Key Points
This study provides proof of concept that SAP gene transfer into HSCs can correct the multiple immune defects seen in XLP1.
Abstract
X-linked lymphoproliferative disease (XLP1) arises from mutations in the gene encoding SLAM-associated protein (SAP) and leads to abnormalities of NKT-cell development, NK-cell cytotoxicity, and T-dependent humoral function. Curative treatment is limited to allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) transplantation. We tested whether HSC gene therapy could correct the multilineage defects seen in SAP−/− mice. SAP−/− murine HSCs were transduced with lentiviral vectors containing either SAP or reporter gene before transplantation into irradiated recipients. NKT-cell development was significantly higher and NK-cell cytotoxicity restored to wild-type levels in mice receiving the SAP vector in comparison to control mice. Baseline immunoglobulin levels were significantly increased and T-dependent humoral responses to NP-CGG, including germinal center formation, were restored in SAP-transduced mice. We demonstrate for the first time that HSC gene transfer corrects the cellular and humoral defects in SAP−/− mice providing proof of concept for gene therapy in XLP1.
Introduction
X-linked lymphoproliferative disease (XLP1) arises from mutations in the SH2D1A gene, which codes for an intracellular adaptor protein (termed SAP [SLAM-associated protein]) expressed predominantly in T and NK cells.1,2 The lack of SAP results in defective T- and NK-cell cytotoxicity, NKT-cell development, and CD4 T follicular cell (TFH) help (reviewed in Ma et al3). The clinical phenotype is characterized by severe immunedysregulation including development of lymphoma, T-cell activation defects, and abnormalities in immunoglobulin production and T-dependent humoral immunity.4,5 Similar immune defects are seen in SAP-deficient murine models.6–8
The only curative option for XLP1 is allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) transplantation, which has high mortality in the mismatched donor setting.5,9 Gene therapy using viral vector–mediated gene transfer into autologous HSCs is curative in several severe monogenic immunodeficiencies.10–14 To determine whether gene therapy is a possible treatment option for XLP1, we investigated whether SAP gene transfer in HSCs could correct the multiple immunologic abnormalities seen in SAP-deficient mice.
Methods
Mice
SAP-deficient mice (SAP−/−) have been previously described.7 Animal experiments were performed under an Institutional United Kingdom Home Office license.
Lin− cell purification and transduction
Lineage-negative (Lin−) cells were isolated from SAP−/− bone marrow cells using MACS Lineage Cell Depletion Kits (Miltenyi Biotec). Lin− cells were infected overnight at an MOI of 100 according to previously described protocols.15
Animal irradiation and reconstitution
SAP−/− mice were lethally irradiated (1100 rad in a split dose over 2 days). A total of 3 × 105 Lin− cells were injected into tail veins of the recipient mice. Data from 2 separate experiments including 9 wild-type, 6 SAP−/− controls, 8 EFSeGFP (elongation factor 1 α promoter [EFS] control vector encoding enhanced green fluorescent protein [eGFP] alone), and 9 EFS-SAPeGFP (EFS–codon-optimized human SAP cDNA linked to the eGFP gene) reconstituted animals were combined to generate the results. Immunization with NP-CGG [(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)acetyl-chicken γ-globulin] was carried out in 1 experiment (see also supplemental Methods, available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article).
