Background: The T6SS assembles from 13 proteins that form two sub-assemblies.
Results: TssK is a cytoplasmic protein that interacts with Hcp, TssC, TssL, and TssA.
Conclusion: The TssK complex is three-arm shaped and links the membrane and phage-like complexes in T6SS.
Significance: The structural and functional characterization of TssK leads to a better understanding of T6SS assembly.
Keywords: Bacterial Pathogenesis, Membrane Transport, Microbiology, Protein Complexes, Protein Secretion, Hcp, TssK, TssL, Type VI Secretion, Sheath Assembly
Abstract
The Type VI secretion system (T6SS) is a macromolecular machine that mediates bacteria-host or bacteria-bacteria interactions. The T6SS core apparatus assembles from 13 proteins that form two sub-assemblies: a phage-like complex and a trans-envelope complex. The Hcp, VgrG, TssE, and TssB/C subunits are structurally and functionally related to components of the tail of contractile bacteriophages. This phage-like structure is thought to be anchored to the membrane by a trans-envelope complex composed of the TssJ, TssL, and TssM proteins. However, how the two sub-complexes are connected remains unknown. Here we identify TssK, a protein that establishes contacts with the two T6SS sub-complexes through direct interactions with TssL, Hcp, and TssC. TssK is a cytoplasmic protein assembling trimers that display a three-armed shape, as revealed by TEM and SAXS analyses. Fluorescence microscopy experiments further demonstrate the requirement of TssK for sheath assembly. Our results suggest a central role for TssK by linking both complexes during T6SS assembly.
Introduction
Bacteria have developed macromolecular nanomachines to inject toxins to either prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells to clear an environmental niche or to cause diseases (1). One of the systems able to deliver toxic effectors to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is the Type VI secretion system (T6SS)5 (2). The current model regarding T6SS function proposes that it acts similarly to the cell puncturing device of contractile bacteriophages (3–5).
Although several accessory proteins are usually necessary for its function, the T6SS assembles from 13 Tss (Type six subunits) proteins whose genes are conserved in all T6SS gene clusters and are thus called “core components” (6–8). A number of these conserved subunits share structural and functional similarities with contractile bacteriophage tail proteins including components of the tail tube, sheath, hub, and baseplate (4, 9–12). For these reasons the structure assembled by these proteins and visualized by cryo-electron tomography and fluorescence microscopy has been called the “phage-like complex.” A second group of core components are the TssJ, TssM, and TssL membrane proteins that assemble a trans-envelope spanning complex. Aside these two groups, the TssA, TssF, TssG, and TssK core components have not been characterized yet.
As briefly described above, the phage-like sub-complex is structurally and functionally similar to the contractile tail of Myoviridae. The crystal structures of the Hcp (hemolysin co-regulated protein) proteins present high similarity with the bacteriophage λ tail tube gpV protein (10, 13–15). Six Hcp assemble into rings of about 80–90 Å wide with an internal diameter of about 30–40 Å (13–15) that stack on each other to form tubes in vitro (9, 13–16). The VgrG (valine glycine repeat protein) trimer is structurally homologous to the bacteriophage T4 gp27/gp5 spike complex which is used as a puncturing device to perforate the host cell envelope (9, 17). TssE is an homolog of gp25, a structural component of the phage baseplate (6, 18) while the TssB and TssC subunits (also called VipA and VipB in Vibrio cholerae) interact with each other and assemble cogwheel-like tubular structures of around 300 Å in diameter with an internal 100 Å-diameter channel resembling the bacteriophage contractile sheath (11, 12). Cryo-electron tomography and immuno-electron microscopy experiments revealed the existence of such “sheath-like” structures in the cytoplasm of T6SS+ cells (4, 19, 20). Interestingly, these structures exist in two distinct conformations. Indeed, by using TssB fusion to the green fluorescent protein (GFP), time-lapse fluorescence microscopy experiments demonstrated that these structures are highly dynamic and cycle between extended and contracted conformations through elongation, contraction, and disassembly (4, 19–21). Disassembly of contracted T6SS sheaths is catalyzed by the ClpV AAA+ ATPase (11, 19, 20, 22). By analogy with the bacteriophage infection process, the current model suggests that the T6SS functions as an inverted bacteriophage and that TssB/C sheath contraction propels the Hcp tube and VgrG outside the cell to puncture the target cell and to deliver toxin effectors (2, 3, 23). In agreement with this model, the Hcp and VgrG proteins are usually found in the supernatant of T6SS-producing cells (13, 24, 25) and contraction of the sheath is correlated with lysis of the prey cell (21).
Based on cryo-electron microscopy images, this phage-like complex has been proposed to be anchored to the membrane (4). An immunoprecipitable complex composed of TssM, TssL, and TssJ was identified in EAEC (26). Biochemical, structural, and protein-protein interaction studies have provided insights onto the characteristics of these subunits (26–31). While TssL is a bitopic membrane protein with its N terminus located in the cytoplasm (28, 30, 31), TssM has three transmembrane helices (TMH) with a large C-terminal periplasmic domain interacting with the TssJ outer membrane lipoprotein (25, 27, 29). A cytoplasmic loop located between TMH2 and TMH3 contains an ATP binding and hydrolysis Walker A motif that was shown to be required for T6SS function in Agrobacterium tumefaciens (28). The trans-envelope complex is usually stabilized by a peptidoglycan-binding motif localized at the C terminus of the TssL subunit or on an accessory component (26, 32).
Regarding this membrane complex, comparative bioinformatic analyses reported a conserved genomic organization between the tssJ, tssK, tssL, and tssM genes (8). Among these genes, tssK encodes an uncharacterized putative soluble protein. The tssK gene is organized in tandem with tssL in 74% of the T6SS gene clusters suggesting a functional link or interaction between these two proteins (8). The association of TssK with the membrane complex is also strongly suggested by the observation that this protein has been found associated with the inner membrane proteome in Pseudomonas aeruginosa (33). Interestingly, although TssK is potentially linked to the membrane complex, the Vibrio cholerae TssK protein was recently shown to co-purify with isolated sheaths (4). TssK is therefore a good candidate to link both the T6SS membrane and phage complexes. In this study, we report the characterization of the TssK protein encoded by the sci-1 T6SS gene cluster in enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (accession numbers: EC042_4526, YP_006098803.1). We found that TssK1 interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of the two inner membrane proteins TssL1 and TssM1. We also identified direct contacts between TssK1 and the T6SS tail components TssC1 and Hcp1. Further biochemical and structural characterization of the TssK1 purified protein using size exclusion chromatography, electron microscopy and small angle x-ray scattering showed that TssK1 is trimeric in solution and forms three arm-shaped particles.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Bacterial Strains, Growth Conditions, and Chemicals
The E. coli strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in supplemental Table S1. E. coli K12 DH5α, W3110, BTH101, and T7-Iq pLys strains were used for cloning steps, co-immunoprecipitation, bacterial two-hybrid and protein purification, respectively. Strains were routinely grown in LB-rich medium or in M9 minimal medium supplemented with glycerol (0.4%) and casa-amino acids (100 μg/ml) with shaking at 37 °C. Plasmids were maintained by the addition of ampicillin (100 μg/ml for E. coli K12, 200 μg/ml for EAEC) or kanamycin (50 μg/ml). Expression of genes from pASK-IBA37 derivative plasmids was induced by addition of 0.1 μg/ml of anhydrotetracyclin (AHT, IBA Technology) for 45 min; gene expression from pBAD was induced with 0.01% of l-arabinose for 1 h while gene expression from T7-Iq pLys cells was induced with 500 μm of isopropyl-β-d-thio-galactopyrannoside (IPTG) for 16 h at 17 °C. For the Hcp release assay, expression of the sci-1 gene cluster was induced by addition of the iron chelator 2,2′-dipyridyl (125 μm final concentration) 30 min prior harvesting the cells (34). Oligonucleotides and plasmids used in this study are listed in supplemental Table S1.
