Abstract
Disodium carbenicillin and gentamicin sulfate have both shown promise in the treatment of infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This study was designed to explore possible synergistic relationships among the new as well as the established antimicrobial agents used to treat such infections. With an agar dilution technique, minimum inhibitory concentrations of 27 strains of P. aeruginosa were determined in two-dimensional tests. Graphs of equal biological activity (isobolograms) demonstrated moderate synergistic effects of the carbenicillin-gentamicin combination over therapeutically feasible concentration ranges. In contrast, the combination of carbenicillin and polymyxin B showed only additive or slightly antagonistic effects. Tests of bacterial killing confirmed the presence of carbenicillin-gentamicin synergy in 3 of 6 strains of P. aeruginosa, but did not show true antagonism between carbenicillin and polymyxin B. Clinical trials of both drug combinations are advisable to determine whether therapeutic results can be improved, and whether the dosages of gentamicin or polymyxin B can thereby be reduced to lessen their toxic hazards.
Full text
PDF
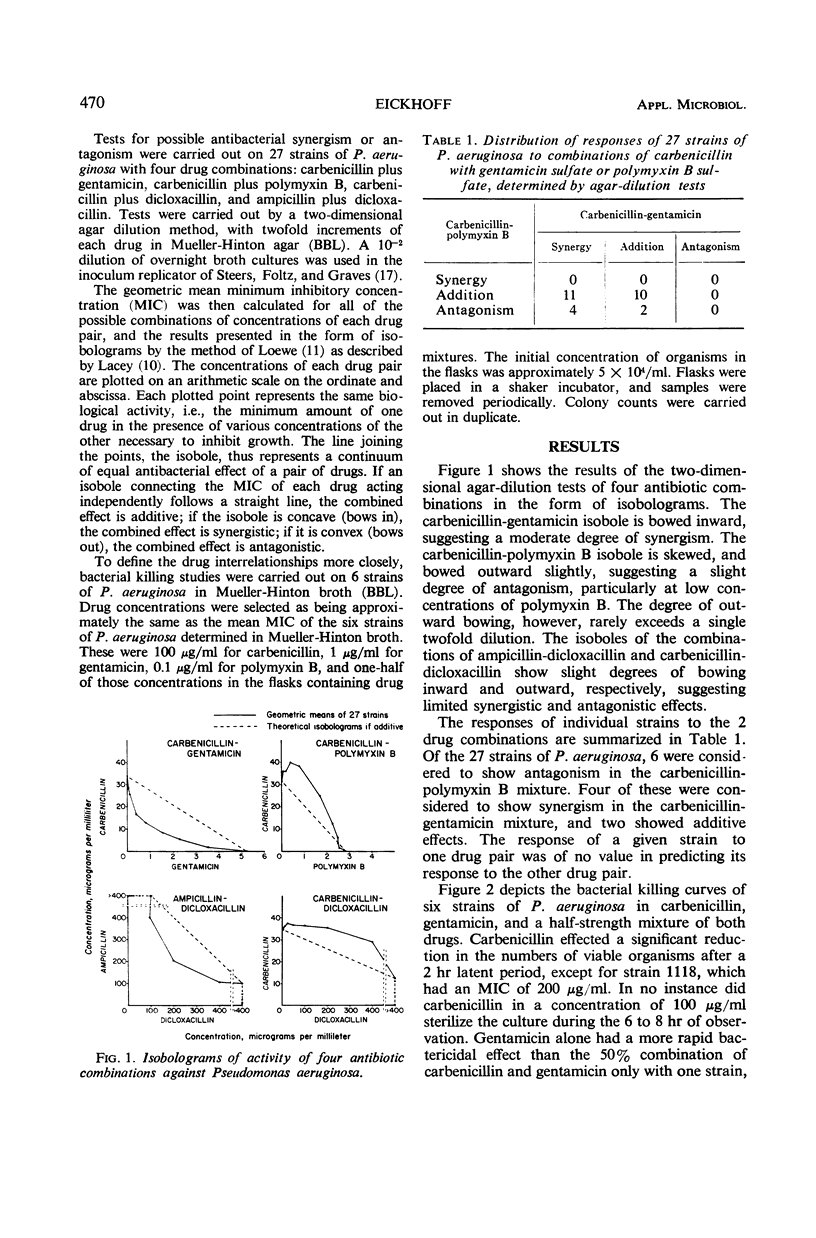
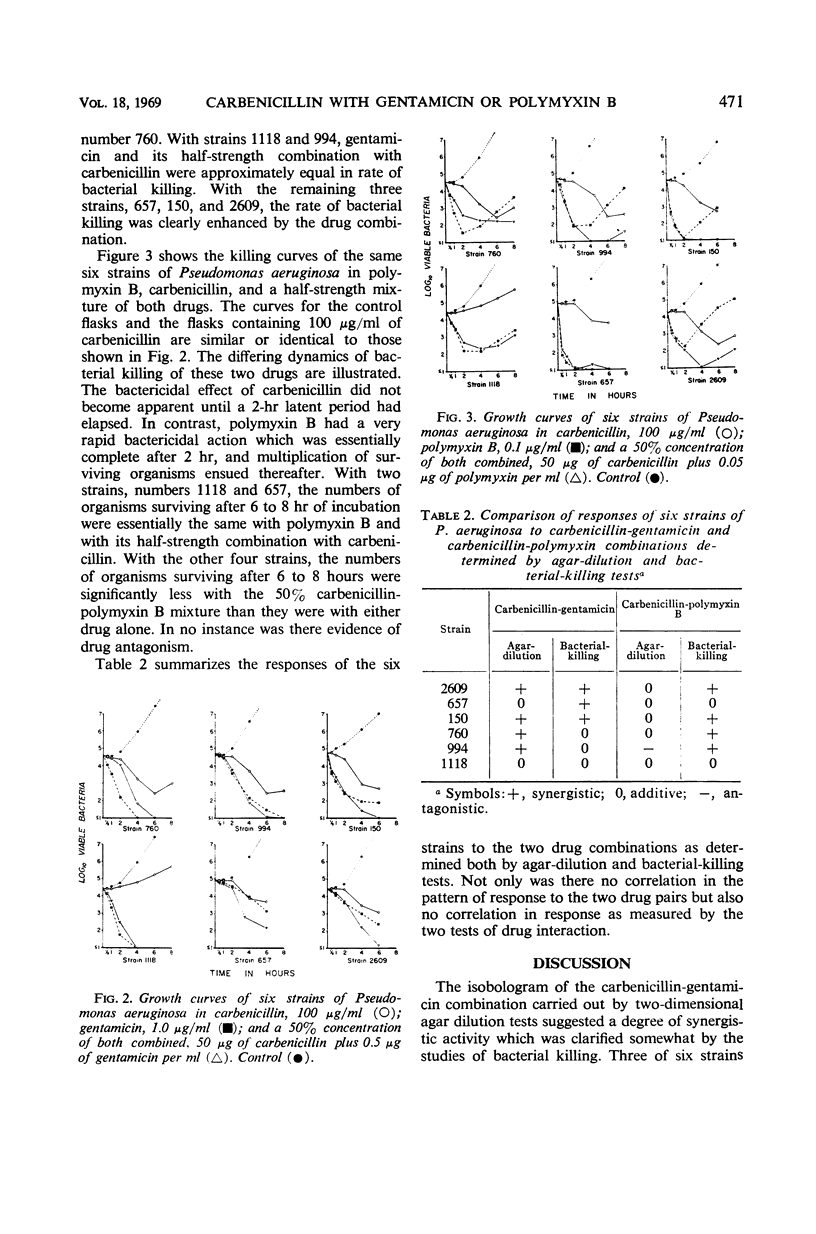


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acred P., Brown D. M., Knudsen E. T., Rolinson G. N., Sutherland R. New semi-synthetic penicillin active against Pseudomonas pyocyanea. Nature. 1967 Jul 1;215(5096):25–30. doi: 10.1038/215025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAYTON R. G., LOURIA D. B. GENTAMICIN IN GRAM-NEGATIVE URINARY AND PULMONARY INFECTIONS. Arch Intern Med. 1964 Aug;114:205–212. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1964.03860080055004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULGER R. J., SIDELL S., KIRBY W. M. LABORATORY AND CLINICAL STUDIES OF GENTAMICIN, A NEW BROAD-SPECTRUM ANTIBIOTIC. Ann Intern Med. 1963 Nov;59:593–604. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-59-5-593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. M., Smith D. D. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to carbenicillin. Lancet. 1969 Apr 12;1(7598):753–754. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91754-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Terrell L. M. In vitro activity of carbenicillin against gram-negative bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1587–1590. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1587-1590.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumfitt W., Percival A., Leigh D. A. Clinical and laboratory studies with carbenicillin. A new penicillin active against Pseudomonas pyocyanea. Lancet. 