Results and discussion
SAP gene transfer into murine progenitors does not affect lineage-specific cell development
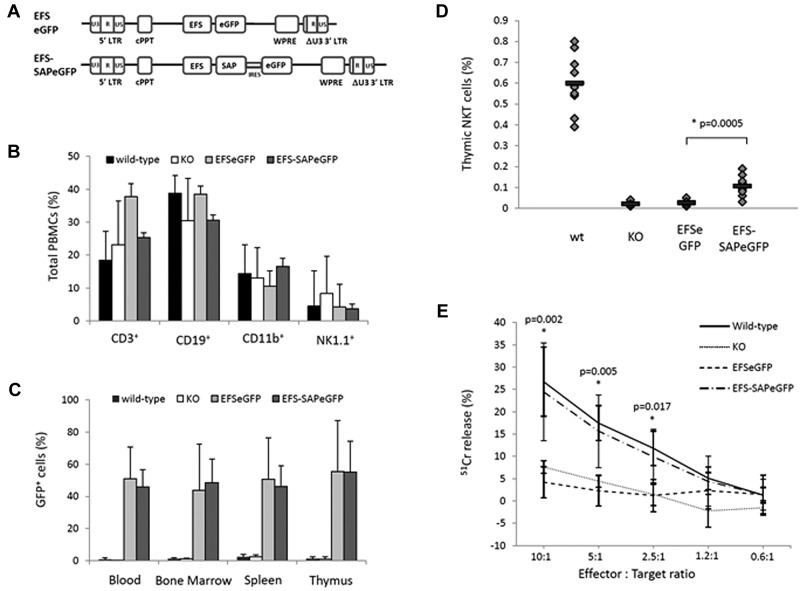
We generated lentiviral vectors encoding the shortened form of the EFS driving the transcription of either EFS-SAPeGFP or EFSeGFP (Figure 1A). Lin− cells from SAP−/− donor mice were transduced with either EFS-SAPeGFP or EFSeGFP and transplanted into lethally irradiated SAP−/− recipients. Transduction efficiencies for both vectors were similar with eGFP expression of 64% and 66% for EFS-SAPeGFP and EFSeGFP, respectively (supplemental Figure 1). Reconstituted animals were analyzed at 13 weeks after transplantation and compared with SAP−/− mice and C57BL/6 wild-type (WT) littermates. The recovery of different immune cell lineages in the periphery was similar in all 4 study groups (Figure 1B). Similarly, after lin− cell transduction and plating in semisolid media, there was no difference between EFS-SAPeGFP and EFSeGFP cells in the number and type of colony forming units seen (supplemental Figure 2). Together, these data suggest that SAP gene transfer into murine progenitors does not affect lineage-specific development.
Figure 1.
Immune reconstitution of SAP-deficient mice after gene transfer into hematopoietic stem cells. (A) Schematic representation of the SAP-expressing lentiviral construct and the corresponding eGFP control used for the reconstitution of SAP-deficient animals. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of hematopoietic lineages in control and experimental animals 12 weeks after reconstitution. (C) Level of eGFP expression in the blood, bone marrow, spleen, and thymus of all animals at the time of sacrifice. (D) Detection of NKT cells in the thymus of control and reconstituted animals by staining for the TCRVβ receptor and NK1.1 surface marker. Values for individual mice are shown as dots, and the mean of all values is represented by a horizontal line. (E) NK-cell cytotoxic activity measured in a 51Chromium release assay against the radiolabeled murine T lymphoma target cells (RMA/S). Assays were done in triplicate and data shown are mean ± SEM of all values.
Reconstitution of NKT and NK cellular defects in SAP−/− mice
After reconstitution at 13 weeks, expression of eGFP in the peripheral blood, bone marrow, spleen, or thymus of either EFS-SAPeGFP or EFSeGFP reconstituted mice was approximately 40%-50% with no significant difference between the 2 groups (Figure 1C). The vector copy number in PBMCs was found to be at mean levels of 1.7 vector copies per cell (range, 0.2-5.4) in EFS-eGFP mice and 2.8 vector copies per cell (range, 0.6-4.6) in EFS-SAPeGFP mice (supplemental Figure 3A). SAP protein expression was clearly visible in all tissues from mice reconstituted with EFS-SAPeGFP–transduced cells (supplemental Figure 3B). To compare the level of SAP expression in EFS-SAPeGFP–transduced cells, we also measured intracellular expression of SAP using the same antibody in normal human PBMCs (supplemental Figure 3C). The level of SAP expression in corrected PBMCs from EFS-SAPeGFP mice is comparable with that seen in normal human PBMCs.