Strain Construction
The tssK1 gene was deleted into the enteroaggregative E. coli 17–2 strain using a modified one-step inactivation procedure (35) as previously described (27) using oligonucleotides DEL-4526–3/DW and DEL-4526-5/DW carrying 50-nucleotide extensions homologous to regions adjacent to tssK1. Kanamycin-resistant clones were selected, verified by colony-PCR. The kanamycin cassette was then excised using plasmid pCP20. The deletion of tssK1 was confirmed by colony-PCR.
Plasmid Construction
Polymerase chain reactions (PCR) were performed using a Biometra thermocycler using Phusion DNA polymerase (Thermo Scientific). Restriction enzymes were purchased from New England Biolabs and used according to the manufacturer's instructions. Custom oligonucleotides were synthesized by Sigma Aldrich and are listed in supplemental Table S1. Enteroaggregative E. coli 17–2 chromosomal DNA was used as a template for all PCRs. E. coli strain DH5α was used for cloning procedures. All the plasmids (except pETG20-TssK1 and pOK-TssK1HA) have been constructed by restriction-free cloning (36) as previously described (26). Briefly, genes of interest were amplified with oligonucleotides introducing extensions annealing to the target vector. The double-stranded product of the first PCR has then been used as oligonucleotides for a second PCR using the target vector as template. For pETG20A-TssK1 construct, tssK1 was cloned into the pETG20A Gateway® vector using standard Gateway® protocols. The final construct allows the production of TssK1 fused to an N-terminal hexahistidine-tagged thioredoxin followed by a TEV protease cleavage site. For pOK-TssK1HA used in co-precipitations experiments, the tssK1 gene was amplified by PCR using oligonucleotides introducing EcoRI and XhoI restriction sites and cloned into the pOK12-derivative vector pMS600 (27) digested by the same enzymes, allowing in-frame fusion with a C-terminal hemagglutinin (HA) epitope. The pBAD-TssB1-sfGFP plasmid used for fluorescence microscopy has been constructed similarly to the pBAD-TssB2-sfGFP previously described (21).
Fluorescence Microscopy and Image Treatment
EAEC 17-2, ΔtssK1, or complemented ΔtssK1 cells carrying plasmid pBAD33-TssB1-sfGFP were diluted to an A600 nm ∼0.05 into M9 minimal medium supplemented with glycerol, casa-amino acids, chloramphenicol, and 10% of LB and grown to an A600 nm ∼1.0. Cells were washed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), resuspended in PBS to an A600 nm ∼50, and spotted on a thin pad of 1.5% agarose in PBS, covered with a coverslip and incubated for one hour at 37 °C prior to microscopy acquisition. For each experiment, ten independent fields were manually defined with a motorized stage (Prior Scientific) and stored (X, Y, Z, PFS-offset) in our custom automation system designed for time-lapse experiments. Fluorescence and phase contrast micrographs were captured every 30 s using an automated and inverted epifluorescence microscope TE2000-E-PFS (Nikon, France) equipped with Perfect Focus System (PFS). PFS automatically maintains focus so that the point of interest within a specimen is always kept in sharp focus at all times despite mechanical or thermal perturbations. Images were recorded with a CoolSNAP HQ 2 (Roper Scientific, Roper Scientific SARL, France) and a 100×/1.4 DLL objective. Excitation light was emitted by a 120-watt metal halide light. The sfGFP images were recorded by using the ET-GFP filter set (Chroma 49002) using an exposure time of 100–200 ms. Phase contrast and fluorescence were adjusted and merged using ImageJ 1.46j.
Bacterial Two-hybrid Assay (BACTH)
The adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two-hybrid technique (37) was used as previously published (38). Briefly, pairs of proteins to be tested were fused to the isolated T18 and T25 catalytic domains of the Bordetella adenylate cyclase. After transformation of the two plasmids producing the fusion proteins into the reporter BTH101 strain, plates were incubated at 30 °C for 48 h. Three independent colonies for each transformation were inoculated into 600 μl of LB medium supplemented with ampicillin, kanamycin, and IPTG (0.5 mm). After overnight growth at 30 °C. 10 μl of each culture were dropped onto MacConkey and LB plates supplemented with bromo-chloro-indolyl-galactopyrannoside (X-Gal) and incubated for 16 h at 30 °C. The experiments were done at least in triplicate, and a representative result is shown.
Co-immunoprecipitation Experiments
100 ml of W3110 cells producing the two proteins from independent plasmids were grown to and A600 of 0.4, and the expression of the cloned genes was induced with IPTG and AHT for 45 min. The cells were harvested, and the pellets were frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C for 1 h. Pellets were then resuspended in Tris-HCl 20 mm, pH 8.0, NaCl 100 mm, sucrose 30%, lysozyme 100 μg/ml, EDTA 1 mm, DNase 100 μg/ml, RNase 100 μg/ml, Complete protease inhibitor mixture (Roche) to an A600 of 80 and incubated on ice for 15 min. Cells were lysed by three passage at the French Press (800 psi), MgCl2 was added at the final concentration of 2.5 mm and lysates were clarified by centrifugation at 13,000 × g for 10 min. Lysates were incubated with Tween 20 0.2% or CHAPS 10 mm for 1 h at room temperature with vigorous shaking and finally centrifuged at 15,000 × g for 10 min. Supernatants were used for co-immunoprecipitation using Anti-FLAG® M2 affinity gel (Sigma-Aldrich). After 3 h of incubation, the beads were washed twice with 1 ml of Tris-HCl 20 mm, pH 8.0, NaCl 100 mm, sucrose 15%, Tween 0.2%, or CHAPS 10 mm and once with Tris-HCl 20 mm, pH 8.0, NaCl 100 mm. Beads were recovered and resuspended in 25 μl of SDS-loading buffer and heated for 10 min at 96 °C prior to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analyses.
