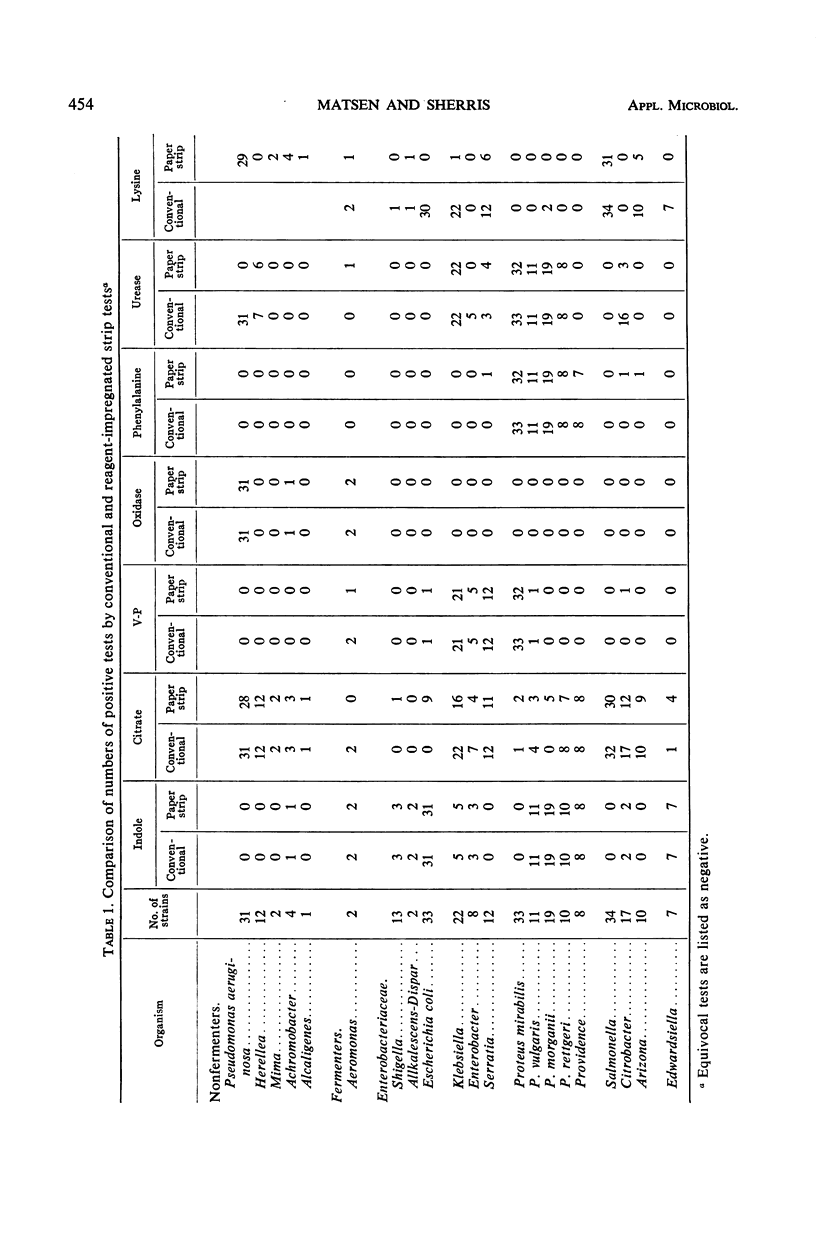
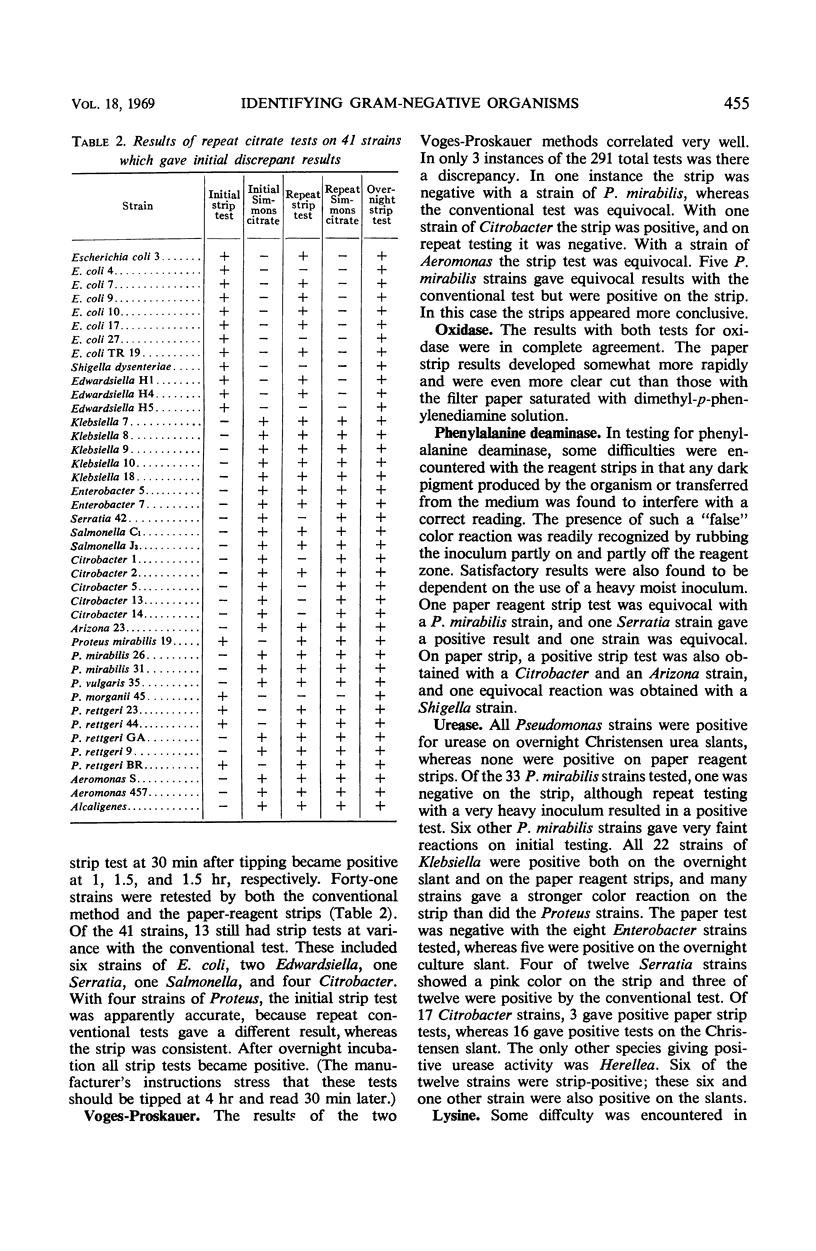
Abstract
Gram-nagative organisms were tested with commercially available reagentimpregnated strips (PATHO-TEC). Of the 291 strains, all were tested by using seven paper tests and their conventional counterparts. Excellent correlation was obtained with the oxidase, phenylalanine-deaminase, and Voges-Proskauer tests. Indole tests made on liquid medium cultures also gave complete correlation, but some false-negative results with indole-positive Proteus strains were obtained when growth from solid medium was tested by the strip method. Paper strip urease tests were positive within 2 hr with all Klebsiella and some Serratia, Herellea, and Citrobacter strains as well as with Proteus strains. Approximately 15% of citrate strip test results differed from those of the conventional tests, and reproducibility was poor on retest. The lysine decarboxylase strip test showed a number of discrepancies and posed problems of interpretation and readability. Paper reagent strip methods are simple and convenient and merit further development to increase the specificity of those which depend on pH change up to that achieved with the Voges-Proskauer, oxidase, phenylalanine, and indole methods.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amsterdam D., Wolfe M. W. Comparison of reagent-impregnated paper strips and conventional tests for distinguishing Escherichia from Aerobacter: correlation with colonial morphology. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Oct;16(10):1460–1464. doi: 10.1128/am.16.10.1460-1464.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen W. B. Urea Decomposition as a Means of Differentiating Proteus and Paracolon Cultures from Each Other and from Salmonella and Shigella Types. J Bacteriol. 1946 Oct;52(4):461–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.52.4.461-466.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DETURK W. E. The adaptive formation of urease by washed suspensions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1955 Aug;70(2):187–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.2.187-191.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALKOW S. Activity of lysine decarboxlase as an aid in the identification of Salmonellae and Shigellae. Am J Clin Pathol. 1958 Jun;29(6):598–600. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/29.6_ts.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANDELMAN A. L., MANN P. H. AN EVALUATION OF REAGENT-IMPREGNATED PAPER STRIPS FOR USE IN THE PROCESS OF IDENTIFYING CERTAIN SPECIES OF CLINICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1965 Feb;7:130–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan K. G., Guinée P. A., Mossel D. A. Use of reagent-impregnated ("Patho-Tec") test papers in the identification of Enterobacteriaceae and similar bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1967;33(2):184–188. doi: 10.1007/BF02045549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevorsek M., Kronish D. P., Schwartz B. S. Rapid presumptive identification of enterics with reagent impregnated paper strips. Am J Med Technol. 1968 May;34(5):271–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J. The urease activity of fluorescent pseudomonads. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):169–174. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. K., Lee E. K., Leahy M. S. Comparison of reagent-impregnated paper strips and conventional methods for identification of Enterobacteriaceae. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968 Apr;49(4):494–499. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/49.4.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



