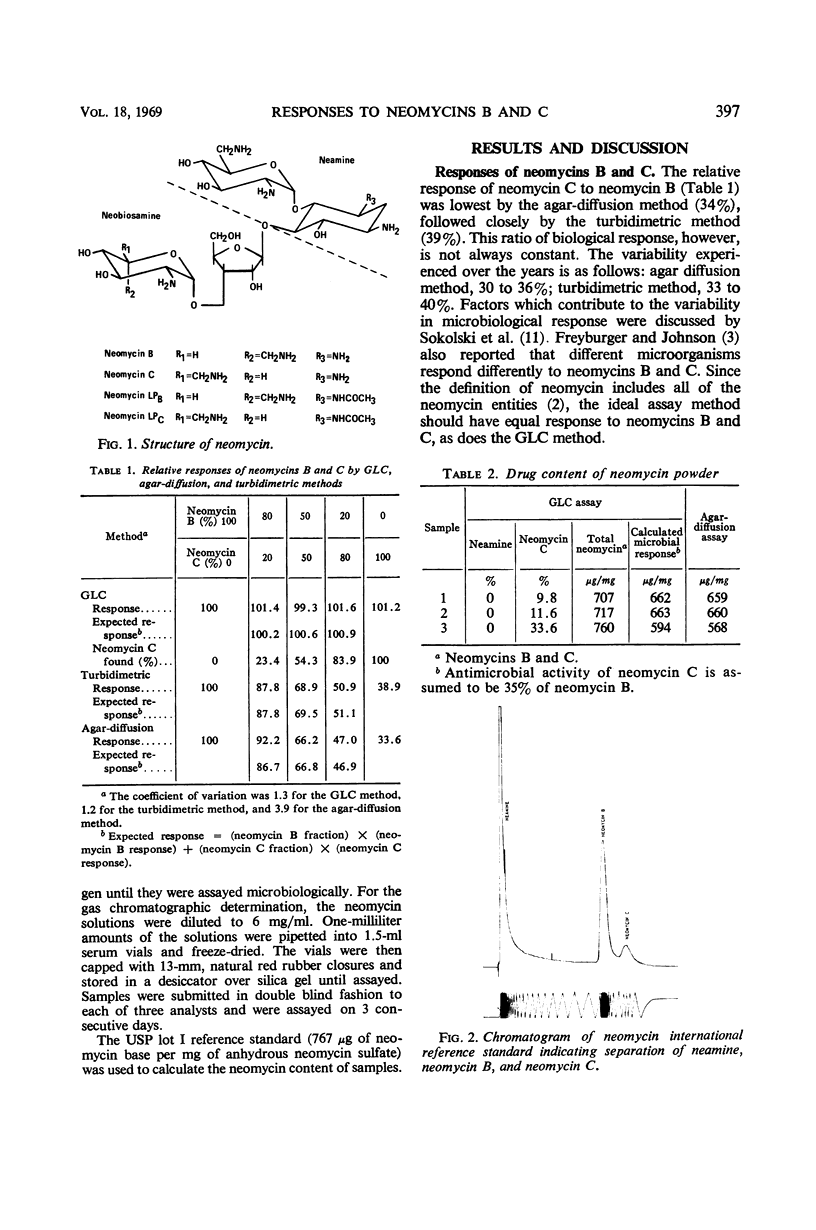
Abstract
The relative responses of neomycins B and C have been determined by a microbiological agar-diffusion method, a turbidimetric method, and by a recently developed gas-liquid-chromatographic (GLC) method capable of separating the neomycin isomers. The ratios of response of neomycin C to neomycin B by the individual methods were as follows: agar-diffusion method, 1:3; turbidimetric method, 1:2.5; and GLC method, 1:1. When neomycin C is assumed to have 35% biological activity of neomycin B, the calculated drug contents of neomycin sulfate powders obtained by the GLC method correlated well with values obtained by the microbiological agar-diffusion assay method.
Full text
PDF