Purification of TssK1
E. coli T7 Iq pLys cells carrying pETG20-TssK1 were grown at 37 °C in terrific broth to an A600 ∼0.9 and tssK1 expression was induced with IPTG (0.5 mm) for 16 h at 17 °C. Cells were harvested, resuspended in Tris-HCl 20 mm, pH 8.0, NaCl 150 mm, and lysozyme (0.25 mg/ml) and broken by sonication. Soluble proteins were separated from inclusion bodies and cell debris by centrifugation 30 min at 20,000 × g. The TssK1 fusion protein was immobilized using ion metal affinity chromatography on a Ni2+ HisTrap prepacked column (GE Healthcare) using an AKTA FPLC system and eluted with a step gradient of imidazole. The fractions containing the TssK1 fusion protein were pooled, and the protein was digested for 16 h at 4 °C by a hexahistidine-tagged Tobacco Etch Virus (TEV) protease using a 1:10 (w/w) protease: protein ratio. The TEV protease and contaminants were then bound on a second Ni2+ affinity chromatography, and the native TssK1 protein was collected in the flow through and concentrated on a preparative Superdex 200 gel filtration column (GE Healthcare) equilibrated in Tris-HCl 20 mm, pH 8.0, NaCl 150 mm. The final concentration of the TssK1 solution was 8.8 mg/ml. The EAEC Hcp1 protein was purified similarly to TssK1, using a pETG20A derivative plasmid encoding TRX-His-Hcp1.
Analytical Gel Filtration Analysis and MALS/QELS/UV/RI-coupled Size Exclusion Chromatography
For analytical gel filtration, 2 mg of each protein standards (ovalbumin [43 kDa], conalbumin [75 kDa], aldolase [158 kDa], and ferritin [440 kDa] (GE Healthcare)) and 1 mg of the purified TssK1 protein were run separately on an analytical Superdex 200 10/30 column (GE Healthcare) equilibrated in Tris-HCl 20 mm, pH 8.0, NaCl 150 mm. Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) was performed on an Alliance 2695 HPLC system (Waters) using KW803 and KW804 columns (Shodex) run in Tris-HCl 20 mm, pH 8.0, NaCl 150 mm at 0.5 ml/min. MALS, UV spectrophotometry, QELS and RI were achieved with MiniDawn Treos (Wyatt Technology), a Photo Diode Array 2996 (Waters), a DynaPro (Wyatt Technology) and an Optilab rEX (Wyatt Technology), respectively, as described (39). Mass and hydrodynamic radius calculation was done with ASTRA software (Wyatt Technology) using a dn/dc value of 0.185 ml/g.
Surface Plasmon Resonance Analysis
Steady state of the interaction between TssK1 and Hcp1 was performed using a BIAcore T200 at 25 °C. All the buffers were filtered on 0.2 μm membranes before use. The HC200m sensor chip (Xantech) was coated with Hcp1 immobilized by amine coupling (ΔRU = 4300). A control flow-cell was coated with thioredoxin immobilized by amine coupling at the same concentration as Hcp1 (ΔRU = 4100). Binding traces resulting from passage of purified TssK1 (Five concentrations ranging from 3.125 to 100 μm) in HBS-EP buffer (Hepes 10 mm, NaCl 150 mm, EDTA 3 mm, Polysorbate 20 0.005%) in the Hcp1 and control flow cells were recorded in duplicate. The signal from the control flow cell and the buffer response was subtracted from all measurements. The KD values were obtained using the fitting tool of the BIAevaluation software (BIAcore).
Transmission Electron Microscopy, Single Particle Analysis, and Image Reconstruction
The purified TssK1 protein (50 μg/ml) was immobilized on a glow-discharged carbon grid by incubation for 1 min, and then stained with 2% uranyl acetate. Then, the grids were air-dried and 2k × 2k images were collected using a FEI Tecnai Spirit microscope operated at 120 kV at 60,000 magnification with a 3.5 Å/pixel size. Approximately 5000 particles were selected from ten images using the Boxer program from the EMAN2 package (40), extracted into boxes of 72 × 72 pixels, and combined into a single dataset. This dataset was pre-treated using the SPIDER package (41) and submitted to maximum likelihood (ML) classification and alignment (42) using the Xmipp package (43). The aligned dataset was then classified by principal component analysis (PCA) using SPIDER into classes with > 10 members/class. The initial model was built to form a shapeless sphere of equivalent size to the class averages and first refined by three-dimensional ML refinement using the class averages and then the entire dataset with a sampling rate of 5° imposing C3 symmetry to obtain the final model at ∼26 Å resolution as estimated by Fourier Shell Correlation (FSC) and ½-bit threshold criterion (44). The EAEC TssK1 electron microscopy map has been deposited to the Electron Microscopy Databank (EMDB) under accession code EMD-5739.
Small-Angle X-ray Scattering Analysis and ab initio Three-dimensional Shape Reconstruction
Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) analyses were performed at the ID29 beamline (European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Grenoble, France) at a working energy of 12.5 keV (λ = 0.931 Å). Thirty microliters of protein solution at 1.1, 2.8, 5.3, 7.9, 11, and 15.7 mg/ml in Tris-HCl 20 mm, pH 8.0, NaCl 150 mm were loaded by a robotic system into a 2-mm quartz capillary mounted in a vacuum and ten independent 10-s exposures were collected on a Pilatus 6 m-F detector placed at a distance of 2.85 m for each protein concentration. Individual frames were processed automatically and independently at the beamline by the data collection software (BsxCUBE), yielding radially averaged normalized intensities as a function of the momentum transfer q, with q = 4πsin(θ)/λ, where 2θ is the total scattering angle and λ is the x-ray wavelength. Data were collected in the range q = 0.04–6 nm−1. The ten frames were combined to give the average scattering curve for each measurement. Data points affected by aggregation, possibly induced by radiation damage, were excluded. Scattering from the buffer alone was also measured prior to and after each sample analysis, and the average of these two buffer measures was used for background subtraction using the program PRIMUS (45) from the ATSAS package (46). PRIMUS was also used to perform Guinier analysis (47) of the low q data, which provides an estimate of the radius of gyration (Rg). Regularized indirect transforms of the scattering data were carried out with the program GNOM (48) to obtain P(r) functions of interatomic distances. The P(r) function has a maximum at the most probable intermolecular distance and goes to zero at Dmax, the maximum intramolecular distance. The values of Dmax were chosen to fit with the experimental data and to have a positive P(r) function. Tridimensional (3D) bead models that fit with the scattering data were built with the program DAMMIF (49). Ten independent DAMMIF runs were performed using the scattering profile of TssK1, with data extending up to 0.35 nm−1, using slow mode settings, assuming P3 symmetry and allowing for a maximum 500 steps to grant convergence. The models resulting from independent runs were superimposed using the DAMAVER suite (50). This yielded an initial alignment of structures based on their axes of inertia followed by minimization of the normalized spatial discrepancy (NSD) (51). The NSD was therefore computed between a set of ten independent reconstructions, with a range of NSD from 0.678 to 0.815. The aligned structures were then averaged, giving an effective occupancy to each voxel in the model, and filtered at half-maximal occupancy to produce models of the appropriate volume that were used for all subsequent analyses. All the models were similar in terms of agreement with the experimental data, as measured by DAMMIF χ parameter and the quality of the fit to the experimental curve.
