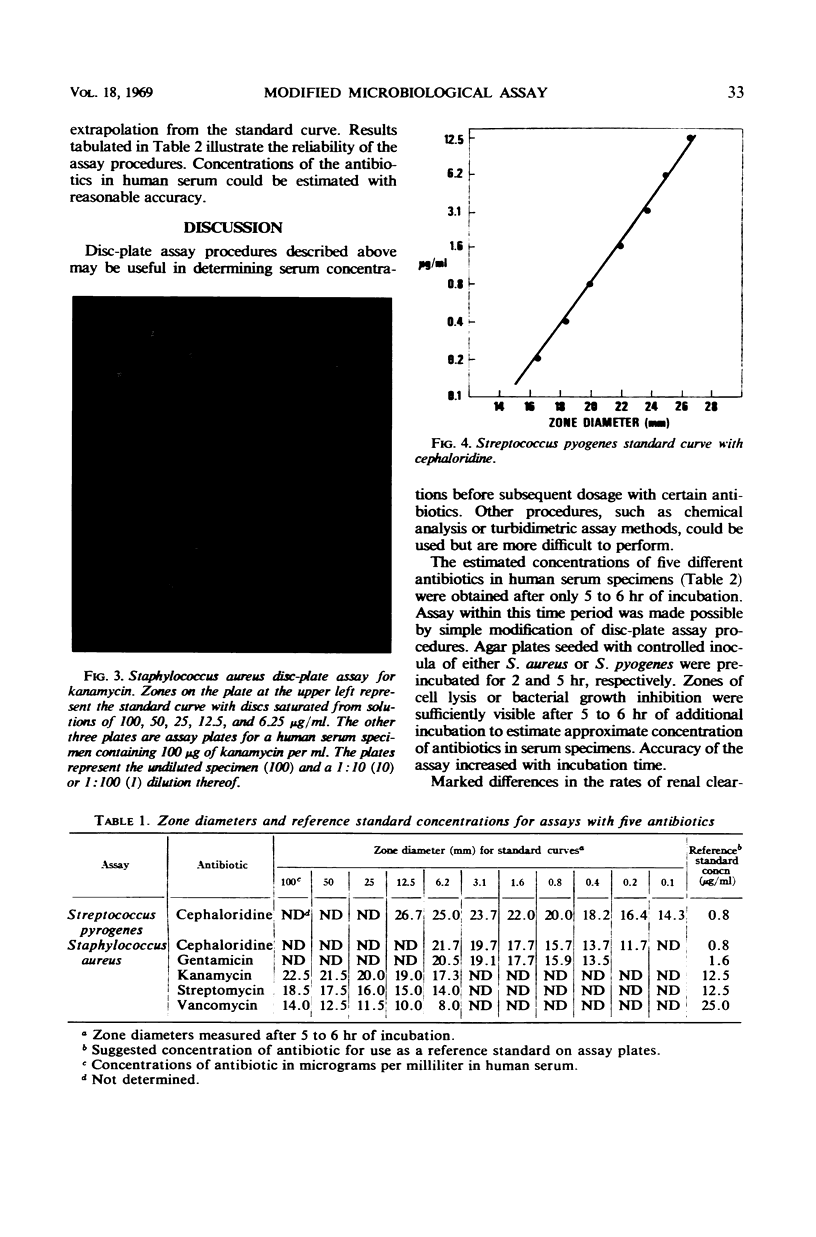
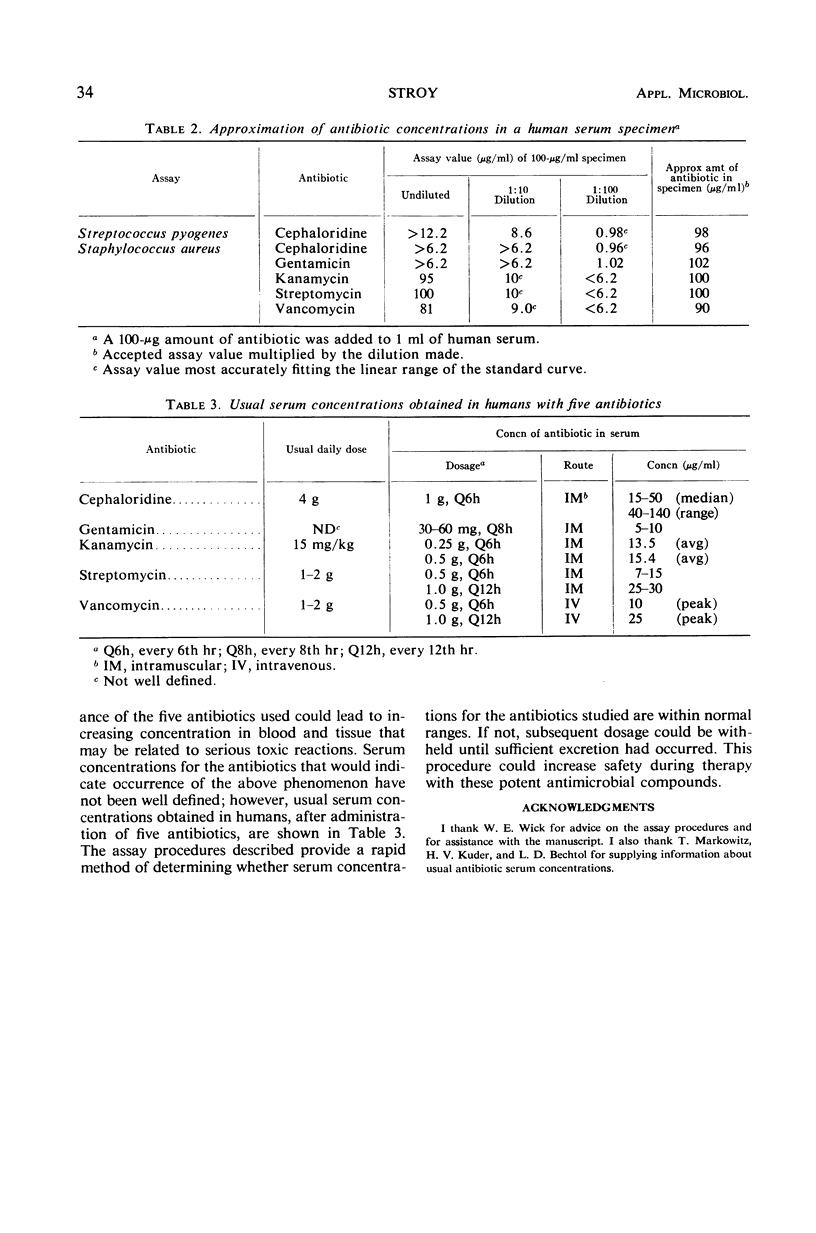
Abstract
Antibiotic concentrations in human sera were estimated in 5 to 6 hr by a modified microbiological assay. By using Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes as the assay organisms, the seeded assay plates were preincubated for 2 to 6 hr and then were stored at 4 C until used for assay. Paper discs saturated with the specimen were placed on the preincubated assay plates with reference discs saturated with known concentrations of antibiotic. After 5 to 6 hr of incubation, zones of antibacterial activity were measured and compared with a standard curve for estimation of antibiotic concentration. Results from this rapid assay method compared favorably with those from the commonly used 24-hr assay.
Full text
PDF