1967 Jun 17;1(7503):1289–1293. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91590-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGH R., LEIFSON E. The taxonomic significance of fermentative versus oxidative metabolism of carbohydrates by various gram negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):24–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.1.24-26.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAO R. L., JACKSON G. G. GENTAMICIN SULFATE, NEW ANTIBIOTIC AGAINST GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI. LABORATORY, PHARMACOLOGICAL, AND CLINICAL EVALUATION. JAMA. 1964 Sep 14;189:817–822. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070110019004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN J. O., EICKHOFF T. C., FINLAND M. GENTAMICIN: ACTIVITY IN VITRO AND OBSERVATIONS IN 26 PATIENTS. Am J Med Sci. 1964 Nov;248:528–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEWE S. The problem of synergism and antagonism of combined drugs. Arzneimittelforschung. 1953 Jun;3(6):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord N. M., Watanabe F., Parker R. H., Hoeprich P. D. Comparative acute toxicity of four drugs. A study of neomycin, gentamicin, kanamycin, and dihydrostreptomycin. Arch Intern Med. 1967 May;119(5):493–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATH L. D., ABRAHAM E. P. SYNERGISTIC ACTION OF PENICILLINS AND CEPHALOSPORINS AGAINST PSEUDOMONAS PYOCYANEA. Nature. 1964 Dec 12;204:1066–1069. doi: 10.1038/2041066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND R., BATCHELOR F. R. SYNERGISTIC ACTIVITY OF PENICILLINS AGAINST PENICILLINASE-PRODUCING GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI. Nature. 1964 Feb 29;201:868–869. doi: 10.1038/201868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Dans P. E., Wilfert J. N., Finland M. Use of gentamicin in combinations with other antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1969 Apr-May;119(4):370–377. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.4-5.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Finland M. Carbenicillin: activity in vitro and absorption and excretion in normal young men. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Nov;16(11):1753–1760. doi: 10.1128/am.16.11.1753-1760.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford H. C., Kind A. C., Kirby W. M. Laboratory and clinical studies of carbenicillin against gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1968;8:286–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