Miscellaneous
Hcp release (27) and fractionation assays (26) have been performed as previously described. For urea solubilization, membrane fractions were incubated on a wheel with urea 8 m for 20 min at room temperature, followed by a 40 min ultracentrifugation at 100,000 × g. For immunostaining, proteins were transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes, and immunoblots were probed with antibodies, and goat secondary antibodies coupled to alkaline phosphatase, and developed in alkaline buffer in presence of 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolylphosphate and nitroblue tetrazolium. The anti-TolB polyclonal antibodies are from our laboratory collection, while the anti-HA (3F10 clone, Roche), anti-FLAG (M2 clone, Sigma Aldrich), anti-EFTu (Roche) monoclonal antibodies and alkaline phosphatase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit, mouse, or rat secondary antibodies (Millipore) have been purchased as indicated.
RESULTS
TssK1 Is a Cytoplasmic Protein
The tssK1 gene is predicted to encode a 50-kDa soluble protein, with no predicted peptide signal or transmembrane segment. To determine its subcellular localization, tssK1 cells producing a N-terminally FLAG-tagged TssK1 protein (TssK1FLAG) were submitted to a fractionation procedure. Fig. 1 shows that TssK1 co-localizes with the cytoplasmic EFTu marker. However, a small amount of protein was detected in the total membrane fraction. This could correspond to peripheral association of TssK with the membrane or with membrane proteins, as it is solubilized with urea such as TolB, a periplasmic protein associated with the membrane (Fig. 1). Alternatively, as tssK1 is overexpressed from a plasmid and likely expressed in higher amounts than the other T6SS components, the TssK1 protein found in this fraction might correspond to aggregates. It is worth noting that a band of ∼36 kDa corresponding to a N-terminal degradation product was also detected in the cytoplasmic fraction. Additionally, bands of higher molecular masses can be observed in total cells and in the cytoplasmic fraction, suggesting that TssK1 may form oligomers that resist SDS-PAGE analyses.
FIGURE 1.

TssK1 co-fractionnates with cytoplasmic proteins. A fractionation procedure was applied to EAEC tssK1 cells producing FLAG-tagged TssK1 (TssK1FL). Total cells (T) were separated from the culture supernatant (SN) and fractionated to isolate periplasmic (P), cytoplasmic (C), and membrane fractions (M). Membranes were treated with urea to solubilize aggregated and/or peripherally-associated proteins (Sol, soluble fraction; Ins, insoluble fraction). Proteins from 109 (T) and 2 × 109 (SN, P, C, M) cells were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunodetected with anti-FLAG monoclonal (TssK1FL), anti-EF-Tu (cytoplasmic marker), and TolB (periplasmic marker, peripherally associated to the outer membrane) antibodies. The positions of TssK1 (TssK1FL) and of a degradation product of TssK1 (*) are indicated on the right. The molecular mass markers (in kDa) are indicated on the left.
TssK1 Interaction Network
To gain insights into the function of the TssK1 protein, we performed a bacterial two-hybrid (BACTH) screen to identify pair wise interactions between TssK1 and T6SS subunits including the TssA1, TssB1, TssC1, TssE1, TssF1, TssG1, Hcp1, and VgrG1 soluble proteins and the soluble domains of the TssL1 (cytoplasmic domain, residues 1–184, TssL1c), TssM1 (cytoplasmic domain, residues 62–360, TssM1c; periplasmic domain, residues 386–1129, TssM1p) and TssJ1 (devoid of the acylation motif) membrane-associated proteins. T18 or T25 domains of the Bordetella adenylate cyclase were fused to the N terminus of TssK1, and the different prey proteins were fused to T18 or T25 either at their N or C terminus. The results presented in Fig. 2 indicate that TssK1 interacts with TssL1c and TssM1c. In agreement with the cytoplasmic localization of TssK1, no interaction with the periplasmic domain of TssM1 or with the TssJ1 outer membrane lipoprotein was detected. In addition to these interactions with components of the membrane complex, TssK1 interacts with the tail tube and sheath proteins Hcp1 and TssC1 and with the uncharacterized TssA1 subunit.
FIGURE 2.
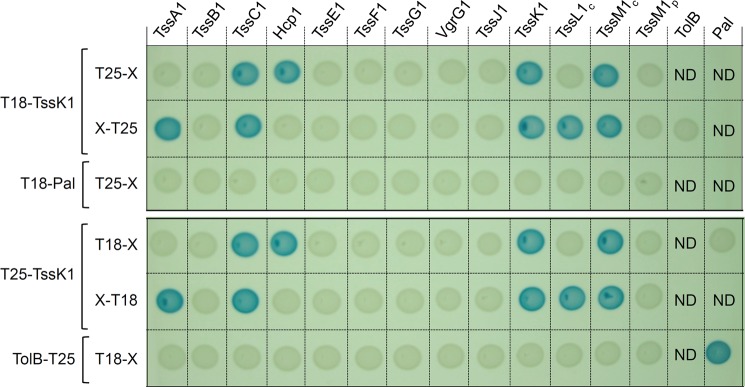
TssK1 interaction network identified by bacterial two-hybrid analysis. BTH101 reporter cells carrying pairs of plasmids producing the indicated T6SS proteins fused to the T18 or T25 domain of the Bordetella adenylate cyclase were spotted on X-Gal-IPTG indicator LB agar plates as described under “Experimental Procedures.” For membrane-anchored proteins, only the cytoplasmic (c) or periplasmic (p) domains were used. Controls include T18 and T25 fusions to TolB and Pal, two proteins that interact but unrelated to the T6SS.
TssK1 Interacts with the Cytoplasmic Domain of TssL1
Consistently with the co-occurrence of the tssK and tssL genes (8), the BACTH assay showed that TssK1 interacts with proteins of the trans-envelope subcomplex. To further confirm these interactions detected using BACTH, we performed immunoprecipitation experiments. To test direct interactions, the proteins were produced in the E. coli K12 W3110 strain, which is devoid of T6SS genes. Cells producing both HA-tagged TssK1 (TssK1HA) and FLAG-tagged cytoplasmic domains of TssL1 (TssL1cFLAG) or of TssM1 (TssM1cFLAG) were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG resin. As shown in Fig. 3, TssK1HA co-immmunoprecipitated with TssL1cFLAG, but not with TssM1cFLAG. As specificity controls, TssK1HA did not react with the anti-FLAG resin and did not form an immunoprecipitable complex with the T6SS unrelated PalFLAG protein. The co-immunoprecipitation assay, therefore, confirmed the interaction between TssK1 and TssL1 but not with TssM1.
FIGURE 3.

TssK1co-immunoprecipitates with the cytoplasmic domain of TssL1 but not with that of TssM1. Soluble lysates from 1011 E. coli K12 W3110 cells producing HA-tagged TssK1 (TssK1HA) alone or in combination with the FLAG-tagged cytoplasmic domains of TssL1 (TssL1cFL), of TssM1 (TssM1cFL) or the T6SS-unrelated Pal protein (PalFL) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG-coupled beads. The total soluble (Tot) and the immunoprecipitated (IP) material were separated by 12.5% acrylamide SDS-PAGE and immunodetected with anti-HA (TssK1HA; upper panel) and anti-FLAG (TssL1cFL, TssM1cFL, andPalFL; lower panel) monoclonal antibodies. Molecular weight markers (in kDa) are indicated on the left.