Analysis of thymic NKT-cell development in the thymus by flow cytometry using NK1.1 and TCRβ antibodies showed a significant increase in NKT-cell numbers in EFS-SAPeGFP mice in comparison to EFSeGFP or SAP−/− controls although total numbers were decreased in comparison to WT mice (Figure 1D and representative flow cytometry in supplementary Figure 4A). Analysis of the NKT-cell population showed that in comparison to the overall population of PBMCs, the majority (> 70%) of these cells were eGFP positive (supplemental Figure 4B left panel). In contrast, in other cell lineages in the peripheral blood, eGFP expression after EFS-SAPeGFP transfer was less than 50% and no different to mice transduced with EFSeGFP only vector, suggesting that only NKT-cell development was particularly dependent on successful SAP gene correction (supplemental Figure 4B right panel). Intrathymic T-cell development in terms of proportions of double-negative, double-positive, and single-positive CD4 and CD8 thymocytes was similar in WT and in gene-corrected mice (supplemental Figure 4C). Analysis of splenic NK-cell cytotoxicity against RMA/S target cells in EFS-SAPeGFP mice showed similar levels of cytotoxicity to WT NK cells and significantly increased activity compared with either EFSeGFP reconstituted mice or SAP−/− controls (Figure 1E). These data demonstrate that SAP gene transfer allows correction of both developmental and functional cellular defects seen in SAP−/− mice.
Reconstitution of humoral defects in SAP−/− mice
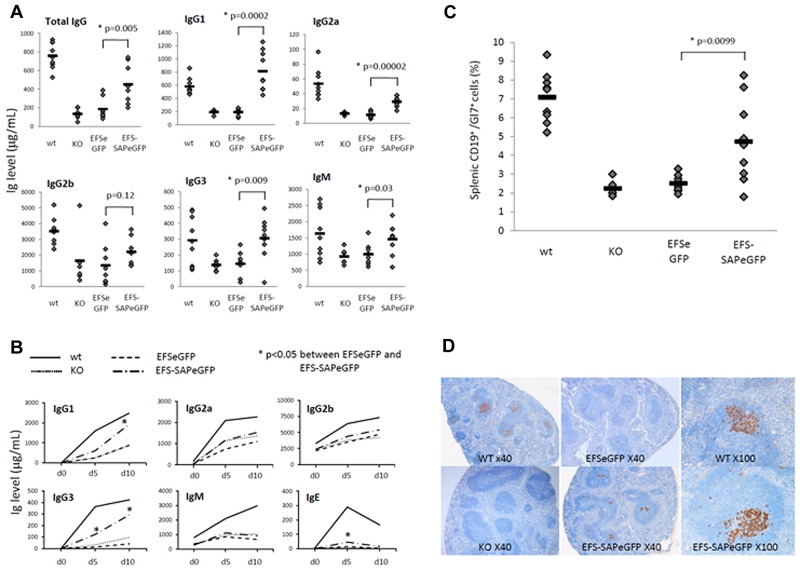
More than 50% of XLP1 patients have abnormalities of immunoglobulin production and this is the most common phenotype.5 In SAP−/− mice, baseline immunoglobulin production is abnormal with decreased production of total IgG, IgM, and IgG subclasses.7 At 13 weeks after transplantation, EFS-SAPeGFP reconstituted mice demonstrated significantly increased mean levels of basal IgG, IgM, IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG3 in comparison to EFSeGFP reconstituted mice and SAP−/− controls (Figure 2A). Levels of IgG1, IgG3, and IgM in EFS-SAPeGFP reconstituted mice were comparable with that seen in WT mice. After challenge with the T-dependent antigen NP-CGG, EFS-SAPeGFP reconstituted mice demonstrated significantly increased levels of IgG1 and IgG3 NP-specific antibody in comparison to EFSeGFP or SAP−/− controls (Figure 2B). In spleens of challenged mice, germinal center formation as evidenced by Gl7 expression on splenic CD19+ B cells was significantly increased in comparison to EFSeGFP reconstituted mice and SAP−/− controls (Figure 2C). In support of this, immunohistochemical staining of spleens with the germinal center B-cell marker PNA (peanut agglutinin) showed positive staining in WT and EFS-SAPeGFP reconstituted mice whereas little or no staining was visible in EFSeGFP reconstituted mice and SAP−/− controls (Figure 2D). Specific EFS-SAPeGFP reconstituted follicles showed germinal center peanut agglutinin (PNA) staining equivalent to WT mice (Figure 2D, ×100 magnifications).
Figure 2.
