Abstract
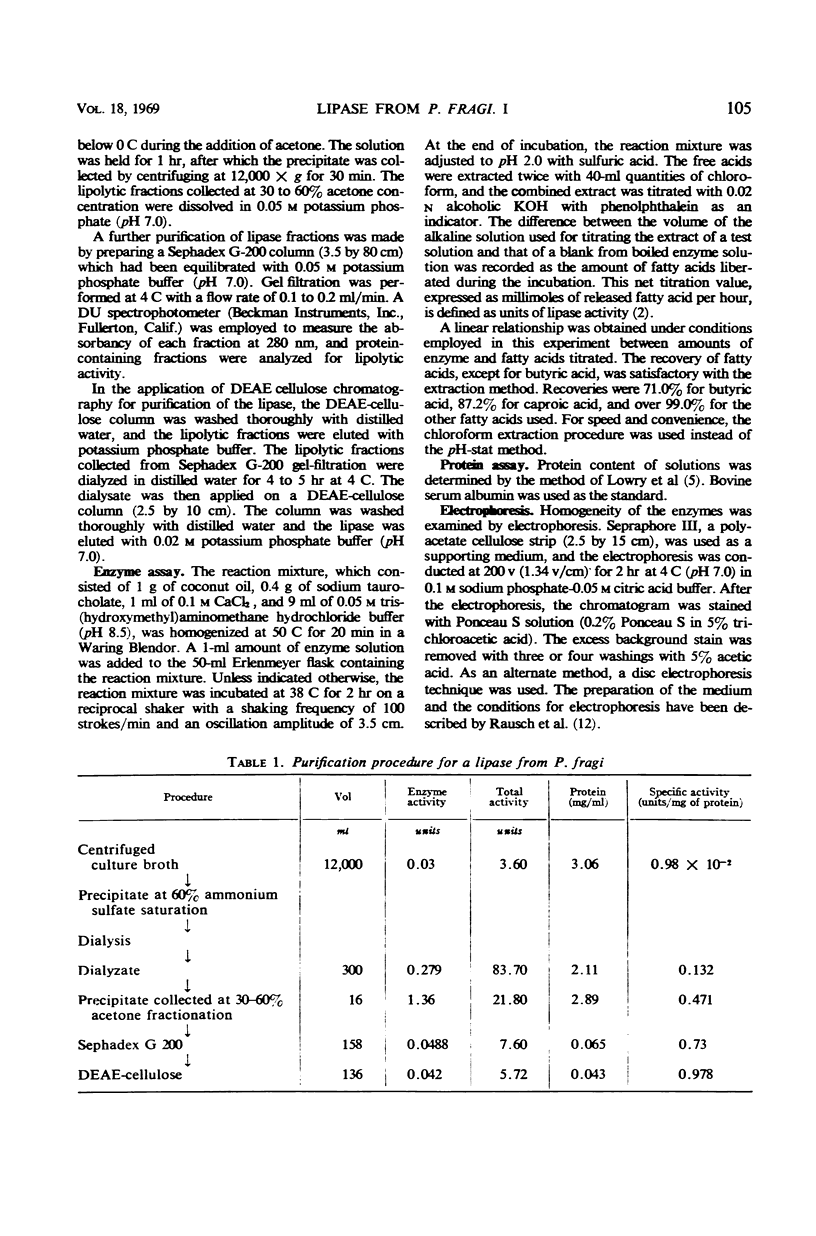
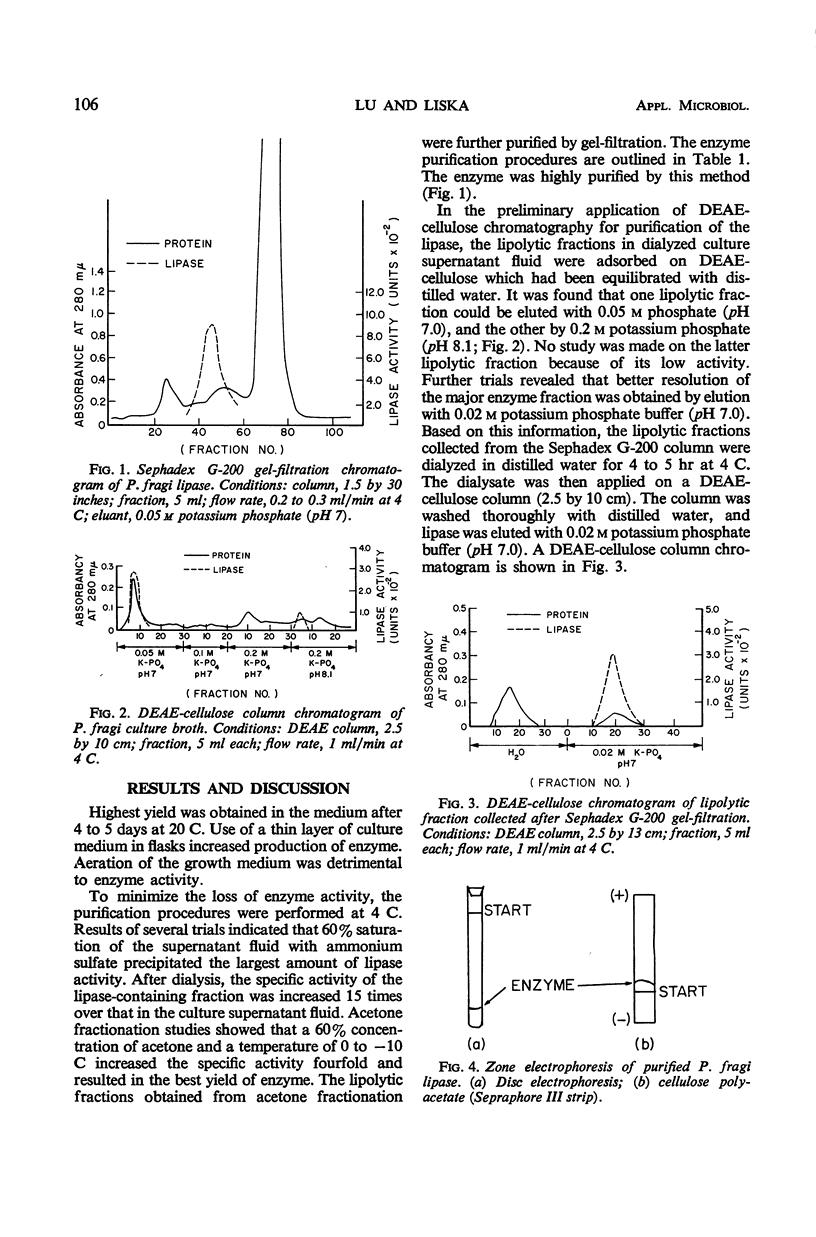
The experimental conditions required to isolate a lipase from Pseudomonas fragi were determined. The organism was grown in a buffered tryptone medium for 4 to 5 days at 20 C. The lipase in the culture supernatant fluid was isolated by fractionation with ammonium sulfate at 60% saturation, followed by acetone precipitation at 30-60% concentration. Further purification was made by using Sephadex G-200 gel-filtration and diethylaminoethyl cellulose chromatography. Electrophoretic analysis of the purified lipolytic fraction showed apparent homogeneity by both cellulose polyacetate and disc electrophoresis. The specific activity of the purified enzyme was about 100 times that of the starting culture filtrate, and the yield was about 1.8% of the original activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alford J. A., Pierce D. A., Suggs F. G. Activity of microbial lipases on natural fats and synthetic triglycerides. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jul;5(3):390–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINHEIRO A. J., LISKA B. J., PARMELEE C. E. HEAT STABILITY OF LIPASES OF SELECTED PSYCHROPHILIC BACTERIA IN MILK AND PURDUE SWISS-TYPE CHEESE. J Dairy Sci. 1965 Jul;48:983–984. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(65)88372-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAUSCH W. H., LUDWICK T. M., WESELI D. F. DETERMINATION OF BOVINE TRANSFERRIN TYPES BY DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. J Dairy Sci. 1965 Jun;48:720–725. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(65)88327-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