TssK1 Interacts with the Hcp1 and TssC1 Phage-like Components and the Uncharacterized TssA1 Protein
We then verified the interaction of TssK1 with the two phage-related subunits identified by BACTH, Hcp1, and TssC1, and the uncharacterized TssA1 protein. Co-immunoprecipitation assays were performed as described above using E. coli cells producing the two proteins to be tested. As shown in Fig. 4, A–C, TssK1HA specifically co-immunoprecipitated with TssA1FLAG, TssC1FLAG, or Hcp1FLAG. The strength of the Hcp1-TssK1 interaction was further analyzed by Surface Plasmon Resonance (Fig. 4D). The Hcp1 and TssK1 proteins were purified to homogeneity using ion metal affinity chromatography and gel filtration. Once the purified Hcp1 protein was immobilized on HC200m chips, TssK1 was injected in the microfluidic channel and sensorgrams were recorded. From these sensorgrams, we determined that TssK1 bound to Hcp1 with a dissociation constant (Kd) of 26.5 ± 2.3 μm (Fig. 4D). The interaction of TssK1 with components of the T6SS tail tube and sheath structure raised the question whether this protein is required for the assembly or contraction of the T6SS dynamic tubular structures. As described previously, the TssB and TssC proteins assemble a dynamic cytosolic tubular structure that undergoes cycles of elongation, contraction and disassembly as observed by fluorescence microscopy using a TssB-sfGFP fusion protein (4, 19–21). The existence of TssB1-sfGFP tubular structures and their dynamic behaviors were analyzed in tssK1 mutant cells. Time-lapse fluorescence microscopy recordings showed that the TssB1-sfGFP fluorescence appears diffuse, and no foci could be observed over time (Fig. 5A), suggesting that TssK1 is required for proper assembly of tubular sheath structures. The current model proposes that T6SS sheath contraction propels the Hcp tube toward the exterior. Indeed the Hcp protein is usually found in culture supernatant of T6SS+ cells. As expected from previous systematic studies performed in Edwardsiella tarda, V. cholera, and Agrobacterium tumefaciens (25, 52, 53), Hcp release assays demonstrated that the Hcp1 protein was not released in the culture supernatant of ΔtssK1 cells (Fig. 5B). The TssB1 dynamics and Hcp1 secretion were restored to levels comparable to WT cells once the FLAG- and HA-tagged TssK1 proteins used in this study were produced in ΔtssK1 mutant cells. Taken together, these data showed that the ΔtssK1 mutation has no polar effect on downstream genes and that TssK1 is required for Sci-1 T6SS function and TssB1/TssC1 tubule assembly.
FIGURE 4.
TssK1 interacts with T6SS phage-like complex components. TssK1 co-immunoprecipitates with TssA1 (A), TssC1 (B), and Hcp1 (C). Soluble lysates from 1011 E. coli K12 W3110 cells producing HA-tagged TssK1 (TssK1HA) and FLAG-tagged TssA1 (TssA1FL, A), TssC1 (TssC1FL, B), or Hcp1 (Hcp1FL, C) proteins were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG-coupled beads. The total soluble (Tot) and the immunoprecipitated (IP) material were separated by 12.5% acrylamide SDS-PAGE and immunodetected with anti-HA (TssK1HA, lower panel) and anti-FLAG (TssA1FL, TssC1FL, and Hcp1FL, upper panel) monoclonal antibodies. Molecular weight markers (in kDa) are indicated on the left. D, surface plasmon resonance analysis of the TssK1-Hcp1 complex. The Hcp1 was immobilized on HC200m chip and SPR sensorgrams (variation of plasmon resonance in arbitrary unit (ΔRU) as a function of reaction time (in seconds)) were recorded upon passage of the indicated concentrations of TssK1 (TssK) (left panel). The graph reporting ΔRU as a function of TssK1 (TssK) concentration (right panel) was used to estimate the dissociation constant of the TssK1-Hcp1 complex (26.5 ± 2.3 μm).
FIGURE 5.

TssK1 is required for sheath assembly and Hcp1 release. A, absence of TssK1 abolishes assembly of the T6SS sheath. Time-lapse fluorescence microscopy recordings showing sheath dynamics in WT, tssK1 and complemented tssK1 (tssK1+) cells producing TssB1-sfGFP. Individual images were taken every 30 s. Assembly and contraction events are indicated above the time-lapse images. The scale bars are 2 μm. B, absence of TssK1 prevents Hcp1 release. Hcp1HA release was assessed by separating whole cells (C) and culture supernatant (SN) fractions from 2 × 109 WT, tssK1 or complemented tssK1 (tssK1+) cells producing HA-tagged Hcp1. Proteins were separated by 12.5% acrylamide SDS-PAGE and Hcp1 was immunodetected using anti-HA monoclonal antibody (lower panel). The periplasmic TolB protein (immunodetected using an anti-TolB polyclonal antibodies, upper panel) was used as a marker to verify that no lysis occurred.
TssK1 Is Trimeric in Solution
Bands of higher molecular masses observed after SDS-PAGE analyses (see Fig. 1) prompted us to analyze whether TssK1 could oligomerize. We first tested in vivo using the BACTH assay. When T18-TssK1 and T25-TssK1 fusions were co-produced, the expression of the reporter gene was activated demonstrating that TssK1 oligomerizes (Fig. 6A). This oligomerization was further confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation experiments, using E. coli K12 cells producing both TssK1FLAG and TssK1HA (Fig. 6B). However these assays, although they confirmed the multimerization of TssK1, were not able to discriminate between different oligomeric states. We therefore took advantage of the availability of the purified TssK1 native protein to analyze its oligomerization state in vitro by analytical size exclusion chromatography. While the expected molecular mass of the TssK1 monomer is 49.9 kDa, the protein was eluted in a single peak with a median mass of 160 kDa, suggesting that TssK1 behaves as a trimer in solution (Fig. 6C). The trimeric organization of TssK1 was confirmed by MALS/QELS/UV/RI (multi-angle laser light scattering/quasi-elastic light scattering/absorbance/refractive index detectors) experiments (Wyatt technology) (supplemental Fig. S1).
FIGURE 6.

TssK1 oligomerizes and is trimeric in solution. A, TssK1 interacts with itself as shown by bacterial two-hybrid analysis. BTH101 reporter cells carrying pairs of plasmids producing the indicated T6SS proteins fused to the T18 or T25 domains of the Bordetella adenylate cyclase were spotted on X-Gal-IPTG indicator LB agar plates as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Controls include TssK1 interaction assays with TolB and Pal, two proteins that interact but unrelated to the T6SS. B, TssK1HA co-immunoprecipitates with TssK1FLAG. Soluble lysates from 1011 E. coli K12 W3110 cells producing HA-tagged TssK1 (TssK1HA) alone or with FLAG-tagged TssK1 (TssK1FL) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG-coupled beads. The total soluble (Tot) and the immunoprecipitated (IP) material were separated by 10%-acrylamide SDS-PAGE and immunodetected with anti-FLAG (TssK1FL; upper panel) and anti-HA (TssK1HA; lower panel) monoclonal antibodies. Molecular weight markers (in kDa) are indicated on the left. C, analytical size exclusion chromatography analysis of purified TssK1 (continuous line) on a Superdex 200 column, calibrated with 43-, 75-, 158-, and 440-kDa molecular weight markers (dotted lines). The molecular weight of each marker (in kDa) is indicated on the top of the corresponding peak. The theoretical mass of the TssK1 monomer being 49.9 kDa, its elution at ∼160 kDa indicates that it behaves as a trimer in solution.
