Abstract
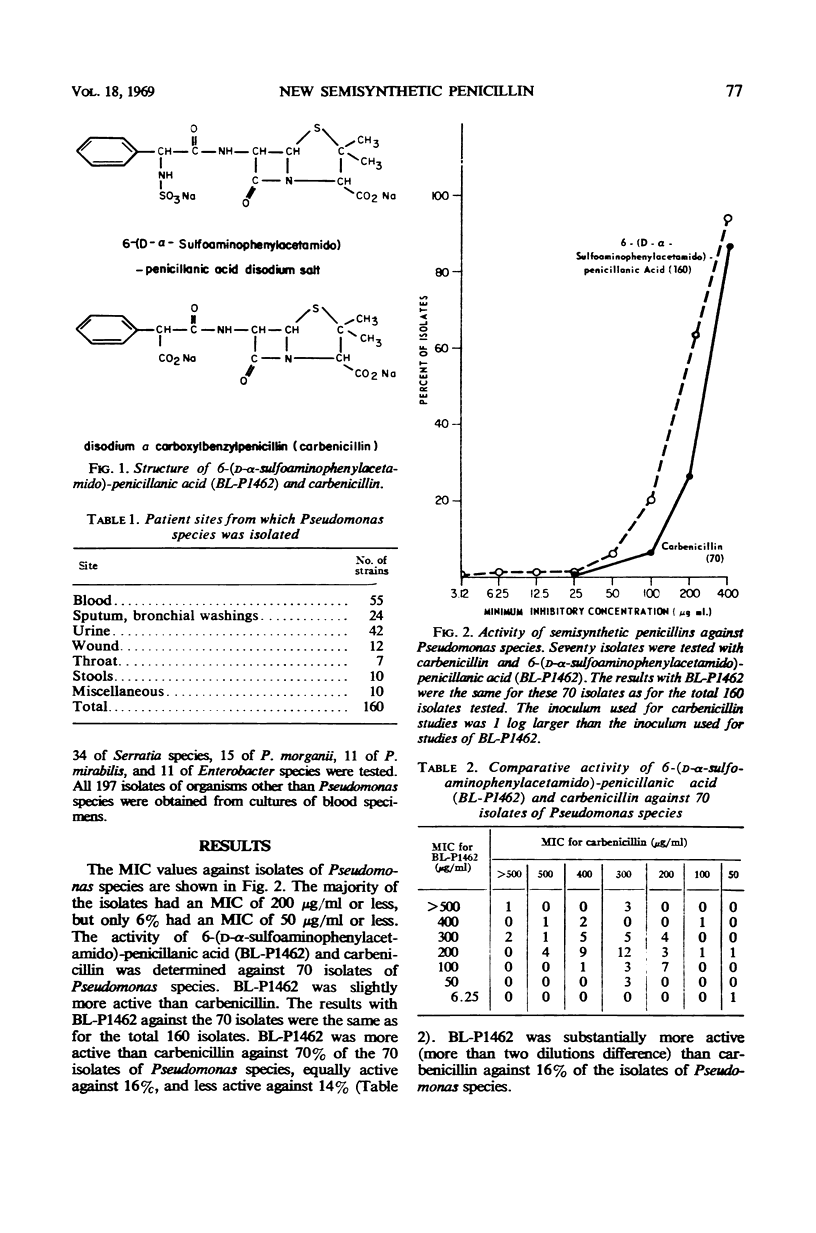
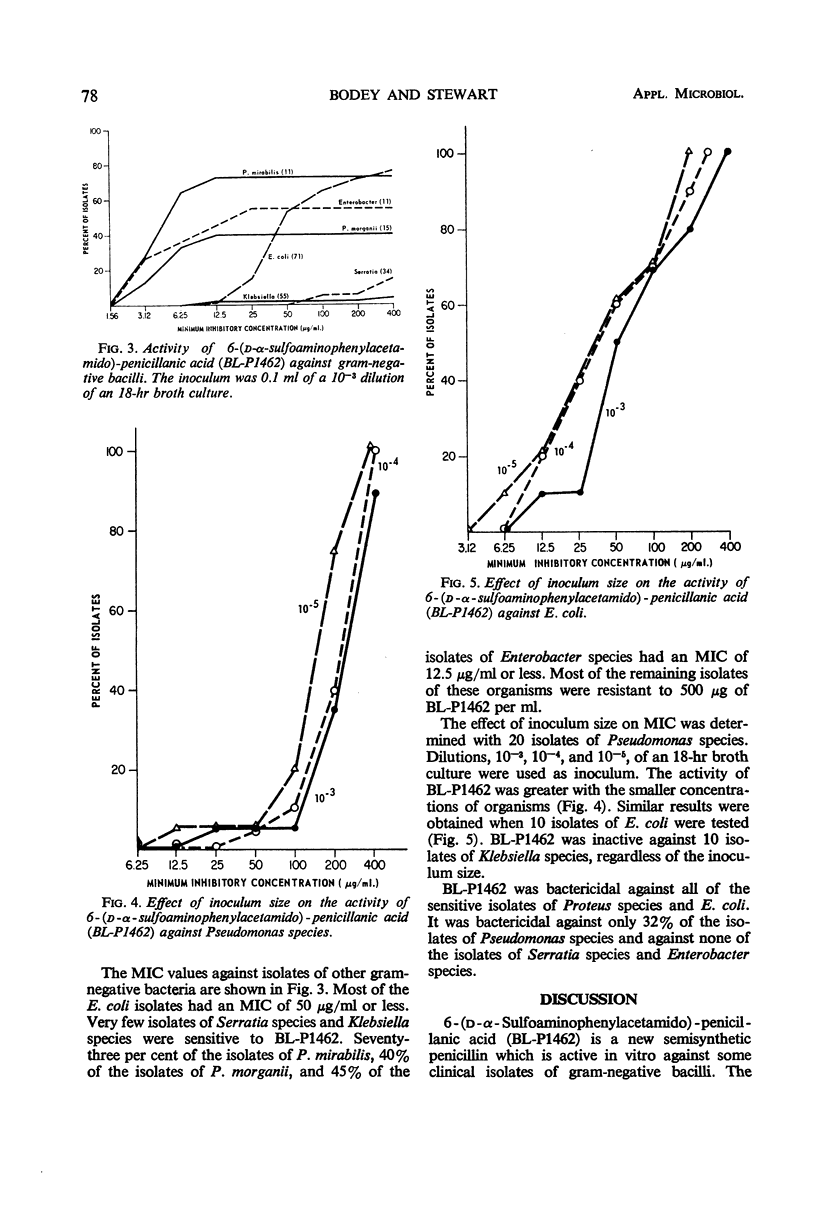
The activity of 6-(D-α-sulfoaminophenylacetamido)-penicillanic acid was determined against 357 clinical isolates of gram-negative bacilli by use of the tube-dilution technique. The majority of the isolates of Pseudomonas species were inhibited by 200 μg/ml or less of this antibiotic. Most of the isolates of Escherichia coli had a minimal inhibitory concentration of 50 μg/ml or less. Seventy-three per cent of the isolates of P. mirabilis, 40% of the isolates of P. morganii, and 45% of the isolates of Enterobacter species were inhibited by 12.5 μg/ml or less, whereas most of the isolates of Klebsiella species and Serratia species were resistant. The activity of this semisynthetic penicillin was affected by the size of the inoculum. The drug was bactericidal against all isolates of E. coli and Proteus species that were sensitive to it, but it was bactericidal against only 32% of the sensitive isolates of Pseudomonas species.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acred P., Brown D. M., Knudsen E. T., Rolinson G. N., Sutherland R. New semi-synthetic penicillin active against Pseudomonas pyocyanea. Nature. 1967 Jul 1;215(5096):25–30. doi: 10.1038/215025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altemeier W. A., Todd J. C., Inge W. W. Gram-negative septicemia: a growing threat. Ann Surg. 1967 Oct;166(4):530–542. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196710000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Terrell L. M. In vitro activity of carbenicillin against gram-negative bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1587–1590. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1587-1590.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freid M. A., Vosti K. L. The importance of underlying disease in patients with gram-negative bacteremia. Arch Intern Med. 1968 May;121(5):418–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERSH E. M., BODEY G. P., NIES B. A., FREIREICH E. J. CAUSES OF DEATH IN ACUTE LEUKEMIA: A TEN-YEAR STUDY OF 414 PATIENTS FROM 1954-1963. JAMA. 1965 Jul 12;193:105–109. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03090020019005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABIN E. R., GRABER C. D., VOGEL E. H., Jr, FINKELSTEIN R. A., TUMBUSCH W. A. Fatal pseudomonas infection in burned patients. A clinical, bacteriologic and anatomic study. N Engl J Med. 1961 Dec 21;265:1225–1231. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196112212652501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. H., Kolb L. Gentamicin sulfate in the treatment of extra-urinary infections due to gram-negative bacteria. South Med J. 1967 Feb;60(2):142–144. doi: 10.1097/00007611-196702000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