Reconstitution of the humoral defects in SAP-deficient mice after immune challenge. (A) Quantification of baseline serum immunoglobulin levels by ELISA 12 weeks after reconstitution. Values for individual mice are shown as dots, and the mean of all values is represented by a horizontal line. (B) Quantification of NP-specific antibody production by ELISA at various time points after immunization with NP-CGG in control and reconstituted animals. (C) Detection of germinal center B cells by flow cytometry in splenic lymphocytes stained with anti-CD19 and anti-Gl7 antibodies. Values for individual mice are shown as dots, and the mean of all values is represented by a horizontal line. (D) Germinal center staining in splenic follicles of control and reconstituted mice 10 days after immunization using the germinal center B-cell marker peanut agglutinin (PNA). In addition to original magnification (×40) for all groups, original magnification (×100) of a single follicle to show degree of germinal center recovery is shown for WT and EFS-SAPeGFP mice.
We also performed transplantation experiments using bone marrow from WT SAP+/+ mice transplanted into lethally irradiated SAP−/− mice. These studies showed very similar results to the gene transfer experiments with full recovery of NK-cell cytotoxicity and partial recovery of NKT-cell development and immunoglobulin production (supplemental Figure 5).
Together, these data demonstrate that SAP gene transfer into SAP−/− HSCs is able to reconstitute major defects in cellular and humoral immunity seen in SAP−/− mice. The mechanisms of reconstitution after gene transfer are due to the expression of SAP in several specific cell lineages, which now allows SAP interaction with specific SLAM family receptors, especially 2B4 and Ly108. In thymic NKT-cell development, SAP gene expression is required in thymocyte-thymocyte interactions and acts to propagate positive signals and also to inhibit negative signaling through Ly108.16,17 The observed generation of T-dependent immune responses is most likely related to the development of SAP-expressing CD4 germinal center TFH cells18 which now allows formation of stable conjugates with B cells to allow germinal center formation and specific antibody production.17,19 Full restoration of cytotoxic function in NK cells is again dependent on SAP expression and its role in controlling positive and negative signaling through 2B4.20 Thus, HSC gene transfer provides multilineage SAP expression to correct the different immunologic defects.
The reason for incomplete immune recovery seen in NKT-cell development and immunoglobulin production is not clear, but seems unlikely to be related to efficiency of gene transfer because copy numbers in PBMCs were not low (mean level of 2.8 vector copies per cell), and the level of SAP expression in the transduced murine PBMCs was comparable with that seen in normal human PBMCs. However, it is possible that human SAP does not function optimally in a murine cell background. In addition, WT transplantation experiments into SAP-deficient mice result in similar patterns of immune recovery suggesting that there may be preexisting microenvironmental deficits that are not easily corrected by reconstitution of adult mice, or that extended time periods are necessary for full correction to be achieved.
The EFS-SAPeGFP vector used in this study constitutively expresses SAP, which may not be desirable given that SAP is not physiologically expressed in specific cell types including HSCs and B cells. However, we did not see any detrimental effect on HSC function and lineage-specific development. The generation of vectors with physiologically regulated SAP gene expression may allow a fuller correction of the phenotype and may offset safety concerns and are under current development. Nevertheless, this study demonstrates for the first time a proof of concept for a HSC gene strategy approach for correction of the different immunologic abnormalities seen in XLP1. These data are important in showing that HSC gene transfer can rescue T-cell help and may be important in development of gene therapy for other immunodeficiencies such as CD40 ligand deficiency or inducible T-cell costimulator deficiency.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by grants from the Leukemia and Lymphoma Research Foundation (C.R.), the Wellcome Trust (C.B., A.J.T., M.B.), and the European Commission's 7th Framework Program Contract 261387 (CELL-PID). The authors acknowledge the support of Great Ormond Street Hospital Children's Charity (H.B.G.).
Footnotes
There is an Inside Blood commentary on this article in this issue.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Authorship
Contribution: C.R. and C.B. designed and performed the experiments, gathered the data, and produced the figures; M.A.-F. generated and tested the codon-optimized vector; M.B. was responsible for the murine injections; N.J.S. performed the immunohistochemical analysis; A.J.T. and H.B.G. conceived the study, designed experiments, and wrote the manuscript; and all authors reviewed the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Prof H. Bobby Gaspar, Molecular Immunology Unit, UCL Institute of Child Health, 30 Guilford Street, London WC1N 1EH, United Kingdom; e-mail: h.gaspar@ucl.ac.uk.