TssK1 Displays a Three-armed Structure
Attempts to crystallize the TssK1 protein were unsuccesful. To get further insights into the TssK1 structure, the purified protein was analyzed by transmission electron microscopy. Approximately 5000 particles were selected and processed using single-particle analysis techniques. Particles and class averages (Fig. 7, A and B) show clear 3-fold symmetry features. Hence, we applied a 3-fold symmetry throughout data processing. The tridimensional reconstruction of the TssK1 particle at ∼26 Å resolution (Fig. 7C) shows that the trimeric protein appears as three “arms” entangled in a pyramidal shape (Fig. 7D). The length of the triangle side is 95 Å whereas the height of the particle is 70 Å (Fig. 7D). The trimer organization of the protein and its overall fold at low resolution were confirmed in solution by SAXS analysis (Fig. 8). In agreement with gel filtration and MALS/QELS/UV/RI analyses, the molecular mass of TssK1 inferred from its experimental I(0) was 151 ± 1.2 kDa (Fig. 8A). Inspection of the Guinier plot of the TssK1 protein at low angles showed good data quality and no protein aggregation (Fig. 8B). The radius of gyration Rg of TssK1 determined by the Guinier approximation is 40.7 ± 0.6 Å (Fig. 8B). The pair-distance distribution functions, P(r), were evaluated from the SAXS curves. The P(r) functions pointed a maximum dimension of 155 Å and exhibited a bell-shaped curve with a slightly extended profile for the higher distances, indicating a mostly globular conformation with elongated elements (Fig. 8C). The overall envelope of TssK1 was calculated ab initio from its scattering profile using DAMMIF (49) at ∼18 Å resolution. The reconstruction with lower normalized spatial discrepancy (NSD = 0.678) was selected as the “best representative” model (Fig. 8D). The ten ab initio models were aligned using DAMAVER (50) to provide an averaged model that displays features identical to that of the “best representative” model (not shown). When the EM map of the TssK1 trimer was fitted into the SAXS envelope (Fig. 8D), it appeared that the arms are in an extended conformation in solution (SAXS) whereas are bent under the central triangular shape after EM sample preparation, suggesting a potential conformational flexibility of TssK1.
FIGURE 7.
The three-dimensional shape of TssK1 revealed by transmission electron microscopy and single particle analysis. Negatively stained raw particles (A) and class averages (B) of purified TssK1. The scale bar is 10 nm. C, Fourier Shell Correlation (FSC) and ½-bit threshold criterion curves used to estimate the resolution of the 3-fold symmetric EM image reconstruction of TssK1 (∼26 Å) shown in D.
FIGURE 8.
Small-angle x-ray scattering data and low-resolution structure of TssK1. A, experimental scattering data (dots) and the fitting curve (continuous line) calculated from an ab initio model of TssK1. B, Guinier plot (dots) with the linear fit (continuous line). C, distance distribution function of TssK1. D, SAXS envelope (light gray mesh) of the “best representative” model of TssK1. For comparison, the EM model shown in Fig. 7 (dark gray plain surface) is fitted in the SAXS envelope. Each view is rotated by 90° around the Y-axis. The scale bar is 3 nm.
DISCUSSION
Important advances have recently been made regarding the assembly of the phage-related T6SS complex and the identification of the effector proteins delivered by this apparatus. However, the roles of several T6SS core components remain enigmatic. In this study we report the characterization of the TssK protein encoded within the sci-1 T6SS gene cluster of enteroaggregative E. coli. A schematic representation of the main results of this work is shown in Fig. 9. We first found that this conserved protein is necessary for T6SS function, a result in agreement with the observations that the tssK genes from E. tarda, V. cholera, and A. tumefaciens have been demonstrated to be required for T6SS function in these microorganisms (25, 52, 53). Time-lapse fluorescence microscopy experiments using a TssB-sfGFP fusion protein further showed that T6SS sheath dynamics is abrogated in tssK1 cells. By contrast to V. cholerae, P. aeruginosa, and EAEC WT cells in which T6SS sheaths undergo cycles of assembly and contraction (4, 19–21) or to V. cholerae ΔclpV cells in which contracted sheaths are not disassembled and form foci (4, 20), the TssB-sfGFP fluorescence was diffuse, and no punctuate foci could be observed in tssK1 cells. This suggests that no tubular assembly of TssB/TssC occurs in the absence of TssK, a phenotype similar to that observed in V. cholerae tssM, fha, hcp, and tssE or EAEC tssE mutant cells (4, 20, 21). TssK1 thus appears to be involved at a stage upstream ClpV during T6SS sheath assembly. Attempts to localize the TssK1 protein using a chromosomal tssK1-sfGFP gene fusion were unsuccessful so far, due to undetectable fluorescence levels suggesting a low representation of the protein.
FIGURE 9.

Schematic representation of the TssK protein interaction network. The localization and topologies of several type VI secretion subunits are represented. Arrows show interactions detected in this study by biochemical (red) or two-hybrid approaches (blue) (summarized in supplemental Table S2). The membrane-associated and bacteriophage-like subassemblies are framed in green and blue, respectively. OM: outer membrane, IM: inner membrane.
Bacterial two-hybrid and co-immunoprecipitation assays revealed that TssK1 forms oligomers. Further gel filtration experiments showed that the TssK1 protein elutes with an apparent molecular weight corresponding to that of a trimer. The 3-fold organization of TssK1 was validated by visualization of the purified protein using electron microscopy. Image reconstruction of TssK1 particles showed that it forms a three-armed structure with an overall pyramidal shape. In electron microscopy, the three arms are bent under the structure while are in an open conformation in solution as shown by SAXS analysis. Although a conformational flexibility of the protein might exist, our data cannot rule out that (i) the length of the arms has been underestimated due to the average between “bent” and “elongated” conformations on EM grids or (ii) the TssK1 conformation on EM grids is induced by preparation of the specimen (fixation or staining procedures).