References
- 1.Sayos J, Wu C, Morra M, et al. The X-linked lymphoproliferative-disease gene product SAP regulates signals induced through the co-receptor SLAM. Nature. 1998;395(6701):462–469. doi: 10.1038/26683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nichols KE, Harkin DP, Levitz S, et al. Inactivating mutations in an SH2 domain-encoding gene in X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(23):13765–13770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.23.13765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ma CS, Nichols KE, Tangye SG. Regulation of cellular and humoral immune responses by the SLAM and SAP families of molecules. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:337–379. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Seemayer TA, Gross TG, Egeler RM, et al. X-linked lymphoproliferative disease: twenty-five years after the discovery. Pediatr Res. 1995;38(4):471–478. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199510000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Booth C, Gilmour KC, Veys P, et al. X-linked lymphoproliferative disease due to SAP/SH2D1A deficiency: a multicenter study on the manifestations, management and outcome of the disease. Blood. 2011;117(1):53–62. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-284935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wu C, Nguyen KB, Pien GC, et al. SAP controls T cell responses to virus and terminal differentiation of TH2 cells. Nat Immunol. 2001;2(5):410–414. doi: 10.1038/87713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Al-Alem U, Li C, Forey N, et al. Impaired Ig class switch in mice deficient for the X-linked lymphoproliferative disease gene Sap. Blood. 2005;106(6):2069–2075. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-07-2731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Czar MJ, Kersh EN, Mijares LA, et al. Altered lymphocyte responses and cytokine production in mice deficient in the X-linked lymphoproliferative disease gene SH2D1A/DSHP/SAP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(13):7449–7454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.131193098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gross TG, Filipovich AH, Conley ME, et al. Cure of X-linked lymphoproliferative disease (XLP) with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT): report from the XLP registry. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1996;17(5):741–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Aiuti A, Cattaneo F, Galimberti S, et al. Gene therapy for immunodeficiency due to adenosine deaminase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(5):447–458. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0805817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Hauer J, Lim A, et al. Efficacy of gene therapy for X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(4):355–364. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1000164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gaspar HB, Cooray S, Gilmour KC, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy for adenosine deaminase-deficient severe combined immunodeficiency leads to long-term immunological recovery and metabolic correction. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3(97):97ra80. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ott MG, Schmidt M, Schwarzwaelder K, et al. Correction of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease by gene therapy, augmented by insertional activation of MDS1-EVI1, PRDM16 or SETBP1. Nat Med. 2006;12(4):401–409. doi: 10.1038/nm1393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Boztug K, Schmidt M, Schwarzer A, et al. Stem-cell gene therapy for the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(20):1918–1927. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1003548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Montiel-Equihua CA, Zhang L, Knight S, et al. The beta-globin locus control region in combination with the EF1alpha short promoter allows enhanced lentiviral vector-mediated erythroid gene expression with conserved multilineage activity. Mol Ther. 2012;20(7):1400–1409. doi: 10.1038/mt.2012.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Griewank K, Borowski C, Rietdijk S, et al. Homotypic interactions mediated by Slamf1 and Slamf6 receptors control NKT cell lineage development. Immunity. 2007;27(5):751–762. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.08.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kageyama R, Cannons JL, Zhao F, et al. The receptor Ly108 functions as a SAP adaptor-dependent on-off switch for T cell help to B cells and NKT cell development. Immunity. 2012;36(6):986–1002. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ma CS, Hare NJ, Nichols KE, et al. Impaired humoral immunity in X-linked lymphoproliferative disease is associated with defective IL-10 production by CD4+ T cells. The J Clin Invest. 2005;115(4):1049–1059. doi: 10.1172/JCI23139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Qi H, Cannons JL, Klauschen F, Schwartzberg PL, Germain RN. SAP-controlled T-B cell interactions underlie germinal centre formation. Nature. 2008;455(7214):764–769. doi: 10.1038/nature07345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dong Z, Davidson D, Perez-Quintero LA, Kurosaki T, Swat W, Veillette A. The adaptor SAP controls NK cell activation by regulating the enzymes Vav-1 and SHIP-1 and by enhancing conjugates with target cells. Immunity. 2012;36(6):974–985. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.