In this study, we determined the TssK1 interaction network (a summary of the interactions is presented in supplemental Table S2). Using a bacterial two-hybrid screen, we revealed that TssK1 interacts with (i) the cytoplasmic domains of TssL1 and TssM1, two inner membrane subunits of the T6SS membrane complex, (ii) Hcp1 and TssC1, two components of the phage tail-related sub-complex and (iii) TssA1, a core-component of unknown function. These interactions are in agreement with the cytoplasmic localization of TssK1 as shown by fractionation, since both Hcp1 and TssC1 are part of the cytosolic tubular tail-like structure. The TssK1-TssM1c interaction detected by BACTH analysis was the only interaction we could not validate by co-immunoprecipitation. TssM1c may not have the same conformation upon fusion with T18/T25 domains and further analysis will be required to confirm this interaction. The interactions of TssK1 with TssL1c, Hcp1, TssA1, and TssC1 were all confirmed using co-immunoprecipitations. The TssK1-Hcp1 interaction was also tested in vitro using SPR, and was shown to have a KD of 26 μm. Overall, these results demonstrate that TssK1 interacts with components of both membrane and phage sub-complexes at the cytoplasmic face of the T6SS apparatus. The link between TssK1 and the membrane complex is in agreement with recent publications. First, a bioinformatic approach showed that the tssK gene co-occurs with the tssL, tssM, and tssJ genes, and a strong link between TssK and TssL in co-occurrence and genomic organization studies has been demonstrated (8). More recently, the TssK protein was shown to co-fractionnate with inner membrane proteins in the P. aeruginosa membrane proteome (33). Regarding the link between TssK and the T6SS phage tail-like structure, no co-occurrence can be found but TssK was co-purified with T6SS sheaths (4), a result in agreement with its interaction with TssC. Thus, one may hypothesize that TssK is a structural component that connects the phage-like structure and the membrane complex at the cytoplasmic side of the inner membrane. What can be its function? The observation that no T6SS sheath-like structures assemble in tssK1 mutant cells suggests that TssK may (i) initiate Hcp tube or TssBC sheath polymerization or (ii) recruit phage-like components to the site of assembly/secretion, i.e. the membrane complex. By analogy with contractile bacteriophages, T6SS likely require a baseplate-like complex. As noted by Basler et al. cryo-electron tomographs showed that the T6SS sheath-like tubular structures are connected to the inner membrane through a flared bell-like density that may correspond to the baseplate (4). The TssE protein, which shares clear homologies with the bacteriophage gp25 wedge protein, is obviously one of the baseplate components (5–7, 18). Although no interaction between TssK1 and TssE1 has been detected in our two-hybrid screen and no co-occurrence between the tssE and tssK genes has been inferred from bioinformatic studies, the cytoplasmic localization of TssK1, its interaction network and its requirement for sheath elongation suggest that it could be part of this baseplate complex. Interestingly, it is worth to note that the three-armed shape of TssK1 has an external diameter of ∼155 Å, a size similar to the diameter of the sheath (∼110 and 145 Å in the extended and contracted conformations respectively, 4). Although our chromosomally encoded TssK1-sfGFP fusion was not sufficiently produced to localize TssK1, defining its position within the T6SS will help to further understand its function.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank the members of the Cascales, Cambillau, Lloubès, Bouveret, and Sturgis research groups for discussion, Tâm Mignot for fluorescence microscopy, Charlotte Gaviard, Valentin Tutagata, Annick Brun, Isabelle Bringer, and Olivier Uderso for technical assistance and Mylène Micautond for encouragement.
This work was supported in part by the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), the Aix-Marseille University, and a grant from the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-10-JCJC-1303-03) (to E. C.). This work was also supported by the CNRS, the Aix-Marseille University, and by grants from the Marseille-Nice Genopole, IBiSA, and the Fondation de la Recherche Médicale (FRM DEQ2011-0421282) (to C. C.).

This article contains supplemental Tables S1-S2 and Fig. S1.
- T6SS
- Type VI secretion system
- IPTG
- isopropyl-β-d-thio-galactopyrannoside
- BACTH
- bacterial two-hybrid assay
- X-Gal
- bromo-chloro-indolyl-galactopyrannoside
- TEV
- Tobacco Etch Virus
- ML
- maximum likelihood
- PCA
- principal component analysis
- FSC
- Fourier Shell Correlation
- SAXS
- small-angle x-ray scattering
- NSD
- normalized spatial discrepancy
- Tss
- Type 6 subunit
- Hcp
- hemolysin co-regulated protein.
REFERENCES
- 1. Hayes C. S., Aoki S. K., Low D. A. (2010) Bacterial contact-dependent delivery systems. Annu. Rev. Genet. 44, 71–90 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Silverman J. M., Brunet Y. R., Cascales E., Mougous J. D. (2012) Structure and regulation of the type VI secretion system. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 66, 453–472 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Bönemann G., Pietrosiuk A., Mogk A. (2010) Tubules and donuts: a type VI secretion story. Mol. Microbiol. 76, 815–821 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Basler M., Pilhofer M., Henderson G. P., Jensen G. J., Mekalanos J. J. (2012) Type VI secretion requires a dynamic contractile phage tail-like structure. Nature 483, 182–186 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Cascales E., Cambillau C. (2012) Structural biology of type VI secretion systems. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 367, 1102–1111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Bingle L. E., Bailey C. M., Pallen M. J. (2008) Type VI secretion: a beginner's guide. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 11, 3–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Cascales E. (2008) The type VI secretion toolkit. EMBO Rep. 9, 735–741 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Boyer F., Fichant G., Berthod J., Vandenbrouck Y., Attree I. (2009) Dissecting the bacterial type VI secretion system by a genome wide in silico analysis: what can be learned from available microbial genomic resources? BMC Genomics 10, 104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Leiman P. G., Basler M., Ramagopal U. A., Bonanno J. B., Sauder J. M., Pukatzki S., Burley S. K., Almo S. C., Mekalanos J. J. (2009) Type VI secretion apparatus and phage tail-associated protein complexes share a common evolutionary origin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 4154–4159 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Pell L. G., Kanelis V., Donaldson L. W., Howell P. L., Davidson A. R. (2009) The phage lambda major tail protein structure reveals a common evolution for long-tailed phages and the type VI bacterial secretion system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 4160–4165 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Bönemann G., Pietrosiuk A., Diemand A., Zentgraf H., Mogk A. (2009) Remodelling of VipA/VipB tubules by ClpV-mediated threading is crucial for type VI protein secretion. EMBO J. 28, 315–325 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Lossi N. S., Manoli E., Förster A., Dajani R., Pape T., Freemont P., Filloux A. (2013) The HsiB1C1 (TssB-TssC) complex of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type VI secretion system forms a bacteriophage tail sheathlike structure. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 7536–7548 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Mougous J. D., Cuff M. E., Raunser S., Shen A., Zhou M., Gifford C. A., Goodman A. L., Joachimiak G., Ordoñez C. L., Lory S., Walz T., Joachimiak A., Mekalanos J. J. (2006) A virulence locus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes a protein secretion apparatus. Science 312, 1526–1530 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Osipiuk J., Xu X., Cui H., Savchenko A., Edwards A., Joachimiak A. (2011) Crystal structure of secretory protein Hcp3 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Struct. Funct. Genomics 12, 21–26 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Jobichen C., Chakraborty S., Li M., Zheng J., Joseph L., Mok Y. K., Leung K. Y., Sivaraman J. (2010) Structural basis for the secretion of EvpC: a key type VI secretion system protein from Edwardsiella tarda. PLoS One 5, e12910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Ballister E. R., Lai A. H., Zuckermann R. N., Cheng Y., Mougous J. D. (2008) In vitro self-assembly of tailorable nanotubes from a simple protein building block. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 3733–3738 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Pukatzki S., Ma A. T., Revel A. T., Sturtevant D., Mekalanos J. J. (2007) Type VI secretion system translocates a phage tail spike-like protein into target cells where it cross-links actin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 15508–15513 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Lossi N. S., Dajani R., Freemont P., Filloux A. (2011) Structure-function analysis of HsiF, a gp25-like component of the type VI secretion system, in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 157, 3292–3305 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Basler M., Mekalanos J. J. (2012) Type 6 secretion dynamics within and between bacterial cells. Science 337, 815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Kapitein N., Bönemann G., Pietrosiuk A., Seyffer F., Hausser I., Locker J. K., Mogk A. (2013) ClpV recycles VipA/VipB tubules and prevents non-productive tubule formation to ensure efficient type VI protein secretion. Mol. Microbiol. 87, 1013–1028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Brunet Y. R., Espinosa L., Harchouni S., Mignot T., Cascales E. (2013) Imaging type VI secretion-mediated bacterial killing. Cell Rep. 3, 36–41 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Pietrosiuk A., Lenherr E. D., Falk S., Bönemann G., Kopp J., Zentgraf H., Sinning I., Mogk A. (2011) Molecular basis for the unique role of the AAA+ chaperone ClpV in type VI protein secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 30010–30021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Kanamaru S. (2009) Structural similarity of tailed phages and pathogenic bacterial secretion systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 4067–4068 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Pukatzki S., Ma A. T., Sturtevant D., Krastins B., Sarracino D., Nelson W. C., Heidelberg J. F., Mekalanos J. J. (2006) Identification of a conserved bacterial protein secretion system in Vibrio cholerae using the Dictyostelium host model system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 1528–1533 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Zheng J., Leung K. Y. (2007) Dissection of a type VI secretion system in Edwardsiella tarda. Mol. Microbiol. 66, 1192–1206 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Aschtgen M. S., Gavioli M., Dessen A., Lloubès R., Cascales E. (2010) The SciZ protein anchors the enteroaggregative Escherichia coli Type VI secretion system to the cell wall. Mol. Microbiol. 75, 886–899 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Aschtgen M. S., Bernard C. S., De Bentzmann S., Lloubès R., Cascales E. (2008) SciN is an outer membrane lipoprotein required for type VI secretion in enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 190, 7523–7531 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Ma L. S., Lin J. S., Lai E. M. (2009) An IcmF family protein, ImpLM, is an integral inner membrane protein interacting with ImpKL, and its walker a motif is required for type VI secretion system-mediated Hcp secretion in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J. Bacteriol. 191, 4316–4329 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Felisberto-Rodrigues C., Durand E., Aschtgen M. S., Blangy S., Ortiz-Lombardia M., Douzi B., Cambillau C., Cascales E. (2011) Towards a structural comprehension of bacterial type VI secretion systems: characterization of the TssJ-TssM complex of an Escherichia coli pathovar. PLoS Pathog. 7, e1002386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Aschtgen M. S., Zoued A., Lloubès R., Journet L., Cascales E. (2012) The C-tail anchored TssL subunit, an essential protein of the enteroaggregative Escherichia coli Sci-1 Type VI secretion system, is inserted by YidC. Microbiologyopen 1, 71–82 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Durand E., Zoued A., Spinelli S., Watson P. J., Aschtgen M. S., Journet L., Cambillau C., Cascales E. (2012) Structural characterization and oligomerization of the TssL protein, a component shared by bacterial type VI and type IVb secretion systems. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 14157–14168 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Aschtgen M. S., Thomas M. S., Cascales E. (2010) Anchoring the type VI secretion system to the peptidoglycan: TssL, TagL, TagP. what else? Virulence 1, 535–540 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Casabona M. G., Vandenbrouck Y., Attree I., Couté Y. (2013) Proteomic characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 inner membrane. Proteomics 13, 2419–2423 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Brunet Y. R., Bernard C. S., Gavioli M., Lloubès R., Cascales E. (2011) An epigenetic switch involving overlapping fur and DNA methylation optimizes expression of a type VI secretion gene cluster. PLoS Genet. 7, e1002205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Datsenko K. A., Wanner B. L. (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97, 6640–6645 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. van den Ent F., Löwe J. (2006) RF cloning: a restriction-free method for inserting target genes into plasmids. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 67, 67–74 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Karimova G., Pidoux J., Ullmann A., Ladant D. (1998) A bacterial two-hybrid system based on a reconstituted signal transduction pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95, 5752–5756 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Battesti A., Bouveret E. (2012) The bacterial two-hybrid system based on adenylate cyclase reconstitution in Escherichia coli. Methods 58, 325–334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Sciara G., Blangy S., Siponen M., Mc Grath S., van Sinderen D., Tegoni M., Cambillau C., Campanacci V. (2008) A topological model of the baseplate of lactococcal phage Tuc2009. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 2716–2723 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Tang G., Peng L., Baldwin P. R., Mann D. S., Jiang W., Rees I., Ludtke S. J. (2007) EMAN2: an extensible image processing suite for electron microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 157, 38–46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Shaikh T. R., Gao H., Baxter W. T., Asturias F. J., Boisset N., Leith A., Frank J. (2008) SPIDER image processing for single-particle reconstruction of biological macromolecules from electron micrographs. Nat. Protoc. 3, 1941–1974 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Scheres S. H. (2010) Classification of structural heterogeneity by maximum-likelihood methods. Methods Enzymol. 482, 295–320 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Scheres S. H., Núñez-Ramirez R., Sorzano C. O., Carazo J. M., Marabini R. (2008) Image processing for electron microscopy single-particle analysis using XMIPP. Nat. Protoc. 3, 977–990 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. van Heel M., Schatz M. (2005) Fourier shell correlation threshold criteria. J. Struct. Biol. 151, 250–262 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Konarev P. V., Volkov V. V., Sokolova A. V., Koch M. H. J., Svergun D. I. (2003) PRIMUS: a Windows PC-based system for small-angle scattering data analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 36, 1277–1282 [Google Scholar]
- 46. Konarev P. V., Petoukhov M. V., Volkov V. V., Svergun D. I. (2006) ATSAS 2.1, a program package for small-angle scattering data analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 39, 277–286 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Guinier A. (1939) La diffraction des rayons X aux très petits angles: application à l'étude de phénomènes ultramicroscopiques. Ann. Phys. 12, 161–237 [Google Scholar]
- 48. Svergun D. I. (1992) Determination of the regularization parameter in indirect transform methods using perceptual criteria. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 25, 495–503 [Google Scholar]
- 49. Franke D., Svergun D. I. (2009) DAMMIF, a program for rapid ab-initio shape determination in small-angle scattering. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 42, 342–346 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Volkov V. V., Svergun D. I. (2003) Uniqueness of ab initio shape determination in small-angle scattering. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 36, 860–864 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Kozin M. B., Svergun D. I. (2001) Automated matching of high- and low-resolution structural models. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 34, 33–41 [Google Scholar]
- 52. Zheng J., Ho B., Mekalanos J. J. (2011) Genetic analysis of anti-amoebae and anti-bacterial activities of the type VI secretion system in Vibrio cholerae. PLoS One 6, e23876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Lin J. S., Ma L. S., Lai E. M. (2013) Systematic Dissection of the Agrobacterium Type VI Secretion System Reveals Machinery and Secreted Components for Subcomplex Formation. PLoS One 8, e67647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.





